In the practice of a gastroenterologist, patients often complain of pain in the right hypochondrium after eating. The condition is unclear for people with a healthy stomach. They believe that pain under the ribs is, generally speaking, not related to digestion. The erroneous opinion is refuted by examination.
Of course, possible causes could be diseases of the ribs, herpes zoster (herpes zoster), diseases of the lower thoracic vertebrae with radicular syndrome, and neuralgia. These reasons are definitely not related to food and do not depend on the time of eating. There are many diseases of the organs located in the hypochondrium on the right, which respond to the quality and diet.
For which organs of the right hypochondrium is proper nutrition important?
Directly in the subcostal zone are the right lobe of the liver, the gallbladder with the excretory tract, and the transverse bend of the colon. The liver produces bile and transports it to the gallbladder for storage. The quantity and quality of bile depends on the incoming “order” from the stomach and is determined by the composition of the food and drinks taken.
Overload with fatty and fried meat dishes, alcohol, and spicy seasonings causes increased functioning. Sometimes, even with a single overeating, pain in the right hypochondrium after eating indicates a breakdown in synthesis, the inability to produce a sufficient amount for splitting. With a regular habit of eating only meat and spicy dishes, such a reaction is inevitable.
The liver works around the clock, getting rid of harmful toxic substances with its enzymes, including trying to convert ingested alcohol and carcinogenic substances into a non-toxic form. It loses its functions when the cells become inflamed due to hepatitis, fatty degeneration, or are replaced by scar tissue. Areas of cirrhosis are formed that are unable to work.
Lack of vitamins in food leads to disruption of the synthesis of liver enzyme systems. And the lack of proper carbohydrate support due to starvation diets causes loss of glycogen stores, which are forced to break down into glucose to produce energy.
Addiction to spicy foods contributes to impaired motility of the muscular wall of the bladder and tracts. A spastic contraction or stagnation of bile is caused. This explains why pain associated with eating occurs.
Particular importance is attached to the concentration of salts in the composition of bile. The influence of food products on precipitation with subsequent gluing and formation of stones has been proven.
Delayed bile secretion is the cause of inflammation and the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into an organ lacking local immunity. Thus, cholecystitis is formed.
It is impossible not to note the role of nearby organs (head of the pancreas, duodenal bulb), which during inflammation, ulcerative process, tumors radiate to the right hypochondrium
Preventive measures and prognosis
To prevent pain in the right side under the ribs, there are no specific preventive measures. However, the likelihood of developing complex pathological conditions can be reduced by following a number of simple measures. The main preventive measures are:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- healthy and balanced diet;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the doctor;
- avoiding any bruises, wounds, injuries;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- early identification and rapid elimination of provoking pathological factors.
In addition, you must periodically undergo a full laboratory and instrumental examination in the hospital, which is accompanied by mandatory visits to all specialists.
The prognosis for the course of the pain syndrome is quite favorable, therefore, it usually responds to therapeutic methods without problems. However, it is worth remembering that treatment will not be complete without eliminating provoking factors, both diseases and physiological causes.
But it must be remembered that the lack of comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease can lead to various kinds of complications, which do not even exclude the possibility of death.
When pain appears in the right side after eating, a person needs to think about his health, especially if it recurs regularly. This pathological condition may indicate the presence of quite serious diseases.
In most cases, pain in the right side indicates a malfunction of the digestive tract.
Causes of pain in the right hypochondrium after eating
Without additional diagnostics, diseases of neighboring organs are difficult to distinguish from local problems. Let's consider the options for the causes of pain in the hypochondrium on the right according to the characteristic symptoms.
Pain with cholecystitis
At the onset of the disease, a functional failure of bile release occurs. There may be an increase or decrease in motor skills. Then the gallbladder gets infected from the liver due to hepatitis, pancreas, and intestines.
Pathogenic pathogens are delivered by lymph or with blood from the tonsils, maxillary cavity, carious teeth, organs of the urinary system, inflamed appendages in women, and the prostate in men with chronic inflammation. A reaction to the introduction of worms and lamblia is possible.
With calculous (stone) cholecystitis, bile stagnation is important. If it is not, then additional factors come into play. Among the provocateurs of gallbladder inflammation are the habit of fatty foods, consumption of alcohol, fried or spicy snacks, and poor physical activity.
Pain in the right hypochondrium in the front appears two hours after eating and can be very intense cramping (in the acute form of the disease) with nausea, vomiting bile, and high fever. Irradiation is observed in the right scapula, shoulder, collarbone, and lower back.
