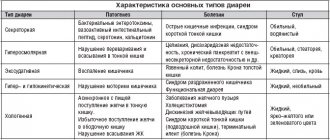
Diarrhea and pain in the lower abdomen
A fairly large number of diseases can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhea, lower abdominal pain, diarrhea and fever, diarrhea and vomiting.
1 One of many diseases, stomach or intestinal ulcers. Food provokes such symptoms, the pain is especially pronounced if the food was quite spicy or sour. Symptoms appear within 20-30 minutes, pain can radiate to the heart, and loose bowel movements are observed.
2 Inflammation of the appendix. With this disease, pain is felt in the lower abdomen, and upon palpation the pain becomes stronger. Inflammation of appendicitis does not affect stool, however, inflammation of the cecum is characterized by diarrhea. In such cases, experts do not recommend taking a drug to relieve pain and placing a cold heating pad on the problematic part of the abdomen. All actions must be coordinated with doctors, since self-treatment will have side effects and may lead to undesirable manifestations.
Infectious lesions of the gastrointestinal tract
Food poisoning is a set of symptoms of a digestive tract disorder (nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature), which can be combined with other unpleasant symptoms. Most often, the disease can be diagnosed in a child, since the immune system is not fully formed.
The causes of the disease are associated with the consumption of poor quality food and water, poisonous plants, inedible mushrooms, chemicals (salts of heavy metals, dyes, toxins, etc.). Food poisoning, depending on the severity, can begin in different ways: starting with an increase in temperature to 37 degrees and ending at 40.
Malaise, general weakness, stool disorder in the form of frequent bowel movements, severe cramping abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, decreased blood pressure and cold sticky sweat appear.
In severe cases, symptoms not related to the digestive tract may appear: decreased vision and hearing, headache and muscle pain, convulsions, and others. Treatment requires emergency hospitalization. In such cases, it is necessary to do dehydration therapy.
Colitis (enterocolitis)
An inflammatory disease characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the small or large intestine. The disease can be either infectious or non-infectious. Most often, the disease is combined with acute gastritis and allergies. There are many reasons why the inflammatory process occurs.
Most often it appears as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by any infection, helminths, poisons, or caustic chemicals. But there are other factors that contribute to the development of the disease: poor diet, prolonged and frequent constipation, primary diseases that result in colitis.
Symptoms of damage to the intestinal mucosa begin with abdominal pain in the navel area, stool upset (diarrhea gives way to constipation), increased gas formation and bloating, and weight loss. An admixture of mucus and blood may appear in the stool, which indicates severe inflammation and a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane.
An infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella. Another name for the pathology is bacterial dysentery. Based on the observations of specialists, it was concluded that people living in large cities are more susceptible to the disease. This is due to the fact that the city has a much higher population density.
People with a low standard of living, who do not have access to clean water and the opportunity to eat quality foods are also more susceptible to infection. Shigella enters the body through food, water or household contact.
Bacterial dysentery begins acutely: nausea and vomiting, cramping pain in the lower abdomen, in which there is a constant urge to defecate, tenesmus after bowel movements, watery diarrhea with streaks of mucus or blood, the number of bowel movements reaches 10 or more times in 24 hours, in which the number of feces is compared to spit.
Due to this condition, patients experience general weakness, malaise, dry skin and mucous membranes as a result of dehydration. The body temperature is high and can reach 39 degrees, severe headache and chills appear. Treatment of the disease is carried out with antibacterial drugs under the supervision of a doctor.
Salmonellosis
Acute intestinal disease caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella. The source of infection can be carriers or sick people, infected animals (poultry, livestock, cats, dogs, etc.), dirty water, contaminated food. It is worth noting that freezing does not affect the virulence of bacteria.
Salmonellosis can begin to appear several hours after the bacteria enter the body. Of all the forms, the gastroenteric form of the disease is the most common. It manifests itself:
- in the form of a sharp rise in temperature and signs of intoxication (headache, malaise, general weakness, body aches);
- paroxysmal pain appears in the abdomen;
- diarrhea with foamy and foul-smelling green stool.
Nausea and vomiting may occur more than 5–7 times a day, depending on the severity of the illness. Treatment of salmonellosis is possible only with hospitalization.
