Abdominal pain after eating is a pathological condition that may be a consequence of a disease. Anyone can face the problem - the anomaly has no restrictions regarding gender and age category.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention and prognosis
The most common causes of pain after eating are physiological factors, such as intolerance or consumption of low-quality foods. Some gastrointestinal diseases can be sources of the disorder.
Pain in the abdomen after a meal in a child or adult is often accompanied by a large number of other symptoms: nausea and vomiting, flatulence, upset stool, rumbling in the intestines.
It is impossible to determine the etiological factor without laboratory and instrumental examinations. A thorough physical examination is important in the diagnostic process.
Abdominal pain after eating can be relieved using conservative therapeutic methods. Treatment of the underlying disease can be complex.
Etiology
The pathogenesis of abdominal pain after a meal is that food passes through the esophagus and reaches the stomach, which increases in size and begins to secrete gastric juice. Active contractions begin, and food enters the duodenum.
If at any stage a digestive disorder occurs, a person experiences pain in the area of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. Unpleasant sensations are formed against the background of the influence of digested food and digestive juices on the damaged membrane.
The most common abdominal pain after eating is the consequences of poor nutrition:
- eating food immediately before bedtime;
- dry food;
- eating “on the run”;
- lack of a meal plan - it is better to eat every day at the same time;
- eating spicy, sour and overly seasoned foods;
- prolonged refusal to eat followed by overeating;
- insufficient amount of food consumed;
- ingestion of excessively dry food;
- eating high protein foods.
Lactose intolerance can cause severe abdominal pain. Allergies to the following foods can cause illness:
- eggs;
- milk products;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- nuts;
- Fish and seafood;
- citrus;
- honey;
- strawberries and wild strawberries;
- flour and pasta;
- soybeans, beans and other legumes.
It is worth noting that food allergies are the most common cause of abdominal pain after eating in a child.
The causes of abdominal pain after eating can be pathological. The underlying disease may be:
- narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- peptic ulcer;
- gastritis;
- esophagitis;
- gastric obstruction;
- colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- hiatal hernia;
- urolithiasis disease;
- intestinal or stomach polyps;
- cholecystitis;
- intestinal flu;
- pylorospasm;
- mesenteric ischemia;
- pancreatitis;
- chronic constipation;
- pathologies of the spleen;
- cholelithiasis.
Cholelithiasis
The anomaly may appear due to a disease that is not associated with the digestive system:
- fractures of the lower ribs;
- sternum injury;
- pleurisy;
- myocardial infarction;
- purulent form of sore throat or pneumonia;
- inflammation of the reproductive organs in women;
- rupture of aortic aneurysm;
- ketoacidosis.
The reason why your stomach hurts after a meal may be indicated by the nature of the pain. For example, long-term nagging pain occurs as a result of such pathologies:
- chronic gastritis;
- binge eating;
- gastric oncology;
- excessively fast food consumption;
- stomach ulcer.
Burning pain can be caused by ingestion of sour or salty foods, the development of gastritis or pancreatitis.
Sharp abdominal pain immediately after eating appears in the following situations:
- consumption of low-quality products;
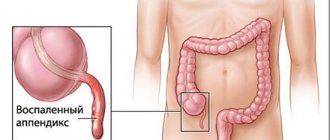
- inflammation of the appendix;
- open stomach ulcer;
- acute food poisoning;
- the course of infectious processes;
- exacerbation of gastritis;
- pancreatitis.
The etiological factor can be indicated by the localization of pain:
- pain in the upper abdomen or in the navel area occurs due to inflammatory damage to the stomach or duodenum;
- in the iliac zone with irradiation to the right hypochondrium they speak of cholelithiasis, inflammation of the bile ducts or gallbladder;
- “in the pit of the stomach” and under the ribs is a sign of an ulcer of the duodenum or stomach.
