Increased gas formation is not such a pleasant phenomenon that every person has encountered. It causes not only discomfort and abdominal pain, but also a feeling of shame in adults and children, especially the fairer sex. Flatulence, which impairs the quality of life, can act as a common digestive disorder, and also indicate a number of diseases of the stomach and pancreas, intestines and liver. In this article we will talk about the causes of increased gas formation in women and how to treat it.
Increased gas production - normal or pathological?
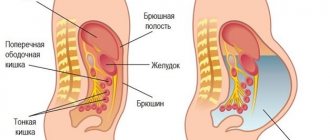
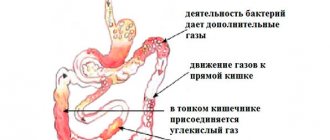
Increased gas formation, also known as flatulence, is a common phenomenon in men and women, causing a lot of inconvenience. The formation of gases in the intestines is considered a normal physiological process. Most of the gases enter the digestive tract along with ingested food (about 70%), and the remaining 30% are produced by bacteria. They may have a strong odor or no odor at all.
Gases in the intestines are a mixture of oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and methane. The presence of about 200 ml of gas in the intestines is considered normal. Every day, during the act of defecation and outside it, approximately 1 liter of gases is removed from the body, some of them are absorbed into the blood. The presence of certain pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and poor nutrition lead to the formation of 2-3 liters of gas in the stomach.
Severe gas formation in the intestines: causes and treatment
In women, increased gas production may be present constantly or appear on certain days of the month. The reasons for this phenomenon are varied - from PMS to poor nutrition and stomach diseases.
Increased gas formation - normal and pathological
Flatulence
- this is the name given to severe gas formation in children and adults - a very common phenomenon: it regularly causes trouble for every tenth inhabitant of the planet.
In general, the production of gases in the intestines is a natural physiological process. A significant part of them (up to 70%) appears due to the ingestion of air with food; a certain amount is produced by bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract.
Intestinal gases are a mixture of oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, nitrogen and methane.
Normally, a person constantly has about 200 ml of gases
. Every day, during and outside of bowel movements, the body excretes about a liter of gases, and a little more is absorbed into the blood. Various diseases and dietary errors lead to the accumulation of up to 2-3 liters of gas in the stomach.
The main forms of flatulence in women are presented in the table.
| Form of increased gas formation | Description |
| Nutritional | Associated with the abuse of certain foods, for the digestion of which the body produces more gases |
| Digestive | Caused by impaired digestion and absorption of food |
| Dysbiotic | Depends on poor quality of intestinal microflora |
| Mechanical | Occurs due to mechanical obstructions in the gastrointestinal tract, constipation |
| Dynamic | The reasons lie in intestinal motility disorders |
| Circulatory | Available if the process of gas production and absorption is disrupted |
| High-rise | Appears when atmospheric pressure decreases |
If there is severe gas formation in the intestines, it is important to clarify the causes and treatment as quickly as possible.
Poor nutrition and gastrointestinal pathologies are the causes of flatulence
All factors that provoke increased gas formation and bloating in women can be divided into temporary, periodically affecting, and permanent (most often these are chronic gastrointestinal diseases). Since with each swallow 2-3 ml of air passes into the esophagus, the following reasons can increase the volume of gases:
- talking while eating;
- drinking drinks through a straw;
- chewing gum;
- increased salivation;
- dry mouth;
- smoking;
- drinking soda.
If a woman eats certain foods, they also provoke excessive gas formation. These include those containing carbohydrates
(lactose, fructose, etc.). Most often, the stomach becomes bloated after consuming legumes, cabbage, apples, kvass, beer, black bread, pumpkin, as well as powdered milk, ice cream, juices, and dietary products with sorbitol.
Of the cereals, only rice does not cause such problems, and all other grains contain a lot of starch and dietary fiber, and therefore contribute to the appearance of gases.
Very often, the causes and treatment of increased gas formation in women relate to chronic diseases of the digestive tract.
They may depend on disturbances in the production of enzymes or bile, disruption of motor function and intestinal microbiocenosis. In most cases, gas formation in women is caused by dysbacteriosis or constipation.
Other possible causes of pathology:
- anomalies in the structure of the DCT;
- condition after operations;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- polyps and other gastrointestinal tumors;
- enzyme deficiency;
- cholecystitis;
- enteritis
- colitis;
- pancreatitis;
- liver diseases;
- intestinal atony;
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer;
- diverticulitis.
