Villous tumor of the rectum is a benign epithelial formation that is prone to malignancy. The insidiousness of the disease is that it may not manifest itself for a long time, while treatment in the initial stages is the least traumatic and very effective.
- Features of villous tumor
- Causes of development and risk factors
- Classification
- Clinical picture
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
Features of villous tumor
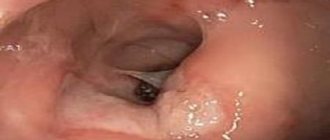
The neoplasm has a round or oval shape, pinkish color and a peculiar papillary or velvety surface. The main element of the tumor is the villus. It is an elongated connective tissue formation that contains many vessels and is covered on the outside with columnar epithelium. Numerous villi merge with each other and form lobules, which are visible to the naked eye on the surface of the formation.
The villous tumor grows mainly in the lumen of the rectum. The size of the tumor can vary: from a few millimeters to 6-8 cm or even more.
Types of benign tumors
A benign tumor can grow in any tissue. There are several types of neoplasms.
Fibroma
Fibroma is a tumor consisting of fibrous connective tissue. It has a small number of connective tissue spindle cells, fibers and vessels.
Fibroids occur most often in women on the genitals. It manifests itself as menstrual irregularities, infertility, severe pain during sexual intercourse, painful and protracted periods. Intermenstrual bleeding often occurs, which leads to a deterioration in overall health and a decrease in hemoglobin levels.
Subcutaneous fibroma is also found, manifested by a flesh-colored formation. It can be diagnosed by its dense structure.
Lipoma
Lipoma is otherwise called a fatty tumor and is a formation that is practically no different from normal adipose tissue. When diagnosing, a capsule is noted that characterizes the disease. Lipoma often forms in women during menopause and can reach enormous sizes.
Lipoma causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient. It is mobile and painful, forcing you to remain in a lying or sitting position for a long time.
Chondroma
Chondroma consists of cartilaginous tissue and has the appearance of hard tubercles. The cause of the development of a benign formation is trauma or tissue damage. Chondroma can appear either in a single instance or in multiples, affecting mainly the limbs. The tumor develops slowly and may not manifest itself. Chondroma can be identified by diagnosing the skin.
Neurofibromatosis
Doctors also call neurofibromatosis Recklinghausen's disease. The disease is the formation of a large number of fibroids and age spots. In this case, inflammation of the nerves occurs. The symptoms are pronounced, although difficulties may arise during diagnosis due to the involvement of several tissues in the process of tumor development. Often there are incomplete forms of the disease, manifested by the formation of nodes on the sensory nerves.
Osteoma
Osteoma is a benign formation consisting of bone tissue. It has clear boundaries and rarely develops into a malignant tumor. Osteoma is a congenital disease and is formed as a result of pathological development of the skeleton. A single tumor of this type is more common.
Myoma
Myoma is a single or multiple encapsulated formations with a dense base. The disease develops in muscle tissue and most often affects the female reproductive system. The cause of the tumor can be hormonal disorders, abortion, obesity.
Myoma manifests itself as menstrual irregularities, heavy and painful menstruation, and infertility. If the disease is not cured before pregnancy, there is a high probability of miscarriage and fetal death. Myoma is inherited.
Angioma
An angioma is a benign tumor that develops from blood vessels. The disease is congenital, spreading mainly on the cheeks, lips, and oral mucosa. Angioma is manifested by greatly dilated tortuous vessels that have a flat, swollen shape. They form under the skin, but are clearly visible on the surface of the integument. Another type of benign tumors, hemangiomas, are very common and are congenital birthmarks with dilated capillaries. Such formation does not always require treatment; it is only necessary to follow the basic rules of caring for moles and systematic observation by a specialist.
But angiomas are not always safe. Under the influence of external factors (ultraviolet radiation, damage), the disease can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Lymphangioma
Lymphangioma is a benign tumor consisting of lymphatic vessels. It is formed during embryonic development and continues to grow in early childhood. More often, lymphangioma stops developing and does not pose a threat to life.
Glioma
Glioma is similar in development to angioma, since it can manifest as hemorrhage. They are neuroglial cells with processes.
Neuroma
Neuroma is a benign neoplasm that develops on peripheral nerves and in the roots of the spinal cord. Neuroma on the cranial nerves is slightly less common. The tumor looks like many small nodes of different sizes.