Stomach pain, diarrhea and fever
1 Such sensations can be caused by inflammatory processes of the intestines, or as they are also called intestinal infections (salmonellosis, yersiniosis and others). Infections enter the body through the oral cavity, and bring with them a general deterioration of the body, headaches, attacks of nausea and vomiting.
In such cases, you need to refuse food until an accurate diagnosis is made. On the recommendation of a doctor, food intake may also be limited in the future. Taking medications without consultation is also highly undesirable; it can cause side effects, but drinking plenty of fluids, on the contrary, will help you with such symptoms. Since diarrhea causes dehydration of the body and leaching of useful substances from the tissues of internal organs. For frequent vomiting and diarrhea, it is recommended to take saline solutions. Salt retains moisture in the body and prevents dehydration. In cases where there is no vomiting, you can take absorbent drugs. Activated carbon, enterosgel.
2 Dysentery. Characteristic manifestations are loose, watery stools, pain has the properties of contractions, the temperature can rise to 38-40 degrees, which carries certain risks with such symptoms. The skin also becomes very pale, the pulse rate increases, and the general condition of the body is characterized by weakness.
Signs of dysentery cannot be ignored; you should definitely contact an ambulance, since the nature of the disease is infectious in nature and the patient must be hospitalized, the process occurs under the supervision of specialists.
Main reasons
The main reasons why the stomach hurts and diarrhea appears in an adult or child are diseases of an infectious or non-infectious nature. They are often accompanied by fever and general malaise.
The problem of the 21st century is poor nutrition and, as a result, diseases of a non-infectious nature, i.e. disrupting the structure of the gastrointestinal tract and their functions. This is primarily due to quick snacks, which have become a part of everyday life.
No less terrible are diseases of an infectious nature that arise as a result of people’s lack of the habit of washing their hands after coming home, using the toilet, before eating and other basic hygiene rules against the backdrop of ever-increasing migration, with which new, hitherto unknown viruses are coming to countries.
Since each type of disease has many characteristics, they will be discussed in detail in this article.
Infectious diseases
All infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract arise due to exposure to an external pathogen. These are bacteria and viruses, which, when they enter the intestines, begin to actively multiply and poison the body with waste products. In rare cases, the microorganisms themselves cause ulcers, thinning of the intestinal walls and other changes.
All diseases of this nature have similar developmental features. These include:
The incubation period differs significantly between bacterial and viral forms of the disease. If in the latter it can last up to two, in rare cases three days, then a bacterial infection can manifest itself within 1-2 hours after entering the intestines. The clinical manifestation of the disease is accompanied by pain, diarrhea, and often vomiting. The peculiarity of infectious diseases is that they are accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature, reaching 38-40 degrees C. After the manifestation of clinical signs, an active fight against foreign organisms begins. But often the strength of the immune system is not enough, since the human intestine contains a huge amount of nutrients for the causative agent of the disease. Therefore, at the first symptoms of an infectious gastrointestinal disease, you should consult a specialist. Recovery period. This event is marked by a decrease in temperature to normal levels, cessation of abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea. However, after the symptoms disappear, there is a long recovery process ahead.
As you can see, all infectious diseases have a similar development pattern, but still, each of them has its own distinctive features that are unique to it.
Here are just a few common infectious diseases that you need to know in detail:
Food poisoning Intestinal infection Dysentery Enteritis and colitis
Food poisoning
All poisonings are infectious in nature.
However, they are divided into bacterial and viral. A distinctive feature of the bacterial form is the rapid manifestation of clinical symptoms. This is due to the fact that toxins (the waste products of bacteria) are already present in large quantities in food. While viral poisoning manifests itself no less than 12 hours later (the virus needs to accumulate colonies in a person). The external symptoms of both bacterial and viral poisoning are the same, the difference lies in the severity of the manifestations.
Acute poisoning is accompanied by vomiting, severe pain in the abdomen, as a rule, the right side near the ilium hurts, and frequent pain occurs in the colon (projected to the left side of the lower back). Feces are light in color, liquid in consistency and have a characteristic pungent odor. Headaches and fever may occur. This condition is treated with rinsing, drinking plenty of fluids and diet.
There are also cases of mild poisoning, when a person does not experience pain or other ailments. The only thing that worries him is diarrhea, which has a strong unpleasant odor, but is not as frequent as in acute poisoning. Such cases occur quite often. They indicate the body’s ability to cope with infection on its own: with the help of diarrhea, pathogenic microorganisms are urgently eliminated. You can only help him by drinking plenty of fluids and abstaining from eating food for 1-2 days.