If a woman has parasites
, they create a mechanical obstacle to the passage of gases. This leads to intestinal obstruction, accumulation of air in the intestines and the development of flatulence. After injuries or operations, intestinal paresis (partial paralysis) is possible, changing motility and leading to unpleasant phenomena.
Other causes of flatulence in women
Diseases of the nervous system can also affect the formation of excess gases. These include brain diseases, neoplasms, spinal cord injuries and even advanced stages of lumbar osteochondrosis.
In women, severe or prolonged stress, mental trauma or depression can also provoke painful symptoms.
Vascular diseases (vasculitis, thrombosis, peritoneal varicose veins) are another possible cause of increased gas formation.
Oddly enough, gynecological problems also often provoke flatulence in women.
Bloating and abdominal pain accompany
thrush, endometriosis, fibroids, and ovarian cysts
. During menopause, due to hormonal changes, the stomach swells in the evening and at night.
With PMS (premenstrual syndrome), as estrogen levels increase, gas formation also becomes higher.
Flatulence and pregnancy
Typically, such problems begin to torment a woman in the second or third trimester. The uterus, which has grown in size, puts a lot of pressure on the intestines, so gas separation (flatulence) increases.
Also, during pregnancy, hormonal levels change dramatically, which causes a decrease in intestinal motility. Gases are not pushed “out”, they accumulate in the stomach and bloat it. Flatulence and constipation are a frequent companion of pregnancy.
In the first trimester, activation of progesterone production causes rotting and fermentation in the intestines, bacteria begin to produce a larger volume of gases.
Seeing a doctor if you experience flatulence is mandatory for pregnant women.
Despite the natural causes of this problem, exacerbation of chronic diseases ( gastritis, colitis)
), which increase gas formation. It is necessary to prescribe suitable treatment that would not harm the baby.
In addition, an overly swollen abdomen in the very early stages of pregnancy often occurs due to ectopic attachment of the fetus, so timely diagnosis is very important!
Symptoms of increased gas formation
With flatulence, gases can accumulate in the stomach and are difficult to pass away, so the person suffers from constant pain and belching. The second variant of the pathology is increased release of gases, when there is almost no pain, but there is seething and transfusion in the abdomen.
The signs by which one can certainly determine the presence of flatulence are as follows:
- elevation of the abdomen above the chest, the abdomen becomes round, the abdominal wall protrudes (clearly noticeable in thin ladies);
- feeling of abdominal distension, severe discomfort, especially while sitting;
- increased gas production (gases may have an unpleasant odor or be odorless);
- loud sounds in the stomach - rumbling;
- aching pain, periodically alternating with cramping, especially when retaining gases inside;
- decreased appetite, constipation or diarrhea, nausea, belching.
To identify the problem, you need to contact a gastroenterologist: he will prescribe a general blood test, biochemistry, ultrasound of internal organs, coprogram, stool analysis for dysbiosis, and, if necessary, FGS and colonoscopy.
What to do if you have flatulence?
Nutrition plays an important role in eliminating the problem in women. It is necessary to eat in small portions and regularly, at regular intervals. If the portion is large, it provokes rotting of food in the intestines. Snacks, especially junk food and fast food, are prohibited!
You will have to give up foods that cause flatulence. For a while, it is better to reduce the amount of milk, cream, bananas, apples, pears, grapes and dried fruits, as well as spicy vegetables with coarse fiber. There is no need to eat fried foods, fatty foods, spices, excess salt, and do not drink alcohol or soda.
If there is gas in the stomach and farting, what else should you do? Here are important tips:
- chew food well, do not rush;
- do not eat on the go, do not watch TV, do not talk during meals;
- refuse cold and hot food;
- stew, boil, steam food;
- eat sweets and fruits 2 hours after the main meal;
- drink more clean water.
To get rid of the problem you will have to quit smoking. Also, do not overuse chewing gum, so as not to increase the volume of swallowed air.
Drug treatment of a delicate problem
If there are no serious diseases, a woman can easily improve her digestion using the methods described above. But often such measures are not enough, so after diagnosis the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment.
It will depend entirely on the diagnosis. For example, for gastritis, drugs are recommended to suppress the production of hydrochloric acid
, antibiotics (in the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria).
For helminthiasis, special anthelmintic drugs are prescribed.
