Knowledge about tumors in the stomach area will help to recognize them in a timely manner and consult a doctor for help, and, accordingly, prevent the development of irreversible processes. A stomach tumor is a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. Happens quite often.
In most cases, the pathological formation is malignant.
The tumor occurs between the ages of 40 and 45 years, predominantly in men.
Causes of stomach tumor
Predisposing factors for the development of the disease include heredity, alcohol abuse and smoking.
An advanced form of gastritis and gastric ulcer can play a fatal role.
Carcinogens in this case are the main pests.
The causes of stomach tumors are poor lifestyle and diet. These factors contribute to the destruction of the mucous membrane, which is fraught with the entry of carcinogens into the cells.
The causes of tumors are the presence of chronic stomach diseases, such as ulcers. Ulcerative lesions occur due to gastritis.
The causes of stomach diseases are infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Genetic factors also play a leading role in tumors.
The reasons may lie in the disruption of hormonal activity and the constitutional characteristics of the body.
Reasons for appearance
A tumor in the stomach (symptoms of the disease require a thorough comprehensive diagnosis) is more often diagnosed in the stronger sex. There are numerous provoking factors against which malignant or benign processes develop in the organs of the digestive system:
- chronic form of gastritis;
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- hereditary factor;
- bad habits (abuse of alcoholic beverages, tobacco products);
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- poor nutrition;
- treatment with certain medications;
- surgical treatment of the digestive system;
- Menetrier syndrome;
- harmful working conditions.
Hormonal imbalances in the human body can also trigger the development of tumor processes. People over 50 years of age are in the risk category.
Features of the clinical manifestations of stomach cancer
In 80% of cases, there are no symptoms at the initial stages of development of stomach tumors.
Seeing a doctor is most often due to the progression of other diseases that are not related to the tumor. Signs of a pathological process should be given special attention to exclude the possibility of cancer progression.
Symptoms of a tumor are very numerous and varied. Signs of the disease are associated not only with the gastrointestinal tract, but also with other internal organs. Changes may occur in the central nervous system. Possible sudden weight loss or increased susceptibility to various types of infections.
Stomach tumors tend to develop slowly. The digestive organs in this case may not show signs of pathology.
This depends on the size of the formation and the area of its localization. The extent of the stage and damage to neighboring organs (metastasis) also has a huge impact on clinical symptoms.
With a stomach tumor, one can identify common signs that are inherent in all pathological processes, without exception, that are associated with formations. The presence of characteristic local symptoms in the abdominal area should not be overlooked.
They are caused by the fact that a tumor grows into the walls, which is accompanied by compression of surrounding tissues, disruption of the evacuation of gastric contents and the functioning of other organs located nearby.
Stages of malignant pathologies
It is difficult to detect an oncological tumor at an early stage of the disease. This happens in 10% of cases. This is due to the fact that at the initial stage the malignant formation hardly manifests itself at all.
Occasionally, a person may feel heaviness in the stomach, mild nausea, and minor pain. But most people mistake these symptoms for overeating or gastrointestinal disorder.
The difficulty is that symptoms can appear periodically over several years. As long as the patient is unaware, the malignant tumor will continue to grow. With large oncology, it is easier to diagnose the disease. But education will be more difficult to treat.
A favorable situation for the patient if the diagnosis is made at an early stage. Gastric cancer progresses through 4 stages. As an additional stage, a precancerous or zero stage is distinguished. It is characterized by the presence of small pathological areas on the walls of the gastric mucosa. Such formations do not require surgical intervention and are removed endoscopically. The prognosis is favorable - 90% of cases of complete recovery.
First stage
At the first stage of oncology, malignant cells grow on the mucous membrane and also appear in nearby lymph nodes. At this stage, it is important to start treatment on time. In 70% of cases the outcome for the patient will be positive. Unfortunately, cancer is diagnosed at the first stage very rarely.
Second stage
The second stage of cancer development is characterized by damage to the muscle tissue of the stomach walls. The size of the tumor increases, it grows into the lymph nodes. It becomes more difficult to recover. In only 50% of cases the treatment should be considered successful.
