An enlargement of the gallbladder can occur if obstructive processes occur in the bile ducts, if there are conglomerates in the canals, if the chronic form of cholecystitis worsens, and also during an attack of biliary colic. This condition is also observed in the presence of polyps in the gallbladder, various neoplasms (both benign and malignant), as well as if it is perforated. Therefore, such a symptom requires immediate treatment and diagnosis in order to avoid dangerous consequences.
Why is the increase dangerous?
An increase in the size of the gallbladder poses a serious danger to the body. If the gallbladder is dilated, this negatively affects the functioning of its ducts, and congestion may occur. The consequence of the bladder stretching is stagnation of bile, and this directly affects the development of cholecystitis and the formation of stones in the organ cavity. The result may be perforation of the organ and the development of peritonitis. Help in this case must be urgent.
Also, with an increase in the volume of the organ, the functions of the digestive system are disrupted . With timely diagnosis and treatment, such consequences can be prevented.
Forecast
Enlargement of this internal organ is fraught with necrosis of its walls, blockage of the bile ducts and breakthrough of bile into the peritoneal cavity, which leads to peritonitis, and this greatly increases the risk of death. In this regard, the appearance of pain in the right hypochondrium should serve as a signal to immediately consult a doctor.
If the pain is unbearable (especially for children), call an ambulance immediately. With timely diagnosis of such a pathology, there are many methods of effective treatment, which often allows one to avoid surgical intervention.
The prognosis with timely diagnosis and proper treatment is very favorable.
YouTube responded with an error: The request cannot be completed because you have exceeded your quota.
Causes of enlargement in adults
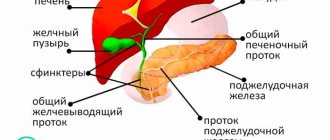
In appearance, the liver is pear-shaped and is located directly under the liver. The main function of the organ is the accumulation and gradual release of this secretion. Fluid production occurs in the liver. After which it enters the gallbladder, where it accumulates and is synthesized. In some cases, the function of the internal organ is disrupted, this is caused by the following reasons:
- Dyskinesia of the bile ducts. In this condition, the gallbladder most often enlarges. The cause of dyskinesia is that the walls of the organ become thinner, resulting in a disruption of the contractile function of the organ and its ducts. Gall disease is manifested by painful sensations in the abdomen on the right, heaviness or discomfort after eating.
- The cause can also often be an increase in the volume of bile, its stagnation in the organ and in the ducts. At the same time, it begins to contract less, and the rate of fluid release into the intestinal cavity decreases.
- The passage of stones from the gallbladder, as a result of which it begins to increase, and its functions are reduced.
- Deposition of a large amount of cholesterol on the walls of the bladder in an adult, due to which it becomes stretched.
- Tumors of the gallbladder and ducts, which become an obstacle to the outflow of fluid.
The reasons for the enlargement of the gallbladder in adults can lie not only in cholelithiasis, but also in other diseases: infectious processes, helminth damage, hepatitis virus, changes in the structure of secretion. This is why the organ enlarges, but the contractile function can decrease significantly. Therefore, timely treatment is very important; with its help, cholestasis can be prevented from removing the gallbladder. The doctor must select a suitable remedy for restoring the gallbladder, with which you can stretch its walls, stimulate the excretion of fluid, and increase the amount of its production in patients with cholecystitis.
Basic functions of the gallbladder
There are three main tasks that the body solves with the help of this organ:
- accumulation of bile produced by the liver around the clock;
- bringing it to the required consistency;
- the release of this enzyme into the digestive system (more precisely, into the duodenum) when food enters the digestive tract.
Bile passing through this organ is involved in the breakdown of heavy fats, has an antibacterial effect, and activates and accelerates the digestive process.
With its help, excess cholesterol is removed from the body and the gastric enzyme (pepsin) is neutralized, and mucus production is also stimulated.