Neuroma
Neuromas are tumors that form on various elements of the nervous system. The cause of the disease is often amputation and nerve damage. Congenital neuromas also occur.
The disease manifests itself as pain in the area of the tumor, and redness of the skin may occur.
Ganglioneuroma
This type of tumor develops mainly in the abdominal cavity and is a dense formation of large size. They consist of nerve fibers and practically do not manifest themselves with slow development.
The disease begins to develop in the womb. There are many reasons for this - disturbances in the development of the nervous system, the impact of unfavorable factors on the mother’s body during pregnancy, various infectious diseases.
Paraganglioma
Paraganglioma is a tumor composed of chromaffin cells. The disease can develop in any organs and tissues where these cells are present. The tumor is congenital and begins to manifest itself at an early age. The disease is dangerous due to the development of metastases.
The disease manifests itself as frequent headaches, increased blood pressure, shortness of breath, and tachycardia.
Papilloma
It is a formation in the form of small stalks or nipples, in the center of which there is a blood vessel. Papilloma is the most common type of benign tumor and is easily removed. There are no relapses after surgery.
Papilloma occurs as a result of exposure to the papilloma virus. More often the disease affects the genitals and mucous membranes. The tumor appears as dense formations, causing discomfort and painful sensation when touched. Also classified as papillomas are warts, which are mostly safe and do not require treatment. Exceptions are formations that bleed and cause pain. Warts that grow and change color pose a danger.
Adenoma
Adenoma has one characteristic feature - it repeats the shape of the organ on which it is formed. The tumor consists of glands and rarely degenerates into a malignant formation.
More often, adenoma affects the prostate in men over 45 years of age. The disease manifests itself as painful and frequent urination, decreased sexual activity, early ejaculation, and infertility. Adenoma does not pose a threat to humans, but can significantly impair the quality of life and lead to mental disorders.
Cysts
A cyst is a benign formation that does not have clear boundaries. It consists of a soft cavity, often filled with liquid. The cyst develops rapidly, which poses a threat to the patient’s life. If the tumor ruptures, there is a risk of blood poisoning. Cysts rarely develop without symptoms. Appear on the genitals, in the peritoneum, bone tissue, and brain.
Appearance of tumors
Benign tumors can have different structures and structures:
- An oval or round node, similar to the structure of a cauliflower and a mushroom cap;
- Tumors associated with body tissues have a stalk (polyps);
- Cysts are elongated formations filled with fluid;
- In many cases, tumors penetrate tissues, due to which their border is not determined.
Causes of development and risk factors
The exact causes of benign neoplasms of the rectum, including villous tumors, are not completely clear. Factors that, according to a number of researchers, may influence the increase in incidence of this type are:
- Decreased level of physical activity.
- Dietary features (addiction to high-calorie foods with high fat content, insufficient fiber intake).
- Deterioration of the environmental situation.
Villous tumors usually form in older people. Men suffer from this disease somewhat more often than women.
What is a benign tumor?
A benign tumor is a disease that occurs as a result of a disruption in the mechanism of cell division and growth. As a result of this, their structure changes in a certain area, a formation appears that is unusual for the normal state of the body and, as a consequence, the manifestation of symptoms.
A feature of a benign tumor is its slow growth. Often the formation retains its original size for several years, after which complete healing occurs or it develops into malignant. Another characteristic feature is the lack of influence on the body and the appearance of metastases. The tumor forms in one area where it develops slowly. Other organs are not affected. If we compare a benign tumor with a malignant one, then in the case of the latter, it is not the tumor that poses the particular danger, but metastases. They rapidly destroy organs and tissues, leaving virtually no chance for a complete recovery. With a benign formation, the prognosis is mostly positive and after a course of therapy, as well as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, the disease recedes.
A benign formation can be determined by the following signs:
- The tumor is mobile, not connected to the surrounding tissues;
- When pressing or touching, discomfort or pain is felt;
- With internal tumors, there is a deterioration in health, fatigue, and sleep disturbances;
- External tumors of the mucous membranes and skin may bleed.
More often, benign tumors do not manifest themselves, which presents difficulties in diagnosis. The disease can be detected during a routine examination and pathological changes in the skin.
Classification
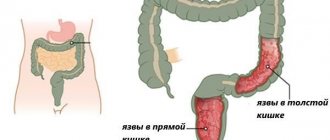
There are two forms of villous tumor:
- Nodular, more common, has the appearance of a single tumor node on a wide base.
