Causes of watery diarrhea in children
Diarrhea is not an independent disease, but is a complication or sign of disorders in the gastrointestinal tract and other body systems. It is in childhood that diarrhea occurs most often, since the immune system is not fully formed, so the body is susceptible to rapid infection.
Main reasons:
- Intestinal infections. Most often, this is the microorganism Helicobacter pylori, which penetrates the digestive organs through dirty hands, unwashed vegetables and fruits. Pathogenic bacteria significantly disrupt the natural microflora of the stomach and intestines, causing an imbalance. As pathogens grow and develop, they release large amounts of waste products that poison the child’s body. Toxic deposits prevent food from being digested, so stool is released as water. The main symptoms include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and low-grade body temperature, which increases as it progresses.
- Dysbacteriosis. It is characterized by a disruption of the normal microflora, in which the stool has a foamy structure and a green tint. A distinctive feature is a sourish specific odor during bowel movements. The main reason for the imbalance between beneficial and harmful microorganisms is the use of antibacterial agents. Diarrhea can be replaced by constipation and vice versa. Read about the manifestations and methods of treating diarrhea in a child after antibiotic therapy in this article.
- Overeating and unbalanced nutrition. The reason lies in excessive consumption of fruits, berries, vegetables, and various sweets. These are foods that are poorly digested by the stomach. The cause may also be intolerance to a particular food or the introduction of a new food into the diet. Intolerance occurs due to the lack of an enzyme that breaks down foods into easily digestible elements.
- Colds. Paradoxical as it may seem, respiratory pathologies have a negative impact on the digestive organs against the background of weakened immunity and viral infection. In this case, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause, that is, cold therapy.
- Stress. Nervous tension, fear, anxiety are neurological problems. It is known that the nervous system is closely interconnected with other internal organs, therefore, in stressful situations, the body reacts with a response in the form of diarrhea. Therapy comes down to calming the baby.
Other reasons and factors:
- allergic reaction to food and certain medications;
- intoxication (poisoning) of the body with spoiled food;
- inflammation of the small intestine (before 3 years of age) or large intestine (after 3 years of age);
- some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in which enzymes and bile are insufficiently produced, and the absorption process is disrupted;
- teething;
- the presence of helminthic parasites;
- dirty hands;
- drinking poor quality water.
When breastfeeding, the cause of the baby's diarrhea may be the mother's poor diet. Most often this is the consumption of foods such as cucumber, apple, beets, and pears.
Difference between loose stools and diarrhea
Loose stools and diarrhea in a child have some differences. Unformed feces appear as a result of ingesting certain foods (fermented milk products, soups). They occur once without repetition.
Diarrhea accompanies many diseases that are directly related to intestinal pathology or secondary to its functions. Diarrheal syndrome occurs four or more times a day. The stool is not just liquid; it may have a watery consistency with a specific odor. In this case, the color of the masses acquires a green, yellow tint. In some pathologies, dangerous impurities are observed (pus, blood, a lot of mucus).
Ordinary loose stools are not accompanied by pathological symptoms. Diarrhea, on the contrary, is often combined with pain in the abdomen or along the large intestine, nausea, and vomiting.
In the first case, the general condition of the child is not disturbed; there is no constant loss of fluid or electrolytes. In the second case, the baby will be lethargic, drowsy, and with decreased appetite.
Loose stool in a child without fever does not mean the development of the disease; a one-time occurrence is not a reason to panic. A baby under one year of age does not have formal bowel movements; the main thing here is that the mother notices in time the initial signs of the development of the disease (pathological inclusions). To eliminate doubts, it is better to visit a doctor.
Symptoms
In addition to watery stools, there are a number of additional symptoms that indicate pathological disorders:
- high body temperature;
- pain syndrome;
- increased tearfulness and moodiness;
- refusal of food;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- Frequent belching (especially with an unpleasant odor).
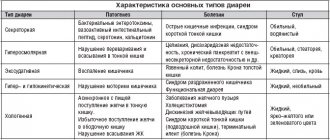
Types of watery diarrhea in children
Watery diarrhea is divided into types depending on the shade of stool, on the basis of which the diagnosis is established:
- Green color indicates intoxication of the body by pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, E. coli, etc.). Greening of stool occurs due to the influence of toxic substances that are released by bacteria during their life processes. Read more about the causes of green diarrhea in a child here.
- White diarrhea indicates problems with the liver.
- Yellow watery diarrhea is considered the safest, as it is caused by immature digestion in newborns. If yellow feces occur at an older age, this indicates a mild degree of food poisoning or an allergic reaction. Find more information about the nature of yellow diarrhea here.
