Antibiotics or antibacterial drugs are a group of pharmacological drugs that have a detrimental effect on bacterial microorganisms.
There are two main groups of antibiotics:
- Bacteriostatic.
They block the proliferation of bacteria by destroying their genetic information.
- Bactericidal.
They cause damage to the cell wall, thereby destroying the bacteria themselves.
Our body normally contains beneficial and opportunistic microorganisms that contribute to the normal functioning of organs and systems.
When the amount of normal intestinal microflora decreases, its protective role decreases, local immunity weakens, and pathogenic microflora joins all this. The body reacts to its influence with a reaction in the form of stool disturbances - diarrhea.
Beneficial bacteria: the main ones are considered to be lactobacilli and bifidobacteria.
They inhabit the skin, intestines, and genitals, protecting against negative environmental factors and promoting the normal functioning of organs and systems.
How do antibacterial drugs work?
Antibiotics are intended for the treatment of acute and chronic infectious processes that occur with severe inflammatory symptoms; their spectrum of action is very diverse.
They are used to treat respiratory diseases, ENT organs, skin, intestinal disorders, respiratory, genitourinary systems, and to prevent bacterial complications in immunodeficiency states.
In addition to the positive therapeutic effect, this group of drugs has undesirable side effects, so all antibacterial drugs must be sold strictly according to a doctor's prescription.
These include diarrhea after antibiotics. The drugs do not have a selective action; they destroy both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria, and as a result, intestinal dysbiosis and diarrhea syndrome develop.
Causes of diarrhea from antibiotics:
- Change in intestinal microflora towards pathogenic.
- The development of inflammation in the intestinal process against the background of dysbiosis.
- The laxative effect of the antibiotics themselves.
- Removal of excessive amounts of fluid through the gastrointestinal tract.
Groups of antibacterial drugs that can cause diarrhea:
- Penicillin series: Amoxiclav, Benzylpenicillin, Penicillin, Bicillin-5.
- Fluoroquinolones: Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin.
- Cephalosporins of various generations: Ceftrixon, Cefotaxime, Cefipime.
- Aminoglycosides: Gentamicin, Amikacin.
- Macrolides: Azithromycin, Clarithromycin.
- Carbapinems: Meronem.
- Tetracyclines: Doxycyline.
- Bacteriostats: Levomecitin.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea is characterized by the appearance of signs on the 3-4th day of taking the drug; this condition necessarily requires correction and treatment; symptoms intensify when using a combination of drugs from several antibiotics.
What conditions require mandatory therapy:
- An increase in allergic reactions to the administration of drugs.
- High fever accompanied by diarrhea.
- A pronounced symptom of intoxication.
- Severe pain accompanied by diarrhea.
- Development of pseudomembranous colitis.
Pseudomembranous colitis is a serious complication of taking antibacterial drugs from the gastrointestinal tract, which develops against the background of dysbacteriosis and the addition of a bacterium such as Clostridium difficile.
Confirming the diagnosis is only possible in a hospital setting using laboratory and instrumental research methods.
How the disease manifests itself:
- Frequent loose stools after taking antibiotics, more than 20 times a day.
- High fever, chills, headache.
- Pain in the abdominal area.
- Impurities of mucus and blood in the stool.
- The duration of the condition is more than 7 days.
- Cannot be treated with antidiarrheal drugs.
The pathology is treated comprehensively, in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor; the etiotropic drug for treatment is vancomycin.
Signs of infection
Bacterial infection is the most common cause of diarrhea. It can enter the body along with dirty water, dirty products, and also as a result of neglecting the rules of personal hygiene.
Antibiotics against diarrhea are prescribed if a person exhibits symptoms such as:
- copious discharge;
- loose stools with impurities or green mucus;
- a large amount of mucus;
- discharge with blood.
Often, bacterial diarrhea is accompanied by high fever, vomiting and tenesmus (painful urge to defecate).
Important! If blood is noticed in the feces, you should urgently contact a specialist. This symptom is very dangerous and may be a consequence of Crohn's disease, tumor or hemorrhoids.
Diarrhea when taking antibiotics: what to do and how to treat it
If diarrhea occurs during or after taking antibiotics in adults, you should first contact your doctor who prescribed the drugs.
Perhaps they are not suitable, then the doctor will individually select another group of drugs for the treatment of the primary pathology.