It is noteworthy that if the pain appears immediately after a meal or after about an hour, the problem lies in the esophagus or stomach, and if the pain occurs after 2 hours or more, the cause of the abnormality is in the intestines.
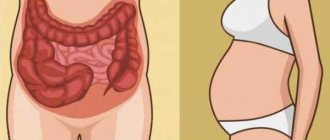
Abdominal pain after eating while carrying a child is most often associated with displacement of organs located in the abdominal cavity. Filling the stomach causes them to compress, causing aching pain.
Diseases accompanied by pain immediately after eating
The stomach almost always hurts after eating in the presence of pathologies of the stomach and duodenum. This is due to the fact that food is an irritant for the inflamed mucous membrane of the digestive organs. Sometimes this symptom occurs even when following a diet.
Abdominal pain after eating is also a sign of chronic pancreatitis and occurs only after eating certain foods. Fatty foods, sweets, and spicy foods provoke pain. Painful sensations with pancreatitis always occur against the background of overeating.
With chronic colitis, pain occurs no earlier than 5-6 hours after eating. They are stronger after eating legumes, cabbage, cucumbers, apples, as well as milk or carbonated drinks. As a rule, in this case the pain is dull and aching. The cause of abdominal pain after eating is irritable bowel syndrome. This pathology is a complex of various functional disorders of the large intestine.
Symptoms
The symptomatic picture of the disorder includes many other clinical manifestations. It is extremely rare that pain will act as the only external sign of illness. The clinic is of a purely individual nature, which is determined by the influence of one or another etiological factor.
Soreness can be of a different nature:
- pricking;
- blunt;
- cutting;
- shooting;
- intense or weak;
- aching or sharp;
- moderate or cramping.
In most situations, pain in the lower abdomen after eating is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increase in temperature indicators;
- constant nausea ending in vomiting;
- feeling of abdominal distension;
- problems with bowel movements;
- the presence of blood, mucus or pus in the feces;
- weakness and general malaise;
- flatulence;
- fast fatiguability;
- bloating;
- heartburn and belching with an unpleasant odor;
- bad breath;
- difficulty swallowing solid food;
- increased sweating;
- the skin becomes pale or yellow (with liver damage);
- rumbling in the stomach;
- heaviness and fullness of the stomach;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- white or yellow coating on the tongue;
- decreased ability to work;
- rumbling in the intestines;
- weight loss;
- attacks of headache and dizziness;
- sleep disorder;
- hiccups;
- emotional instability.
This is not all the symptoms that can develop against the background of pain in the abdomen immediately or some time after eating food. The clinical picture is dictated by the etiological factor; only the intensity of symptoms in children and adults may differ.
Prevention
- Try to eat healthy, avoid spicy, fatty, fried foods that complicate the digestion process.
- Avoid drinks containing large amounts of caffeine: coffee, strong black tea. Both coffee and strongly brewed tea can cause severe irritation. Drinking too much coffee can also lead to increased acidity.
- I'll have to give up chocolate too. As you know, chocolate contains a large amount of caffeine. Therefore, eating chocolate invariably leads to even greater irritation of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, eating chocolate in large quantities can lead to an increase in blood sugar levels.
- Eat small portions 5-6 times a day.
- Try not to overeat.
- It is also worth avoiding foods that increase acidity in the body: strawberries, mushrooms.
- Don't eat late.
- Do not lie down immediately after eating.
- It is recommended to do regular exercise.
- Drink fermented drinks or milk to stabilize the digestion process.
- If your stomach gets sick and continues to hurt, consult a doctor immediately and do not self-medicate.
Diagnostics
Only a gastroenterologist can find out the causes of pain after eating in a child or adult and prescribe the most effective treatment.