A normal (not enlarged) gallbladder is shaped like a hollow pear. The norm is the length of this organ from six to ten centimeters (depending on the person’s build), the width is from three to five centimeters, and the thickness of its walls is 4 millimeters. Exceeding these indicators indicates the development of some pathology that enlarges this organ.
Reasons for enlargement in children
An enlarged gallbladder in a child can also be observed. If the gall bladder enlarges in a child, regardless of age (in a newborn, infant, 1- or 2-year-old child), the causes most often are concomitant diseases, which include:
- a large bladder in babies is observed with the development of hepatitis or obstructive jaundice, the causes of which are small stones in the ducts,
- in children the organ is enlarged during the development of scarlet fever,
- in infants and older children, this symptom may accompany pancreatitis or gastroenteritis,
- an infant or an older child may suffer from biliary dyskinesia,
- if the bile ducts are twisted,
- when an organ is infected with E. coli or helminths.
Most often, this symptom appears with abnormal development of an organ or with polyps in it. Such factors cause fluid stagnation, organ functions are disrupted, and ducts are blocked. Why can this condition occur in infants? The reason may be improper feeding with artificial formulas, force-feeding of the child, lack of a diet, feeding children with low-quality or excessively fatty foods in large quantities.
Diagnostics
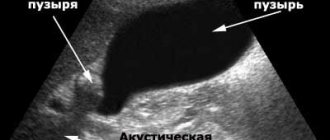
An enlarged gallbladder is detected by palpation of the area of the right hypochondrium - a painful or painless round formation is determined. However, palpation does not allow one to determine the exact size of the organ, especially in a child. Therefore, instrumental diagnostics are required. It is possible to detect deviations in the size of an organ and identify functional disorders of its functioning using ultrasound.
Ultrasound examination is an informative method that allows you to make an accurate diagnosis. At the same time, ultrasound is the safest diagnostic method; if necessary, it can even be used to examine a newborn.
With the help of ultrasound, in addition to an increase in the size of the organ, you can detect:
Dycholia of the gallbladder and its treatment
- thickening or thinning of the walls, inclusions in the lumen of the gallbladder (usually with cholecystitis and cholelithiasis);
- violation of the contractility of the organ (with dyskinesia of the bile ducts);
- narrowing or twisting of the bile ducts, bending of the bladder neck (in children, as a rule, these are caused by congenital structural anomalies, in adults they are more often acquired);
- dilated common bile duct (noted with cholelithiasis and stenosing papillitis);
- stretching of the bladder, thickening of its walls over 5 mm, fluid inside the organ (found with empyema - accumulation of a large amount of purulent contents in the cavity of the gallbladder);
- stretching without thickening of the walls, fluid inside (develop with a mucocele - mucous cyst);
- obstruction of the bile duct, thickening of the walls of the bladder (may indicate helminthic invasion, when helminths block the bile duct, preventing the outflow of bile, or inflammation of the head of the pancreas, while thickening of the walls of the bladder may be a sign of suppuration);
- benign or malignant formation, polyps.
Help: in case of cholelithiasis, ultrasound and x-rays can not only detect stones in the bladder and ducts, but also determine their number, shape, size, appearance, structure.
The advantages of ultrasound are the absence of radiation, the ability to perform the procedure on pregnant women and children of any age.
Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient is referred for additional diagnostic procedures:
- computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdominal organs;
- endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) – radiography with contrast of the bile and pancreatic ducts;
- gastroscopy (FEGDS).
These methods allow you to accurately determine why the gallbladder is enlarged, identify structural changes and disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the biliary and digestive system, and confirm or refute a previously made diagnosis.
Symptoms of pathology
If the bubble increases in size, the liver hurts under the rib in the right hypochondrium, what should you do in this case? With such symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor and receive timely treatment. The key clinical sign of the pathological condition is pain on the right side, which cannot be eliminated with medications. The nature and intensity of pain may vary, but it has been noted that they become more pronounced after eating fried, fatty, or smoked foods.