- If possible, the antibacterial drug should be discontinued or replaced with another, more gentle one.
- You should follow a diet.
- Prescribing medications that will help normalize intestinal microflora.
Contraindications to antibiotic treatment
Most intestinal infections tend to resolve quickly on their own, so the prescription of specific antibiotic therapy is justified in no more than 20% of cases of acute diarrhea. The prescription of antibacterial drugs must be justified, and the expected clinical effect must exceed the possible risk of side effects.
Infectious forms of diarrhea.
Not all infectious forms of diarrhea require antibiotics; rehydration therapy is often sufficient to cure. In some cases, antibacterial drugs can be harmful. There is a group of pathogens that produce enterotoxins. With the massive death of these bacteria during antibiotic therapy, there is a high risk of developing life-threatening infectious-toxic shock. A similar situation can arise when infected with E.Coli, which produces Shiga toxin with a hemolytic-uremic effect. The use of antibiotics for salmonella infection often increases the period of bacterial excretion even after relief of diarrhea.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
There are several reasons for this condition. Antibiotics lead to the death of part of the natural intestinal flora. This changes the metabolism of carbohydrates and the production of fatty acids, causing osmotic diarrhea. Against this background, pathogenic microorganisms often begin to multiply. Some drugs (erythromycin, clavulanic acid) affect intestinal motility, and drugs of the penicillin and tetracycline groups can cause inflammation of the wall of the large intestine. As a result, while taking antibiotics or after their withdrawal, diarrhea syndrome occurs, often intermittent and prone to recurrence. The development of severe intestinal complications and intoxication is possible. For treatment, it is necessary to discontinue the antibiotic taken, rehydrate and, if necessary, prescribe strictly defined antibacterial agents.
Treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea
In order to avoid side effects, you must follow the rules for taking antibacterial agents.
How to take antibiotics correctly:
- The use of drugs only as prescribed by a doctor in the required dosages and with the correct frequency of administration, all this is stipulated by the attending doctor.
- Avoid stress during treatment.
- Observe the work and rest schedule.
- Eat properly.
- Do not use the product on an empty stomach, only after eating.
- Do not drink alcohol during the course of treatment.
Treatment comes down to basic rules and goals:
- Stop diarrhea.
- Restore imbalance in microflora.
- Drinking large amounts of fluid to eliminate intoxication syndrome.
Drug therapy
There are main groups of drugs for treating stool disorders and restoring microflora:
- Prebiotics.
These are enzyme preparations that contain nutritional elements necessary for the growth and reproduction of beneficial bacteria; they are used to treat diarrhea after taking antibiotics, when the effect of the antibacterial drug has already ended.
The drugs are: Oligosaccharides, Sorbitol, Sucrose, valine, Arginine and others.
- Probiotics.
Products that contain ready-made living bacteria colonize the digestive tract: Linex, Enterol, Hilak Forte, Acipol, Normobakt and others.
They are produced in a wide variety of forms: tablets, capsules, powders, drops. The use of capsule probiotics is justified; the capsule component, when passing through the gastrointestinal tract, protects the active substance and beneficial bacteria from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Under the action of intestinal enzymes, the capsule dissolves, and beneficial bacteria populate the environment unchanged. A true probiotic that can stop diarrhea during and after taking antibiotics is Linex, it is indicated from the first day of taking the drugs.
All other remedies should be used after completion of the course of treatment:
- Metabiotics.
Combined preparations that contain a probiotic and a prebiotic: Normobact, Bifiform.
- Sorbents.
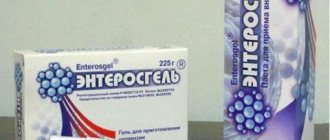
Substances that bind toxins and foreign substances, removing them from the intestinal lumen, the most effective sorbents include: Activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel, Polysorb, Filtrum.
In order to replenish the supply of fluid lost with loose stools, they resort to rehydration, prescribing oral saline solutions: Regidron, Trisol, Polysorb, the patient must take at least 2 liters of fluid per day.
Treatment of diarrhea during chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs that have a detrimental effect on the body's cells, killing them; it is one of the main methods of treating malignant tumors.
Like every medicinal substance, chemotherapy has its own side effects, the disadvantage of treatment is that the substances affect and kill not only cancer cells, but also healthy elements of the body.