Given the existence of a wide variety of predisposing factors, the process of making a correct diagnosis should only take an integrated approach. The first stage of diagnosis consists of manipulations that are performed directly by the clinician:
- familiarization with the medical history - to determine the influence of the pathological factor;
- study of life history - to clarify the impact of predisposing sources that have a physiological basis;
- deep palpation and tapping of the anterior wall of the peritoneum;
- measuring temperature and pulse, heart rate and blood tone;
- a detailed survey of the patient will enable the doctor to draw up a complete symptomatic picture, determine the location and nature of the pain, which may indicate an underlying disease.
Laboratory research:
- general clinical blood test;
- microscopic examination of feces;
- bacterial tests;
- immunological tests;
- PCR diagnostics;
- blood biochemistry.
The following instrumental procedures can accurately determine the etiological factor that provokes the appearance of pain in the abdomen after eating:
- gastroscopy;
- X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract with contrast agent;
- ultrasonography of the abdominal organs;
- colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- endoscopic biopsy;
- FEGDS;
- CT and MRI.
Colonoscopy
In some cases, malaise may be the result of pathologies not related to the digestive system, so the gastroenterologist refers the patient for additional examination to specialists from other fields of medicine, for example, a cardiologist or pulmonologist.
Treatment options
When abdominal pain occurs after eating, it must be diagnosed. Only after this can treatment be carried out.
First time stomach pain
When your stomach first hurts after eating, you immediately need to analyze what foods you ate. This is because the most common cause is poor nutrition. In addition, you should analyze the fact whether food allergies can cause pain after eating.
Against this background, you need to take appropriate measures, namely: monitor your diet and remove allergens from your diet. If the pain does not recur, then it is unlikely that you should consult a doctor.
An hour after eating or at night
Pain that occurs approximately an hour after eating is associated with the development of stomach ulcers or gastritis. Early pain is a symptom of damage to the upper parts of the stomach. Their first manifestations are observed almost immediately after food enters the stomach. Gradually, the pain syndrome intensifies, this is due to the process of digesting food. This process requires the production of hydrochloric acid, which is an irritant to the mucous membranes. After food moves into the duodenum, the production of gastric juice decreases, which means the concentration of hydrochloric acid decreases, so the pain subsides. With a duodenal ulcer, pain occurs on the right side, sometimes it radiates to the back and can be of a very different nature.
Constant stomach pain
When your stomach hurts constantly after eating, this is a reason for an urgent examination by a gastroenterologist.
In order to facilitate diagnosis, it is necessary to indicate the exact location of pain and report accompanying symptoms:
- Aching pain in the epigastric region and left hypochondrium indicates the development of peptic ulcer and gastritis.
- Intense pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the scapula and collarbone, may indicate cholelithiasis and cholecystitis.
- If the upper half of the abdomen hurts and the nature of the pain is girdling, then this indicates the development of pancreatitis.
- When dull stabbing or cutting pain is observed throughout the abdomen, including around the navel, this indicates various intestinal diseases.
source
Treatment
When a person experiences abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting after eating, conservative therapeutic methods are used to eliminate them. The attending physician individually, based on the underlying disease, general condition, severity of illness and age of the patient, will formulate the most effective treatment tactics:
- use of medications;
- diet therapy;
- a course of therapeutic exercises;
- hardware, manual or water massage of the abdomen;
- alternative medicine.
In most cases, patients are prescribed:
- antibacterial agents;
- analgesics and antispasmodics - for pain relief;
- NSAIDs;
- immunomodulators;
- medications to eliminate associated symptoms, such as constipation and diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, bloating and flatulence, high fever, etc.;
- mineral and vitamin complexes.
The most effective medicines:
- "Omeprazole";
- "Ultop";
- "Gastal";
- "Papaverine";
- "Festal";
- "Almagel";
- "Lansazole";
- "Motilium";
- "Mezim Forte";
- "Pancreatin";
- "Creon";
- "Besalol."
Treatment with physiotherapy is no less effective:
- ultrasound;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- warming up;
- acupuncture;
- magnetic therapy;
- darsonvalization;
- UHF;
- inductothermy;
- Diadynamic therapy.