If there are gastric diseases, the following clinical manifestations additionally appear:
- attacks of nausea and vomiting,
- hyperthermia, with indicators most often subfebrile,
- a person loses his usual weight,
- there is a bitter taste in the oral cavity, the mucous membrane is dry,
- feces become much lighter, and urine acquires an intense dark color,
- yellowness of the epidermal layer is observed,
- the surface of the tongue becomes crimson.
Symptoms
Enlargement of the liver and gallbladder leads to aching pain. There is periodic paroxysmal pain that intensifies after eating fatty, spicy, sweet or carbonated foods. After 20–30 minutes, the attack usually passes, and there is a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach. Babies, when their liver and gall bladder hurt, begin to twist their legs and press them towards their tummy.
If the yolk sac is clogged, the following occurs:
Flatulence
- flatulence;
- belching;
- stool disorder;
- decreased appetite;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- fever, chills;
- itching on the body, irritation;
- excessive muscle strain on the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of aching in the shoulder joint and scapula on the right;
- increase in pain during exercise.
The main characteristic symptom is pain (regardless of the cause of the increase) localized to the right in the hypochondrium in the epigastric region, with intensification after eating fatty, fried and spicy foods.
Obstructive jaundice is characterized by belching, bitterness in the mouth, and the appearance of yellowness on the skin due to blockage of the bile ducts.
When stones form, nausea, pain in the right hypochondrium and periodic vomiting appear. The phenomenon is common in genetically predisposed people and in old age with excess weight and poor nutrition. The appearance of cholesterol plaques clogs the bile ducts, bile stagnates, leading to a malfunction of the gallbladder. As a result, contractions become inactive, potassium salts accumulate inside the cavity, and the frequency of secretions produced by the gland is sharply reduced.
Treatment methods
If the organ is enlarged, it is important not to delay with therapeutic measures. If the gallbladder is enlarged, treatment is carried out only after preliminary medical prescriptions. How to treat an enlarged gallbladder:
- taking hepatoprotectors,
- taking medications based on bile acids,
- use of antispasmodics,
- litholic therapy.
It is important to remember that drug treatment will be advisable only if the gallbladder is enlarged for a short time, if the initial stage of the disease develops. No traditional methods should be used in this case. Otherwise, the patient's condition may worsen, and the disease will progress rapidly. In advanced cases, only surgical treatment using laparoscopy, ultrasound, laser or abdominal surgery is indicated.
Treatment
What to do if the bubble is too large depends on the exact diagnosis. When the gall bladder is enlarged, drug therapy, surgery (for stones or tumors), and a special diet are used for treatment.
Drugs
How to treat an enlarged gall bladder depends on the diagnosis. Depending on the identified diseases, doctors prescribe:
- Choleretic drugs – Allohol, Ursosan, Holosas. They do not eliminate the cause of the disease, but they prevent stagnation of bile and related problems.
- Antibiotics. Selected individually. The indication is bacterial inflammation of the bile ducts and bladder walls.
- No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine. Antispasmodics reduce pain by relieving spasm of the gallbladder walls.
- Antiparasitic drugs. They are selected depending on the type of parasites found during the examination. Medicines are taken in a course, therapy is carried out in a hospital setting under the supervision of a doctor.
Diet
When drawing up a nutrition plan, you need to take into account that the bile ducts are dilated or blocked. This disrupts the supply of bile, which is especially needed for processing fatty foods. Therefore, table No. 5, which is prescribed to patients with gall pathologies, excludes:
- fatty foods;
- sweets;
- alcohol;
- hot spices;
- fried foods.
You need to eat often, in small portions. Food is boiled and steamed. Frying is prohibited.
Traditional methods
Alternative treatments should be used with caution. Self-medication can be harmful if you take choleretic herbs for stones. Therefore, before self-medicating, you need to find out your diagnosis and consult a doctor. This will eliminate the problem of incompatibility of therapy with home treatment.
Effective means are:
- Black radish juice. To prepare it, the radish is peeled and grated, then the liquid is squeezed out. The collected juice is infused for several hours in the dark and away from heat. After infusion, drink the juice one tablespoon 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment is 5 days, then a break for 3 days. Repeat until recovery.
