General information
The name intestinal infection refers to a whole group of diseases in which the digestive organs are damaged. There are about 30 species in total. What they have in common is that they are all caused by pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria), are acute and are characterized by the same type of symptoms.
Intestinal infections are common among people of all ages, most often occurring in children, as well as people with weakened immune systems. In terms of frequency of visits to a doctor, they rank second after ARVI.
Germs and pathogenic bacteria enter the environment through feces, saliva, and during sneezing. They remain viable on objects and products for a long time.
Classification
TTH in newborns - what is it, symptoms and treatment
All intestinal infections can be divided into two groups according to the type of pathogen: viral and bacterial. Each type of disease has its own unique symptoms, and in many ways the diseases are similar.
Common bacterial intestinal diseases include:
- staphylococcal;
- salmonella;
- Escherichiosis;
- typhoid.
Young children most often suffer from the following infectious diseases caused by viruses:
- rotavirus;
- enterovirus;
- adenoviral.
Each of these infections is dangerous, occurs rapidly and can significantly harm the baby.
Depending on the course, 3 degrees of severity can be distinguished:
- Light form. All symptoms are mild, the temperature is low. Vomiting and diarrhea are observed 6-8 times a day.
- Moderate severity of the disease is characterized by high temperature (up to 40°C). The condition remains difficult throughout the week.
- Severe form. All symptoms of intoxication are pronounced, gastric emptying occurs up to 25 times a day. Convulsions and toxic shock may occur.
Pathogenic organisms are found on common objects and products
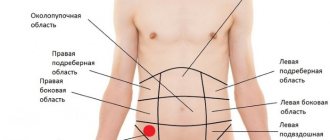
Only parts of the digestive system are affected; the area of inflammation is determined by the corresponding symptoms.
Incubation period of intestinal infection in children
The incubation period of the disease, that is, the time from the onset of infection to the appearance of specific symptoms, varies depending on the specific infection. On average it ranges from 12 hours to 1–2 days, although exceptions are possible:
- epidemic hepatitis (15–50 days);
- dysentery (24 hours – 1 week);
- rotavirus infection (15 hours – 7 days).
Young children under the age of three are more susceptible to intestinal infections than others. The duration of the disease depends on the type of pathogen and severity, as well as the correctness of the treatment provided. On average, the disease goes away within 4–5 days.
Antiviral drugs
If the intestinal infection is caused by a virus (enterovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus, etc.), antiviral drugs are prescribed. Children are prescribed complex immunoglobulin drugs that perform three functions at once:
- destroy bacteria;
- fight viruses;
- strengthen the immune system.
The most common of them is Viferon. It includes components based on alpha-26 interferon, vitamins A and E. This medicine blocks the receptors of the virus, prevents its reproduction and spread, and increases the body's resistance. Viferon is available in the form of capsules that contain powder. It is used for preparing suspensions in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
In addition, Kipferon, a suppository for rectal use, is prescribed to young children as an antiviral drug. Its principle of action is similar, but the dosage should be agreed with your doctor so as not to cause excessive irritation of the mucous membrane.
How does intestinal infection occur?
ARVI in infants - what is it, symptoms of virus infection
Pathogens are transmitted through household and airborne droplets. Pathogenic bacteria are released into the outside world through saliva, during sneezing, and with feces.
On a note. On the surface of household items, vegetables and products, pathogenic microorganisms remain viable for at least 5 days.
There are several reasons why infection can enter a child’s body:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- improper storage of household products;
- swimming in dirty ponds, pools;
- insufficient heat treatment of products;
- drinking untreated bad water;
- unsanitary conditions;
- poor nutrition, which causes weakened immunity.
After entering the baby's mouth, the bacteria move to the digestive system, in particular, the intestines, colon, and other parts of it. They begin their life activity inside and provoke inflammatory processes in the stomach, mucous membrane and other organs.
Stages of development of rotavirus infection
Most often, intestinal infections occur in children aged 1 to 5 years. Breastfed newborns get sick less often, as they are protected by the mother's immunity.
What is important to know about intestinal infections in children
Try to determine the source of infection and prevent further spread of the disease. If the infection occurred at home, protect family members; if in a catering establishment, contact its administration. The point is not about retribution and restoration of justice: perhaps this way you will save someone’s life.