Therapy for excess gas formation may include the following:
- sorbents for abdominal upset - activated carbon, Polysorb, Smecta;
- carminatives for removing gases from the intestines - Espumisan, Sab simplex;
- enzymes to improve the functioning of the pancreas - Pancreatin, Mezim, Panzinorm;
- medications for irritable bowel syndrome and spastic colitis - Duspatalin, Sparex;
- drugs for reflux esophagitis - Cerucal, Motilium, antacids - Phospholugel, Maalox;
- probiotics to combat dysbiosis - Normobakt, Linex;
- remedies for constipation - Duphalac, Normaze.
If the pain from flatulence is severe, you can take painkillers, antispasmodics - No-shpu, Revalgin.
Types of flatulence in women
The following forms of flatulence are distinguished:
- nutritional – its appearance is associated with the consumption of food rich in fiber, cellulose, pectin, during the digestion of which a large amount of gases is produced;
- mechanical – observed when there are adhesions or neoplasms in the intestines that impede the movement of gases;
- dynamic – associated with impaired intestinal motility;
- dysbiotic – occurs when there is an imbalance in the intestinal microflora, accompanied by diarrhea or constipation;
- circulatory – caused by impaired blood circulation in the gastrointestinal tract or in the abdominal area;
- psychogenic – manifests itself against the background of stress, neuroses, psychosomatic disorders;
- high altitude – observed when atmospheric pressure decreases.
Errors in nutrition and other reasons
The causes of intestinal flatulence in women are associated with foods that are often eaten in large quantities:
- dairy (in any form) with a lack of lactase in the body - an enzyme that takes part in the breakdown of lactose - milk sugar;
- products that cause gas formation - legumes, fresh and sauerkraut, apples, carbonated drinks;
- products that trigger fermentation - black bread, kvass, beer, kombucha.
Causes of flatulence in women, which also need to be remembered:
- taking certain medications that have a depressing effect on the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice and indirectly enhance the processes of fermentation and gas formation;
- impaired absorption in the intestine due to various enzymopathies (not only hypolactasia - lactase deficiency).
Causes of flatulence in women
High gas formation can be caused by a number of certain factors. This includes a woman’s unbalanced diet and hormonal imbalance. Excessive gas production can also act as the body's response to allergens.
The main cause of bloating and gas formation is decreased intestinal motility. Moving slowly through the digestive tract, food stagnates and the fermentation process begins.
Factors that provoke flatulence in women can be divided into temporary and permanent (usually gastrointestinal diseases).
The volume of gases in the intestines may increase for the following reasons:
- talking while eating;
- chewing gum;
- drinking drinks through a straw (especially soda);
- smoking;
- excessive salivation;
- dry mouth.
Eating certain foods also causes increased gas production. These include foods high in carbohydrates. Most often, bloating is observed after consuming food - legumes, dairy products (whole milk, ice cream), black bread, cabbage, apples, pumpkin, as well as beer, kvass and various juices.
Consuming grains rich in starch and coarse fibers also contributes to the accumulation of gases in the intestines. The only exception is rice, which does not cause such problems.
Often the reasons for increased gas formation lie in the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. These include impaired production of digestive enzymes, bile, impaired intestinal motility and microbiocenosis. Gas formation in women may be accompanied by constipation or dysbacteriosis.
Increased gas formation can be caused by pathologies such as:
- polyps and tumors in the gastrointestinal tract;
- colitis;
- enteritis;
- cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- gastritis;
- stomach or intestinal ulcer;
- intestinal atony;
- liver diseases;
- lack of enzymes;
- diverticulitis;
- postoperative condition.
The presence of parasites in a woman’s digestive tract also prevents the elimination of gases. As a result, intestinal obstruction, air accumulation, and flatulence develop. Intestinal paresis (partial paralysis) after surgery or injury can also affect motor skills.
Folk remedies
Recipes from witch doctors and healers will not help cure the underlying disease. It is important to use the products in complex therapy along with traditional drugs. It is also recommended to consult a doctor to choose the most effective prescription and prevent complications.
