Causes
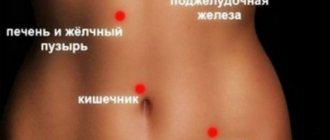
The causes of rotavirus are not the same - contact with a patient, banal dirty hands. Bacteria enter the human body through the mouth. You need to monitor the quality of food and hygiene. This applies to a pregnant woman in the early stages - diseases in the first trimester of pregnancy are dangerous for the unborn child.
The infection is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. After infection, pathogens are released during defecation, easily spread through household means, and begin to multiply in the human body. If an infection is found in the home, be careful.
Routes of infection:
- From an infected person by airborne droplets.
- From spoiled food, water (oral-fecal route). The pathogenic microbe enters the mouth, passes through the digestive tract, and multiplies in the intestines.
- Through contaminated surfaces, the bacterium enters a person through the mouth.
Infants, adults, old people, and pregnant women are susceptible to rotavirus. Often, the cause of rotavirus infection in pregnant women is weakened immunity - the expectant mother’s body is subjected to overestimated stress. Due to a weakened immune system, a pregnant woman will become infected more quickly than an ordinary person.
Rotavirus during pregnancy: route of infection and mechanism of disease development
During the active stage of the disease, as well as for several days after its main symptoms have subsided, the source of the dangerous virus is the feces of the sick person. The danger to healthy people is posed not only by a patient with severe signs of infection, but also by its asymptomatic carriers.
The main method of infection is fecal-oral. Penetrating into the intestines, the pathogen begins to rapidly multiply in the mucous membrane of the organ. Affected cells with viable particles of the virus peel off from the mucosa and are excreted from the body along with feces.
The greatest danger to a healthy person are objects with traces of feces from an infected person:
- the soil;
- the toilet is not clean enough;
- towels;
- handle on the door in the toilet;
- poorly washed hands of the patient.
Through these objects, the virus quickly passes into the hands of a potential victim. If you take food with dirty hands or put your fingers in your mouth (which, for example, is what small children do), the virus enters the gastrointestinal tract and rushes to the intestines. Such a “guest” quickly disrupts the normal absorption of nutritional components from the lumen of the small intestine, provokes the development of ischemia of its mucous membrane and contributes to the development of an extensive inflammatory reaction.
Rotavirus poses a great danger to all age categories of children and adults. Pregnant women and preschool children tend to get sick with rotavirus more often than others - the reason lies in weakened immunity, which cannot resist infection for a long time.
Symptoms
After the appearance of infected flora in the body, it begins to progress rapidly. The first symptoms of the disease appear a few days after infection. The incubation period of the disease in a pregnant woman is 1-2 days.
Rotavirus infection in pregnant women occurs in a mild form. The reason is the body’s natural defense mechanism. Symptoms for women expecting children are no different from those of other people:
- Nausea is not dangerous.
- Diarrhea – frequent trips to the toilet cause dehydration in a woman’s body. The baby experiences oxygen starvation, causing miscarriage and premature birth.
- Vomiting is dangerous for an unborn boy or girl, causes severe muscle spasms, and threatens miscarriage.
- An increase in body temperature poses a danger to the child - the consequences are unpredictable.
- In rare cases, palpitations may occur.
Because of the danger to the child, a woman must be careful. When the first signs of the disease appear, immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe appropriate treatment during pregnancy. 2-4 days after the start of therapy, the symptoms subside. Complete cure occurs after 5-6 days.
Treatment of rotavirus infection in pregnant women
When the first symptoms of the disease occur, you must immediately begin to replenish the fluid lost by the body through vomiting and diarrhea. Treatment of rotavirus infection in pregnant women should be aimed, first of all, at preventing and eliminating signs of dehydration.
Any powder for preparing a water-salt solution, for example, Regidron, is suitable.
If you don’t have this at hand, you can prepare the solution yourself; you will need:
- liter of boiled water;
- 1 teaspoon salt;
- 2 tablespoons sugar.
Mix everything in a clean container and take a few sips every 10-15 minutes.
The absence of urination for several hours, as well as the lack of sweating, may indicate the development of dehydration. In this case, oral dehydration may not help. It is necessary to urgently seek qualified medical help.
Drug treatment
An increase in body temperature during rotavirus infection is a common symptom, including during pregnancy. The only antipyretic drug approved for use in pregnant women is Paracetamol. The permissible dose is 500 mg once. Repeated use is possible after 3-4 hours. If the temperature does not decrease or reaches high numbers, you must call an ambulance.