In the first hours after the appearance of alarming symptoms, you should not forcibly stop vomiting or diarrhea - on the contrary, in this way the body tries to free itself from harmful substances that have entered.
For newborns and children under one year of age, additional risk factors are identified:
- artificial feeding;
- complementary foods without heat treatment;
- immunodeficiency;
- perinatal pathology of the central nervous system;
- the summer season, which promotes the active spread and reproduction of microorganisms.
It is important to monitor not only the baby’s hygiene and compliance with sanitary standards when preparing complementary foods, but also to monitor the cleanliness of toys, pacifiers, and household items. You cannot “disinfect” a baby’s pacifier with the mother’s saliva - bacteria that are safe for an adult can be dangerous for him.
Symptoms of intestinal diseases
Nervous cough in a child—symptoms, treatment
After pathogenic bacteria enter the child’s body, they begin to be affected by saliva, hydrochloric acid, and beneficial bacteria. With weakened immunity, such protection does not work, pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply. An improper, unbalanced diet contributes to their faster development.
Signs of intestinal infection in infants and older children:
- flatulence;
- loss or decrease in immunity;
- increase in temperature;
- lethargy and weakness;
- stomach ache;
- frequent and foamy diarrhea;
- skin rashes.
Bloody streaks are often visible in the child’s stool, and the frequency of bowel movements reaches 20 times a day. In rare cases, urinary retention may occur.
Symptoms for children and adults are the same; in children they are more pronounced
On a note! Symptoms for children and adults are almost the same, but children experience the disease more severely and experience it much more often.
Diagnostic measures and treatment
When the first signs of an intestinal infection appear, you should consult a pediatrician at the hospital, since the course of the disease is rapid. Based on the examination, epidemiological and clinical data, the doctor makes a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribes the necessary tests.
The most important role is played by stool examination, which determines the type of pathogen and treatment. Blood cultures and additional urine and cerebrospinal fluid tests may be prescribed.
Important! When diagnosing an intestinal infection, it is important to exclude pancreatitis, acute appendicitis, biliary dyskinesia, lactase deficiency and other pathologies.
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment, which includes:
- therapeutic nutrition;
- oral rehydration;
- systematic, etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy.
Children, according to indications, are prescribed antibiotics, intestinal antiseptics, absorbents and other medications that help cope with infection and the spread of the pathogen.
Only specialists can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Every mother should know what an intestinal infection is in a child, how it manifests itself, and what to do. If a disease is suspected, parents should be able to provide first aid to their child. If you suspect a disease, before a diagnosis is made and a doctor prescribes, you must not:
- give antiemetics and painkillers;
- do an enema, especially with warm or hot water;
- use fixatives;
- warm up your stomach with a heating pad.
All treatment actions must be prescribed by a pediatrician.
How long does it last
The duration of an intestinal infection depends on the complexity of the course. Mild forms disappear in 2-3 weeks. It is considered normal if recovery occurs no later than after 1.5 months. The disease is assigned the status of a protracted chronic infection if the symptoms bother the baby for six months or more.
What to feed a child with an intestinal infection and after
If a child is affected by an intestinal infection, special nutrition is required. In this case, the doctor prescribes diet No. 4 according to Pevzner, which must be used while the little one is being treated.
To prevent nausea and vomiting, you can eat:
- weak broths;
- slimy cereal soups;
- crackers, dried white bread;
- twisted boiled meat and fish (low-fat);
- baked apples without peel.
During the first days, while the symptoms are pronounced, the child is given only weak, light soups and broths. All dairy products, spicy, fried, smoked foods, onions, garlic, and carbonated drinks are prohibited until recovery. The baby's food volume is reduced, but the frequency of feedings is increased.
For your information. It will take about 3 months to completely restore the digestive function of the stomach.
Taking rehydration measures
In addition to proper nutrition, preventing dehydration is very important. To restore the water-salt solution, the doctor will prescribe various drugs (Regidron, Maratonic, Glucosolan).
On a note! With a mild stage of intestinal infection, according to Dr. Komarovsky, it is not necessary to treat the baby with medications. The body has enough strength to cope with bacteria and produce the required amount of antibodies. It is important to monitor your drinking regime and ensure proper nutrition.