Third stage
At the third stage of cancer, more pronounced symptoms appear. Therefore, it becomes easier to diagnose a tumor. However, by now the formation has already grown deeply into the muscle tissue, can spread to other organs, and is characterized by strong growth into the lymph nodes. The mortality rate at this stage, even with treatment, is 60%.
Fourth stage
Stage 4 cancer is diagnosed in almost 80% of cases when symptoms become obvious. At the fourth stage, the tumor can no longer be removed surgically. It affects almost all the walls of the organ, metastases spread to distant lymph nodes and neighboring organs. Stage 4 cancer is almost incurable. Patient survival is about 5%.
Stomach cancer
Symptoms of a tumor in the stomach
The symptom, which depends on the stage of the pathological process, can progress quickly or slowly.
In this case, as a rule, there are a number of general signs that indicate the presence of an oncological process in the body.
Such manifestations include increased fatigue and constant fatigue.
These symptoms are common to all cancers.
In order to suspect a stomach tumor, it is important to pay attention to the accompanying gastric symptoms.
For this, experts recommend using the “small sign syndrome” - the so-called complex of symptoms.
These signs include signs of gastrointestinal dysfunction.
This allows you to identify the malignant process in a timely manner and take therapeutic measures in the initial stages of progression of stomach cancer.
Such measures help prevent metastasis of the affected tumor cells to other vital organs.
Symptoms of a stomach tumor, which belong to the “small sign syndrome”, are accompanied by:
- quite pronounced discomfort in the abdomen;
- bloating;
- a sharp decrease in weight and appetite;
- increased fatigue and constant fatigue;
- drooling and nausea.
A stomach tumor can cause the patient to become apathetic. He is feeling worse. When gastric functions are impaired, a constant feeling of heaviness appears in the abdomen. This occurs due to the fact that the contents of the stomach are difficult to pass into the next digestive section.
In this case, the food stagnates, which causes putrefactive belching. A frequent companion to the pathological process is heartburn. The symptom occurs regardless of food intake and the position of the person’s body after eating. As a rule, heartburn goes away on its own and does not require additional measures.
If the cancerous tumor is localized in the initial parts of the stomach (in the cardia), then dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing) occurs.
This is due to the fact that food does not pass further through the stomach and stands in the way of new portions of food coming from the esophagus.
However, there is a high risk of developing serious complications.
In the area of the cardiac part of the stomach, near the mucous membrane itself, the vagus nerves are located.
When a tumor appears in this area, characteristic salivation appears, which is caused by constant irritation of the nerve endings.
With such signs, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the pathological condition depends on the nature of the neoplasm. As the disease progresses, symptoms intensify and benign processes degenerate.
Symptoms of a tumor in the stomach, depending on the nature of the tumor that appears, are as follows:
| Name | Symptoms |
| Benign |
|
| Malignant |
|
Vomiting blood is a symptom of a progressive tumor in the stomach.
In most cases, a gastric tumor develops without obvious clinical signs and can be detected during a preventive examination. Sometimes a tumor is detected during treatment for other diseases.
Classification of signs of stomach tumor
Signs of a stomach tumor are uncharacteristic. A number of symptoms can be identified that only help to suspect the development of a malignant process.
They are divided into two main groups:
- Nonspecific - increased body temperature, loss of appetite and sudden weight loss.
- Specific – characteristic abdominal pain, discomfort in the epigastric region (left edge of the ribs). The pain appears immediately after eating. It becomes permanent over time. Over time, the inflammatory process joins and the tumor grows into neighboring organs that are located next to the stomach.
Specific symptoms of tumors in the stomach area include nausea, which is accompanied by vomiting.
This symptom is accompanied by peptic ulcer disease and acute gastritis.
With stomach cancer, this symptom occurs due to the fact that the tumor blocks the exit from the gastric region.
Vomiting, as a rule, occurs with stagnant contents, that is, with food that was eaten 1-2 days ago.