Diadynamic therapy
It is not prohibited to use traditional medicine after consulting a doctor. At home, you can prepare medicinal drinks intended for oral administration based on the following ingredients:
- rowan and blueberry berries;
- horsetail;
- plantain;
- calendula;
- burdock;
- Melissa;
- mint;
- buckthorn;
- rose petals;
- St. John's wort;
- sagebrush;
- cottonweed;
- Linden;
- nettle;
- flax and dill seeds;
- rose hip;
- yarrow;
- chamomile;
- valerian.
It is impossible to completely get rid of abdominal pain after a meal without treating the underlying pathology.
Why it hurts: reasons
Quite often, the stomach begins to ache after eating if a person eats incorrectly. The following factors can provoke pain, heaviness in the stomach and other unpleasant sensations:
- a lifestyle in which a person eats 1-2 times a day and eats a lot at one time is stressful for the stomach;
- the habit of drinking a lot of liquid while eating or overeating - the walls of the stomach are stretched;
- intolerance to certain products, for example, dairy or fish - the reaction to eating them can be bloating, nausea, cramps, upset stool;
- abuse of heavy, unhealthy foods - fatty, spicy, fried, pickles, smoked meats, fast food - has a detrimental effect on the gallbladder and causes stomach pain;
- very cold or hot food has a traumatic effect on the stomach;
- low-quality, stale products can cause poisoning, one of the symptoms of which is cramping pain.
Diseases and pathologies of the stomach that cause pain
With systematic abuse of food that is difficult to digest, irritable stomach syndrome can develop, a disease manifested by cramps, heaviness and pain in the first hours after eating. Other symptoms of this condition include:
- belching that does not stop for 1-1.5 hours;
- causeless nausea;
- heartburn not associated with the consumption of specific foods;
- with prolonged course – loss of appetite and weight.
The symptoms of this disease are similar to gastritis; it can also be caused by poor diet. But often inflammation of the mucous membrane and ulcers are caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Chronic or acute gastritis is one of the typical causes of pain that occurs in the stomach after eating. If gastritis is caused by increased secretory function of the stomach, it begins to hurt even while eating; this form of the disease, along with belching and nausea, is characterized by constipation. With decreased secretion, the pain is diffuse, the belching has a rotten taste, and there is a tendency to diarrhea.
With a peptic ulcer, the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum is ulcerated; numerous small wounds or one larger one form on it. Pain can be caused by exposure to damaged areas of gastric juice or food, especially rough, irritating food. An ulcer of any location is characterized by “hunger pains” that disappear temporarily after eating; with a stomach ulcer, they recur after about half an hour to an hour. If the ulcer affects the duodenum, pain appears after a few hours, when the digested food passes from the stomach to the intestines.
Some abnormalities in its structure can cause pain in the stomach. With malignant tumors, the pain is constant, but if it appears after eating, it may be associated with a spasm of one or another part of the stomach.
- The upper part of the stomach can prolapse into an enlarged hole in the diaphragm (diaphragmatic hernia); after eating, the full stomach is pinched by this hole, which causes pain.
- Closer to the duodenum there is a section of the stomach called the pylorus; its spasm (pylorospasm) is often caused by disorders of the nervous system and causes severe pain, which manifests itself a quarter of an hour after eating and stops only after the stomach has completely emptied. This disease is usually accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Similar symptoms are characteristic of stenosis of the esophagus, a narrowing of the opening between it and the stomach caused by a tumor, injury or penetration of a foreign body. Pain occurs as soon as the stomach is filled with food.
- Part of the stomach may become blocked due to tumors or spasm of the walls, preventing food from entering this section. This condition is called obstruction, when the load on another part of the stomach increases, the walls stretch greatly after eating, which leads to pain.
Prevention and prognosis
To date, there are no specially designed preventive measures to prevent abdominal pain after breakfast or other food consumption.