Dill
Abdominal bloating (the causes in women will be determined by a doctor after a complete diagnosis) can be removed with dill. The seeds of the plant reduce cramps, slow down the fermentation process, eliminate gases and improve appetite.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Tincture | Pour 1 tbsp. dill seeds with boiling water (0.5 l), leave for 3 hours. | It is recommended to take the resulting product 150 g 3 times a day. per day before meals. |
| Decoction | Mix 1 tbsp. dill seeds with water (200 ml), put on fire, bring to a boil and heat for 20 minutes. Cool, strain and take according to the scheme. | The medicine is drunk 200 ml 2 times a day. a day before meals. |
Thyme together with dill helps reduce bloating and eliminate increased gas formation, even with chronic diseases. It is enough to add greens to salads, side dishes and first courses.
Garlic
Garlic has an unpleasant odor, but it helps to cope with various disorders of the digestive system. To prepare the remedy, it is recommended to use the raw product.
Medicinal properties of garlic
| Recipe | Application |
| Place water (1 tbsp) on fire. Add garlic (3-4 cloves), black peppercorns (6-7 pieces) and cumin seeds (0.5 tsp). Bring the resulting mixture to a boil, heat for 3-5 minutes. Cool, strain and take according to the scheme. | If you have bloating, it is recommended to drink garlic broth several times a day. |
To reduce chronic flatulence, it is recommended to eat 1 head of garlic every morning before breakfast, washing it down with cold water. The full course of therapy includes 10 appointments.
Potato
Potatoes have a positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract. The juice of the product restores the protective forces of the mucous membrane in the stomach and intestines, and also removes toxins from the body.
| Recipe | Application |
| Grate 2 medium sized potatoes. Place the resulting mass on cheesecloth and squeeze out the juice. | It is recommended to drink the finished juice every day, 1 r., preferably in the morning. After taking the product, you need to rest for some time. The course of therapy lasts 10 days. After this, you can take a break for 2 days and continue treatment. |
If there is increased acidity in the stomach, it is recommended to drink 100 ml of potato juice. It is useful for gastritis, heartburn and belching.
Dandelion
Dandelion decoction helps not only eliminate flatulence, but also spasms of the abdominal muscles. The plant has an anti-inflammatory effect. Recipes with its participation are also recommended for use in neurological disorders.
| Recipe | Application |
| Pour the root of the plant (2 tbsp) with water (250 ml). Mix everything well and leave for a day, wrapped in warm material. Strain the resulting medicine and take it according to the schedule. | The product is drunk 5 rubles. per day 35-50 ml. |
| Mix dandelion, thyme, chamomile, lemon balm, cumin and valerian in equal proportions. Pour boiling water (0.5 l) over all components. Leave for 30 minutes in a dark place. | It is recommended to take the finished product 0.5 tbsp. 4 rub. per day. |
Decoctions of medicinal herbs help to quickly cope with bloating, but in individual situations an allergic reaction may occur. Therefore, it is important to discuss treatment with your doctor to prevent negative consequences.
Other factors that cause gas in women
Excessive production of gases in the intestines can be affected by diseases of the nervous system. These include brain diseases, tumors, spinal cord injuries and a complicated form of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. Prolonged stress in women, depression and mental trauma can cause digestive disorders.
Another reason for intense gas formation is vascular diseases, such as thrombosis, abdominal varicose veins, and vasculitis.
Often the cause of flatulence is gynecological problems. Bloating and pain are often accompanied by thrush, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and ovarian cysts.
Pregnancy. In pregnant women, increased gas formation is associated with the active production of progesterone. The hormone progesterone helps relax the smooth muscles of the uterus and reduce the risk of miscarriage if it contracts accidentally. A woman’s intestines are also affected by progesterone. This, in turn, prevents the normal movement of digested food; it is slowly absorbed. Stale food begins to ferment and as a result, flatulence occurs.
In addition, increased gas formation during pregnancy is promoted by:
- low physical activity;
- pressure of the growing fetus on the intestines, leading to constipation or diarrhea;
- consumption of foods that cause flatulence in case of existing digestive problems;
- taking medications containing iron, as well as medications for high blood pressure.
After childbirth, progesterone production decreases and the woman forgets about flatulence, provided she follows a diet and leads an active lifestyle.
Menopause and PMS can also provoke increased gas formation. Abdominal discomfort, belching and passing gas occur more often at night and early in the morning.
Increased gas formation in women during menopause occurs for the following reasons:
- hormonal changes in the body;
- weight gain and increase in stomach size;
- insufficient intestinal permeability;
- unhealthy diet, overeating;
- sudden mood changes.
Before menstruation during ovulation, many women also suffer from flatulence. Gases are released mainly in the evening and at night. The cause of its occurrence is again hormonal changes that affect the functioning of smooth muscles. During menstruation, the release of gases from the rectum weakens.