Intestinal infection
This concept includes many diseases of a viral nature. Rotaviruses, astroviruses, adenoviruses and many other viral forms can cause illness.
Infection most often occurs by airborne droplets, but it can spread through food. Since the virus has a capsid (a special protective shell), it can remain outside the host’s body for a long time.
A distinctive feature is the localization of the pathogen in the small intestine, less often in the large intestine. Since the stomach has a natural defense - hydrochloric acid, the virus passes through it in an inactive form. After entering the place of its future breeding, at least 24 hours must pass for the population to increase in order for the organism to notice it. After this, the body temperature rises to 40 degrees, which indicates the beginning of the immune system’s struggle. This is accompanied by frequent diarrhea, as the body thus tries to wash the infection out of itself. Vomiting occurs less frequently with this disease. Pain occurs in the epigastric region. Also, pain can change its location throughout the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to intestinal spasms (where there is spasm, pain occurs). Feces have a characteristic liquid consistency, a pungent odor and are often light in color (comparable to the color of clay).
At the onset of an intestinal infection, it is best to consult a doctor who will take stool tests to rule out the possibility of a bacterial infection, and also prescribe a strict diet and medications to help the body cope with a viral infection, for example Enterofuril.
Everyone knows that diarrhea causes dehydration, so the sick person should increase the amount of fluid they drink. The best option in this case would be simple boiled water or unsweetened tea. During the illness, it is better to refuse food, since it will give the pathogen “soil” for development and delay recovery. If there is no vomiting, you can use
Smecta
or activated carbon.
Dysentery
A dangerous disease of infectious nature. The causative agent is the dysentery bacillus, therefore the disease is of a bacterial nature. Has such symptoms as: very frequent diarrhea, weakness, general malaise. In the acute form, the stomach begins to ache in a cramping manner (pain occurs in the iliac regions, along the white line of the abdomen and in the navel), the general condition worsens, tachycardia occurs, and body temperature rises to 40 degrees. Dysentery is marked by a very pungent, often putrid odor of feces. During long-term treatment, the person defecates with water containing the same odor.
The danger is that the bacteria need some time to grow a colony, in other words, the incubation period lasts several days (usually 3-4 days, it all depends on the body’s immune system), and as a result, the disease takes a person by surprise, without previously visible signs. Dysentery is called the disease of dirty hands. From the name it is clear that the stick is transmitted through dirt on the hands. It is found much less frequently in contaminated food products.
If there are obvious signs of dysentery, you should call an ambulance. The disease has a pronounced infectious nature and is dangerous both for others and for the sick person. Therefore, it is treated in the infectious diseases department under the strict supervision of a doctor, in contrast to outpatient treatment of intestinal infections.
Enteritis and colitis
These diseases have much in common and differ only in localization: enteritis in the small intestine, colitis in the large intestine. Both diseases are accompanied by periodic pain, and in the acute form, constant pain. The reasons for this are the presence of a bacterial or viral infection (typhoid, cholera), which disrupt intestinal function.
The secretion of the small and large intestines is disrupted due to inflammation of the mucous membrane. The ability to absorb nutrients is lost. It can also lead to disruption of intestinal motility. In this regard, a person suffers from light sand-colored diarrhea with a pungent odor. Each bowel movement is accompanied by acute pain in the lower abdomen, and when the disease degenerates into a chronic form, the pain becomes permanent and dull.
Diagnosis occurs in several stages:
First of all, the attending physician collects anamnesis and interviews the patient, percussion and auscultation. To confirm the primary diagnosis, a coprogram, an x-ray, an endoscopic examination, a functional study for dysbiosis and a biochemical blood test are performed to determine the presence of malabsorption.
Inpatient treatment of the disease includes lavage and antibacterial or antiviral treatment. This happens in acute cases, when there is a risk of intestinal atrophy followed by an infectious process leading to ulcers. Home treatment involves drinking plenty of fluids, taking medications that enhance intestinal motility, and eating any astringent foods.
Non-communicable diseases
There are enough diseases that are caused by external factors not related to infection. Their occurrence is often associated with a person’s negligent attitude towards his own body - frequent snacks on the go, lack of adequate nutrition and timely examination by a specialist. Exacerbation of chronic diseases accounts for about a third of all non-communicable diseases. At the same time, there are often cases when diseases of other organs not related to the digestive process are the causes of gastrointestinal disorders.