The danger of rotavirus during pregnancy
The expectant mother, who has had an intestinal infection, is worried about the danger: the risk of detection in a boy or girl after birth. The consequences of an illness for a child are an important topic.
Rotavirus infection during pregnancy often occurs in a mild form, is not harmful to the unborn baby, and is not detected in the child after birth. Complications appear with severe infection - this is important in the later stages. A mild form of the virus will not affect the child - the disease affects the gastrointestinal tract and does not penetrate the placenta. If a woman has suffered from intestinal flu, antibodies remain in the body and are passed on to the baby through milk. This means that the baby will have immunity.
There are known cases of a pregnant woman falling ill with a severe form of the virus, which affects the child in an unpredictable way.
Frequent consequences in the early stages:
- Weakening of the body.
- Dehydration of the mother leads to a lack of oxygen for the baby and leads to early miscarriage.
- The amount of circulating blood decreases - the concentration of oxytocin increases, leading to uterine contractions and miscarriage.
- A drop in blood pressure is dangerous during pregnancy.
- Toxic shock in a woman, which occurs with a rapid increase in body temperature.
- Renal failure leads to the cessation of urine production in the kidneys - an indication for termination of pregnancy.
- Pneumonia, pneumonia.
Late consequences
A common consequence in later stages is dehydration of the mother. This is the most dangerous thing that happens due to the illness. Loss of fluid leads to complications:
- blood thickening – affects the formation of blood clots in the legs;
- reduction in the amount of amniotic fluid;
- malaise - constant presence will complicate childbirth;
- the presence of tension in the large intestine provokes uterine tone and premature birth.
Rotavirus during pregnancy: signs of rotavirus infection in pregnant women, treatment and consequences
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's immunity weakens. For this reason, when contacting any viruses and bacteria, the risk of contracting various ailments increases. Often pregnant women become infected with rotavirus, an infection that affects the gastrointestinal tract and disrupts its functioning.
Another name for rotavirus is intestinal flu. It is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, but is quite easy to treat even in pregnant women.
How to recognize rotavirus infection in pregnant women?
Rotavirus infection during pregnancy is tolerated in a mild form due to the actively working defense system of the expectant mother’s body. However, all manifestations of the disease are present.
Symptoms of rotavirus:
- Nausea and vomiting. Vomit is not watery and consists of undigested food debris and bile. In this way, the body tries to protect itself from the pathogenic process, preventing it from developing. Most often, vomiting occurs within 24 hours, but can last up to 3 days.
- Diarrhea. In severe cases, the woman visits the toilet every hour; in mild cases, diarrhea repeats up to 4 times a day. There is a discharge of watery stool that foams and has a foul odor. This manifestation can last up to 6 days. It is dangerous due to dehydration and requires quick elimination. Diarrhea usually occurs after a woman has vomited.
- Temperature increase. A mild form of the disease may be accompanied by a temperature of 37 - 37.5 degrees, and in severe cases, the thermometer sometimes shows more than 39 degrees. This manifestation is the reaction of the body, which triggers the immune system to overcome the foreign intracellular parasite. The temperature with rotavirus can remain elevated for two to three days.
- Pain in the stomach and abdomen. There may be nagging pain or discomfort reminiscent of contractions. The pain may be in the upper or lower abdomen. With diarrhea and vomiting, the pain usually intensifies. The cause is a strong spasm of the intestinal muscle tissue.
- Increased heart rate (only in severe cases).
Treatment of rotavirus during pregnancy
Rotavirus in pregnant women requires treatment to prevent adverse consequences.
Analyzes
To identify the cause and treatment, tests are performed:
- A general blood test will determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the number of leukocytes, the excess of which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- A general urine test will determine the presence of changes in leukocytes, proteins, and erythrocyturia.
- A stool test will show the presence of an infectious agent.
- A pregnant woman may have E. coli in her smear, which gives similar symptoms.
After recovery, the tests return to normal.
Drug treatment
It is more difficult to treat rotavirus during early pregnancy - most medications cannot be taken due to the lack of a placental barrier. Without a doctor’s permission, you cannot start taking medications on your own - you risk harming your unformed body. During pregnancy, treatment is based on safety for the fetus.
