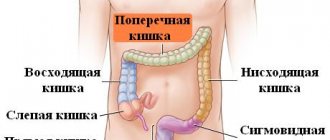
Dysfunction of large intestinal motility provokes a whole complex of pathological changes associated with the activity of all parts of the digestive system. In this case, the organ itself is not damaged, but processes occur in it that can not only slow down or accelerate its peristalsis, but also provoke a disruption of this process in the stomach, intestines, and esophagus.
Thus, colon dyskinesia leads to negative manifestations associated with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The disease is very common; about 30% of the world's inhabitants are faced with this problem. It is observed in both adults and children. Symptoms of the pathology are especially common in the female part of the population.
To find out what dyskinesia is, you need to familiarize yourself with its clinical picture, treatment options and preventive measures to prevent the disease.
Factors causing pathology
Among the provocateurs of this negative process, the following diseases should be noted:
- gastritis;
- cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- diabetes type 1 or 2;
- hypothyroidism;
- infections affecting the intestines;
- gynecological diseases.
In the development of the disease, pathological changes in the endocrine system, disruption of hormonal levels and nervous system activity play an exceptional role.
The reasons for the development of the disease are not limited to this list.
It should be noted that dyskinesia of the large intestine, like all diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract, is provoked in most cases by the following factors:
- Violation of healthy nutrition standards, which include moderate consumption of high-calorie foods. Ignoring vegetables, fruits and cereals rich in fiber.
- Lack of acceptable physical activity.
- Prolonged stay in a stressful state can be a provocateur of dysfunction of the colon.
- The genetic factor is the most common prerequisite for the appearance of functional disruptions in intestinal motility and peristalsis.
- Excessive use of medications.
If we talk about the occurrence of the disease in childhood, it should be noted that the leading factors are hypovitaminosis, hormonal and nervous disorders in the body.
Clinical manifestations
The most expressive signs cannot be fundamental for making an accurate diagnosis. But you should know them so as not to miss the favorable time to start timely treatment. Among them:
- Painful sensations. They can be short-term and long-lasting, aching and acute. The localization is quite varied, but most often it is the area around the navel. A distinctive feature of the pain syndrome is an increase in its intensity after a meal, during stress, and a decrease after the release of gases or bowel movements. At night the pain does not appear, but resumes in the morning.
- Constipation, followed by diarrhea and accompanied in some cases by the appearance of mucus in the feces.
- Stagnation of feces causes bloating, a feeling of fullness and increased gas production. This provokes an increase in pain, seething or rumbling in the intestines, and spasms.
- Increased nervousness, depressed state.
- The presence of pain in the back, joints, heart (in the absence of health problems in these systems).
Such symptoms, the lack of regular bowel movements and the normal state of stool cause intoxication, poor health, and aversion to food. This leads to sudden weight loss and dizziness.
Diagnostics
The uniformity of symptoms of dyskinesia and other pathologies of the digestive system greatly complicates diagnosis. This makes it necessary to gradually exclude possible diseases such as colitis, polyposis, tumor processes, and diverticula.
Blood and stool tests are carried out, as well as scatological examination. Instrumental diagnostics include:
- colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- irrigoscopy.
To exclude oncological problems, a biopsy is performed. But malignant neoplasms, like organic damage, are not detected with dyskinesia.
Basically, the examination results indicate weakened motility and peristalsis, hypo- or hypertonicity of the intestine. Dysbacteriosis is often detected.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosing pathology only on the basis of patient complaints is quite difficult, since the symptoms of the disease are similar to many other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Diagnostic measures are carried out in several stages, excluding other pathologies (diverticula, tumors, polyps, non-ulcerative colitis). When carrying out diagnostics, laboratory and instrumental research methods are used.
Laboratory methods include blood tests, stool testing for occult blood and dysbacteriosis, and scatological analysis.