Many rehydrating preparations are presented in powders. They are diluted in water and given to the baby to drink every 10-15 minutes. In the absence of the necessary medications, prepare a water-salt composition yourself: add 1 tbsp to 1 liter of water. l. sugar and 1 tsp. salt and soda.
Prevention
Many infections can be avoided if you follow the rules.
- Strengthening immune defense is the first requirement. Therefore, pediatricians strongly do not recommend stopping breastfeeding before one year. This will protect the baby from infections and future diseases.
- Hygiene. This applies not only to the child himself, but also to other family members. Dishes, clothes, baby diapers - everything should be clean. Even a fallen pacifier should first be washed with boiling water and disinfected, and only then given to the baby.
- If your baby has the first symptoms of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication is not recommended.
- The mother herself should stick to the diet. You need to eat only healthy foods, more cereals, fruits, vegetables, wholemeal bread. But sweets and baked goods should be limited. Vegetables and fruits must be washed thoroughly and with boiling water. This is especially true in the summer, when the risk of contracting an infection arises.
Complications of acute intestinal infection
If treatment is incorrect or untimely, there is a high probability of dehydration, disruption of the functions of many internal organs, a decrease in the level of the immune system, the appearance of bacteriosis and other health problems for the baby.
If the intestinal infection is severe, other equally serious pathologies may develop:
- Neurotoxicosis. There is a disorder of consciousness, convulsions and hallucinations appear.
- Circulatory disorders. A decrease in blood pressure is typical, problems with the cardiovascular system appear, and the skin turns pale.
- Kidney failure. Dull pain appears in the lumbar region, urination becomes rare and scanty.
- Hypovolemic shock. It develops as a result of dehydration of the body, sunken eyes become noticeable, and weight decreases.
Only a negligent attitude to the treatment of intestinal infection can provoke the development of such serious complications.
Prognosis and prevention
Complete recovery of the child can only be ensured by early and timely identification of the causative agent of the disease. Severe forms of the disease lead in some cases to serious complications.
Worth remembering! After intestinal infections, children have unstable immunity.
The most effective way to prevent the development of infection is prevention
The main and effective preventive measures are:
- full compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- drinking water purification;
- proper storage and preparation of food;
- Before feeding, mothers need to treat their breasts, sterilize nipples and pacifiers.
All children who have been in contact with a sick baby are recommended to be placed in slight isolation, since an intestinal infection can manifest itself within 7 days.
To prevent an acute intestinal infection from causing more serious health problems for the baby, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms and follow all his prescriptions.
Diet for intestinal infections in children
During the acute onset of the disease, it is advisable to limit food intake. Some experts even recommend abstaining from food during this period: the gastrointestinal tract is not able to perform its functions, and nutrients from the diet simply will not be absorbed by the body. But these measures are contraindicated for children with reduced body weight. In addition, during the rehabilitation period, diet is important to restore the correct intestinal microflora.
Mild forms of the disease allow food intake, but in reduced volumes (by 30–50%). It is better to eat in portions, 5-6 times a day. On the second or third day you can give in small amounts:
- cottage cheese with a low fat content;
- semolina, oatmeal and rice porridge;
- unpalatable white crackers;
- biscuits;
- vegetable broth;
- jelly;
- vegetable puree soup;
- dried fruits compote;
- low-fat kefir;
- baked sweet apple without peel.
The following foods on the menu are not recommended until the end of the rehabilitation period:
- juices;
- whole milk;
- yogurt;
- fermented baked milk;
- cream;
- citruses;
- beet;
- beans;
- meat and fish broths.
The diet for intestinal infections in children should be liquid and vegetarian, consisting mainly of first courses based on vegetables and cereals. Reduced enzyme activity persists for some time after recovery, so you need to return to a normal diet slowly and gradually. On average, dietary restrictions are observed for two weeks.
Children under four months of age should not be given fermented milk formulas. In acute cases, infants are recommended to be fed formulas with additional protective factors and biologically active additives. If the disease provokes iron deficiency, the diet is corrected with compounds that include this trace element. Specialized medicinal mixtures are introduced into the diet when symptoms of malabsorption develop and the exocrine function of the pancreas is impaired.