Indications
Passage of barium through the small intestine is used in several situations. First of all, it is prescribed in case of causeless diarrhea. If a person leads a healthy lifestyle and eats right, but has constant diarrhea, then this study is necessary to identify the cause of the disorder. In addition, such a symptom may indicate the development of a more serious pathological process.
The procedure is also necessary when blood impurities are found in the stool. However, in this condition, the study must be carried out with extreme caution, since incorrectly performed actions can provoke even more severe bleeding.
An indication for the passage is pain in the abdominal area. An X-ray with a contrast agent is performed if the pain syndrome is accompanied by other symptoms. However, it must be remembered that if the pain is pronounced, then this type of examination cannot be prescribed.
On this topic
- Digestive system
Differences between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2021
A specialist can refer you for a barium passage even if you are rapidly losing weight. This is explained by the fact that unreasonable weight loss along with proper nutrition may indicate the appearance of cancer.
The procedure is also used for congenital anomalies. Thanks to x-rays, it is possible to identify the abnormal structure of the intestines, as well as determine how it affects the digestive process.
X-ray of the abdominal cavity (survey)
Survey radiography of the abdominal cavity is a method of non-contrast X-ray diagnostics of the condition of the abdominal cavity.
For the abdominal organs, this method is not very informative, since the soft tissues of the body are mostly X-ray negative, i.e. with such a study, the radiologist will not see images of the abdominal organs. Based on survey X-ray data, the doctor can only judge the presence and distribution of gas, liquid, as well as stones or foreign bodies in the abdominal cavity and digestive tract. The method is effective in diagnosing ruptures and perforations of the genital organs of the abdominal cavity. The images will show free gas in the abdominal cavity, which normally should not be there. Plain radiography is the main method for diagnosing intestinal obstruction (the images will show shadows of distended intestinal loops with levels of liquid and gas, the presence and location of which can be used to judge the presence and location of obstruction). Survey images can also show kidney and gallstones, the presence of blood and ascitic fluid in the abdominal cavity.
For what diseases is an abdominal x-ray performed?
- cholecystitis;
- nephrolithiasis, urolithiasis;
- pancreatitis;
- blockage of the intestinal lumen by a tumor;
- intussusception;
- abscess;
- diverticulitis;
- appendicitis;
- injuries;
- inflammatory bowel diseases;
- intestinal ischemia;
- small bowel obstruction
Most often, the examination is performed without special preparation (for emergency indications); a cleansing enema (1.5 liters) is routinely administered the night before and on the day of the examination 2 hours before the scheduled time. You can eat.
X-ray of barium passage through the small intestine
Diagnosis of diseases of the small intestine remains a serious problem to this day. Diagnostic difficulties arise due to the large extent of the small intestine, the presence of numerous bends in it and the difficult accessibility of this part of the digestive tract for instrumental diagnostic methods, as well as the low information content of the diagnostic methods used.
X-ray of barium passage through the small intestine - X-ray visualization of the progress of contrast through the small intestine. Radiography reveals diverticula, strictures, obstructions, tumors, enteritis, ulcerations, malabsorption and motility of the small intestine. X-ray contrast examination of the small intestine is carried out after ingestion of a barium suspension solution (barium sulfate). As the contrast moves through the small intestine, targeted radiographs are taken at intervals of 30-60 minutes. X-ray is completed after all its parts have been contrasted and barium has entered the cecum.
Radiography of the passage of barium through the small intestine requires preparation of the intestine for the study: the use of a slag-free diet and laxatives in order to accelerate the passage of barium during the study.
The drug "Fortrans". The package of the drug is dissolved in 1 liter of boiled water or mineral water without gas. Preparation includes taking 3-4 sachets (dissolved in 3-4 liters of water) depending on weight. Take once in the evening, on the eve of the test, starting at 18:00, 1 liter of the drug with an interval of 1 hour. Take 2 liters of solution the evening before the examination and 2 liters on the day of the examination 3-4 hours before the procedure.
Recommended diet during the day:
Recommended: white bread, boiled meat, fish, butter, cheese, pasta.
Not recommended: dairy products, vegetables, apples, brown bread, spicy seasonings, coffee, chocolate, alcohol.
To achieve the best image quality, your stomach should be empty. On the day of the examination, it is advisable not to eat or drink anything (including any medications, especially antacids), and refrain from chewing gum and smoking.
Return to RADIOGRAPHY section
Contraindications
Despite the fact that this technique is effective and informative, there are certain limitations to its implementation. Experts identify a number of conditions and situations when examination cannot be carried out.
Pregnancy
Doctors do not recommend the procedure during pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that when the intestines are full, there is pressure on the uterine body. In addition, barium can negatively affect fetal development.
X-ray radiation also poses a danger to children. An examination can be carried out only when there is an emergency need, and the use of other diagnostic techniques is not possible for some reason.
Biopsy
This study involves taking a small piece of biological tissue for further study. If barium is present in this area of the mucosa, irritation or an inflammatory process may begin.
Severe pain
During the procedure, the patient must remain motionless. Severe pain usually disrupts this process. In addition, when exposed to a contrast agent, the pain can only intensify until loss of consciousness.