- Sage decoction. Add 2 tablespoons of dry herb to 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Drinking a tablespoon of infusion every 2 hours reduces the symptoms of inflammation.
- Egg yolks. They are drunk on an empty stomach, 1-2 pieces. in a day.
The gallbladder changes its size due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and the organ itself. Seeing a doctor in a timely manner and following instructions is the only way to recover with a minimum of complications. Therefore, at the first signs of problems with the gallbladder, you need to visit a therapist or gastroenterologist to begin treatment before irreversible changes occur.
How to treat pathology in childhood
If a child is found to have an increase in organ volume, treatment involves hospitalization, the prescription of antispasmodics, hepatoprotectors, bile acids, and proper nutrition. The diet must be followed until the main cause of the pathology is eliminated. After which the child must be observed by a hepatologist or gastroenterologist, children are registered at a dispensary, periodically they need to visit a doctor and undergo prescribed diagnostic measures. If there are stones in an organ or in its canals, even in childhood, a procedure is performed to remove them - laparoscopy (or another option).
To prevent this condition in the future, it is recommended to eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, give the body feasible physical activity, and also promptly consult a doctor for treatment of concomitant diseases of the abdominal organs.
Cholelithiasis
Gallstone disease is one of the most common and most dangerous causes of gallstone dysfunction in adulthood or old age. The child has a minimal risk of development.
Typically, symptoms appear gradually along with an increase in the number and size of stones in the bladder cavity. Stones are pieces of hardened bile that form in adults due to the accumulation of large amounts of cholesterol in the bile, which combines with bilirubin with calcium salts.
If you suspect the presence of gallstones, you should immediately consult a doctor to undergo appropriate examinations.
At first, the diameter of the stones is very small (these are literally grains of sand), but gradually, as negative conditions persist, they begin to grow until they fill the bladder or clog one of its ducts. In this case, emergency surgery is required.
There may be several causes for cholelithiasis
- hereditary factor (the presence in the family of patients with this disease significantly increases the risk of cholelithiasis in descendants);
- high blood sugar;
- overweight;
- unhealthy diet;
- concomitant liver diseases;
- obstruction of the bile ducts;
- hormonal imbalance (in pregnant women).
Gallstone disease manifests itself in different ways, which directly depends on the size of the formations, their total volume and the age of the patient. A typical symptom of cholelithiasis is considered to be a sharp stabbing pain in the liver area (pain caused by the passage of stones from the gallbladder into the bile ducts with further exit into the intestines). The pain in the right side is sharp and acute, radiating to the right shoulder or shoulder blade.
The patient may have a fever, yellowing of the skin, urine becomes dark, and feces, on the contrary, become discolored. These are very alarming symptoms for the patient.
When the stone passes into the intestines, the symptoms are sharply weakened or disappear completely. If the stone gets stuck in the duct, completely blocking the exit of bile, the symptoms begin to increase. In this case, immediate surgical intervention is required. The clock can count!
The main methods of examination if gallstones are suspected are ultrasound and x-rays, which determine not only the size of the stones, but also their composition, size and quantity.
Treatment most often consists of radical removal of all formations through surgery. Nowadays, low-traumatic laparoscopic surgery has become widespread, in which stones or the entire bladder are removed through a puncture in the skin of the abdomen. Ultrasonic crushing of stones is also possible, but the procedure does not become widespread because it has its contraindications.
Non-surgical removal of gallstones is allowed in rare cases when cholelithiasis is diagnosed at an early stage and the size of the stones does not exceed the size of the bile ducts. In this case, drugs can be prescribed that dissolve the formations (for example, Ursofalk), after which they enter the intestines in the form of sand and are eliminated from the body naturally. Such treatment is long-term - medication must be taken for at least 6 months, and for the entire duration of therapy a strict diet and gentle regime are prescribed (the patient is prohibited from heavy physical and mental stress, which can provoke a sudden release of stones with severe pain).