12.12.2019
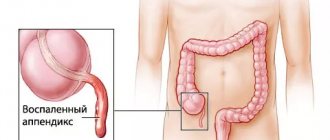
Females experience appendicitis more often than males. The signs of gynecological diseases are similar to the symptoms of appendicitis in women; it is important for everyone to know how to determine the source of pain at home. Diagnosis can be difficult due to the location of reproductive organs near the appendix.
Causes of the disease
Appendicitis can occur at absolutely any age. But more often young women encounter it. The causes of the disease are as follows:
- disturbance of the blood flow of the appendix or its displacement;
- inflammatory process in nearby organs;
- intestinal infection;
- excess serotonin;
- blockage of the organ with small objects (seeds, bones, etc.);
- clogging of the lumen with feces.
In women, appendicitis often occurs due to gynecological diseases. One of the most common causes of the disease is considered to be an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. Diet, lifestyle and stress have no less influence on the condition of the appendix. The development of the disease occurs in stages:
- The initial stage of inflammation is called catarrhal.
- The next stage is characterized by the formation of purulent ulcers.
- The phlegmonous stage is characterized by an increase in the appendix and its filling with pus.
- At the last stage, the appendix ruptures.
Other causes of abdominal pain
Many diseases can cause abdominal pain, especially if they affect the digestive tract or abdominal organs.
These include:
- food poisoning or allergies
- stomach flu
- pneumonia
- constipation
- inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
- gastroenteritis
- peptic ulcer
- urinary tract infections
- intestinal obstruction
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
- abdominal adhesions
- ectopic pregnancy
- ovarian cysts
- abdominal trauma
- pancreatitis
- diverticulitis
- ovarian follicle rupture
- diabetic ketoacidosis
How to identify the signs
The main symptom of appendicitis is abdominal pain. It gets worse when laughing or moving. In some cases, discomfort radiates to the right leg. At the initial stages, it is difficult to understand the symptoms of appendicitis in women; how to determine their manifestation at home, you need to learn in advance. Inflammation develops rapidly, so it is important to consult a doctor in time. There are certain signs that you should pay attention to. At the initial stage, the pain is aching in nature. It can radiate to any area of the peritoneum. Its signs can easily be mistaken for cholecystitis, gastritis or gynecological diseases. A little later, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced.
External
External signs of appendicitis include low-grade fever. It is characterized by fluctuations in body temperature in the range from 37.1 to 38 degrees. Deterioration in health is accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring significant relief. Pregnant women experience abdominal stiffness and shortness of breath. The skin becomes pale, the tongue becomes covered with a yellowish coating.
Domestic
With inflammation of the appendix, appetite may disappear. There may be difficulty urinating and bowel dysfunction. Diarrhea occurs most often. Clinical symptoms depend on the location of the process. When it is located behind the cecum, the pain is muted. Localization of the appendix in the pelvis leads to atypical pain.
Internal signs of appendicitis are determined by palpation. The right iliac region and umbilical ring are examined. With light palpation, the tone of the anterior peritoneal wall increases. When you take a deep breath, you feel an increase in pain.
The first symptoms of appendicitis
Symptoms of appendicitis are manifested mainly by sharp pain in the abdomen. The usual pathogenesis of appendicitis is manifested by the following sequentially developing symptoms: pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, dyspepsia.
Learn more about each symptom at the onset of appendicitis.
- Sudden pain in the solar plexus or above the navel is the most typical first symptom of acute appendicitis. During this period, pain in the abdominal area without a specific localization is also possible. It is characterized by pain of varying intensity (strong, weak) and nature (constant, intermittent). Next, there is a shift in the emphasis of pain to the right iliac region, that is, to the area of the topographic projection of the appendix. The nature of the pain is constant, moderate intensity, intensifies with coughing, movement, and changes in body position in space.
- Nausea and vomiting. Vomit consists of previously consumed food mixed with bile. Vomit when the stomach is empty in the form of liquid, yellow mucus. Vomiting with appendicitis develops as a reflex to pain, accompanied by a decrease in appetite, often one-time.
- Fever. A frequent companion to appendicitis is an increase in body temperature. Usually it does not rise above febrile fever levels (37.0-38.00C).
- Dyspepsia. The increase in intoxication is accompanied by a disorder of the act of defecation - dyspepsia in the form of constipation or loose stools. Dyspepsia occurs against the background of frequent urination, the result of the involvement of the bladder in the pathogenesis. The color of urine is intense, dark.