Intestinal perforation
If this pathology is suspected, the method is also not used, or the contrast is replaced with a water-soluble one. In case of perforation during the use of barium, the risk of developing peritonitis increases several times.
Passage of barium through the intestines: purpose, procedure and contraindications
When examining the intestines, an X-ray of the intestine with barium plays an important role. This is a very informative and modern procedure that allows you to detect disturbances in the intestines, find the cause of the disturbances and make a correct diagnosis.
Because X-rays show mostly dense tissue, the hollow intestine appears blurry on the images. To increase the information content, the patient is prescribed a passage with barium, which acts as a contrast agent.
Purpose and advantages of the method
Most often, barium passage through the intestines is carried out if intestinal obstruction is suspected.
X-ray examination of the intestine with barium is not prescribed for preventive purposes. This is a serious procedure that is performed only if there are obvious problems with the large or small intestine and no other examination is possible.
The passage of barium through the intestines significantly increases the information content of the procedure. Without it, it will be difficult to make a diagnosis. The advantage of this method is that the likelihood of pain with it is lower than with a colonoscopy, which allows you to examine only the large intestine. Using X-rays, you can assess the condition of the entire gastrointestinal tract, including the small intestine.
X-ray of the intestine is not the most expensive examination method, but it takes a long time, ideally about a day, if we are talking about the small intestine. For the large intestine, the procedure lasts much less.
X-rays of the lower gastrointestinal tract are prescribed in the following cases:
- Causeless diarrhea. Constant diarrhea, as well as severe constipation with a healthy diet and healthy lifestyle, require examination. Both are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and can be a symptom of a serious illness.
- The appearance of blood in the stool. If blood streaks appear in the stool or black stool, an examination of the intestines is mandatory, but carried out with caution, as the bleeding may increase.
- Stomach ache. For chronic abdominal pain accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, a colonoscopy or barium X-ray is prescribed. Pain syndrome accompanies many diseases, including colon cancer. However, if the pain is intense, the examination is not carried out.
- Weight loss. Unexplained weight loss with a normal diet can be a sign of serious disorders of the gastrointestinal tract or cancer.
- Congenital anomalies. Using X-rays, you can identify congenital abnormalities of the intestinal structure and determine their effect on the digestive process.
The patient cannot prescribe this procedure for himself, but it is also undesirable to refuse it. X-ray examination can detect many diseases at an early stage.
Preparation and procedure
To obtain reliable examination results, you must adhere to certain preparation rules.
The procedure cannot be called painful, but it can be unpleasant and requires special preparation. The X-ray itself is just pictures; the patient takes a certain position and does not feel any impact. The barium passage is much more difficult.
The procedure has its own characteristics, which the doctor warns about in advance:
- If a colon examination is being performed, a barium solution is injected directly into the colon. If you need to examine the small intestine, then you need to drink the solution, wait a certain time and only then take pictures.
- 3-4 days before the examination, the patient goes on a slag-free diet, eliminating all sweets, carbonated foods, and fatty foods. It is not recommended to eat fresh fruits and vegetables, as they increase gas formation.
- The day before the procedure, the patient only has breakfast, and then the process of cleansing the intestines with Fortrans begins. This is the only drug that allows you to thoroughly cleanse both the large and small intestines. A sachet of the drug is diluted in a liter of water and drunk within an hour. You need to drink all 4 packets during the day. After the drug, painless loose stools begin. The intestines are considered clean when uncolored water appears instead of stool.
- You cannot eat on the day of the examination.
When examining the small intestine, the patient drinks a barium solution in the amount of 500 ml. It tastes like lime and is milky white in appearance. After this you need to wait several hours. After about 5 hours, the barium will reach the small intestine and you can start taking pictures.
A total of about 8 x-rays are taken, the procedure stops when the barium reaches the cecum.
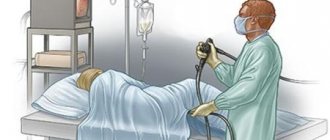
When examining the large intestine, the solution is administered rectally. The patient lies down on the couch and draws his knees to his chest. A thin tube is inserted into the anus, through which barium begins to flow. The patient feels a strong feeling of fullness.
After barium is injected, a small amount of air is introduced. After this, several pictures are taken in different positions. It is important that the barium does not leak out. After the procedure is completed, the intestines are emptied. The stool will be loose and white.
Contraindications and explanation
X-ray of the intestine with barium is a very serious examination procedure, which has a number of contraindications
The doctor deciphers the results. The patient receives a conclusion and photographs. The entire process is evaluated in dynamics. For example, if the image shows that the barium solution in the intestines resembles flakes, then absorption in the small intestine is impaired.
X-rays of the intestine may reveal elongation, numerous tumors (they will appear as darkened areas), and diverticula. If the fluid in the intestines spreads in stages, then there is intestinal obstruction. Diverticula look like filling defects: irregularities, protrusions.