How to treat increased gas formation
Medicines: what to take for flatulence
Drugs that suppress gas formation and improve digestion are sold in pharmacies without a prescription. These include:
- activated carbon is a natural, inexpensive sorbent that binds and removes excess gases from the intestines;
- Mezim Forte is an enzymatic agent that normalizes the digestive tract and improves food absorption;
- Pancreatin is a medicine based on digestive enzymes of the pancreas (animals), available in the form of tablets, capsules, dragees;
- Espumisan capsules and drops contain simethicone, a substance that binds and removes gas bubbles, preventing the formation of new ones. The medicine has a narrowly targeted effect and is used directly to eliminate unpleasant symptoms;
- in case of food or other poisoning, polysorb, enteros gel, smecta will help reduce gas formation and remove toxins;
- Linex and other probiotics normalize the composition of the intestinal microflora, suppress the activity of pathogenic bacteria, reducing the symptoms of dysbiosis;
- if excessive gas formation leads to intestinal spasms, severe pain and discomfort, no-spa or another antispasmodic drug will help.
How to get rid of flatulence with proper nutrition
A diet with increased gas formation should exclude “dangerous” foods:
- prunes, figs;
- cabbage;
- radish, radish, turnip;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- apples, pears, grapes;
- dairy products;
- carbonated drinks
Symptoms of flatulence in women
How to understand that a woman needs treatment for increased gas formation? First, you should find out what symptoms accompany gas formation. Symptoms can vary.
The most common are:
- bloating, accompanied by a feeling of fullness and pain. A woman’s belly becomes dense and increases in volume, which makes it difficult to wear tight-fitting clothes;
- frequent passing of gas with an unpleasant odor;
- nausea. This symptom is observed in diseases of the stomach and duodenum;
- moderate to severe abdominal pain. After the gases are eliminated, the pain may decrease for a short time. Depending on which part of the intestinal tract intense gas formation is observed, the localization of pain may also vary. Most often, pain is observed in the lower abdomen, and this can be easily confused with gynecological diseases. Pain in the upper abdomen occurs with gastritis and diseases of the duodenum, which are also accompanied by excessive gas formation;
- delay in the emission of gases at the moment when there is an urge, but problems arise with this;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach, colic;
- rumbling, indicating the process of fermentation in the intestines;
- diarrhea as a result of fermentation and inflammatory processes in the intestines.
Medicines for gas formation
Abdominal bloating (causes in women are provoked by physiological or pathological factors) is often treated by a person with medications that quickly eliminate discomfort and associated symptoms. There are medications for flatulence in every medicine cabinet, but it is recommended to take them strictly according to the instructions or following the doctor’s prescription.
Motilium
The medicine not only affects intestinal motility, but also breaks up large gas bubbles.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Domperidone |
|
| The adult dosage is 1 tablet. 3-4 r. per day. |
The discomfort caused by bloating and other associated symptoms (nausea, belching, heaviness) are reduced.
White coal
The medicine acts faster compared to activated carbon. Due to its powerful absorption capabilities, it easily eliminates increased gas formation and bloating. White charcoal also restores intestinal motility.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Silica Microcrystalline cellulose |
|
| It is recommended to take the medicine in 3-4 tablets. 3-4 r. a day before meals 1 hour. |
The medicine reduces the physiological load on the liver and kidneys, restores metabolism, and increases the body's defenses.
Espumisan
The drug is prescribed not only to patients with flatulence, but also before undergoing a special examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Simethicone |
|
| The drug is taken 2 drops. 5 rub. per day. |
Espumisan reduces the number of bubbles that form in the intestinal tract. It also eliminates heaviness in the abdomen, bloating and pain.
Bobotik
The medicine destroys the bubbles that form and prevents the re-accumulation of gas. Reduces bloating, flatulence and pain.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Simethicone |
|
| The children's dosage is 8 drops. up to 4 p.m. per day. Adults are prescribed 16 drops. |
It is recommended to stop treatment with the drug as soon as all symptoms of flatulence have disappeared.