Abdominal form of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction occurs due to myocardial vasospasm. Its abdominal form occurs with spasm from the diaphragm. Of course, the heart attack itself has many associated factors such as:
Genetic predisposition Obesity Alcohol abuse Smoking Sedentary lifestyle
This form of heart attack is dangerous because it has clinical signs similar to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Accompanied by sharp, cutting pain in the stomach, spleen and liver. This is caused by irritation of the vagus nerve, which can cause headaches, nausea and diarrhea (it's worth noting that the frequency of bowel movements will vary from person to person). The stool has a liquid consistency and is lighter in color than normal. However, it does not have a sharp putrid odor, as in case of poisoning or other infectious diseases. The condition is also accompanied by increased blood pressure, tachycardia and bloating.
In order to diagnose abdominal myocardial infarction, it must be differentiated from diseases such as:
Ulcer Enteritis Cholecystitis Pancreatitis
This form of heart attack can be distinguished using the methods indicated below:
Anamnesis is collected: patient complaints and cases of heart attack in the family. The latter plays a big role, since often, if close relatives have had a heart attack, the patient is immediately included in the risk group. First of all, this is done in elderly patients, since all of them, without exception, are at risk. The final diagnosis is made after an ECG, MSCT and coronary angiography. In rare cases, with an abdominal form of myocardial infarction, blood is taken for analysis.
A distinctive feature of the disease is that after some time (from 12 hours to 8 days), it flows into its usual form.
Myocardial infarction is treated in a hospital setting. The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit, where doctors stabilize his condition. Afterwards he is transferred to a regular ward. For the first three days, you must observe strict bed rest (you cannot sit down and it is undesirable to roll over). During 2 weeks of inpatient treatment, medications are prescribed: beta blockers, statins, nitrates, Aspirin, Clopidrogel. A doctor should prescribe supplements that strengthen the heart muscle. Required: magnesium, coenzyme Q10 and L-carnitine. The patient continues to take the medications selected in the hospital after being discharged home. In this case, it is necessary to follow a salt-free diet, give up fatty foods, alcohol and smoking, and limit physical activity.
Gastritis and ulcer
Today, gastritis, or rather its catarrhal form, and, as a consequence, gastric and duodenal ulcers are very common diseases. This is due to poor nutrition, namely the abuse of fatty and spicy foods. The disease is non-infectious and occurs due to thinning of the stomach walls and loss of their functions.
The first stage of the disease is gastritis, accompanied by periodic paroxysmal pain in the epigastrium. Any spicy, fried or fatty food increases these pains and provokes diarrhea, which is characterized by a lighter color and the presence of undigested foods. In the absence of treatment and non-compliance with the diet, an ulcer develops against the background of gastritis.
Essentially, an ulcer is a severe thinning of the wall of the stomach and intestines, followed by hemorrhage and loss of cell function. The advanced form is considered to be a perforating ulcer (a through hole in the stomach or intestines). This disease can cause very strong, burning, cutting pain, from which a person can lose consciousness. If an ulcer is detected, immediate hospitalization is required, followed by drug treatment and strict adherence to a diet excluding fatty and spicy foods, baked goods, alcoholic and carbonated drinks. Particularly severe cases - exacerbation (open ulcer) or perforation - require surgical intervention.
These diseases are diagnosed primarily by palpation. To confirm the disease, gastroscopy and FGDS (helps to distinguish an ulcer from gastritis), and x-rays are used. A biopsy is prescribed for chemical analysis of gastric juice.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendage of the cecum has many causes. One of the most common is poor nutrition and, as a result, disruption of intestinal microflora and motility. In this regard, stool stagnates and accumulates in the cecum. Without proper treatment with microorganisms, they become dangerous to the human intestines. Since the appendix is a concentration of lymphoid nodes, it primarily responds to such accumulations with inflammation. This may subsequently be aggravated by an infectious process.
Appendicitis does not involve uncontrollable bowel movements or vomiting. A distinctive feature is severe pain in the area of the right ilium, projected to the groin area.
Inflammation can only be prevented by a balanced diet and taking care of your own health. Otherwise, appendicitis, which can only be treated surgically, that is, removal, cannot be avoided.