This occurs when the tumor is located in the outlet sections of the stomach, that is, at the border with the duodenum.
In this case, stenosis occurs, which provokes the development of congestion in the area of the gastric lumen.
In the presence of tumors, vomiting may occur like coffee grounds.
In this case, loose stools with black contents are observed. This occurs in the presence of an ulcerative process, and the development of bleeding against this background.
This requires urgent treatment aimed at eliminating bleeding and removing ulcerative and tumor processes.
Tumors of the initial part of the stomach or esophagus are accompanied by such signs as difficulty passing food. This process progresses until it fails completely, which is fraught with quite sad consequences for the patient.
If there is a tumor in the stomach area, there may also be signs such as rapid satiety and a feeling of severe fullness after eating. At the same time, heartburn intensifies and belching appears.
The intensity of complaints changes quite rarely, which the patient himself can notice if treatment of the pathological process is not started on time.
Causes
A combination of factors leads to the occurrence of cancer. When DNA mutations occur in the body, the damaged cells are removed by immune cells (natural killer or NK cells). If antitumor immunity fails to remove defective cells, they become susceptible to uncontrolled division.
An initial tumor node is formed, destroying the affected organ from the inside, which then grows into nearby tissues and spreads throughout the body in the form of metastases to distant organs. The same thing happens with stomach cancer. These processes at the cellular level take a long period of time, so the asymptomatic stage of the disease can last for years.
Provoking environmental factors:
- radiation (ionizing radiation) - affects the cell nucleus with the DNA it contains, causing cell mutations
- smoking, alcohol abuse - irritate the gastric mucosa
- medications - painkillers, corticosteroid hormonal drugs, antibiotics, etc.
- products - refined white flour, sugar, refined oil, excesses in spicy, fried, fatty foods, food additives, residues of agricultural fertilizers in greenhouse vegetables and fruits, etc. - cause damage to the gastric wall with a decrease in its protective properties.
- associated diseases, that is, provoked by Helicobacter Pylori bacteria that live on the inner wall of the stomach, they come in several types, some provoke stomach ulcers and chronic gastritis. Chronic gastritis with high acidity can lead to stomach ulcers, which, in turn, can lead to malignancy.
- unfavorable environmental conditions, smoke in cities with exhaust gases, industrial waste, an abundance of harmful chemicals in everyday life (household chemicals - harmful to health, cosmetics, low-quality furniture, household appliances, toys made of toxic materials) - reduce overall immunity, contribute to the accumulation of carcinogenic substances in the body .
Internal factors:
- genetic predisposition - scientists have proven that most diseases are hereditary in nature and a predisposition to cancer too
- predisposing diseases - benign formations of the stomach (polyps, adenomas), which can transform into malignant ones, as well as deficiency of vitamin B12, folic acid, which are involved in cell reproduction and are responsible for the “correct” division of the cell nucleus without mutations
- age - after 50-60 years, the risk of developing cancer increases tenfold
- metabolic disorders - hormonal, immune, as well as disorders in the metabolism of vitamins.
Symptoms of a tumor in the stomach of serious stages
Untimely treatment of stomach tumors leads to the development of inevitable complications in the form of bleeding, perforation of the tumor and food obstruction. With advanced malignant lesions of the stomach, the tumor is palpable in the abdomen.
It increases in size. This occurs due to the presence of fluid (ascites) in the peritoneal area. There may be a characteristic enlargement of the liver, which also affects the size of the abdomen.
In this case, as a mandatory sign, there is jaundice and anemia, which is characterized by pale skin. When metastasis processes are activated, damage to nearby lymph nodes in the navel and armpits is noted. It is important to note that they only occur on the left side.
If such symptoms occur, then you must go to a doctor who will diagnose and prescribe the safest and most effective treatment.
In the primary stages of cancer, cure is still possible. If the tumor is not detected in time and metastases begin to spread to other organs, then the prognosis in this case is unfavorable.
Perforation of a stomach tumor is its breakthrough, which is accompanied by damage to the wall of the digestive organ. In this case, peritonitis is inevitable. Damage to the stomach is accompanied by very severe pain, fever and characteristic weakness.