- The color ranges from burgundy-dark to black - the most dangerous, as the cause may be internal bleeding.
Causes of diarrhea without fever in a child
The main factors that provoke stool disorder include:
- Eating disorder. Almost all parents, one way or another, deviate from healthy eating recommendations. The child’s body cannot digest a large amount of “wrong” food (a lot of salty, fried, etc.), as a result, intestinal function increases, and a condition such as diarrhea in a child occurs, which occurs without an increase in temperature.
- Infectious diseases. Viruses and harmful microorganisms often attack the baby’s body, and in this case, diarrhea in a child can last more than 3 days and rarely goes away without fever. The culprits of this condition are dysentery, salmonellosis, enterovirus, influenza, rubella, and intestinal infection.
- Intestinal dysbiosis. If the balance of beneficial and opportunistic flora in the intestines changes, dysbiosis develops - a condition whose symptoms are diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and allergies in children.
- Enzyme deficiency. Due to the functional immaturity of the child’s enzymatic system, the body does not always cope with digestion. As a result, diarrhea develops with the presence of particles of undigested food in the stool. Such problems are more common before one year of age, that is, among infants, due to lactase deficiency - the body’s inability to fully absorb lactose. In this case, diarrhea in a child 6 months and older will occur without fever in the form of foamy, copious stools immediately after finishing feeding.
- Diseases of non-infectious etiology. Diarrhea in this case often occurs in the summer as a result of the child overheating in the sun or heat stroke. In addition, stressful situations, allergies, and surgical pathologies in the abdominal cavity can become non-infectious factors.
- Reaction to medications. Each child tolerates medications individually. There are cases when children react to a medicine prescribed by a doctor with digestive disorders - diarrhea and vomiting, skin rashes without fever, which is a side effect of taking a specific medicine, for example, a child who is 4 months old. Most often, such an inadequate reaction of the body is caused by antibiotics.
- Food allergies. A hypersensitivity reaction to foods can also cause abdominal discomfort, itchy skin, diarrhea and vomiting. The temperature in this case may or may not be elevated.
First aid
Parents should never panic. You need to act decisively and confidently. First of all, feeding is excluded (permissible during breastfeeding) and the drinking regime is turned on. This is necessary to prevent the development of dehydration. If diarrhea persists throughout the day and is accompanied by other symptoms, you should immediately call an ambulance. Further actions (before the doctors arrive):
- After each bowel movement, carry out hygiene procedures, and then lubricate the skin with baby cream.
- Leave some stool for healthcare workers (based on this, the cause of diarrhea is suspected).
- Give the baby Regidron solution. If you don't have it, prepare it yourself. Take 1 liter of boiled water. Add 1 tsp. salt, 4 tsp. glucose (1 – sugar). Before the age of one year, give the baby 600-700 ml of liquid, up to 2 years - 800-900, from 2 to 5 - 1,000-1,200, over five - 1,400 ml. You need to drink in small portions over several hours.
- You can stop diarrhea with activated charcoal or Smecta.
- Be sure to measure your body temperature (if it is very high, give you an antipyretic drug in a dosage appropriate for your age category).
Pathological causes
Due to the imperfection of the immune and digestive systems, loose stools or diarrhea quite often occur in children of different ages. It is important to distinguish these concepts:
- loose stools usually occur due to digestive disorders and cause virtually no discomfort in the baby; they go away on their own after 1-2 bowel movements;
- With diarrhea, the urge to defecate is frequent (more than five times a day), which threatens dehydration and deterioration of the baby’s condition.
The absence of fever and vomiting against the background of diarrhea often reassures parents, but diarrhea can be a symptom of many diseases that are not always safe for the baby’s health.
Important! When making a diagnosis, parents should inform the doctor about the frequency of bowel movements, quantity, color, smell and consistency of stool.
Dangerous causes of diarrhea without fever and vomiting:
- Food poisoning;
- Intestinal infection;
- Enteritis;
- Infectious diseases;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Food allergies;
- Parasitic intestinal infestation;
- Appendicitis;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Each of these disorders can lead to serious complications, so even before the doctor arrives, parents should try to determine the true cause of diarrhea and try to help the baby.
Diarrhea without vomiting and fever can be a sign of other dangerous diseases. Therefore, if this condition does not go away within 24 hours, then you should definitely consult a doctor.
Food poisoning
Diarrhea caused by intoxication of the body can be caused by eating low-quality dairy, meat or other products.
Symptoms of this disorder are severe abdominal pain in the form of cramps, liquid and frequent stool, sometimes with a green tint and a sharp, unpleasant odor. The child may be capricious and excited, but as the condition worsens, he becomes, on the contrary, lethargic and drowsy, refusing food and water.