Contraindications for examination:
- Pregnancy. The procedure is not recommended during pregnancy. A full bowel will put pressure on the uterus, and the barium can affect the fetus. X-ray radiation is also dangerous for the fetus. It is advisable to take a pregnancy test before the procedure. The procedure is possible only if there is an urgent need for examination, and other diagnostics are impossible.
- Severe pain. The procedure requires immobility, and severe abdominal pain can disrupt the process. In addition, when barium is introduced into the intestines, the pain can become unbearable, and the patient will lose consciousness.
- Intestinal biopsy. A biopsy removes a small piece of tissue for examination. Barium can cause irritation and inflammation of the damaged area of the mucosa. You must wait a few weeks before taking an x-ray.
- Intestinal perforation. If intestinal perforation is suspected, the procedure is either not performed or the contrast is replaced with a water-soluble one. Barium in case of perforation can cause severe peritonitis.
You can learn more about how to properly prepare for an intestinal x-ray from the video:
Side effects occur infrequently, but they include prolonged constipation after the procedure, flatulence, abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhea, and severe bloating. Side effects go away on their own. Your doctor may prescribe a laxative to help remove barium from your intestines more quickly.
Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Source: https://DiagnozLab.com/mrt/mrt-abdomen/passazh-bariya-po-kishechniku.html
Preparation
Despite the fact that the examination is a painless procedure, during the procedure the patient may experience discomfort. To keep their manifestation to a minimum, it is necessary to follow some preparatory rules.
About four days before the appointed date, it is recommended to follow a slag-free diet. It is necessary to exclude fatty, fried, sweet foods, carbonated drinks, fresh vegetables and fruits from the diet, as they can cause increased gas formation.
The day before the examination, you are only allowed to have breakfast. After this, the patient cleanses the intestines using Fortrans. This medication is the only one that allows cleansing procedures to be carried out simultaneously for the large and small intestines.
On this topic
- Digestive system
The role of hormonal contraceptives in the development of liver hemangioma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2021
The drug in the amount of one packet must be diluted in a liter of water and drunk within 60 minutes. Throughout the day you need to take 4 of these sachets.
After using this remedy, painless diarrhea appears. Colon cleansing ends at the moment when clean water flows out of the anus instead of feces.
It is prohibited to eat barium on the day of the passage.
How to do it
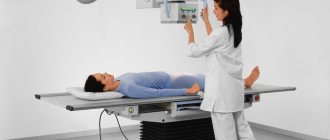
The patient removes all metal jewelry, clothing and underwear, and takes a position chosen by the doctor.
Depending on what kind of research will be carried out, this may be a horizontal or vertical position. In the first case, the examination of the intestines will be more qualitative and accurate, and the second allows you to speed up the process of barium dissolution.
In some situations, the specialist recommends taking the Trendelenburg position. The patient's pelvis should be located above the body at an angle of 45 degrees. This position allows you to more accurately examine the intestines, stomach and diaphragm.
On this topic
- Digestive system
What causes thickening of the intestinal wall
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2021
There is a gradual passage and filling of all parts of the organ with barium. Thanks to the massage movements of the abdomen, the contrast agent is evenly distributed throughout the gastrointestinal tract.
When it is necessary to examine the large intestine, the drug is injected directly into the anatomical structure being examined.
In a comprehensive study, the solution is taken orally by the patient before the procedure.
The mixture is also prepared before starting the study. Its composition contains elements such as air, barium sulfate and aluminum gel. Additionally, sorbitol, sodium citrate or an antispasmodic drug may be added. A single dose is about 400-650 grams.
The resulting solution must be drunk in several doses. First, take a small sip. This is necessary so that the specialist can assess the quality of the mixture, as well as at what speed it moves through the esophagus.
Next, the patient drinks the remaining amount. After this, the entire gastrointestinal tract is filled with barium for some time.
The duration of radiography takes no more than forty minutes. During this time, it is possible to capture 6-10 images. The last picture is taken after the solution is removed from the human body.
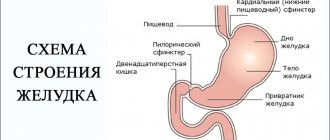
The essence of X-ray examination of the intestine
The method of X-ray diagnostics of the intestine involves exposing the human body to rays invisible to the eye. They pass through tissue, reflecting differently from areas of different density. The process is recorded on film (photograph) or reflected on the monitor. Depending on this, the following types of method are distinguished.
- X-ray of the intestines. It can be direct, when the object is captured in the photograph, or digital - the result is recorded by a special device.
- X-ray of the intestines. Allows you to take a series of pictures and/or watch what is happening on the screen.
Barium is usually used for the procedure. By creating contrast, the substance creates a clearer picture of the state of the organ. It can be taken orally, or liquid with barium during an X-ray of the intestine is administered using the Bobrov apparatus through the anus. In the first case, the method allows you to view the lumen of the stomach, small and large intestine, but the procedure can last up to 5 hours (it takes time for the connection to pass through the entire digestive tract).
If the contrast agent is administered through the rectum, then double contrast can be used. Together with barium, a gaseous substance is injected into the lumen of the organ. The diagnostic time is reduced to half an hour (on average), but changes can only be seen in the rectum and colon.