Actions before going to the doctor
If you can’t see a doctor right away, start following a diet to alleviate the condition.
Do not eat if you have rotavirus infection:
- Sweets.
- Fat.
- Fried.
- Salty.
- Dairy.
- Raw fruits, vegetables.
Allowed to be consumed during intestinal flu:
- Porridge cooked in water.
- Vegetable stew.
- Rice water.
- Crackers, sugar-free cookies.
Those who have recovered say that if the diet is followed correctly, the condition improves the next day.
Medicines
Medicines to treat stomach flu:
- Antiseptics – Nifuroxazide, Baktisubtil.
- Drinks to restore water-salt balance – Regidron, still mineral water.
- Adsorbent preparations – Smecta.
- To restore the intestinal microflora - Linex, Hilak Forte.
- If there is a sharp jump in temperature, it is permissible to take Paracetamol. Water rubdowns and cool compresses with vinegar will help reduce the temperature. Apply to the forehead, on the wrists.
It is permissible to take antibiotics after identifying the source of the disease. The doctor prescribes them if a woman has become infected with salmonellosis or dysentery. In other cases, you can do without taking serious medications, but not all are contraindicated during pregnancy. Taking antibiotics is prohibited from 38 weeks. The medicine is prescribed by a doctor, nothing can be taken without recommendations - even a harmless, proven remedy can affect pregnancy.
Folk remedies
Rotavirus infection is often treated with folk remedies. A proven method is to combine two treatment methods. The recipes are based on herbal mixtures that have a positive effect on the intestinal microflora.
- To get rid of the disease, rice water is used. Cook rice in a ratio of 1 to 7 over low heat. When the rice is boiled, leave it to steep, then drain the liquid. Take 70 ml every 2 hours.
- A decoction of oak bark is designed to remove toxins from an adult and improve intestinal function. Boil 40 g of the collection in a liter of water, drink half a glass hot five times a day.
- Shilajit is not contraindicated during pregnancy. An ordinary lemon will help remove the unpleasant odor. Take mummy 0.2-0.5 g twice a day - morning and evening.
Each product has its own contraindications. Before using this folk remedy, you should consult your doctor!
Rotavirus during pregnancy: how to treat it, is the infection dangerous in the early stages, reviews
Any infectious disease is a risk for the fetus and the expectant mother. The causative agent of infectious diseases in pregnant women and children is rotavirus. The danger of this infection during pregnancy in case of timely initiation of treatment is practically absent. However, a prolonged course can lead to significant dehydration and severe intoxication syndrome.
It is very easy to become infected with rotavirus. The transmission mechanism is fecal-oral and contact-household. Most often, infection occurs through poorly washed vegetables or fruits. Signs of the disease appear 2-3 days after infection.
During illness, the pregnant mother is a carrier, so it is necessary to limit contact with children who are highly susceptible to this pathogen.
Rotavirus infection is manifested by the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- vomiting 3-4 times in the first days of the disease;
- temperature rise above 38.5 degrees;
- abdominal pain;
- loose stool.
The temperature remains high during the first days of the disease. Then it becomes normal. Vomiting is also observed for the first 2-3 days. However, if left untreated, the above complaints may persist for a longer period of time.
The effect of rotavirus on pregnancy
Rotavirus is a member of the Reoviridae family. It has double-stranded RNA surrounded by a protein shell. It is very well preserved in the external environment and is very resistant to low temperatures.
Sanitary measures taken against other viruses and bacteria are not sufficient to affect rotavirus, so the incidence rate still remains high.
How dangerous is rotavirus in the early stages?
The main danger is the possible development of congenital pathologies. The disease suffered from 7 to 11 weeks can lead to an increased risk of the following complications:
- fetal hypoxia;
- placental abruption;
- development of intrauterine infection.
The risk of developing these conditions due to infection is extremely low.
The danger of rotavirus in later stages
Caution! If the infection develops in the last weeks of pregnancy (38,39) there is always a danger of complications of labor. When a child passes through the birth canal, he can also become infected from a sick mother. During the neonatal period, the disease is very severe and requires qualified medical care, so discharge from the maternity hospital can be greatly delayed.
Consequences for the child
Often, they are missing. However, severe disease can lead to the following problems:
- hypoxia;
- developmental delay;
- increased risk of intrauterine infections.
If signs of infection appear, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. This will significantly reduce the risk of possible complications.
