General rules
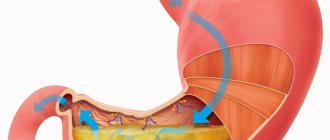
The main functions of the stomach are the deposition of food, its partial digestion under the influence of hydrochloric acid, the initial processes of absorption and the passage of the bolus of food to the intestine. Hydrochloric acid is secreted by the parietal cells of the stomach, which are more abundant in the body of the stomach. The destruction of these cells due to inflammation leads to hypoacid gastritis and poor digestion of food.
With widespread gastritis, when the inflammatory process covers the body of the stomach and the entire stomach ( pangastritis ), the function of hydrochloric acid production is sharply reduced. Normal biochemical and physiological processes in the stomach, a sufficient acid-enzyme barrier, good regeneration of the epithelium and full peristaltic activity are protective factors that prevent the penetration of bacterial and fungal flora.
Low acidity is a pathological condition in which not only the digestive function is impaired, but it contributes to the colonization of the mucous membrane by H. Pylori. This bacterial infection maintains chronic inflammation and causes it to progress, further reducing parietal cell function. The progression of the disease leads to the development of atrophy, a sharp decrease in acidity, down to zero acidity. The duration of this process can be from 12 to 18 years.
The role of stomach acid is also great in preventing the introduction of fungi into the mucous membrane. In an environment with low acidity, Candida acquires pathogenic properties and pseudomycelium or mycelium is formed, which damages the mucous membrane. In certain concomitant diseases (for example, in HIV-infected persons), Candida fungi cause gastric candidiasis.
In turn, the inflammatory process affects the motility of the stomach and intestines - it decreases. With low acidity, proteins are poorly broken down in the stomach, which leads to bloating and intoxication of the body. Patients complain of gastric (nausea, belching, vomiting) and intestinal (rumbling, flatulence , bowel dysfunction) dyspepsia . More often they are worried about unstable stools - alternating constipation and diarrhea . Also characteristic is a decrease in appetite and the appearance of an unpleasant (often metallic taste) in the mouth.
severe secretory insufficiency and impaired gastric digestion, special attention is paid to replacement therapy - replenishing the deficiency of hydrochloric acid in combination with multienzyme drugs ( Pepsidil , Creon acidin-pepsin , A bomin , Pan citrate ). When motor skills are impaired, sometimes it is enough to prescribe these drugs or in combination with M otilac or Motilium .
In complex treatment, medicinal herbs are used that reduce the inflammatory process and stimulate the secretion of gastric juice: wormwood, thyme, oregano, fennel, cumin, parsnip, mint, parsley, St. John's wort, yarrow, plantain leaves (or the drug Plantaglucid ). In summer, you can drink juice from fresh plantain leaves (1 tablespoon 20 minutes before meals), and add young leaves to salads.
Proper nutrition and its regimen play a major role in the treatment of such patients. Fractional meals in small portions improve the rhythmic activity of the stomach and prevent stagnation of food contents in the stomach.
A diet for low gastric acidity during an exacerbation involves mechanical and chemical restrictions. Dishes are prepared boiled, steamed and pureed. As the exacerbation stops, nutrition should be complete and in compliance with the stimulating principle.
Outside the period of exacerbation, nutrition for low stomach acidity is organized within the framework of the therapeutic Diet No. 2 . Its characteristic feature is the inclusion of food stimulants of gastric juice, which stimulate appetite. At the same time, dietary nutrition is aimed at reducing fermentation processes in the intestines. Since the diet is complete and varied, it is prescribed for a long period.
Dishes can be prepared by baking, stewing and frying, which also increases the production of gastric juice. Frying foods can be used 1-2 months after an exacerbation. The diet is rich in foods that enhance the production of gastric juice:
- snacks (tomato salads, herring, mincemeat, jellied dishes with broths, salads of boiled vegetables with meat, pickled vegetables);
- extractives (meat, fish and rich vegetable broths);
- sauces based on meat broths;
- fermented milk drinks;
- vegetable caviar, stewed vegetables;
- fruits with a high acid content (citrus fruits, cranberries), adding them to tea, drinks and compotes;
- coffee, cocoa, tea, vegetable and fruit juices.