In this case, you cannot do without professional medical help, since the situation is quite serious.
Symptoms of the disease
The danger of cancer is that at an early stage they practically do not manifest themselves. Especially formations of a benign nature. If the tumor reaches a large size, the patient may feel pain after eating, heartburn, and nausea.
Symptoms are often similar to those of other gastrointestinal diseases, so the sensations are easy to confuse.
If the gastrointestinal tract is severely damaged, vomiting mixed with blood, dizziness, and weakness may occur. As the tumor grows, the pain will intensify.
Malignant tumors are more aggressive and have a variety of symptoms.
In the early stages - loss of appetite, feeling of heaviness in the stomach. Gradually, periodic aching pains appear after eating food. Soon the patient notices a loss of taste. A person refuses to eat many foods, which leads to weight loss.
There may be difficulty swallowing food. If after eating the patient takes a horizontal position, vomiting often occurs.
Clinical signs of cancer at the last stage:
- pain becomes constant;
- the patient vomits food that was eaten a couple of days ago;
- heartburn often occurs;
- gastrointestinal upset occurs;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- Metastases spread from the diseased organ to the liver, intestines, and pancreas.
Even in the presence of pronounced symptoms, it is possible to accurately diagnose cancer only after a complete examination of the patient.
Differential diagnosis of a tumor in the stomach
Treatment of a tumor in the stomach area begins only after confirmation of the diagnosis. For this purpose, diagnostics are carried out in laboratory conditions.
All possible measures must be taken to differentiate the malignant process from other diseases with similar symptoms. Subsequent treatment depends on what tumors you are dealing with.
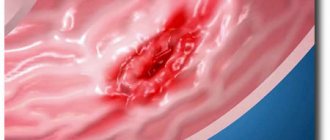
Ulcer and tumor
Stomach cancer can occur against the background of an ulcer. However, there are characteristic differences. First of all, such signs as the unevenness of the edges of the ulcer (the elevation of one and the undermining of the other) are taken into account.
Unconventional forms of ulceration, for example, amoeba-like ones, are also dangerous. Thickening of the mucous membrane and its granularity are not ignored. The bright red color of the mucous membrane, pallor, lethargy and bleeding around the ulcerative spot are alarming. The bottom of the ulcer, as a rule, has a gray color and a flat shape. It is characterized by shallow depth and granularity. The edges of the ulcer are ulcerated.
Treatment in this case is carried out after a targeted gastrobiopsy. A pinch of material is taken from the edges and bottom of the ulcer. Only after the diagnosis is made, treatment for stomach cancer is prescribed.
Polyps and cancer
Polypous tumors of the stomach are neoplasms of significant size. They resemble nodes on legs that have wide bases (up to 2 cm). The appearance of polyps resembles cauliflower.
At the apex of malignant formations, ulcers, necrosis, edema and erosions may appear. A benign tumor of this type is characterized by the presence of a small stalk, a narrow base and non-expanded mucosa.
Most gastric polyps are hyperplastic. But it should be noted that in 40% of cases they eventually turn into an adenomatous state. If polyps are present, they must be removed.
Other types of tumors
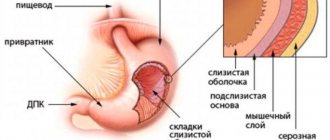
Benign stomach tumors are quite rare. They are accompanied by a characteristic symptom, which is the integrity of the mucous membrane.
Gastric peristalsis and folding in this case are also preserved. The gastric mucosa is not changed and its color is even. If the shell has a yellowish tint, then we are talking about the development of xanthoma.
Kinds
Considering the nature of pathological processes, stomach tumors are classified into benign and malignant neoplasms. In most cases (90%) it is stomach cancer.
Benign tumor
The neoplasm is characterized by moderate growth and a favorable outcome. In some situations, there remains a risk of tissue degeneration.