What to do if a pregnant woman gets sick with rotavirus infection
The first thing every pregnant woman should do is seek help from a specialist. If it is not possible to receive qualified medical care, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Immediately begin to unseal the patient. Drinking more fluids is one of the main rules for most infectious diseases accompanied by vomiting and loose stools.
- If the temperature rises, bring it down with paracetamol. It is important to remember that you should not take this drug more than 4 times in 24 hours. Exceeding the daily dose may cause excess stress on the liver.
- Give activated carbon to drink. For every 10 kg of a pregnant woman’s weight, 1 tablet of coal is needed. Thus, if she weighs 60 kg, 6 tablets are needed.
- Call an ambulance or get to the hospital yourself.
There is no need to self-medicate. In addition to rotavirus, a number of diseases have a similar clinical picture. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Diagnostics
No specific examinations are required. It is enough for a specialist to collect an anamnesis and evaluate the patient’s complaints in order to make the correct diagnosis.
In some cases, the following examinations are additionally prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- stool culture;
- ELISA for rotavirus.
Treatment of rotavirus in pregnant women
Therapy consists of several main components.
So, the following is needed:
- Restoration of water and electrolyte balance. Regidron is used for this purpose. It is recommended to drink it in small sips every 15-20 minutes. Also, after each episode of loose stools or vomiting, you should drink 200 ml of water.
- Normalization of temperature. To reduce it, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, in particular paracetomol, are used.
- Application of adsorbents. To quickly remove toxins and bacterial waste products, you can use activated carbon. Also suitable are drugs such as Polysorb and Smecta.
- Normalization of intestinal microflora. To restore normal flora, it is recommended to use products such as Hilak-Forte or Linex.
In general, treatment is purely symptomatic. No specific measures are required. Most importantly, if signs of infection appear, you should immediately seek help from a specialist. Timely initiation of treatment will help avoid serious complications.
In 1st trimester
The treatment is no different. The only thing that expectant mothers should remember is that if the disease occurs in the first weeks, it carries a greater risk.
The symptoms of rotavirus are very similar to the manifestations of toxicosis, therefore, when it occurs at 12 or 13 weeks, the pregnant woman associates her condition with this.
Fever is not a characteristic sign of toxicosis, therefore, if vomiting is combined with an increase in temperature, you should immediately seek help from your doctor.
How to treat at home
Treatment of rotavirus infection is quite possible at home.
In addition to the above treatment methods, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- drink more fluids;
- follow a diet;
- bring down the temperature in a timely manner (no more than 4 times a day);
- Avoid contact with healthy people.
If you cannot quickly cope with the manifestations of the disease, and your complaints intensify, you should consult a doctor. It is not recommended to use folk remedies for treatment, especially for various herbal decoctions. If used incorrectly, the condition can significantly worsen.
What can you drink and eat during pregnancy?
Diet therapy for rotavirus is one of the main parts of treatment. Without fail, a pregnant woman should exclude the following from her diet:
- dairy products;
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- fatty and fried foods;
- sweet;
- strong coffee;
- sweet carbonated drinks.
On days of exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to give preference to dishes made from lean boiled meat, broths and porridges cooked in water. You need to drink a lot, preferably bottled water. Frequent use of Borjomi shows a good effect. This mineral water helps to quickly restore the acid-base balance.
Prevention
To protect yourself from illness during pregnancy, it is recommended to follow the following rules.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules. You should always wash your hands before eating.
- For cooking, use only boiled or bottled water.
- Wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly before eating.
- Avoid contact with sick children and adults.
Effect on the fetus if untreated
During a normal pregnancy, when a woman becomes ill, consult a doctor immediately. The infection does not pose a danger to the fetus. The only danger for the child is a lack of oxygen due to loss of fluid from the natural dehydration of the mother’s body.
Consequences for a woman’s body
If a pregnant woman does not start taking the necessary therapy, there is a risk of unpleasant complications for the body. The virus causes complications in the form of transition to a chronic form. Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, malfunction of the pancreas, and functional dyspepsia may occur.
Symptoms of intestinal flu
The acute stage of the disease develops 1–4 hours after the first symptoms appear. The duration of the latent course of the pathology is 1–3 days. Sometimes the latent period is reduced to 14 hours.
Signs of rotavirus can easily be confused with food poisoning or toxicosis. The difference is that with infectious pathology the temperature rises.