The likelihood of illness can be reduced by following these simple rules:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- constant increase in immune resistance;
- body weight control;
- avoiding emotional exhaustion;
- taking medications strictly as prescribed by the clinician;
- early identification and treatment of any disorders that may lead to pain.
Do not forget about regular preventive examinations in a medical institution with visits not only to a gastroenterologist, but also to other doctors at least 2 times a year.
Abdominal pain after a meal can easily be treated with conservative therapy; patients often have a favorable prognosis. Ignoring or eliminating pain on your own can aggravate the problem, and refusing medical help will inevitably cause the progression of the underlying disease. The combination of such oversights is dangerous with negative consequences, even death.
Treatment and medications
Pain in the abdominal area can also be observed in some serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, therefore, it becomes necessary to consult a specialist to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms and correctly treat the diagnosis. Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal cavity is used for diagnosis.
The treatment process depends on the causes of the disease and the degree of damage to the gastric tissue. If the cause of the pain is an infectious disease, patients undergo a course of antibiotics to alleviate the condition.
Diet and exercise are mandatory during treatment. Meals should be small, but frequent. Avoid eating late at night. It is recommended to pay special attention to the process of eating food. Chew food slowly, softening it in your mouth as much as possible. In addition, the fast process of eating disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the diet. Avoid overeating.
Relief during intense pain can come if you apply a compress. To do this, wet a soft towel with warm water and apply a compress to the stomach area. It will ease difficulty breathing.
Try not to drink tea too hot.
It is useful to brew not very hot tea and make an infusion of chamomile. Chamomile effectively relieves irritation and has an anti-inflammatory effect. For example, I drink chamomile tea without sugar after I eat, since sugar reduces the healing properties of chamomile.
It is recommended to eat more fresh vegetables and fruits. However, you should avoid those fruits that can potentially lead to pain and increase acidity levels. For example, you should stop eating watermelon. Of course, we all love watermelon. However, watermelon can lead to irritation of the mucous membranes. It's not so much the watermelon itself that is harmful, but the juice from the watermelon. For certain gastrointestinal syndromes, watermelon and watermelon juice can only increase pain. It is especially not recommended for children to consume watermelon during periods of pain.
Try to sleep on your back. Doctors have proven that sleeping on your stomach is not only not beneficial, but even harmful. Therefore, all experts unanimously recommend sleeping on your back. Sleeping on your back promotes the normal functioning of body systems. Sleeping on your back is beneficial for normal heart function and stable blood circulation. Sleeping on your back creates normal conditions for the gastrointestinal tract.
Include a salad of fresh fruits and vegetables in your daily menu. For example, you can make a salad from fruits such as peeled and finely chopped apples, melons and sweet cottage cheese. Or you can make a salad of boiled beets, peeled apples and cabbage.
To get rid of constipation, you need to eat more apples. In general, you should eat at least half an apple a day. An apple will cleanse the body of toxins and stabilize digestion. You can juice apples by adding sugar to make it sweet. In addition, they promote weight loss.
It's good to eat beets. It is recommended to eat beets for constipation. Beets normalize the microflora of the digestive tract and contribute to its normal functioning. Beetroot is good for obesity because beets regulate metabolism and promote accelerated metabolism.
Eliminate strawberries from your menu.
Eliminate strawberries from the menu. First of all, because it contains a colossal amount of acid, and the seeds can corrode the mucous membrane. Although it is recommended to eat strawberries for weight loss, vitamin deficiency and anemia, and the enzymes contained in strawberries help cope with various intestinal infections, eating strawberries is strictly prohibited for abdominal pain. It will not be especially beneficial for children to consume strawberries in large quantities. Because strawberries are the strongest allergen. In addition, excessive consumption of strawberries causes kidney problems.
Among fruits, eating banana will be useful. Bananas are good for constipation. You can notice improvements in stool after eating even one banana. However, to eradicate this problem, eating bananas in large quantities is not recommended. Including bananas in the menu helps stabilize the gastrointestinal tract. However, bananas are not an easily digestible fruit. Bananas have enveloping properties. Therefore, eating bananas has a healing effect.