The insidiousness of appendicitis can manifest itself as a debut with the priority of other symptoms, against the background of a weak pain reaction. In addition, pain can subside under the influence of painkillers, as well as with necrosis of the wall of the appendix.
Localization of pain
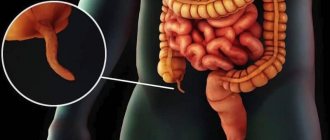
When alarm signals occur, it is necessary to pay attention to the local location of painful sensations. The appendix is located on the right side, so the greatest concentration of sensations is noted there. Pain is noted in the area from the navel to the lower abdomen, where the ovaries are located in women.
A few hours after the first symptoms appear, discomfort spreads to other organs. Discomfort appears in the epigastric region, aching pain in the lower back develops, and discomfort when walking increases.
The first signs of appendicitis in adult men
The main symptoms in males are acute pain in the abdominal area. They also appear due to pressure. Symptoms of appendicitis in adult men may be accompanied by an increase in temperature, nausea and vomiting.
Experts point out that:
- The initial symptomatic complex of acute appendicitis does not always make it possible to identify the present pathology. Initially, the inflammatory process can be disguised as another, less critical one, as a result of which the attack is mistaken for renal colic or worsening gastritis.
- The leading symptom of appendicitis should be considered permanent acute pain in the peritoneum. Typically, such sharp pains occur unexpectedly (at night or in the morning).
- In the catarrhal stage, painful sensations spread throughout the abdomen or occur in its upper part, namely in the epigastrium. However, subsequently the pain is concentrated in the right lower abdomen, below the navel and above the thigh area.
The algorithm for moving the pain focus is called Kocher's symptom and is one of the leading defining symptoms of the condition.
In 90% of cases, it is this that indicates inflammation of the appendix, and not other diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract.
The following picture should be considered specific to male representatives:
- when pulling at the base of the scrotum, acute painful sensations are formed in the right testicle;
- Tightening of the right testicle may develop, which resolves spontaneously after treatment of appendicitis;
- palpation of the most painful place provokes the pulling of the right testicle towards the scrotum.
Diagnosis at home
The final diagnosis is made by specialists. There is no need to take any measures on your own. If you suspect appendicitis, you should not drink water or engage in active movements. This will prevent premature rupture of the appendix. It is advisable to wait for an ambulance in a horizontal position. At temperatures below 38 degrees, antipyretic drugs are not required
You can distinguish appendicitis from other diseases at home. The main thing is to carry out all manipulations carefully. Initially, the symptoms of appendicitis in women are assessed; how to determine the source of pain at home is no less important. You need to press your fingers into the place on two fingers to the right of the navel and quickly release them. The pain at this moment will be more intense.
In the hospital
After entering the hospital, diagnostic tests are carried out. It includes the following steps:
- examination by a surgeon;
- visit to the gynecologist;
- blood donation;
- Ultrasound monitoring.
The gynecologist conducts an examination for the presence of gynecological diseases. If they are not there, the woman is referred to a surgeon. He will palpate the abdominal area and ask questions about your stool and last meal. Donating blood helps determine the level of leukocytes and ESR. An increase in indicators indicates an inflammatory process. An ultrasound examination is prescribed if doctors have doubts about making a diagnosis.
Temperature
With the development of appendicitis, body temperature usually rises to 37 degrees and chills appear. However, in an advanced state, complications can arise, and the temperature can rise to 40 degrees. If your temperature rises sharply, you should immediately seek medical help, as complications can be fatal.
Appendectomy
The operation to remove appendicitis is performed using a classic appendectomy or laparoscopy. Appendectomy is a classic abdominal operation. Laparoscopy is an operation that does not require abdominal incisions in the skin. It is less traumatic, but has a number of significant contraindications. Classic appendectomy is performed much more often.
Before the operation, general anesthesia is given. Then access to the affected organ is provided. In the case of laparoscopy, small punctures are made in the skin. The appendix is completely removed, after which the abdominal cavity is drained. The final step involves placing stitches on the puncture or incision sites.
Treatment of inflammation of appendicitis
After using various methods, the factors that influenced the inflammatory process of the internal organ have been established, the doctor prescribes surgery.
There is no cure for appendicitis; it can only be eliminated through surgery.
As soon as symptoms appear indicating the presence of acute appendicitis, the patient is sent to the surgical department of the hospital. If the diagnosis of appendicitis is confirmed, emergency surgery, called appendectomy, is prescribed. The essence of this operation is this: the surgeon removes the appendix, which causes inflammatory processes in the body.