Intestinal flu during pregnancy is accompanied by:
- Vomiting. The attack is often one-time. The vomit is not watery; it contains fragments of bile and undigested food. Nausea lasts for 24 hours, less often for 2–3 days.
- Diarrhea. Begins 1–2 hours after vomiting. Bowel movements occur 3–8 times a day, in severe cases - more than 20. The stool is watery, foamy, with a lot of mucus, and has a pungent odor. There should be no blood in the stool.
- Pain in the abdomen of a cramping or pulling nature. Localized in the upper or lower part. Discomfort increases with vomiting and diarrhea. Secondary symptoms are flatulence, bloating.
- Increasing temperature. Hyperthermia occurs immediately after the end of the incubation period. In mild forms, the readings do not exceed 37.5°, in severe cases they reach 39°.
- Intoxication. The patient is worried about weakness, headache and joint pain, shortness of breath, decreased or complete lack of appetite, and severe thirst.
Attention! In rare cases, a runny nose and cough may be diagnosed.
In mild forms of the disease, obvious manifestations begin to subside 2–4 days after the onset of the active stage, and disappear completely by 5–6 days.
Sometimes rotavirus infection occurs without significant symptoms. Infection is indicated by weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, and rumbling in the stomach.
Prevention of rotavirus infection
Rules for protection against rotavirus infection:
- Wash your hands with soap before eating and after returning home from the street.
- Wash food before eating.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Do daily wet cleaning.
- Drink purified water.
- Protect prepared dishes and products from insects.
- Carefully follow the correct diet.
- Heat processing of food will help kill germs.
- Do not eat mushrooms.
- Do not swim in bodies of water.
Remember: every trimester of pregnancy is important. The rules are followed scrupulously during the entire period of pregnancy.
Diet after rotavirus infection
During the acute period of intestinal flu, it is not recommended to eat anything at all. This is especially true for those dishes and products that irritate the intestines and digestive tract as a whole. After an illness, it is also necessary to follow a specific gentle diet.
Since the body of a pregnant woman is faced with an active inflammatory process, fibrinogen is increased in her blood. To normalize its value, it is necessary to eat properly for at least 5-7 days after the final disappearance of the unpleasant symptoms of this disease.
- The basis of the diet of the expectant mother during the period of recovery from intestinal flu should be porridge cooked in water.
- For lunch, it is very healthy to eat stewed or pureed vegetables, as well as mashed potatoes without adding milk.
- Among drinks, it is best to give preference to jelly, which has a viscous consistency.
- You can treat yourself only with crackers or unsweetened cookies.
It is better not to consume any fried foods, dairy products, fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as sweets and confectionery products at this time, so as not to aggravate the situation and not provoke the recurrence of unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Other dangers associated with the gastrointestinal tract during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the expectant mother may experience various gastrointestinal diseases. Common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, similar in symptoms to rotavirus: E. coli, poisoning. With rotavirus infection, body temperature rises. A pregnant woman may have a high temperature throughout the first trimester - this is normal, do not panic. The symptoms as a whole are taken into account. It is worth knowing and taking preventive measures.
Methods of infection
The peak incidence of rotavirus infection occurs in the warm seasons - spring and summer. There are only 2 types of transmission of rotavirus from an infected person:
- Fecal-oral – due to insufficient hygiene of the patient. Viral particles can persist for a long time in water (therefore, infection often occurs after swimming in the sea), on household objects, and on hands.
- Airborne transmission is through coughing or sneezing in close contact with an infected person. This method of infection is rarer, since the concentration of viral particles in saliva is much lower than in feces.
After the virus enters the human body, it multiplies in the intestines. Clinically, this time does not manifest itself in any way and is called the incubation period. Its duration averages from 2 to 5 days. The duration of the incubation period depends on the number of viral particles that have entered the body and the presence of concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Escherichia coli
Often, analysis shows the presence of E. coli in urine and culture during pregnancy. When discovered, the woman is very frightened. The bacterium can have a strong effect on the intestinal system, causing severe disorders - vomiting, diarrhea. Habitat: large intestine, bladder. An acceptable limit for the content of E. coli in urine has been established, but it should not be present there.
Symptoms:
- Diarrhea.
- Vomit.
- Fever.
- Nausea.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nagging pain in the abdomen.