In a chronic course, such signs appear only during exacerbations. They are associated with poor diet and stress.
In the interictal period, the pain is dull, nagging in nature (can be replaced by a feeling of heaviness after eating). A person complains of constant bitterness in the mouth, nausea, and loss of appetite. Often the pain moves from the right hypochondrium to the solar plexus and is felt in the pit of the stomach and closer to the navel.
Calculous cholecystitis is accompanied by yellowing of the skin and sclera after an attack of pain. If left untreated, the inflamed wall suppurates and cholecystitis turns into a phlegmonous and gangrenous form. The pain becomes dull, high fever and chills remain, and weakness increases. Necrosis of the bladder tissue leads to the disappearance of pain against the background of a severe general condition.
Pain due to cholangitis
The entry of opportunistic intestinal flora into the bile ducts causes inflammation (cholangitis). It is almost impossible to distinguish it from cholecystitis, since the infection quickly spreads to the gallbladder.
Spasmodic pain (hepatic colic) is typical after eating fatty and fried foods. Inflammation causes blockage of the bile outlet and stagnation in the bladder. Patients develop jaundice and itchy skin against a background of elevated body temperature. Long-term course of cholecystitis and cholangitis leads to biliary cirrhosis of the liver and renal and hepatic failure.
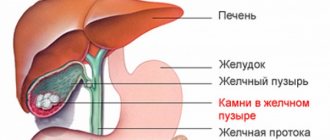
Pain from a gallstone
Cholelithiasis is associated with cholecystitis: inflammation creates conditions for the formation of stones in the bladder and ducts.
Stones differ in size, surface nature, and are able to move
An attack of pain in the right hypochondrium appears after fatty foods and alcohol. The pain is acute, very intense. Irradiates to the right side, scapula, shoulder, collarbone, and epigastric zone. At the same time, the patient shudders and vomits bitterness. The attack lasts several minutes or hours. This leaves a strong general weakness, aching pain in the gallbladder area.
Liver pain after eating
Pain in the right hypochondrium, depending on liver disease, is provoked by fatty foods and fried foods, drinking alcohol-containing drinks (including beer), carbonated water, and spicy seasonings.
Symptoms of liver problems
Hepatitis is a disease of inflammatory nature, toxic and autoimmune lesions. Viral hepatitis is the most common. The latent latent stage of the disease is characteristic, in which the patient notes:
- temporary nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- intolerance to the smell of food.
At the clinical stage, dull pain appears in the hypochondrium on the right in response to swelling and stretching of the liver capsule. Violation of the outflow of bile causes its components to enter the blood. As a result, yellowness of the skin, sclera, mucous membranes, itching of the skin, dark urine and grayish feces, and unstable stools appear. The temperature is not high, but weakness and headache are pronounced.
In case of fatty liver degeneration, which occurs as a result of chronic alcoholism or prolonged intoxication, hepatocytes lose fat and die. Gradually, the liver is switched off from digestion. There is a dull pain after eating and outside of it, pain on palpation of the liver, enlargement of the organ, and increased fatigue.
The next stage in the development of fatty degeneration is chronic hepatitis and the transition to cirrhosis.
Pain due to peptic ulcer
Pain in the hypochondrium on the right can be caused by an ulcer localized in the area of the duodenal bulb. The preceding disease is often bulbitis - inflammation of this area.
Ulcers can vary in size, depth, and nature of the edges
Myocardial infarction of gastralgic form
Usually, myocardial infarction is diagnosed quite easily - the patient complains of shortness of breath and pressing pain under the heart. But in the case of the gastralgic form of this pathological condition, there will be slightly different symptoms:
- pain in the left hypochondrium;
- nausea and uncontrollable vomiting;
- persistent hiccups;
- stool disorders.
Two characteristic features will help differentiate myocardial infarction of the gastralgic form from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- shortness of breath on inspiration;
- cyanosis and puffiness of the face.
Please note: after the administration of drugs with an analgesic effect, the patient’s condition normalizes to the classic symptoms of myocardial infarction.
Doctors distinguish between pain under the ribs and from the back - it occurs with renal colic (movement of a stone) and retroperitoneal hematoma. These two conditions are characterized by strict localization of the pain syndrome and the absence of irradiation. In this case, the patient will complain of general weakness, increased sweating, and lack of appetite.