Stomach pain, diarrhea and vomiting
A symptom that fits this description is enteritis, or inflammation of the small intestine. With the acute nature of this manifestation, disturbances in the body’s water balance, deterioration in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, and general intoxication of the body are possible. The cause of the disease may lie in food. An unbalanced diet can lead to a lack of vitamins in the body and a lack of protein, this leads to deterioration of the small intestine, the function of food absorption is weakened, which leads to weakening and disruption of secretory and motor functions. Treatment for enteritis has a fairly simple structure; success is due to the precise implementation of recommendations and their consistency.
1 a cleansing procedure (enema) is applied;
2 drinking plenty of water;
3 taking medications of an absorbent and astringent nature;
4 diet.
Food poisoning, or colitis, causes similar symptoms. The cause of poisoning is poor quality food consumed. Food may expire, or food storage conditions may not meet standards, resulting in a spoiled product. Such food contains toxic substances of a bacteriological nature that cause poisoning, and to this are added pain, attacks of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The general condition is deteriorating.
1 poisoning of a bacterial nature is characterized by diarrhea, abdominal colic, and vomiting after eating for an hour.
2 poisoning caused by viruses, manifests itself within a day or two after eating, causes vomiting, headaches, the person has a fever, and severe chills are felt.
3 chemical poisoning manifests itself within half an hour after ingesting low-quality products. Characterized by severe sweating, accompanied by diarrhea, vomiting, strong salivation, and pain in the abdominal area. A gastric lavage procedure, drinking large amounts of liquid, and an enema are recommended. When poisoning is caused by different foods, treatment may vary.
Colitis is characterized by stomach cramps and diarrhea, causing general deterioration of the body. The manifestation of acute colitis, caused by bacteria that have entered the intestines and stomach, leads to high fever. The stool is mucous with traces of blood. Colitis can develop into a chronic stage; it is also characterized by stomach cramps causing pain, which intensifies before or after defecation. Loss of appetite, vomiting, possible constipation or diarrhea.
It is imperative to understand that all the symptoms described in this text can be caused by diseases completely unrelated to the intestines or stomach. Diseases unique to women can cause similar problems and symptoms in the body. Any decision when certain symptoms occur should be made only after consultation with a specialist. Perform the prescribed procedures clearly and in a timely manner, do not interrupt the treatment process until complete recovery. Be sure to get examined at the end of treatment and consult with your doctor.
Treatment
Treatment can be carried out both in a hospital and at home - everything will depend on the patient and the diagnosis. In most cases, they are limited to conservative methods; a diet is always recommended along with a course of therapeutic measures.
Drug treatment may include the following drugs:
- painkillers;
- antispasmodics;
- drugs that remove toxins – Smecta, Atoxil, activated carbon;
- antidiarrheal;
- antimicrobial;
- antibiotics;
- probiotics;
- antipyretic.
Since vomiting and diarrhea lead to fluid loss, the patient must maintain proper fluid intake to prevent dehydration. Additionally, a dropper may be prescribed to restore water and electrolyte balance.
Also, if there is fever, diarrhea or abdominal pain, you should definitely adhere to a special diet. The exact dietary table is determined by the attending physician, but there are several general principles of nutrition during treatment for children and adults:
- for an adult, fatty, fried, pickled, seasoned, spicy, canned foods are excluded from the diet, and these foods should not be given to a child;
- food should be light, in small portions;
- food should be boiled, steamed or stewed without fat;
- do not drink alcohol;
- confectionery with creams is also prohibited;
- Dairy products with a high percentage of fat content should not be consumed;
- food should be warm;
- The optimal consistency of dishes is liquid, mushy.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis is expected to be favorable, and improvement in well-being occurs within 2-3 days.
Stomach pain and severe intestinal upset (diarrhea) due to poisoning
The most common cause of vomiting and diarrhea is food poisoning; it is for this reason that diarrhea, severe diarrhea and stomach pain very often appear. These symptoms indicate the body’s attempts to cleanse itself of contents harmful to its normal functioning.
Food poisoning can be recognized by the patient's general malaise, nausea ending in vomiting, and diarrhea. If abdominal pain occurs, you need to do a gastric lavage, drink more fluids and take sorbents. Painkillers are ineffective in such cases. If discomfort symptoms persist on the second day, you should seek medical help. Taking into account the causes of poisoning, they are divided into three types:
1 Bacterial or viral. It has the main distinctive features: the patient suffers from severe cramping pain in the intestinal area, diarrhea, and vomiting begins after eating. In case of viral infection, fever and fever appear. First aid measures: hunger and drinking plenty of fluids, immediate contact with a medical facility.