The disease is dangerous for the expectant mother and fetus. It can greatly reduce a woman’s immunity, making the body vulnerable to disease. First, the bacterium (Escherichia coli) enters the urinary tract, from where it rises to the bladder. The child develops pathologies that can lead to death.
Escherichia coli bacterium
Prevention
To ensure that E. coli is not found in bacterial culture or discharge from the bladder, careful prevention of the disease is carried out.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene. You need to wash in the direction from the vagina to the anus. Otherwise, fecal residues will be carried into the vagina and the bacteria will appear in the urinary tract.
- You can't wear thongs all the time. Lingerie creates a friction effect and affects the transfer of infection to the vagina.
- Avoid sexual intercourse with a mixture of intestinal and genitourinary microflora.
- Do not use scented pads or toilet paper.
The rod can live in the body without manifesting itself. A woman lives her life to the fullest and is unaware of the presence of E. coli in her bladder. It is recommended to undergo tests periodically. The doctor prescribes a culture and a smear during pregnancy to determine the presence of infection. Pregnancy management is carried out in such a way that tests are taken from trimester to trimester. It is impossible to miss E. coli in the culture - the analysis is taken frequently in order to catch a possible infection in time and prevent its progression.
Escherichia coli test
Treatment
If the analysis shows the presence of infection, begin treatment. It causes a serious kidney disease - pyelonephritis. The disease is dangerous during pregnancy. With pyelonephritis, severe pain occurs. It is easier to prevent than to cure - the kidneys suffer. There remains a danger for the child. Pregnancy ends in miscarriage, intrauterine death of the fetus, and death of the mother.
During pregnancy, gentle treatment is used. Less commonly prescribed are serious drugs that affect the child - Canephron, Amoxiclav, Furagin.
E. coli is treated with folk remedies. Plantain decoction, sunflower, and celandine are used. Before self-medication during pregnancy, you should consult your doctor.
Is rotavirus infection dangerous during pregnancy?
Intestinal flu is a pathology named after a pathogen that looks like a wheel. More often the disease is diagnosed in the fall.
The pathology is transmitted by airborne droplets and food. People with obvious manifestations of the disease and asymptomatic carriers of the infection pose a danger to a healthy person. You can become infected by using dirty sanitary fixtures (toilet) and household items (dishes), by contact with soil, or by shaking hands.
People over 20 years of age develop immunity to rotavirus, but pregnant women are still at risk. After conception, a natural weakening of protective functions occurs, the body loses the ability to fight any pathogens.
Rotavirus infection is very dangerous during pregnancy. High fever and vomiting increase the risk of dehydration.
Rotavirus is not directly dangerous for the child, since it cannot penetrate the placental barrier. If infected during pregnancy, antibodies will be transferred to the newborn through breast milk, but only with a mild form of pathology. The consequences of a severe disease are difficult to predict.
Attention! There are 9 types of rotavirus pathogens. But only 6 types of viruses are dangerous for people.
Poisoning during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman needs to be doubly careful in consuming foods. At risk are meat and sausage products, dairy products, canned food, and mayonnaise salads. Fungi pose a great danger to the life of the embryo - toxins are able to overcome the placental barrier and affect the fetus.
Symptoms of poisoning during pregnancy:
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Diarrhea.
- Stomach ache.
- Rare fever.
If vomiting occurs once, loose stools 2-3 times a day, and the temperature does not rise, you can treat yourself. If the condition is severe, it is better to consult a doctor.
Treatment
Remove the poison from the stomach. It is better not to induce vomiting - the body will cope. The only help is drinking plenty of fluids. With the help of water, the toxic product will leave the body faster. After emptying your stomach, take an absorbent (Activated Charcoal) that binds toxins for further elimination.
When the condition improves, restore the loss of fluid - boiled water will do.
Poisoning during pregnancy requires a diet. Do not refuse food - you need to eat light food, in small portions. You can eat porridge with water, mashed potatoes, boiled meat, fish, tea with dry bread, cookies.
Rotavirus in a child
Rotavirus in children: symptoms, treatment, prevention.
Rotavirus infection
- an acute infectious disease with fecal-oral transmission, characterized by damage to the gastrointestinal tract such as gastroenteritis with the development of dehydration syndrome (dehydration).
Rotavirus is the leading cause of gastroenteritis in children under 5 years of age. .In Russia it is most often recorded in the winter-spring period.