All of the above pathological conditions require immediate hospitalization of the patient and the provision of professional medical care. Otherwise, the risk of death increases to 99%.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the doctor checks the tongue, the color of the sclera, and the condition of the lymph nodes. Palpation of the abdomen allows you to identify the most painful areas, enlarged liver, dense or soft edge, lumpy surface with cirrhosis, enlarged gallbladder.
Laboratory tests include:
- general and biochemical tests - confirm the inflammatory process, the phase of the disease, the degree of dysfunction, and the composition of enzymes allows us to identify the role of the pancreas and liver;
- for viral hepatitis, immunological tests are performed to identify the specific type of virus;
- glucose and protein are examined in urine. bilirubin, diastase;
- a stool analysis is checked for helminthic infestation and Giardia;
- the contents of the duodenum are obtained by probing, the composition of bile is examined, and elements of inflammation in cholecystitis are identified;
- Ultrasound examination is a common technique that allows you to determine the size of organs, the presence of stones in the bladder and passages, and identify irregularities in shape due to cicatricial changes.
If necessary, contrast radiography of the gallbladder and fluoroscopy of the stomach and duodenum are used. The fibrogastroscopic method allows you to examine the lower parts of the stomach and duodenal bulb and establish the localization of the ulcer.
Causes of pain
In medical practice, it is customary to classify types of pain in the side by type of care: emergency pain, that is, requiring immediate anesthesia and medical intervention, and therapeutic pain, that is, when the patient needs long-term treatment.
The second type of pain is usually chronic, there is no threat to life, and there is no urgency for drastic medical measures.
In case of urgent pain, the level of threat to the patient's life sharply increases to the maximum and the need for emergency medical care arises.
So, the causes of emergency type of pain on the right can arise against the background of acute forms of diseases such as:
- Pancreatitis;
- Duodenitis;
- Cholecystitis (with or without stones in the cavity);
- Biliary dyskinesia;
- Cholangitis;
- Bulbit;
- Gastritis.
All these same diseases, but in a chronic form, will cause pain on the right after eating a therapeutic meal.
Also, any pathological process in an organ such as the liver, pancreas, gallbladder and stomach can cause right-sided pain in the period after ingestion, in the hypochondrium.
Treatment
A treatment plan for each disease is drawn up by a doctor after a general examination. It is impossible to choose one healing remedy for pain in the right hypochondrium. The patient will require serious efforts to comply with the regimen and diet.
Gastroenterologists recommend:
- stop heavy physical activity, just walk, do gymnastics in the morning, you can do yoga, Pilates, go to the pool;
- If you are overweight, arrange fasting days;
- learn to manage the condition after anxiety or take light herbal sedatives;
- Pay very close attention to the contraindications indicated in the instructions if treatment with different drugs is necessary.
The diet will have to be maintained throughout your life. It is necessary to exclude from consumed products:
- alcoholic drinks regardless of strength, carbonated water, strong tea and coffee, all fatty meat products, sour cream and mayonnaise, fatty cottage cheese;
- canned food;
- fried and smoked dishes from meat, fish, vegetables;
- fatty confectionery products with cream;
- legumes, fresh and sauerkraut, radish;
- chocolate, candy.
Cottage cheese is necessary in the diet, but in low-fat form
Use in food:
- chicken, turkey, lean beef;
- soups and broths should not be rich;
- milk and vegetable soups;
- porridge with limited butter;
- pasta;
- boiled or stewed potatoes with vegetables;
- kefir and low-fat cottage cheese;
- vegetable oils;
- fruits.
You should eat often, in small portions. Avoid long breaks, dry snacks, and overeating.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is pain or discomfort in the side, it is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist or therapist. In the future, you may need to consult doctors of related specialties: surgeon, cardiologist, osteopath.
Initially, you should visit a therapist. A general practitioner will conduct an examination, question you, and prescribe an examination. Based on the diagnostic results and established pathology, it will become clear who will treat the patient:
- If the deterioration in health is caused by problems with the intestines, gall bladder or liver, a gastroenterologist deals with the therapy.
- When pain is caused by neuralgia, it is advisable to contact a neurologist.
- If right-sided discomfort is caused by cholelithiasis, appendicitis, pancreatitis, the patient is treated by a surgeon.
- If pain is associated with dysfunction of the right lung, therapy is prepared and supervised by a pulmonologist.
Pain in the right side of the body that occurs in pregnant women suggests an unscheduled visit to the observing gynecologist. If it is impossible to visit a gastroenterologist, but it is definitely established that the source of pain is the gastrointestinal tract, treatment is carried out by a therapist.