2 Chemical. In case of intoxication caused by the ingestion of chemical products into the body, the patient experiences abdominal discomfort, bouts of vomiting, loose stools, and increased salivation and sweating. First aid is the same as for bacterial poisoning. Also, to collect and remove toxins, you should take sorbents, the simplest and most accessible of which is activated carbon. To prevent dehydration and maintain fluid balance in the body, saline solutions, for example, Regidron, are used.
3 Food. Most often it results from eating poorly washed, dirty, low-quality or expired food. Symptoms: diarrhea accompanied by abdominal pain, vomiting. In mild forms, self-treatment is allowed, without the assistance of doctors. During the first day, it is advisable for the patient not to eat, drink large amounts of liquid, and take sorbents.
Self-diagnosis for pain localization
Now let’s see what the localization of pain can tell us, because it can be different for different diseases. We will consider only those situations where pain in the abdomen is accompanied by the development of diarrhea.
When the stomach hurts in the navel area and a person complains of diarrhea, one can first suspect pathologies in that part of the small intestine that is located in the very middle. This section is commonly called the jejunum. On one side (above the gastrointestinal tract) the duodenum is adjacent to the jejunum, and on the other, the ileum. The jejunum receives partially digested food from the stomach and duodenum, flavored with juice secreted by the pancreas and bile. It is in this part of the intestine that most of the nutrients are absorbed into the blood and the secretion of the digestive glands is reabsorbed.
When the jejunum is affected, the liquid food bolus quickly moves out, leading to diarrhea up to 5 times a day. In this case, pain is observed in the navel area.
The described symptom complex may be evidence of:
- Serious disturbance of the blood supply (ischemia) of the small intestine. The disease begins with severe spasmodic pain in the navel area, which is difficult to relieve with painkillers; patients suffer from vomiting and diarrhea. Next, signs of tachycardia appear, cold sweat appears, sudden attacks of fear appear, blood pressure rises, blood is found in feces and vomit.
- Development of the inflammatory process in the jejunal mucosa (pathology is called jejunitis). This disease is characterized by pain around the navel of varying nature and strength, which is almost always combined with repeated diarrhea (up to 15-18 times a day). In some cases, diarrhea is accompanied by severe weakness, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, and hand tremors.
- Enzyme deficiency enteropathies (gluten and disaccharidase deficiency). Symptoms of the pathology appear immediately after eating foods that contain gluten or disaccharides. Soreness occurs around the navel, gas formation increases, and liquid, foamy stool appears, in which pieces of unprocessed food are noticeable.
- Malignant tumor processes in the jejunum. Pain in the navel area, which has a cramping nature, is considered the first sign of oncology (cancer) of the small intestine. In addition, nausea, heartburn, belching, accumulation of gases in the stomach and a specific rumbling occur. Diarrhea occurs regardless of the type of food consumed. You should suspect something is wrong with the occasional appearance of tarry stools and the development of anemia.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). In this case, again, the patient experiences cramping pain in the navel area and notes increased gas production. Diarrhea often changes to constipation, and the stool takes the form of sheep feces with or without mucus. Blood and pus in the feces of IBS are usually not observed. But the patient may suffer from belching and burning along the esophagus. Abdominal pain becomes less severe after bowel movement or as a result of the passage of gas. Symptoms are most pronounced in the first half of the day.
If you have a high fever and diarrhea, frequent loose stools and a stomach ache?
Diarrhea with abdominal pain and fever
Intestinal upset, frequent loose stools in combination with fever and high body temperature signal a high likelihood of infectious diseases of the digestive system. Infectious infections of the stomach require mandatory treatment in a hospital hospital, since in such cases the patient needs constant medical supervision. These symptoms in most cases indicate diseases such as dysentery or intestinal infection (intestinal flu).