Phosphalugel
The drug has an enveloping effect, reduces stomach acidity, and protects the mucous membrane from the negative effects of pathogenic microflora.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Aluminum phosphate |
|
| The medicine is pre-diluted in 0.5 tbsp. water. The standard dosage is 1-2 packets of 2-3 rubles. per day 30 minutes before meals. |
Phosphalugel helps eliminate discomfort and pain in the epigastric area, also with heartburn and sour belching. The medicine allows you to cope with flatulence, which occurs as a result of non-compliance with the diet, after drinking large amounts of coffee. The same thing happens with nicotine or alcohol addiction.
Gas in the stomach - what to do?
Proper nutrition plays an important role in eliminating intestinal flatulence in women. You should eat regularly, in small portions and at regular intervals 5-6 times a day. When eating large portions, the process of food rotting begins in the intestines.
It is not recommended to snack on junk food, especially fast food.
To reduce intense gas production, the following recommendations should be followed:
- chew food thoroughly and slowly;
- refrain from talking and watching TV while eating;
- eat stewed, boiled or steamed food;
- avoid consuming too hot or cold food;
- drink about 2 liters. water;
- Eat fruits and sweets 2 hours after eating.
Following a diet can help combat excessive gas production.
The following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- milk, cream;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- sweets, baked goods, rye bread;
- pork;
- processed foods, fast food and artificial additives;
- eggs;
- onion, garlic, hot pepper;
- mushrooms.
You should enrich your diet with the following products:
- broths;
- porridge;
- fermented milk products in moderation;
- stews;
- fruits for a snack between main meals (with the exception of grapes, pears, apples, bananas).
Causes of gas incontinence
Physiological factors
Increased gas formation and, as a result, difficulties with gas retention are provoked by the consumption of large amounts of legumes, cabbage and radishes, and whole grain products.
Increased gas formation is caused by fruits: pears and apples, grapes, peaches. If gas incontinence is caused by nutritional factors, the symptom occurs 1-2 hours after eating. In the morning before breakfast, bloating is not observed. Flatulence (gas production), which occurs in old age, is a normal variant. Incontinence is associated with age-related weakening of the muscular apparatus of the anal sphincter. The problem is aggravated by a deficiency of digestive enzymes, which causes partially digested food to accumulate in the intestines, leading to increased gas formation.
Irritable bowel syndrome
With IBS, intestinal motility and coordination of the muscular sphincters of the rectum are impaired. The disease is characterized by gas incontinence without bloating. The patient is not able to control this process; sometimes a person becomes aware of an unpleasant situation only when a specific smell appears. Less commonly, flatulence develops against the background of severe pain in the rectum. Symptoms typically worsen in the morning and improve after bowel movements.
Anal sphincter insufficiency
Isolated gas incontinence is characteristic of the first degree of the disease, when the act of defecation has not yet been disrupted. At the second stage of insufficiency, the separation of not only intestinal gases, but also liquid feces is not controlled - the so-called “wet anus”. In the third degree, the patient cannot retain gases, liquid and formed feces. Incontinence and other symptoms are not related to eating habits. Incompetence of the anal sphincter is caused by the following diseases:
- Proctological pathology
. External and internal hemorrhoids, rectal fissures and fistulas, rectal prolapse. - Injuries
. Perineal rupture after childbirth, consequences of sphincterotomy, household injuries. - Anorectal anomalies
.
Intestinal diverticula
With intestinal diverticulosis, increased gas formation is constantly observed, which inevitably leads to flatulence. Diverticula are characterized by rumbling in the abdomen and the passage of gases with a strong unpleasant odor. The condition is aggravated by errors in diet. With diverticulosis, incontinence is also accompanied by pain and cramps in the abdomen, and irregular bowel movements similar to “sheep feces.”
Gynecological diseases
Pathologies of the internal genital organs are the main cause of gas incontinence in gynecological practice. The symptoms are due to the close location of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system and their joint innervation. Incontinence is more often diagnosed in women after 50 years of age, but can also affect patients of reproductive age after multiple births. The main diseases that may cause gas incontinence are:
- Pelvic floor dysfunction.
The symptom occurs with “posterior prolapse,” when the rectum descends along with the vaginal wall and a rectocele occurs. Uncontrolled release of gases occurs during physical exertion, laughter, and in advanced stages of the disease it occurs without provoking factors. - Prolapse of the uterus.
Incontinence is observed in a third of women with this pathology. Often the patient is unable to retain both gases and liquid feces. When the uterus prolapses or prolapses, proctological symptoms are combined with urological ones - urinary incontinence, frequent painful urination. - Elongation of the cervix.