It is recommended to drink warm, but not hot, milk every day at night if your stomach hurts. You can drink milk with dry cookies and crackers. Milk coats the walls of the stomach and normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If you want, you can drink a glass of sweet, not hot milk with honey or sugar.
It is useful to drink a glass of kefir at night. Consuming kefir improves the digestion process and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, doctors unanimously recommend drinking kefir for stomach diseases. In addition, it is useful to know that fresh kefir weakens. But kefir, which is already more than three days old, strengthens. If you have increased acidity of gastric juice or constant heartburn, then kefir is strictly contraindicated for the reason that kefir is a fermented milk drink.
Drinking herbal or green tea, not hot and not sweet, with chamomile or sage is beneficial. It has a great effect on the digestive system and cleanses the body of toxins. They are also good for weight loss.
It is good for the digestive tract to eat cottage cheese. Cottage cheese is a real storehouse of nutrients. It is recommended to eat it for all gastrointestinal diseases. If you want, you are allowed to eat sweet cottage cheese with added sugar or honey. Eating cottage cheese is useful for maintaining a stable metabolic process. In addition, cottage cheese, even sweet, is an easily digestible product.
It is recommended to use pumpkin seeds for diseases of the digestive tract. It is useful to eat melon as a fruit. Melon contains many enzymes, is easily absorbed by the body and improves digestion. It is recommended to eat melon while taking antibiotics, since melon reduces their toxicity to the body. In addition, it promotes weight loss.
If you want sweets, eating them is allowed. Of course, you can only eat sweets when you do not suffer from diabetes. Consumption of sweets such as chocolate and sweets with citrus additives is not allowed. But it’s better to avoid salt.
Cabbage is considered healthy. If you want, you can prepare dishes with the addition of stewed cabbage. Stewed cabbage contains a large amount of fiber, which activates the digestion process. In addition, stewed cabbage stabilizes the metabolic process.
But you will have to give up mushrooms. The chitin contained in them is not digested by the body. Therefore, eating mushrooms can lead to digestive problems. In addition, mushrooms increase the concentration of gastric juice and the level of acidity in the stomach. You can also often get poisoned when you eat mushrooms.
Green radish is no less useful. Radish contains a huge amount of substances and vitamins that are beneficial to the digestive tract. Among other things, green radish promotes the secretion of gastric juice, and when you eat, it activates the digestion process. Eating green radish is beneficial for constipation. However, it is not recommended to eat green radish every day if you have high acidity. Radish is best eaten in salads because of its bitter taste. It promotes weight loss.
You can include milk soup in your daily menu. It is better to make it with grains containing a lot of fiber: oats, rice, barley. Consumption of each of them promotes digestion.
It is good to take a variety of herbal baths.
You can take a variety of herbal baths from pine needles, oak bark, sage, and St. John's wort. If the cause of the disease is food poisoning, it is recommended to take activated charcoal and perform gastric lavage.
Excellent antispasmodics and painkillers are “No-shpa”, “Spazmolgon” and other drugs. For heartburn, Motilak and Motilium will help. They should be drunk a few minutes before meals. You can take enzymatic agents that activate the digestion process. In particular, “Mezim” and “Pancreatin”. For nausea and vomiting, it is recommended to drink Regidron, which is a cleansing agent.
Anti-anxiety medications are sometimes prescribed to treat, stabilize and calm the nervous system. It is better to take medications with milk rather than water. Since milk has an enveloping effect, it does not irritate the gastric mucosa. Delicate in its structure, it is recommended for patients with peptic ulcers.
However, these medications are not a panacea and do not eliminate the very cause of the disease. They provide relief for a while. The disease itself does not go away. Therefore, it is imperative to consult a doctor to establish a diagnosis and prescribe therapy. In some cases, intensive therapy and even surgery are required.