Before the operation, the patient must undergo a complete cleansing of the stomach in order for the anesthesia to be effective. But if the patient reports that he had severe vomiting, then the cleansing procedure may not be carried out. The patient's intestines are also cleansed using special enemas and a solution with a cleansing effect. Then, under general anesthesia, the operation itself is performed to remove the inflamed organ.
The patient's recovery period should be determined depending on his response to the surgery and anesthesia. It can be one week or more. The doctor must give the patient recommendations that he will need to follow for a speedy recovery.
From this moment on, a person must follow a proper diet and perform special physical exercises that exclude excessive stress. In the initial stages after removal of the appendix, the patient may experience an increase in body temperature. However, you should not be alarmed by such a symptom, as this is considered a normal reaction of the body to surgery. In any case, the person should be under inpatient observation for some time after the operation. If all sorts of negative consequences do not appear, the doctor can give a discharge to the patient.
In the modern world, acute appendicitis among men is no longer a serious and fatal disease. The level of medical and surgical support allows us to eliminate even the most complex consequences of the disease. However, you need to remember that it is necessary to contact an ambulance in a timely manner at the first symptoms. It is better to play it safe if the diagnosis is not confirmed than to be on the verge of death due to a severe attack of appendicitis or a ruptured appendix.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy. Medicines and their regimen are selected on an individual basis. If there is a predisposition to thromboembolism, anticoagulants are prescribed.
A scar measuring up to 10 cm is formed at the site of the operation. It heals for about six months. Immediately after the operation, it has a burgundy tint, and over time it turns white. To resolve it, specialized ointments and creams are prescribed. Following your doctor's recommendations ensures a quick recovery. With proper care, the likelihood of wound suppuration is significantly reduced.
Diagnosis is simplified by specific symptoms of appendicitis in women; how to determine the disease at home becomes clear after studying physiology. The main difference is the location and nature of the pain. But only a specialist can make a final diagnosis.
Why does appendicitis occur?
Doctors studying appendicitis have identified several options for the development of this disease. The reasons may be many factors, but the main one will be infection. If a man develops acute appendicitis, we can talk about the presence in his body of Staphylococcus aureus bacilli, Escherichia coli, streptococci and other bacteria that contribute to suppuration. Such bacteria should be located in the intestinal area, but if hygiene principles are not followed, they can enter the body.
Other reasons that can provoke inflammation of the appendix may be:
- narrowing or complete blockage of the appendix located in the appendix. This blockage can occur due to congenital pathologies or as a result of the presence of abnormal tumors or foreign bodies there. As a result of the blockage, stagnation in the blood may develop, which leads to necrosis of the appendix tissue;
- deterioration of blood supply to the walls of intestinal blood vessels;
- various kinds of neurogenic reactions and slowing of intestinal wall peristalsis, accompanied by the formation of mucus and excessive expansion of the intestinal lumen.
Symptoms of appendicitis in men most often appear if a person has problems with bowel movements and suffers from frequent constipation. Diseases of the heart muscle and infectious diseases can also provoke inflammation of the appendix. The first signs of appendicitis in men at risk will be more pronounced. Under no circumstances should they be ignored.
Men who have bad habits: alcohol abuse, smoking are also at risk.
It is important to monitor your health and at the first symptoms indicating a possible manifestation of appendicitis, contact a medical facility for those who suffer from infectious diseases of the pelvis.
Symptoms
The signs of an inflamed appendix in women are quite vague, so its symptoms are often perceived as gynecological diseases, especially if the woman has a history of chronic pathologies. Therefore, it is very important to identify the signs of this pathology and diagnose them in time.
Lack of appetite
Lack of appetite is one of the common signs of appendicitis. In most patients, appetite disappears almost simultaneously with the appearance of pain. The cause of the disorder is intoxication, which can cause severe weakness and drowsiness. Patients experience a sharp decrease in concentration and performance, forcing them to stop daily or work activities.
Weight loss may also occur. If a woman's weight decreases by more than 700 g per day, it is necessary to consult a doctor, as acute dehydration may develop.
Early manifestations of intoxication
With inflammation of the appendix, nausea is constant. As the disease progresses, it increases. The maximum symptom appears on days 2-3 of the inflammatory process, after which a slight weakening of symptoms is observed. Vomiting is also considered a typical symptom of appendicitis, which can occur on the first or second day after the onset of inflammation.
Is the temperature rising?