- Creeping - lobular growths line the inner surface of the rectum. Damage to the mucous membrane can have a significant extent.
Based on the nature of the surface, these new formations are:
- Fringed, which have pronounced villi.
- Lobed, resembling cauliflower in appearance.
Solitary villous tumors are more common. Multiple formations of this type are diagnosed extremely rarely.
general description
Benign diseases of the colon are mostly represented by polyps.
Lipomas (benign tumors from adipose tissue) are extremely rare in the colon. Colon polyps are benign tumors from elements of the colon mucosa and submucosal layer. The reason for the appearance and growth of polyps is unclear. With the exception of diffuse familial polyposis, in which the hereditary nature of the disease is clearly established, heredity in relation to single colon polyps has not yet been proven. Colon polyps are divided according to histological characteristics and the possibility of malignancy, which directly depends on the size of the polyp, the duration of its existence, and the histological picture. Glandular polyps (tubular adenomas) are the most often malignant.
The risk of malignancy of a polyp increases with its size and duration of existence: the larger the size of the polyp, the higher the risk of its malignancy.
Clinical picture
The disease may be asymptomatic for a long time. Therefore, often a neoplasm is discovered only when a person consults a proctologist as planned or for another reason.
Patients with rectal villous tumor may complain of:
- Constipation and difficulty in defecation, feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
- Discharge of a mucous nature, which can lead to maceration and itching of the perianal area.
- An admixture of blood in stool and mucus. With regular bleeding, the patient may experience a clinical picture of anemia: pale skin, weakness, dizziness.
- Pain in the rectum.
If located low, the villous tumor of the rectum may fall out during defecation, and the patient has to straighten it with his fingers. With large tumors, partial or complete intestinal obstruction may form.
Treatment methods
It is completely impossible to cure papillomas in the intestines. The strain is dangerous for relapses, so doctors combine pharmaceutical drugs with excision with a laser, scalpel, current, and radio wave therapy. Since the main cause of the problem is weakened immunity, therapy is aimed at strengthening it. In addition to traditional methods, herbal infusions are used, and applications from the juices of poisonous plants are used for external treatment. There are a great many options and methods for treating intestinal papillomas with folk remedies.
Conservative treatment
Classic therapy for intestinal papillomas includes antiviral drugs that suppress the activity of the pathogenic strain. For this purpose, Reaferon, Genferon, and other drugs of this group are prescribed. Immunomodulatory formulas restore the biological activity of the body. These are: Pentoxyl, Likopid, Immunal, Lavomax, Viferon, Interferon derivatives.
General strengthening agents - vitamins C, B6, tinctures of Eleutherococcus, Schisandra also effectively strengthen the natural barrier.
For the treatment of papillomavirus in the rectum, suppositories with interferon, vitamin C, and α-tocopherol are suitable. Viferon suppositories with antiviral and immunomodulatory effects inhibit pathological cell growth and relieve painful symptoms. Anal suppositories "Genferon" With interferon alpha-2 have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Suitable for this purpose: Panovir, Galavit, Laferobion, Kipferon, Betadine.
To eliminate small condylomas around the anus, use Kryopharma adhesive tape. The skin is moistened with water, and a tape soaked in medicine is fixed on top for 3 hours. The procedure is painful, but effective. Iodine is suitable for this purpose. The surface of the condyloma is treated with a solution until it disappears completely.
Surgical removal
The most effective hardware methods for removing papillomas in the intestines. They are recommended for large growths or an existing risk of degeneration.
Surgery offers non-traumatic methods that remove and prevent the appearance of growths:
- The laser beam burns the warts on the root outside and inside.
- Electrocoagulation is no less effective. The hardware method is combined with colonoscopy.
- Electrocoagulation destroys pathological cells with molecular energy concentrated at the tip of the electrode.
- Cryodestruction is used to remove condylomas near the anus. Liquid nitrogen affects pathologically altered tissues and completely eliminates unaesthetic growths.
- Classic excision with a scalpel is used to remove large intestinal papillomas.
Folk remedies
Despite their viral nature, papillomas in the intestines are successfully treated with folk remedies. To do this, use an enema with celandine. Take 50 dry powder, brew 400 ml of boiling water. Leave it for an hour and insert it into the anus.