With dysentery, a person experiences cramping pain in the stomach, the skin turns pale, body temperature rises, and in more rare cases, tachycardia is observed. Stomach flu and similar infections are caused by adeno-, rota-, or noroviruses that enter the stomach. In the acute form of the disease, a person feels weakness, nausea, pain in the stomach, cutting pain in the abdomen, and vomiting. Until receiving the doctor’s recommendations, the patient should refuse any food, drink plenty of water, and not take medications. Self-medication of infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can lead to death; if you suspect their course, you should immediately contact the hospital; if the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is admitted to a hospital for treatment.
Infections and viruses - causes of diarrhea
The main indicators indicating the presence of an intestinal infection are abdominal pain and diarrhea. These unpleasant symptoms are the result of the activity of harmful microorganisms that enter the human digestive system by contact.
First of all, if your stomach hurts and diarrhea begins, there is vomiting, you should suspect intestinal flu (rotavirus infection). The pain in this case is usually cutting and is felt in the central part of the abdomen. Due to a sharp jump in temperature, general malaise and weakness appear. With dysentery, painful symptoms occur under the influence of the dysentery bacillus on the body. To the signs of pathological processes described above, characteristic of intestinal flu, is added a disturbance in the heart rhythm and cramping pain.
Therapy and prevention of the disorder
1. It is not recommended to treat prolonged diarrhea on your own, especially if a child has indigestion. In case of severe abdominal pain, you should urgently call a doctor. Sometimes ignoring symptoms leads to disastrous consequences. It is not advisable to take strong painkillers before the doctor arrives. They will blur the picture of the disease, which will complicate diagnosis. To relieve pain, it is permissible to take a couple of No-shpa tablets. It relaxes smooth muscles and relieves spasms.
2. If the cause of indigestion is known, you can relieve pain with the following medications:
- In case of overeating, lack of enzymes, especially with low stomach acidity, the following will help: Festal, Mezim forte, Creon, Panzinorm, Plantex, Trienzyme.
- Stomach pain caused by gastritis or ulcers is relieved by coating medications. These include: Maalox, Almagel A, Gaviscon, Flacarbine.
- For increased acidity of gastric juice, Omez, Omeprazole, Gastal, Gastrofarm, Rutacid are prescribed.
- Spasms are relieved with No-shpa, Buscopan, Besalol.
3. Diarrhea is treated comprehensively. They use drugs that improve digestion and normalize microflora. To eliminate intestinal infections, targeted antibiotics are used. The body is rehydrated, replacing fluid and microelements lost during diarrhea.
4. You can quickly cure diarrhea by taking an Imodium or Loperamide tablet. This should only be done in extreme cases. They inhibit peristalsis, causing prolonged stool retention, which is dangerous in case of poisoning and intestinal infections. Pri- and probiotics (Duphalac, Lactusan, Normaze, Acipol, Bifinorm) help restore the balance of beneficial bacteria. They contain a set of microorganisms that live in the human intestine, their metabolic products and substances that promote their growth.
5. If you have an upset stomach, it is better to use probiotics with combined action (Maxilak, Laktofiltrum, Laktofiltrum-Eco). They are made on the basis of absorbent substances that absorb and remove toxins from the body. Intestinal antiseptics (Enterofuril, Ersefuril, Stopdiar, Alpha Normix, Intetrix) help cure bacterial infections. They are active against certain pathogens and do not disrupt normal microflora.
6. If the cause of diarrhea is a viral infection, it is treated with antibiotics (Rifaximin, Cefixime, Azithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin). The appropriateness of use should be determined by a doctor. You cannot do this yourself. Antibiotics kill beneficial intestinal microflora, which leads to dysbiosis.
7. Stomach pain can be caused by the activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. This microorganism is able to live in an acidic environment. The bacterium destroys the mucous membrane and provokes inflammatory diseases of the stomach and the appearance of ulcers. If Helicobacter pylori is present in the body, bismuth preparations (De-Nol) are included.
Prolonged diarrhea causes dehydration. This condition is treated with special solutions (Regidron, Gastrolit). They contain glucose and microelements necessary for the body. You can make them yourself by adding sugar, salt and soda to water.
8. If you feel very sick, take Anestezin, Aeron, Cerucal. They relieve attacks of lightheadedness and prevent vomiting, which increases the risk of dehydration.
9. Therapy and prevention of disorders necessarily includes strict adherence to a certain diet. It is selected taking into account the acidity of gastric juice and the symptoms of the disease.