There are the following types of benign tumors:
| Name | Description |
| Polyps | Single and multiple growths on the surface of the gastric mucosa. In most cases, they transform into a malignant tumor. There are adenomatous, fibromatous and hyperplastic polyps. |
| Fibroma | Pathological processes affect connective tissue. |
| Lipoma | Neoplasms appear in the submucosal layer of the stomach. |
| Angioma | A benign tumor is formed by blood vessels and capillaries. |
| Neuroma | Pathological processes affect nerve tissue. |
| Gastric leiomyoma | A tumor that appears due to degeneration of the muscle tissue of the stomach. |
A benign tumor should also be treated without fail. The neoplasm will increase and put pressure on nearby tissues, causing serious problems.
Malignant tumor
Stomach cancer is treated taking into account the type of malignant process.
In medicine, the following types of tumors are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Fungiform (polypous) | The tumor affects the gastric mucosa and penetrates deep into the organ. It has a structure and clear boundaries, located on a stalk. |
| Ulcerated lump (saucer-shaped tumor) | The neoplasm is located in the lumen of the stomach. It will take a long period of time before metastases appear. |
| Ulcerative-infiltrative form of pathology | The tumor grows infantilely, without clear boundaries. |
| Diffuse cancer | Malignant processes affect the upper and lower layers of the mucous membrane and are characterized by small lesions. |
| Adenocarcinoma | A malignant tumor, which is more common and is accompanied by damage to secretory cells. |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Pathological processes affect the cells that are responsible for the production of mucus. |
| Glandular tumor | The provoking cause is the degeneration of glandular cells. |
Each type of neoplasm is accompanied by characteristic clinical symptoms. A person needs to go to the hospital when the first disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system appear. Undergo a comprehensive examination and begin treatment under the supervision of a specialist.
Macromorphology
Gastric malignant syndrome is quite common, as confirmed by statistics:
- Polypoid tumors – occur in 3-10% of cases.
- Saucer-shaped formations are observed in 10-40% of patients.
- Fibrous diffuse cancer (scirrh) - diagnosed in 25-30% of cases.
In approximately 10-15% of cases, stomach tumors have mixed symptoms, which are characteristic of a transient form of the disease.
The above forms of the disease are not complete and help patients consult a doctor in a timely manner.
This reduces the incidence of serious stages of stomach cancer and significantly increases the percentage of favorable outcomes from treatment.
Disease prognosis
How long do people with this diagnosis live? To answer this question, it is necessary to remember that timely consultation with a doctor is the key to success in the treatment of gastric cancer. The prognosis in this situation is determined by five-year survival. Depending on the stage of stomach cancer at which you are diagnosed, survival rates vary significantly.
- The first stage is the most favorable prognosis: 80 out of a hundred people survive, and 70% of patients achieve full recovery.
- The second stage has a less favorable prognosis, since only 56% of patients survive the first five years after diagnosis.
- The third stage - the prognosis is unfavorable, since 38 out of a hundred people survive, the rest die from further spread of cancer and/or its complications.
- The fourth stage of survival is significantly reduced and is achieved in only 5% of cases of gastric cancer.
In conclusion, I would like to note that at the present stage of development of medicine, the diagnosis of “malignant neoplasm” in general, and “stomach cancer” in particular, is not a death sentence. The capabilities of domestic and foreign oncology allow for early diagnosis, mass screening (in Russia this is an annual examination using FEGDS) and adequate antitumor treatment, which will not only lead to an improvement in the quality of life of a cancer patient, but can also significantly prolong it.
It is important for the patient to remember that self-diagnosis and self-medication are fraught with a threat to life and health, since only a doctor during an in-person examination will make the right decision regarding the presence or absence of a tumor lesion of the stomach.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
Survival prognosis for stomach tumors
- At the initial stages of the malignant process, the prognosis is quite favorable. Survival rates range from 80 to 90%.
- At stages 2-3 of cancer, the prognosis depends on metastasis and damage to regional lymph nodes.
- With stage 4 cancer, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable. Hope for recovery remains only with extensive surgery.