Instrumental research methods include irrigoscopy, endoscopic examinations through sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, during which a biopsy is taken. Examination of a biopsy (a piece of intestinal tissue) is required to exclude malignant formations.
In most cases, in patients suffering from dyskinesia, organic intestinal lesions and tumor processes are not detected, but weakened peristalsis or intestinal hypertonicity and dysbiosis are detected.
To eliminate an unpleasant pathology, you can also use folk remedies, but only after the approval of the treating doctor has been obtained.
- Irritable bowel syndrome can be eliminated by drinking a glass of cabbage or potato juice every morning.
- A medicinal decoction will help normalize intestinal activity and eliminate constipation. To prepare it, you need to prepare a decoction based on lingonberry berries, rhubarb, buckthorn, hay leaves and Alexandria leaves.
- A decoction based on raisins, dried apricots, and boiled beetroot salad are excellent laxatives.
- Compresses made with vinegar are designed to relieve pain in the abdominal area. 100 ml of this product is diluted in 3 liters of water. A piece of gauze is soaked in the prepared composition, which is then applied to the problem area for 1.5 hours.
- With the help of a sedative infusion of herbs, you can get rid of intestinal hypertonicity. To prepare it, you need to take equal quantities of sage, mint, motherwort and yarrow leaves, St. John's wort flowers and oak bark. 2 tablespoons of this herbal mixture are poured with 200 grams of boiled water. The decoction should steep for 2 hours. Strain the finished drug. Drink a third of a glass in the morning, lunch and evening for 7 days.
Classification
According to pathogenesis, primary and secondary dyskinesia of the large intestine are distinguished. In the first case, pathological processes develop as an independent disease. A disease that occurs against the background of other ailments of the gastrointestinal tract is considered secondary.
According to the clinical course, the classification distinguishes three types of the disease:
- The first is characterized by pronounced intestinal signs. Among them, the most common is diarrhea, followed by a prolonged absence of stool.
- The second is accompanied by intense pain.
- The third is characterized by the predominance of symptoms characteristic of nervous disorders.
The possibility of manifestation of symptoms of a mixed type, when there are symptoms of all types of the disease, cannot be excluded.
Etiological classification
In its origin, dyskinesia of the large intestine is quite diverse. There are several varieties, including:
- neurogenic, occurring against the background of pathologies associated with the nervous system;
- psychogenic, developing as a result of prolonged depression, neurotic conditions, asthenic syndrome;
- endocrine-hormonal, which is a consequence of dysfunction of the endocrine system - disruption of the pituitary gland and the activity of the gonads, hypothyroidism;
- toxic, provoked by malicious use of alcohol and poisoning with toxic chemicals;
- medicinal, resulting from the uncontrolled use of medications for constipation or diarrhea;
- nutritional, which occurs with all kinds of diets, insufficient or excessive consumption of food products;
- hypodynamic, developing as a result of surgical intervention in the abdominal organs, hypokinesia and asthenia; the manifestation of this variety also occurs in cases of metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, and allergies.
The treatment method directly depends on the etiological factor. This is why it is so important to undergo a thorough diagnostic examination.
Species categories
The disease, depending on the impairment of motor functions, has two main types.
Hypotonic dyskinesia
The pathological process, which occurs in a hypotonic type (atonic), causes a significant weakening of the tone of the colon and its peristalsis. This, in turn, provokes stool retention and the following symptoms:
- aching dull pain without specific localization;
- heaviness and feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- significant weight gain caused by a slow metabolic process;
- rare bowel movements and excretion of feces in small quantities leads to increased gas formation, intoxication and the development of allergic reactions.
Hypomotor dyskinesia contributes to the development of hemorrhoids and dilation of veins in the pelvis. The disease, which occurs in a hypomotor type, often leads to intestinal obstruction.
Hypertensive appearance
Pathology developing according to the hypertensive type (spastic) is characterized by increased tone and spastic contractions of the colon. They provoke:
- Intestinal colic and prolonged constipation.