Causes of infection:
The causative agent is rotavirus, belongs to the family
RNA viruses. Types 1 - 4, 8 and 9 of the virus are considered infectious to humans.
The source of infection is a person (patient or virus transmitter). The number of asymptomatic carriers of the virus among children can reach 5–7%. The virus is able to remain viable in the external environment for several months, is stable at low temperatures, and quickly dies when heated.
In the Russian Federation as a whole, the proportion of sick children under 1 year of age is 20.6%, and 44.7% at the age of 1–2 years. By the age of 2, almost every child experiences rotavirus infection at least once, and more than 2/3 become ill again. Given its high contagiousness (infectiousness), it is a common cause of outbreaks in organized groups (kindergarten, school) and hospitals.
The mechanism of transmission
of rotavirus
is fecal-oral: it is realized through food, water and household contact. Given the extremely high contagiousness of rotavirus and the resistance of the pathogen to household chemicals, even very strict hygiene measures (including washing hands after each contact with a sick person) can often be ineffective. The incubation period is only a few days - on average from 1 to 3 days.
Clinical picture
The main symptoms of rotavirus gastroenteritis are general intoxication (fever, lethargy, vomiting, headache) and changes in the gastrointestinal tract: abdominal pain, frequent loose, watery stools. Rotavirus gastroenteritis is characterized by two variants of onset of the disease: acute (about 90% of patients), when all the main symptoms appear on the 1st day of the disease, and subacute, when 1-2 symptoms (usually abdominal pain and intoxication) on the 2-3rd day illnesses include diarrhea, vomiting, fever.
General infectious syndrome.
Most cases of rotavirus infection begin acutely with an increase in temperature to febrile levels (38.0 degrees) or even hyperthermia, but the duration of fever, despite its severity, rarely exceeds 2-4 days. Fever is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication: weakness, lethargy, decreased appetite, up to the development of anorexia and adynamia in severe forms of the disease. In older children, with mild forms, the disease can occur against a background of low-grade fever with moderate symptoms of intoxication or their absence.
Syndrome of local changes (gastritis, gastroenteritis and/or enteritis).
One of the first, and often the leading, manifestations of rotavirus infection is vomiting. It can occur simultaneously with diarrhea or precede it, and be repeated or repeated over 1-2 days. Damage to the gastrointestinal tract occurs as gastroenteritis or (less commonly) enteritis. Diarrheal syndrome due to rotavirus infection is one of the most important and constant manifestations, in some cases determining the clinical picture of the disease. The stool is copious, watery, foamy, yellow in color, without visible pathological impurities, or with a small amount of clear mucus, sometimes there is a characteristic sour smell of stool. The frequency of stools on average does not exceed 4–5 times a day, but in young children it can reach 15–20 times. The duration of diarrhea on average ranges from 3 to 7 days, but can persist for a longer time (up to 10-14 days, more often in young children). Rotavirus infection is characterized by a combination of diarrhea and flatulence, which are most pronounced in children of the first year of life. Abdominal pain syndrome due to rotavirus infection appears at the onset of the disease. Abdominal pain of varying severity can be diffuse or localized in the upper half of the abdomen, and episodes of cramping pain can also occur.
Dehydration syndrome.
The severity of rotavirus gastroenteritis is determined by the amount of pathological fluid loss with vomiting and diarrhea and the development of exicosis (dehydration) of I–II, less often II–III degrees. The degree of exicosis in patients depends not only on the severity of pathological losses of fluid and electrolytes, but also on the adequacy of the rehydration therapy (adequate fluid replacement). The development of dehydration is signaled by the following signs: constant thirst, sunken eyes and fontanel, dry skin, sclera and mucous membranes. The skin acquires an earthy-gray tint, lips become bright and dry, skin turgor decreases, and the amount of urine decreases. The most dangerous condition is considered to be the stage of dehydration, in which thirst is replaced by a complete refusal to drink and a pronounced decrease in urination occurs, up to its complete absence.
Syndrome of catarrhal changes.
In 60–70% of patients with rotavirus infection, catarrhal symptoms occur in the upper respiratory tract, which may precede intestinal dysfunction. It is characterized by moderate hyperemia and granularity of the posterior wall of the pharynx, soft palate and palatine arches, nasal congestion, and coughing. However, the presence of catarrhal symptoms in some cases may be due to a concomitant respiratory viral infection, especially during the seasonal rise in incidence.