With low acidity, it is recommended to include foods with a choleretic effect in the diet: vegetable oils, beets and beet juice, lemons, watermelon, turmeric, melons, fresh herbs. At the same time, coarse fiber, spicy foods, spices, and whole milk are limited.
As health improves and in a state of stable remission, the patient can follow Diet No. 15 - this is a common table, characterized by physiologically complete nutrition and a normal amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates. The Diet does not provide for mechanical and chemical sparing of the mucous membrane.
However, fatty varieties of lamb, poultry, pork, spicy dishes and seasonings are excluded. Limit the consumption of smoked meats, canned food, vegetables with coarse fiber (turnips, radishes, radishes). Rye bread and raw vegetables and fruits are allowed.
What foods are not recommended to be consumed if you have low acidity?
In fact, there are no completely prohibited foods for hypochlorhydria. However, in order to avoid the development of unpleasant symptoms, nutritionists recommend avoiding certain types of food.
First, it is necessary to eliminate gluten from the diet as much as possible. The results of numerous studies have proven the relationship between gluten in the diet and hypochlorhydria. Therefore, if the concentration of gastric juice is confirmed to be low, it is worth following a gluten-free diet. The accumulation of byproducts of grain processing in the stomach causes dyspepsia, acid reflux, as well as flatulence and constant bloating.
Secondly, it is worth minimizing the consumption of products with antacid properties. Ignoring this rule will ultimately lead to the need for treatment for achlorhydria (complete lack of gastric juices).
One common antacid fruit is banana. The sweet pulp is actively promoted by nutritionists as an indispensable part of a healthy diet. However, yellow fruit is contraindicated for people with hypochlohydria. Banana is rich in fiber and rich in potassium, which leads to inhibition of gastric juice production.
Dairy products with unnatural additives (ice cream, yoghurts with fillers) also have a certain degree of danger. Of course, no one is calling for completely giving up milk, because all-natural fermented milk products will only help digestion. But it is better to avoid store-bought sweets that contain refined sugar, preservatives, and dyes altogether.
Authorized Products
The diet includes:
- Lean meat and poultry without skin and tendons. You can cook all kinds of dishes: cutlets, zrazy, stew, goulash, quenelles, meatballs, beef stroganoff. If desired, you can bake it.
- First courses in low-fat broth, in which vegetables should be finely chopped, rassolnik (with chopped or mashed vegetables), borscht and cabbage soup with fresh cabbage.
- Low-fat varieties of fish (hake, pink salmon, ice cod, pike, pike perch, pollock) in pieces, baked with vegetables, cutlets, meatballs, quenelles.
- Sauces and jellied dishes based on broths.
- Vegetables in the form of puree (potato, zucchini, pumpkin, carrot, beetroot, cauliflower), stewed and baked vegetables, fresh tomato salads. You can add greens (dill, parsley) to vegetable dishes. Periodically, it is worth including sorrel in your diet. Cabbage dishes, sauerkraut and cabbage juice increase acidity, but they should only be used during remission. It is believed that turnips baked with vegetable oil facilitate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Wheat bread (dried), you can eat cookies and savory flour products.
- Porridges cooked in broth or water. Corn millet and pearl barley are difficult to digest, so they are limited or excluded from the diet.
- Kefir, curdled milk, cheese (grated or sliced), sour cream, omelette with cheese, cottage cheese and dishes made from it, yogurt. Milk and cream are allowed as additives in dishes.
- Ripe fruits, tangerines, oranges, apples, black currants, gooseberries, kiwi, watermelon, grapes (remove skins), oranges and lemons (in tea). Sour fruits and berries help increase the acidity of gastric juice: cranberries, viburnum, lemon, lingonberries, cherries, apricots eaten on an empty stomach.
- Tea with lemon, vegetable juices, coffee and cocoa, fruit juices (at first it is recommended to drink all juices diluted). Increases acidity by drinking black tea and strong coffee (occasionally), rosehip and sea buckthorn drinks, honey water, lingonberry water, cranberry fruit drinks, carrot juice (0.25 cups after meals).
- The following are allowed as desserts: creamy toffee, marshmallows, marmalade, jam, pastille, preserves, honey. Sugar can be added to dishes and tea.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 9,2 | 40 |
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fully or partially limited products
- Foods that are difficult to digest and linger in the stomach for a long time: coarse meat, fatty meat and fish, baked goods, brown bread, fried pies, pancakes, pancakes, mushrooms, raw fruits and vegetables, legumes, fresh milk, corn, pearl barley, millet.