- Paroxysmal pain, localized in the lower abdomen and lower lateral zones. The pain goes away after defecation.
- Excretion of feces in large quantities becomes a prerequisite for an increase in the volume of the colon, which subsequently becomes the cause of involuntary bowel movements.
Spastic dyskinesia is accompanied by other characteristic symptoms:
- bloating, flatulence;
- pungent odor from the mouth;
- formation of fecal stones;
- the appearance of a white coating on the surface of the tongue.
In most cases, the disease “starts” after poisoning and infectious diseases, accompanied by severe intoxication.
Features of dyskinesia in children
The etiology of the disease in childhood almost always has a neurogenic basis.
The disease is more complex than in adults . Children have a harder time with changes in bowel movements from diarrhea to constipation and vice versa.
The most noticeable symptom of illness in a child is acute pain. It is sometimes difficult to eliminate it even with strong painkillers.
In most cases (excluding severe diarrhea and intoxication), it is possible to save a child from suffering by adjusting the diet.
Symptoms of dyskinesia
Pain in the abdominal area of varying intensity and character (paroxysmal, constant, cutting, dull). Most often, their location is the navel area. The pain may intensify after eating food, during stressful situations and emotional turmoil, and subside after the passage of gas and bowel movements.
A characteristic feature is the absence of pain at night and its resumption after waking up. Dyspeptic symptoms: nausea, belching of air, flatulence, bloating and heaviness in the abdomen. Flatulence. Its symptoms often worsen in the evening or before bowel movements and are accompanied by pain in the abdomen and rumbling.
Stool disorders. A characteristic symptom is constipation, which is followed by short-term diarrhea. In some cases, mucus is discharged along with the stool. Neurotic disorders. Psychoneurotic symptoms such as anxiety, nervousness, depression, which are accompanied by weight gain, are observed. Sometimes patients experience pain in the cardiac region or spine, even though these organs are in absolute health.
With this pathology, patients often complain of unstable stools with constipation. In this case, the process of defecation is difficult, after which there is a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying, the feces are fragmented.
Constipation may be followed by diarrhea, which is accompanied by stool more than three times a day. Sometimes mucous colic occurs when, due to stress, mucous impurities appear in the stool. Constant accumulation of feces in the intestines leads to intoxication of the body, dizziness, loss of appetite, general weakness, decreased performance and allergic reactions.
Treatment
The fundamental principle of the treatment course is an integrated approach, including:
- drug treatment;
- nutrition adjustments;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- therapeutic exercises.
The use of traditional medicine is allowed only in consultation with the attending physician.
Medication prescriptions
In order to normalize the motility and peristalsis of the large intestine and relieve acute symptoms, drugs that normalize stool, psychotropic and sedative medications are prescribed.
The most effective drugs that promote complete and regular bowel movements are Kafiol, Laminaride, Duphalac, Regulax.
For concomitant diseases of the digestive organs, antispasmodics are used, which have a beneficial effect on the motility of the organ. The most effective are Nifedipine and its analogues.
Polytropic drugs are also prescribed to relieve acute symptoms. Halidor, Papaverine, Gastrotsepin, No-shpa have proven themselves well.
From physiotherapeutic procedures
Paraffin baths, electrophoresis, and diathermy are recommended.
Oxygen and pine baths, acupuncture, massage, and enemas have a beneficial effect on the patient’s condition.
Other recommendations
Among them, special importance is given to:
- physical therapy, which is based on exercises that strengthen the muscles of the abdomen and pelvis;
- hydro procedures;
- use of rectal mud tampons.
The following have a good effect:
- daily consumption of mineral water, which should be drunk without gas;
- rinsing the intestines with mineral water at room temperature.
Folk remedies
There are recipes that help quickly get rid of the disease. Here are some of them:
- Herbal infusion. It is an excellent sedative. It's easy to prepare. Yarrow, oak bark, St. John's wort, sage and motherwort (1 teaspoon each) pour 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 20 minutes, strain. Drink 50 ml 3 times a day after meals.