With catarrhal inflammation of the appendix, body temperature, as a rule, remains within normal limits and rarely exceeds low-grade fever. In some cases, low-grade fever may be recorded, which manifests itself on the second day of illness, however, an increase in body temperature above 39°C with appendicitis rarely occurs. If the indicators exceed this mark, there is a risk of developing a phlegmonous or gangrenous form of appendicitis.
Change in daily urine output
Appendicitis in women is often accompanied by dehydration. This is expressed by a change in daily diuresis (a decrease in the volume of urine excreted). The woman's mucous membranes and skin become pale and dry, and there is a feeling of thirst. The number of urinations increases sharply, while the volume of urine gradually decreases, and on the 2-3rd day a false urge to urinate appears. Emptying the bladder during inflammation of the appendix is painless, the appearance of urine is unchanged.
Changing the stool
When the appendix is inflamed, the stool also changes. In most cases (about 60%), patients complain of constipation, which begins several days before the onset of the attack. In most cases, this is typical for women who do not follow a diet, eat few foods containing fiber and suffer from gastrointestinal disorders. Constipation is accompanied by bloating, accumulation of gases in the intestines, and the release of large amounts of gas. Diarrhea is less typical for appendicitis. Unlike constipation, it occurs immediately on the first day of the onset of the attack, and the number of bowel movements can sometimes reach up to ten times a day.
Changes in the cardiovascular system
Symptoms from blood vessels and the heart do not appear in everyone, but these signs cannot be excluded from the clinical picture of this pathology, since their prevalence remains quite high - at least 25%. Women may experience shortness of breath, increased heart rate, and difficulty breathing.
Other signs related to this clinical group: dizziness, decreased blood pressure, changes in heart rate, cold sweat; in people suffering from hypotension, the development of a hypotensive crisis is not excluded.
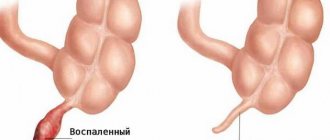
Inflammation of appendicitis has several stages:
| Stage | Term | Signs |
| Catarrhal | First 8-10 hours | Pain in the epigastric region |
| Phlegmonous | 12-24 hours | Pain in the right iliac region |
| Gangrenous | 2-3 days | Feeling relieved from pain, general signs of the inflammatory process |
| Perforated | End of 3 days | Appendix rupture: Sharp sharp pain throughout the abdomen |
What are the forms of appendicitis?
The inflammatory process occurs in an acute, complicated, and less often chronic form. The intensity of symptoms is determined by the clinical and morphological classification of the disease.
Morphology of acute appendicitis:
- catarrhal – damage to the epithelial cells of the mucous layer;
- phlegmonous - inflammation of the mucous and submucosal layers, accumulation of pus;
- gangrenous - suppuration and necrosis of the appendage;
- perforated - perforation (violation of integrity) of the walls, with the release of pus into the abdominal space.
On average, in the body of an adult, inflammation of the appendix develops within 2 days, followed by death of the neural endings of the peritoneum and other complications.
Signs of acute appendicitis in adults and children are identical, but appear at different speeds. In childhood, symptoms develop more rapidly, and the risk of purulent complications is higher than in adults.
Morphology of complications:
- peritonitis - purulent inflammation of the abdominal cavity;
- abscess - accumulation of purulent masses in the peritoneum;
- appendiceal infiltrate - a tumor spreading to the cecum, appendix and visceral fold of the peritoneum;
- pylephlebitis – purulent inflammation of the hepatic portal vein;
- empyema of the appendix - blockage of the appendix filled with purulent contents (without effusion into the abdominal cavity).
Classification of chronic inflammatory process:
- primary;
- recurrent (repeated).
In contrast to the acute and complicated condition, the symptoms of chronic appendicitis in men are mild. The disease is characterized by a wave-like course and is diagnosed in the acute phase.
Chronic appendicitis
The most common signs of chronic appendicitis include:
- regular bowel disorders in the form of constipation or diarrhea;
- moderate paroxysmal or constant pain in the right side of the abdomen;
- during exacerbations, nausea and vomiting often appear;
- sometimes the pain radiates to the lower back, right thigh or groin - this depends solely on the location of the appendix in the peritoneum of each person.
The main symptoms that occur with chronic inflammation of the appendix are similar to many gastrointestinal diseases. The specialist will have to differentiate this pathology from chronic diseases of the uterine appendages, cholecystitis, peptic ulcers and urolithiasis.
First aid
First of all, if symptoms of appendicitis appear, you should call a doctor. There is no need to try to quench the pain with painkillers and “endure it.” In addition, drugs can prevent the doctor from making the correct diagnosis and the extent of damage to the body. Until the cause of acute pain is identified, it is better to refuse to eat; in extreme cases, you can take a few sips of water.