Stomach cancer is dangerous for relapses. Metastases predominantly occur in the peritoneum and liver.
Tumors grow quickly, and all cells lack nutrition. At the same time, they are separated and enter the bloodstream, thus spreading throughout the body.
Possible complications
Lack of timely therapy will lead to progression of pathological processes. The patient's condition will worsen, symptoms will intensify, and there is a high probability of serious complications, including death.
| Name | Description |
| Stomach bleeding | Damage to the vascular walls provokes blood loss, against which anemia develops. In such a situation, a person loses consciousness, weakness, nausea, and vomiting with blood occur. |
| Pyloric stenosis | The pathological condition is characterized by gastric obstruction. A person experiences belching with an unpleasant odor, nausea and weakness. After repeated vomiting of stagnant contents, the patient feels better. |
| Secondary infection | As a result of reduced immunity, the body's resistance to pathogenic bacteria decreases. |
| Tumor perforation | The pathological condition is accompanied by the appearance of a through hole in the walls of the stomach. The contents of the organ and digestive juice penetrate into the abdominal area, provoking a severe inflammatory process (peritonitis). |
| Exhaustion of the body | As a result of treatment, the patient's appetite worsens and he loses a lot of weight. An extreme degree of exhaustion (cachexia) develops. |
Stomach cancer is dangerous due to the appearance of metastases that form in the liver or abdominal cavity. Complications can arise not only as a result of the development of tumor processes, drug therapy can also be the cause. Anticancer drugs cause serious side effects. The same goes for radiation therapy.
A tumor in the stomach is a serious disease that does not always occur with pronounced symptoms. It is necessary to undergo a preventive examination to identify pathological processes at an early stage. Timely therapy increases the chances of recovery and life expectancy, preventing complications of pathological processes.
Treatment
If the doctor chooses conservative therapy, it will basically coincide with the prescriptions for chronic gastritis with reduced secretory function.
The choice of surgical method for destroying tumors that have arisen in the stomach greatly depends on the size, quantity and histological examination of the polyp itself.
- If the formation is adenomatous, there are a large number of polyps , endoscopic resection is recommended.
- If a wide-based polyp is detected , resection occurs in parts to avoid bleeding or perforation of the stomach wall.
- For multiple polyposis, subtotal resection or gastrectomy is recommended.
- Gastric resection may be prescribed in cases where the polyp is larger than 1.5 cm, is located on a wide base and has the potential to degenerate into a malignant tumor.
After surgical treatment, concomitant drug therapy is prescribed:
- medications that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid;
- antibiotics that suppress the action of pathogenic microorganisms.
This video shows how a polyp is removed using endoscopic resection:
Survival prognosis
Doctors tend to have a favorable prognosis if a patient has a benign tumor. However, after treatment or surgery, the patient must be observed by an oncologist and gastroenterologist.
In the case of oncology, the prognosis depends on the stage of development of the pathology. In 70% of cases of cancer detected in the early stages, patients are cured.
If oncology is detected in the final stages, which are characterized by the spread of metastases, then the survival rate is about 5%. Patients live no longer than 6 months.
Classification
Experts distinguish two main types of benign neoplasms affecting the stomach: epithelial and epithelial. They have certain differences.
Epithelial
This group includes polyps and adenomas. They can form singly or form groups. They do not pose a danger to the body, especially if they are small in size. But if growths are identified, surgical removal is prescribed.
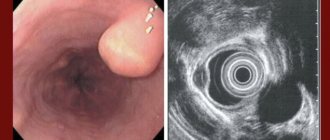
Polyps
These are round-shaped formations with a wide base. But they can attach to the surface of the organ using a thin stalk.
Gastric polyposis is considered a result of age-related changes, as it is most often found in patients over the age of 40 years. Growths are overgrown epithelial or glandular tissues that have their own vasculature.
Adenomas
They are benign growths that affect not only the stomach. Consist of glandular tissue. They are installed less frequently than polyps.
But an adenoma poses a danger to the human body, since it most often transforms into a malignant tumor.