- Applications with vinegar. Pour 10 ml of vinegar with warm water (100 ml). Soak 1 meter of gauze, folded four times, in the solution. Apply to the affected area and leave for 25-30 minutes.
- Decoction of dried plums.
It is recommended to use folk remedies only in consultation with your doctor.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the disease, it is necessary to take into account the advice of specialists on adjusting nutrition, maintaining an active lifestyle, and giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs).
You should not ignore undergoing a regularly scheduled examination once a year. Stressful situations must be avoided.
How to cure intestinal atony
Treatment of intestinal atony should be comprehensive, aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease and eliminating factors that negatively affect intestinal motility.
For atony, the following are used simultaneously:
drug treatment (homeopathic remedies that restore normal innervation of the muscular walls of the intestine, remove the effects of fecal stagnation, regulate fecal excretion, eliminate the underlying diseases);
By combining all of the above treatment methods, you can quickly achieve a good result and prevent the recurrence of atony by improving gastrointestinal motility.
When treating intestinal atony, medicine uses the following medications:
Laxatives (for example, Regulax);
Vegetable juices, fruit compotes, jelly;
It is advisable to eat small portions - 5 times a day, at the same time, combine proper nutrition with walks and exercises. It is advisable to eat food not dry, cook or bake food, and not smoke or fry. By adhering to this treatment, you can improve gastrointestinal motility.
The absence of the following products in the diet also helps to normalize intestinal function and motility:
Promote the treatment of atony with folk remedies, including in the diet the frequent use of mixtures made from products that have a beneficial effect on intestinal motility.
Aloe mixtures: wash several aloe leaves, remove thorns, and chop. Heat one and a half glasses of honey in a saucepan (the temperature should not be higher than 40 degrees, otherwise honey may lose its beneficial properties), add aloe and leave for 24 hours. Reheat again, take 1 tbsp every day 1 hour before breakfast. within 7-10 days. After completing the treatment, take a week break and repeat the course again.
The functioning of intestinal motility at home can be improved by doing physical exercises, as well as properly massaging the abdominal area. This will help the intestines move feces to the exit, normalize the process of emptying and cure atony.
Remember that all this is done only when the person does not experience critical complications due to fecal retention (bleeding, inflammation, tears and perforations). In this case, physical activity can aggravate the patient's condition with atony.
About nutrition
There is no special diet, but it is recommended to adhere to proper nutrition standards, excluding the consumption of fatty, fried, spicy foods, and alcohol.
Preference should be given to products with a high content of coarse dietary fiber (fruits, vegetables, cereals).
In case of severe dyskinesia, you should consult a nutritionist or gastroenterologist for advice on the composition of a gentle diet.
A properly designed menu should take into account the need for all nutritional components, vitamins and microelements in the diet.
Treatment of intestinal atony
Treatment of this condition in modern gastroenterology begins with diet. In some cases, only proper nutrition is enough to correct the frequency of bowel movements. For constipation, diet table No. 3 is prescribed. It is recommended to consume fresh vegetables and fruits. Your daily diet should include foods that contain anthraglycosides - dried apricots, figs, prunes. It is mandatory to include fermented milk dishes, juices with pulp (plum, apricot), and vegetable fats in the menu. It is necessary to limit products containing tannin (tea, blueberries, cocoa). Food should be chemically and mechanically irritating; food should not be prepared in the form of puree or jelly.
Possible complications
Among the negative consequences of the disease are:
- bowel prolapse, which can only be treated surgically;
- intestinal obstruction;
- intoxication;
- cholelithiasis;
- diseases of the liver, pancreas;
- gastritis, damage to the mucous membrane.
It is possible to avoid serious consequences with careful attention to health and timely seeking medical help. Self-medication only leads to a protracted course of the disease and complications.