Increased gas production is observed in 15% of women suffering from elongation of the uterine cervix. The sign is typical for stage 2-3 disease. Spontaneous flatulence appears when coughing, sneezing, or laughing. Urine leakage usually occurs simultaneously, and in severe cases, fecal incontinence.
CNS damage
Flatulence is associated with damage to the parts of the spinal cord that are responsible for the innervation of the rectum and anal sphincters. Less commonly, incontinence is caused by damage to certain areas of the brain. Uncontrolled passage of gases is combined with involuntary passage of feces and urine. A similar clinical picture is observed with spinal and head injuries and demyelinating diseases.
Mental disorders
In patients with mental disorders, control over the passage of gases is lost. In this case, the disorder develops during normal bowel function and does not depend on diet. The symptom is most characteristic of senile dementia, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. Sometimes gas incontinence worries patients with neuroses and post-stress psycho-emotional disorders. The condition is completely normalized after eliminating the stress factor.
Treatment of increased gas formation in women
Before starting treatment for flatulence, it is worth going through a series of diagnostic measures to find out the cause of increased gas formation. The easiest way to detect diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is by ultrasound. If pathologies are detected, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment aimed at eliminating the disease. If the cause of frequent gases is banal abdominal disorders caused by poor diet and lifestyle, medications that reduce gas formation are prescribed. Following a special diet will also help eliminate signs of flatulence.
Flatulence is not a disease, but a symptom indicating a certain kind of disturbance in the functioning of the digestive organs.
The drugs Espumisan, Motilium, Dimethicone, and adsorbent Activated carbon will help you get rid of increased gas formation at home.
Traditional medicine for flatulence
Often, to eliminate increased gas formation, they resort to traditional methods of treatment. An infusion of dill seeds, fennel, anise, mint and dandelion roots has a good effect. Tea with chamomile will also help cope with gas formation. Brew a tablespoon of herbs with a glass of boiling water and leave for an hour. The finished infusion should be drunk three times a day, 100 ml.
Another way to get rid of frequent flatulence is to take licorice decoction. To prepare it, you need to pour a teaspoon of crushed roots into 300 ml of boiling water, then boil for another 10 minutes. The chilled decoction should be taken on an empty stomach, 2 tablespoons 4 times a day.
An effective remedy for uncontrolled gas release is a decoction of parsley roots. A tablespoon of roots should be poured into a glass of water and boiled in a water bath for 15 minutes. Add 5 drops of anise oil to the cooled decoction and take 100 ml in the morning and evening.
Treatment regimen for bloating in women
In most cases, the fight against flatulence is carried out at home. It is important to choose a treatment method that will eliminate the symptoms of the uncomfortable condition and cure the underlying disease.
Medicines are prescribed by a gastroenterologist. If necessary, consultation with other specialists may be necessary. Complex therapy involves the use of folk remedies if there is no allergic reaction to natural components.
In some situations, simple exercises can help you cope with increased gas formation. Do not forget that during the treatment of flatulence, a woman is recommended to eat properly.
Consequences of flatulence in women
Chronic bloating in a woman causes a lot of inconvenience. This can lead to stress, low self-esteem, a woman begins to lose self-confidence, and complexes appear. Abdominal pain, heartburn, belching, bloating and involuntary release of gas impair quality of life. Therefore, if you experience increased gas formation, you should consult a doctor and find out the cause. Properly selected treatment will help make excess gas formation less obvious or get rid of it altogether.
If you do not take any measures to eliminate constant flatulence, a number of complications may arise, including the need for surgical intervention to remove a section of the intestine, which is very dangerous.
References: https://www.invitro.ru/library/simptomy/18433/ https://www.invitro.ru/library/simptomy/18379/ https://www.kp.ru/putevoditel/zdorove/gazoobrazovanie -v-kishechnike-u-vzroslykh/ https://t-pacient.ru/articles/6178/ https://aif.ru/health/food/bez_shuma_i_boli_kak_borotsya_s_povyshennym_gazoobrazovaniem https://medportal.ru/enc/gastroenterology/reading/ 42/ https://www.lvrach.ru/2018/02/15436909/ https://onclinic.ua/blog/kak-lechit-disbakterioz-kishechnika Pakhomovskaya N.L., Venediktova M.M. Flatulence: causes and ways of correction // Pediatrics. Supplement to the journal Consilium Medicum. 2017. No. 2 Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 04/28/2020