- Irritating to the mucous membranes: garlic, fresh onions, salted and smoked foods, canned snack foods, turnips, radishes, hot seasonings, radishes, rutabaga.
- Causing bloating: raw vegetables, legumes, pea and bean soup, okroshka, millet soup.
- Excessively hot and cold foods.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet for the stomach and raw food diet
A raw food diet is often perceived as a way to eat properly and eliminate many health problems. However, are raw food diet and gastritis really compatible? After all, experimenting with food during such an illness is absolutely not worth it.
Considering that a raw product is quite tough for an unprepared stomach, you cannot load it right away. Obviously, rushing headlong into such an event is quite risky. Especially if before this the person preferred processed vegetables and fruits.
But even if you begin to gradually introduce raw fruits and vegetables that increase acidity into your diet, it will not be possible to fully replace treatment. Most experts recommend that you first get rid of gastritis, and only then practice a raw food diet.
Menu (Power Mode)
The menu of this diet is varied, as it includes snacks (salads, aspic, herring, minced meat), almost all vegetables and cereals, meat and fish. Expanding the possibilities of culinary processing of dishes makes the diet even more diverse. The menu is supplemented with fruits, eggs, cottage cheese and fermented milk products.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Reviews and results
Therapeutic nutrition for gastrointestinal diseases is of great importance. First of all, because it allows you to achieve long-term remission and prevents the progression of the disease. This diet is quite varied, which allows you to follow it for a long time. Reviews from patients indicate the effectiveness of this diet, and rapid improvement in condition allows you to gradually expand the diet.
- “... The acidity was checked 2 years ago, and it was reduced. I didn't check again. During an exacerbation, heaviness in the stomach and discomfort, belching and bloating appear. I go on a diet and drink Plantaglucide (it relieves pain and increases acidity). I brew St. John's wort and yarrow. I have been following the diet for 3 weeks: I eat porridge, boiled meat, soups and exclude vegetables, except pumpkin, zucchini and potatoes. In three weeks, the condition improves significantly - apparently, with gastritis, proper nutrition is the main thing. By the end of the month, I allow myself lightly fried and then stewed cutlets, more boiled and chopped vegetables”;
- “... I was treated in a hospital, and then they diagnosed gastritis with low acidity. During an exacerbation, I make sure to follow a diet. Everything in combination (herbs, Acidin-pepsin, proper nutrition) helps. In general, this takes 3 weeks: the heaviness in the stomach, bloating decreases, and I can even eat milk porridge. The diet is not complicated and you don’t have to starve. You can eat any fish and meat dishes, broth-based soups and porridges. I’m on it for about 3 months, and then I expand it a little. This type of nutrition allows you to improve your health and lose weight. The important thing is that you don’t need meals for yourself separately, since the whole family adheres to this diet”;
- “... Once a year I have an exacerbation, during which I experience pain and heaviness in my stomach. Once upon a time we checked the acidity - it was low, I think that over the years it could not increase, so I take a collection of herbs that increase acidity (St. John's wort, plantain, wormwood). It is important to eat right during an exacerbation: you cannot eat hot sauces, smoked foods, or seasonings. I introduce porridge with water, soups, vegetables (only stewed) and boiled meat or fish.”
The importance of diet for gastritis
This pathology is often accompanied by atrophy of glandular cells. As a result of the chronic inflammatory process, the mucous membranes begin to thin out. The amount of hydrochloric acid, which activates digestive enzymes, decreases, as a result of which the process of fragmentation and absorption of protein molecules is disrupted.
If during remission a person feels relatively well, then the exacerbation stage is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. Patients complain of stomach pain, constant bloating, nausea, loss of appetite, belching, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. All these signs are associated with disruption of digestive processes - food is not completely digested and is not absorbed by the body. The evacuation of the food bolus from the stomach is disrupted - food stagnates, fermentation processes are activated.
Nutrition for this disease should increase appetite and stimulate the activity of mucous membranes. With the help of a diet, you can relieve discomfort, prevent weight loss, and reduce the likelihood of developing cancer.