Recipe No. 2. Squeeze 1 tsp from fresh leaves. juice, diluted with 4 glasses of warm water. Using a mug, Esmarch is introduced inside and kept for up to half an hour. The course is 2 weeks, after 15 days the sessions are repeated.
Recipe No. 3.
Tampons are inserted into the rectum for 8 hours according to the following scheme:
- for the first 3 days, the tampon is moistened with celandine juice diluted half with water;
- on the next three days, take 2 parts juice + 2 water;
- then dilute 3:1;
- For the last 3 days the juice has been used in its pure form.
To combat external condylomas, the following are useful:
- baths with chamomile and St. John's wort;
- compresses with rowan juice;
- celandine juice;
- ammonia;
- Castor oil.
For immunity, drink fortified drinks. If there is no allergy, 180 g of honey is mixed equally with grated horseradish. The mixture is infused for 3 days, then taken before meals in a spoon. A handful of crushed viburnum is poured with 350 ml of water. Let the fruit drink brew, drink 50 ml up to 4 times a day.
Diagnostics
Instrumental methods for diagnosing a neoplasm include:
- Total colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy with biopsy is an informative study that allows you to detect a tumor, identify its size and location, and also obtain biological material for histological analysis. This requires 3-5 grips with standard endoscopic forceps. The specificity and effectiveness of the method increases with the use of modern technologies (magnifying and narrow-spectrum endoscopy, fluorescent diagnostics).
- Ultrasound using a rectal probe makes it possible to assess the degree of invasion of the walls of the rectum by the tumor.
- MRI of the pelvis, which is preferably performed in the presence of large tumors (more than 3 cm) and if malignancy is suspected. The method helps to clarify the main characteristics of the tumor and assess the condition of regional lymph nodes.
If it is impossible to perform an endoscopic examination, irrigoscopy or CT colonography is recommended.
Treatment
All villous tumors of the rectum must be surgically removed due to the precancerous nature of these tumors. Depending on the size of the lesion and its location, the following types of surgical treatment can be used:
- Endoscopic removal using a diathermic loop. The method is preferable for tumors less than two cm, with the exception of signs of malignancy. The operation is performed in an endoscopy room without anesthesia. The patient can be operated on using one of the technical methods: one-step excision of the tumor, or fragmentation by removal in one stage or during several planned visits.
- Transanal excision of a tumor using mirrors. This method is used for tumors whose lower edge is no higher than 7 cm of the skin of the perianal area. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia or epidural anesthesia.
- Posterior proctotomy - removal of highly located tumors the size of the rectal wall.
- Resection of the rectum is a full-fledged abdominal operation under endotracheal anesthesia with removal of the tumor along with the affected area of the intestine. The use of this method is preferable when detecting large tumors located in the rectosigmoid region.
If at the diagnostic stage signs of malignant degeneration were identified, the scope of surgical intervention is significantly expanded. In this case, the rectum can be partially or completely removed, and pararectal tissue and regional lymph nodes are also excised.
Complications
Possible complications of the disease are:
- Tumor malignancy.
- Formation of partial or complete intestinal obstruction.
- Bleeding with the formation of iron deficiency anemia.
- Impaired water-electrolyte balance and dysproteinemia, which can be observed with giant tumors.
The most dangerous and at the same time very common complication of villous tumor of the rectum is its malignant degeneration. The malignancy index of this type of neoplasm is 30-70%.
Symptoms
Often this disease is asymptomatic, and a benign tumor (polyps) is discovered by chance when the patient consults his doctor because of another disease. The main symptoms are:
- Pain in the abdomen, which most often occurs in the lateral part of the abdominal region, as well as near the anus. The pain subsides after bowel movement or after using a warm heating pad.
- Discharge of blood clots during bowel movement (defecation).
- Pain during bowel movements.
- Changes in stool (alternating diarrhea and constipation).
- Flatulence.
- Anemia.
- Vomiting (with no symptoms of cancerous intoxication of the body).
Prevention
The main method of prevention is regular (once a year) endoscopic examination of the rectum by people over 40 years of age. Such measures make it possible to identify a tumor in the early stages of development and carry out the necessary treatment, preventing the possible development of cancer.
It is worth noting that currently there are various options for helping cancer patients suffering from villous tumor of the rectum, even with a widespread tumor process. Having qualified oncologists on staff allows us to achieve the best possible result in each specific case.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78