Nonepithelial
Rarely diagnosed. Formations begin to form in the walls of the organ and can consist of various tissues.
Experts identify many different tumors of this type. The most common are fibroids, which are overgrown muscle tissue and fibroids, which are formed from connective tissue.
Neuromas, lipomas, lymphangiomas, and hemangiomas are also diagnosed. In addition, other formations are identified that have a mixed nature of occurrence. They can consist of various fabrics.
On this topic
- Digestive system
The role of hormonal contraceptives in the development of liver hemangioma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2021
But they are all distinguished by smooth and clear edges, a smooth surface, and a round shape. They can reach large sizes, causing not only discomfort, but also painful sensations of varying intensity. Nonepithelial tumors are detected more often in women.
Non-epithelial benign tumors of the stomach most often degenerate into malignant tumors. That is why, when detected, they require immediate removal.
Diagnostics
It is often difficult to diagnose a benign stomach tumor based on complaints alone, so additional research methods should be used.
Physical examination data are uninformative:
- the appearance of the patients is not changed, the skin and mucous membranes are of normal color;
- when palpating the abdomen, slight pain in the projection of the stomach may be observed, but it is more likely to be associated with a violation of the diet than with a benign tumor.
The most important in the diagnosis of most benign tumors are instrumental diagnostic methods, namely:
- plain radiography - this method allows you to suspect a neoplasm due to the fact that deformation of the contours of the stomach is revealed, as well as displacement of organs located in the neighborhood. In this case, a preliminary diagnosis is made, which must be confirmed using other, more targeted diagnostic methods, but it is thanks to plain radiography that most benign stomach tumors are detected;
- X-ray with contrast – it is informative if the tumor grows into the stomach cavity or grows into the gastric wall with protrusion into the cavity. As evidence of the presence of the process, filling defects are detected (their contours correspond to the contours of the tumor);
fibrogastroscopy (FGS) is informative in the same cases as radiography with contrast. During it, a biopsy is performed - a fragment of the gastric wall is taken, which will be examined using a microscope. FGS is a fairly accurate method: if the endoscopist is experienced, then in 80-95% of cases it is during FGS that the correct diagnosis is made;- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (ultrasound) - with its help, the diagnosis is clarified, and also preliminary differential diagnosis is carried out between different types of tumors;
- computed tomography (CT) - copes with the same tasks as ultrasound, but with better quality;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - has the same capabilities as CT;
- laparoscopy - during it gastrotumors that are located closer to the outer surface of the organ may be accidentally discovered.
Prognosis and prevention
After surgery, it is necessary to get rid of bad habits.
After following doctor's orders or after surgery, gastric leiomyoma usually has a favorable prognosis for recovery. This also depends on early diagnosis and the correct method of tumor removal.
There are no specific methods for preventing this type of disease. Since leiomyoma often develops asymptomatically, the best option for prevention is regular visits to specialists. Methods for preventing gastric cancer include a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and giving up bad habits.
Treatment methods for gastric leiomyoma
When prescribing a treatment method, the size of the tumor and the general condition of the patient play an important role. If the submucosal formation is up to 3 cm, in this case gastroendoscopy is performed. Local removal of the tumor will preserve healthy gastric tissue. Abdominal surgery is used only for large tumors. In the postoperative period, anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics are prescribed. Medicines that reduce hydrochloric acid levels are also prescribed. In this case, the submucosa recovers much faster.
Prevention
The basis of preventive measures for benign tumors of the stomach is a systematic visit to a gastroenterologist and undergoing the examinations prescribed by him. It is necessary to diagnose and treat chronic diseases of the digestive system in a timely manner. A balanced, balanced diet plays a significant role in the prevention of stomach tumors. It is also important to adhere to the canons of a healthy lifestyle, maintain adequate functioning of the immune system, eliminate unfavorable environmental factors, etc.
Benign tumors of the stomach, as a rule, do not threaten the patient’s life, but they require a highly qualified doctor. Our clinic has various methods that allow us to provide adequate treatment even in the most difficult cases.