The doctor must decide how to treat diarrhea and abdominal cramps. You cannot make your own choice of certain medications. At best, they will not have the desired effect, and at worst, they will lead to undesirable consequences.
source: gastroguru.ru
Any disorder in the functional activity of the digestive tract indicates problems in the body. But when abdominal pain, diarrhea and high fever develop simultaneously, such a symptom complex should cause alarm. It indicates the development of an infectious process in the body - food poisoning, dysentery or another serious disease.
Both adults and children can be susceptible to this condition. In each case, immediate medical attention will be required; the severity of the pathology may increase in a matter of minutes.
Why else can diarrhea begin with abdominal pain?
Diarrhea, the discomfort of which is intensified by pain, is a manifestation of a deficiency of digestive enzymes. It can be congenital or acquired, as a complication of certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Prerequisites for the occurrence of diarrhea due to enzyme imbalance are:
1 Lactase deficiency, or the inability to digest milk. Causes short-term disorders such as bloating, flatulence, pain and diarrhea after drinking milk.
2 Overeating, especially when it comes to eating fatty, fried, spicy, salty foods. Often occurs after holiday feasts, manifests itself through abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea.
3 During a stomach or duodenal ulcer, so-called hunger pains are observed. They make themselves felt approximately half an hour after eating. Localized at the site of damage to the mucous tissues by the disease.
4 Digestive disorders. A sharp stabbing pain in the abdomen indicates an ulcer. This symptom may indicate perforation of the ulcer or peritonitis. If it occurs, the patient should be immediately taken to the hospital.
5 Viral and bacterial infections. They cause contraction-like pain near the stomach and loose stools. Body temperature may rise to critical levels. The stool has a thin, watery consistency and may contain mucus, blood, or pus.
Surgical diseases
Next, we consider the main pathologies requiring surgical intervention and their symptoms.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum. There are many reasons why the inflammatory process begins: blockage of the lumen of the appendix (stones, helminths, tumors, etc.), disruption of blood microcirculation in the organ.
Also, poor nutrition (eating food that slows down intestinal motility, as a result of which feces stagnate in the intestines), allergies, and a tendency to constipation. The symptoms of appendicitis are the same in 95% of cases: pain in the lower abdomen, mainly on the right, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. The temperature can reach up to 38 degrees or not rise at all.
Pancreatitis
Inflammatory disease of the pancreas. There are many causes of inflammation of the endocrine gland: alcohol abuse, fatty, smoked, fried foods, diseases of the stomach and duodenum, cholelithiasis.
Previous infectious pathologies, taking certain medications (antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids), abdominal injuries and allergies can also trigger the onset of the inflammatory process.
The clinical picture is expressed:
- severe girdle pain;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief;
- a slight increase in body temperature in adults and above 38 degrees in children.
Diarrhea may be replaced by constipation, severe weakness, increased fatigue, and bloating appear. Treatment of pancreatitis is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor in a hospital. An important condition on the path to recovery is diet, taking anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic drugs.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder. The appearance of cholecystitis is provoked by the following factors: the presence of stones in the bile ducts, helminthic infestation, infectious agents (staphylococcus, E. coli and others), decreased acidity of gastric juice, biliary dyskinesia, unhealthy diet (dry food, eating with a long break in time), obesity, tendency to support, poor circulation of the gallbladder, abdominal injuries.
Cholecystitis begins to appear after a certain push and has certain symptoms: acute pain in the upper abdomen, most often on the right, nausea and vomiting, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, increased body temperature, in case of complications - yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the eyes . Cholecystitis must be treated in a hospital.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
A group of diseases characterized by damage to the mucous membranes of the digestive system with the formation of erosions. The main cause of the disease is the active reproduction of Helicobacter pylori.
There are many provoking factors for this: increased acidity in the stomach and intestines, constant stress, decreased immunity, poor diet, bad habits. First, the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum swells and becomes inflamed; if no treatment is carried out in time, ulcers begin to appear.
The clinical picture is very similar to gastritis: patients complain of stomach pain, heartburn, sour belching, nausea. Body temperature rises no more than 37.5 degrees. But there are cases when a peptic ulcer occurs without fever. Over time, problems with appetite appear, patients lose a lot of weight and experience fear before eating.
Constipation can often be observed, lasting from several days to 4-6 days. Treatment can be carried out either on an outpatient basis or in a hospital, depending on the severity of the disease. If no therapy is carried out, vomiting with blood may begin, which indicates gastric bleeding.