Extraintestinal complications:
- dehydration
- secondary infection
- possible development of seizures
— improper water regime RVGE can cause cerebral edema, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, acute renal failure and other life-threatening conditions
The most alarming signs! (You need to call an ambulance
)
- marked weakness and lethargy, almost constant sleep or, on the contrary, incessant restlessness
- incessant vomiting
- inability to give a child something to drink
- absence of urination or very rare concentrated urine
- in children under one year of age - retraction of the fontanel
- blood in the stool
Disease prognosis:
The prognosis of the disease with adequate hydration is usually favorable; the duration of the disease rarely exceeds 5-7 days. After rotavirus gastroenteritis, a child may become infected again due to seasonal changes in circulating rotavirus serotypes, but a natural infection may reduce the severity of subsequent infections.
Diagnostics:
Stool ELISA and OKI test (also includes PCR testing for other types of viruses that cause acute intestinal infections, salmonellosis and dysentery)
First aid:
-Drink plenty of small amounts. For this, it is preferable to use specialized saline solutions - Regidron, Regidron - Bio. In the first hours, in order not to provoke vomiting, you can give 1 tsp. or tbsp. every 5 - 10 minutes.
IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER! Depending on age, a child should drink at least 1 - 1.5 liters of water per day. Therefore, especially during the first knocks of the child, you SHOULD continue to give water during sleep, making sure that the child does not choke.
- Place a small child on his side so that in case of an attack of vomiting he does not choke on the vomit.
- Antipyretics - only if the temperature is above 38.5.
- Do not feed for the first 3 hours after vomiting, then in small portions.
Be sure to continue breastfeeding!
— In the acute period, to accelerate the normalization of stool and remove the virus from the body, astringent and adsorbent substances (carbolene, polyphepan, smecta, enterosgel, etc.) are used.
Diet:
When treating intestinal infections that provoke the development of fermentopathy, special attention is paid to diet. Since the development of the pathological process disrupts the activity of a number of digestive enzymes, in particular lactase, during the acute period of the disease, whole milk and dairy products should be excluded from the child’s diet and the intake of foods rich in carbohydrates (sweet fruits, fruit juices, baked goods, legumes) should be limited. culture). Also, during the acute period of illness, it is not allowed to feed children meat, broths, meat products, fatty and fried foods. Food is given to a sick child often, in small portions. The list of permitted foods includes slimy porridges, vegetable purees and soups, white crackers and baked apples.
Breastfeeding in the presence of an intestinal infection is not stopped, since breast milk contains antibodies that neutralize rotavirus and immunoglobulins, which alleviate the course of the disease.
Common mistakes:
- Giving antibiotics. In this case, the culprit is a virus and any antibiotic is completely powerless against it. It will not bring any benefit, it will only increase the likelihood of complications.
- in case of profuse diarrhea, use any antidiarrheal drugs such as loperamide (without consulting a doctor). Taking them can increase intoxication and lengthen the recovery period.
Prevention:
There is specific prevention against rotavirus - vaccination
Vaccination (Rotatec). The course consists of three doses with an administration interval of 4 to 10 weeks. The first vaccine is administered at the age of 6 to 12 weeks. Last administration before 32 weeks of life. (Compatible with any vaccines from the national calendar except BCG)
Besides:
Patients with mild forms of rotavirus infection are isolated at home for 7 days, after which the person who has recovered from the disease can be admitted to an organized group (including children) on the basis of a doctor’s certificate of recovery without additional virological examination.
• Use only boiled water for drinking;
• Thorough hand washing before eating;
• Pre-washing fruits and vegetables with a brush;
• Sufficient thermal processing of food.
Possible complications
Pneumonia on x-ray
The dangerous consequences of rotavirus develop against the background of severe dehydration and severe infectious pathology in the early stages of pregnancy.
Possible complications:
- a sharp decrease in immunity, frequent colds;
- hypotension;
- toxic shock (develops with a strong increase in body temperature);
- renal failure;
- pneumonia, bacterial bronchitis.
The consequences of dehydration are low water intake, premature birth, and lack of breast milk. When there is a lack of fluid in the body, the volume of circulating blood decreases and the production of oxytocin, which is responsible for uterine contractions, is activated.
With dehydration, the blood becomes more viscous, increasing the risk of blood clots. When the fetus lacks fluid, neural tube defects occur and hypoxia develops.