You should not try to cure appendicitis on your own, especially by applying a heating pad. This can only intensify the inflammatory process and lead to organ rupture. It is best to assume the fetal position so that the pain subsides a little and wait for the doctor.
Possible complications
Delay in surgical intervention is characterized by complications:
- Perforation of the appendix . It is characterized by the melting of the wall of the appendix, the spillage of pus into the peritoneal area. Occurs 5 days after the first spasms appear. Manifests: nausea, vomiting; feverish condition; severe pain in the abdominal area; tachycardia; paleness of the skin. Requires immediate surgical removal of the inflamed organ.
- Appendicular infiltrate - indicates the transition of inflammation to neighboring internal organs. Appears in 1-3% of all identified pathologies of the appendix during late presentation to the hospital. If detected, antibacterial therapy is prescribed prior to surgery.
- Intestinal fistulas. They are found when the walls of the intestinal loops are damaged. They are detected 4-5 days after the operation. They often arise due to a medical error made during an operation when the wound is not completely closed.
- Appendiceal pylephlebitis is a purulent-septic inflammation of the collar vein of the liver, with the formation of multiple ulcers. Symptoms: intoxication; severe pain in the liver area; enlarged liver and spleen; pallor of the skin. Very dangerous. The fatality rate reaches 98% of all diagnosed cases.
- Appendiceal abscess - appears in various organs. Characterized by: general intoxication of the body; hyperthermia; an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood; stabbing pain.
- Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum caused by fluid spilled into the peritoneum. Accompanied by unpleasant cutting sensations, hyperthermia, tachycardia. Requires urgent surgical treatment. Can cause death.
The signs of appendicitis in 50% of women during puberty are similar to the symptoms that appear with inflammation of the appendages, ectopic pregnancy, cystitis, and spontaneous abortion. A timely visit to a doctor will allow appendectomies to be performed with minimal consequences for the body, eliminating the risk of complications that can lead to death.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Features of the flow
Stages of the disease:
- Catarrhal – characterized by the onset of an inflammatory process due to pathogens entering the walls of the appendix. Has a secretive nature. Body temperature may rise to 37.1 degrees. An increase in the number of leukocytes is detected in the CBC. Duration up to 12 hours.
- Phlegmonous – the middle of the disease. There is a strong piercing, cutting pain that intensifies with the slightest movement. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever appear. Duration is about 38 hours. The operation at this stage is quick, does not cause complications, and is accompanied by an easy postoperative recovery process.
- Gangrenous - indicates necrosis of the tissues of the appendix. The transition occurs after 39-40 hours from the onset of the disease, symptoms: sudden loss of sensitivity in the previously painful area of the abdomen, sudden disappearance of previously occurring symptoms.
- Perforation is the most dangerous stage of the disease. It is characterized by rupture, perforation of the walls of the appendix, release of pus into the abdominal cavity. In the absence of urgent surgical treatment and washing of internal organs, death occurs.
The duration of the pathology is 48-50 hours. Surgical intervention up to 40 hours is the least traumatic for the patient’s body.
Chronic appendicitis is accompanied by nagging pain in the right lower abdomen that persists for a long time. There are no nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. With CBC, changes in the level of red blood cells are detected. Pathology is treated conservatively. The exacerbation is eliminated surgically.
In pregnant women
Diagnosing the inflammatory process during pregnancy is quite difficult. This is largely explained by the fact that pain of various etiologies during pregnancy is most often perceived as physiological processes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman under the influence of hormones. The prevalence of this pathology in expectant mothers is low, only 2-3%. However, such cases do exist, so it is important to know how appendicitis hurts, where it is located and not try to numb the pain with painkillers, but quickly call an ambulance.
The main symptom of this pathology in pregnant patients is the “acute abdomen” syndrome. This condition is characterized by acute or paroxysmal pain, gradually shifting to the area of the right hypochondrium. After which it becomes permanent and acquires an aching character.
Diagnosis of appendicitis is especially difficult in the third trimester. This is due to the natural weakening of the peritoneal muscles, which do not allow detection of tension in the abdominal walls, characteristic of inflammation of the appendix. Also, making a diagnosis of appendicitis difficult can be caused by inaccurate determination of the location of pain, since under the pressure of the growing uterus, almost all abdominal organs in women are displaced.
Important! It is almost impossible to diagnose pathology in pregnant women on your own, so women with similar symptoms are immediately hospitalized in the inpatient department of the hospital for hardware diagnostics.