The functions of all major organs and systems are affected; the main manifestation of intestinal disorders during chemotherapy is diarrhea. Drugs that cause diarrheal syndrome are: topotecan, doxorubicin, teniposide, irinotecan, ftorafur and others that kill healthy epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract.
Patients with cancer are treated in a hospital; if diarrhea occurs, patients require special attention and treatment. It is important to ensure that the stool is free of mucus, blood, fever, and dehydration.
If the patient notices such changes, it is necessary to urgently inform the doctor about his condition.
What must be observed for treatment:
- Rehydration
This is the process of replenishing fluid in the body, achieved by drinking the required amount of fluid by the patient or by intravenous infusion of solutions.
If the patient is able to drink the liquid himself, then it is recommended to use Hydrovit, Regidron solutions, the contents of the sachets are diluted with a certain volume of water.
The products replenish the mineral, electrolyte and water balance of the body. Saline solution, Ringer's solution, Trisol, Quadrosol and others are infused intravenously, all this is prescribed by the attending doctor.
- Proper nutrition
The diet should be followed fractionally, in small portions, often; it is recommended to consume boiled poultry, chicken breast, fish, eggs, cereals without milk, boiled vegetables, potatoes, carrots, meatballs, goulash.
For such patients, dairy products, beans, cheeses, bread, and foods that may contain mold are completely excluded. In patients with immunodeficiency after chemotherapy, infection with a fungus can aggravate the course of the disease.
- Probiotics and prebiotics
These products influence and restore normal intestinal microflora, create a favorable nutrient environment for the growth and reproduction of bacteria, since they contain the beneficial bacteria themselves in the required quantity.
For patients undergoing chemotherapy, probiotics Linex and Probifor are indicated; they can be taken from the very first day of chemotherapy. Sorbifor contains bifidobacteria, their number is 500 million cells per single dose.
The therapeutic amount required to restore the flora, the frequency of a single dose, is prescribed by the doctor. The standard regimen is 2 sachets 2 times a day, the course lasts 7-10 days.
Another effective drug is Bifidumbacterin, its distinctive feature is that it contains a smaller number of bifidobacteria, therefore, the frequency and dosage of administration increases.
- Enterosorbents
They perform the function of removing toxic substances and cell decay metabolites, these include Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon, Filtrum, Smecta. It is important to note that with long-term treatment they can cause irritation to the intestinal wall.
Smecta or Neosmectin protect the mucous membrane, prevent the development of toxic reactions, and increase local immunity. The dose is 1 sachet 3 times a day, the duration is determined by the attending physician.
Restoring the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract after taking antibiotics
Amoxicillin and other components of treatment have negative consequences in the intestinal microflora. The active components do not distinguish whether they attack pathogenic bacteria or destroy beneficial microorganisms. When determining the course of treatment, additional probiotic substances are prescribed. The main consequence of long-term use of antibiotics for diarrhea is the same (that is, it appears again). Paradoxically, the symptom that worries the patient accompanies him even after the course of treatment. Most often, restoration of the proper functioning of the body occurs independently and does not require an additional course of medications.
The first symptom appears after 7-10 days of taking a course of antibiotics. The main indications for independently restoring the intestinal microflora and its proper functioning will be diet (exclude heavy fatty foods from the diet), drinking plenty of fluids (impairing the water-salt balance of the body). List of symptoms: diarrhea, bloating, abdominal pain. In this case, it is better not to burden the gastrointestinal tract, but to limit food intake. Avoid sweet, fried, fatty and salty foods. Eat oatmeal, its high fiber content will help restore the intestinal mucosa faster. Shown are light soups and broths. Include fermented milk products in your diet, they will help restore microflora. If symptoms cause severe anxiety or persist for a long time, it is necessary to start taking components that restore microflora.
Treatment after chemotherapy
If diarrhea occurs after chemotherapy, you should consult a doctor with these complaints to prescribe the necessary therapy. Initially, the doctor will prescribe a strict diet.
The diet prescribed is the same as for chemotherapy, the next step is taking intestinal antiseptics that suppress the growth of pathogenic bacteria: Nifuroxazide, Stopdiar. The course of treatment lasts 5-7 days.
After intestinal antiseptics, prebiotics are prescribed; they normalize the enzymatic composition for beneficial bacteria. The next step is a course of probiotics; they can be taken together with prebiotics; the most effective are Normobact, Linex, Enterol.