In case of food poisoning, the decision on hospitalization is made by the doctor, depending on the severity of the patient’s condition. But children under three years old must undergo hospital treatment.
To avoid serious consequences such as dehydration, if the disorder does not go away during the day, you should call a doctor
Intestinal infection
When the body is poisoned, frequent diarrhea occurs (more than five times a day), feces have an unusual color and mucous consistency, and particles of undigested food may be present in the stool. Additional symptoms may appear: white coating on the tongue, abdominal pain, rash. In mild cases, the child is treated at home; in more severe cases, the child is hospitalized.
Enteritis
Frequent and severe diarrhea (more than 6-7 times a day) may indicate inflammation of the small intestine. Additionally, pain appears in the navel area, the child becomes lethargic, and appetite disappears. Treatment is carried out at home.
Metabolic disorders
Diarrhea without fever can occur with pathologies associated with metabolic disorders. In older children, this may indicate the development of diabetes.
Food allergies
In children, diarrhea can occur due to the lack of certain enzymes, which causes an allergic reaction to food, fruit acids, glucose, etc. In this case, red spots and a rash may form on the child’s body, and shortness of breath, wheezing, watery eyes, difficulty breathing, and a runny nose may occur. If such symptoms appear, treatment should be carried out immediately.
If you experience symptoms indicating an allergic reaction, you should immediately call a doctor
Parasitic intestinal infestation
Frequent diarrhea may be followed by prolonged constipation. At the same time, the child loses weight, becomes restless, and sleep is disturbed. Other symptoms may appear: colic in the abdominal area, lethargy, increased drooling. Treatment is carried out at home using anthelmintic drugs.
Appendicitis
At the initial stage of development, appendicitis can cause frequent diarrhea with mucus in infants, without fever or vomiting. The child refuses food and complains of pain near the navel or in the epigastric region. This condition requires immediate medical intervention.
Dysbacteriosis
With intestinal disorders, frequent diarrhea occurs, feces have an unpleasant odor, and stool has a liquid consistency. The child experiences a deterioration in appetite, bloating, and abdominal pain after eating. Allergic reactions on the skin may occur, and a white coating appears on the tongue.
The causes of dysbiosis can be: taking antibiotics, acquired intestinal infections, unbalanced nutrition, diseases of the digestive system, chronic diseases accompanied by decreased immunity, helminthic infestations. Treatment takes place at home.
Dysbacteriosis in a child is quite common. The doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment after receiving the results of an analysis for dysbacteriosis.
Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract
In the early stages, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract can occur without fever.
Symptoms of this condition, in addition to diarrhea, can be: poor appetite, belching, weight loss in the child, weakness, blood in the stool, pain in the epigastric region, bloating, heartburn, increased gas formation.
This condition does not require immediate hospitalization, but you should not delay your visit to the doctor.
Infectious diseases
Diarrhea can occur due to damage to the body by viruses or bacteria. This symptom may accompany:
- Initial stages of salmonellosis and dysentery;
- Gastroenteritis, colitis and other diseases of “dirty hands”;
- Acute respiratory tract diseases: ARVI, sore throat, pneumonia.
In such conditions, diarrhea occurs due to intoxication of the child’s body with waste products of pathogenic bacteria.
Treatment depending on the child's age
If children have watery, loose stools, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician, who will conduct an examination and prescribe a treatment regimen.
What to do for diarrhea at different ages:
- Infants under one year of age need to reduce the amount of breast milk they feed. If a child is fed artificially, it is not recommended to give formula. Preference should be given to warm boiled water. Smecta and Hilak are suitable medications.
- From one to 3 years, enterosorbents are needed. Smecta, activated carbon, Polysorb are allowed. To prevent dehydration - Regidron.
- From 3 to 6 years old, you can additionally introduce Phosphalugel to cleanse the intestines.
- From 6 and older, therapy is supplemented with traditional medicine. To restore the water-salt balance, it is also allowed to give Glucosolan.
The baby is hospitalized in case of severe and prolonged diarrhea, excessively persistent high body temperature, severe pain, and dehydration.
Drug therapy
Specific medications are prescribed by the attending pediatrician after making an accurate diagnosis and receiving examination results. For diarrhea in children, the following medications are used:
- Sorbents: Polysorb, Smecta, Enterosgel, Polyphepan, Neosmectin, activated carbon.
- To eliminate symptoms: Tanalbin, Bismuth, Imodium, Diarol.
- For microflora (probiotics, bacteriophages): Bifidumbacterin, Bifilin, Linek-s, Acipol, Enterol, Bificol, Colibacterin, Lactobacterin.
- For high fever Paracetamol in the form of tablets, suppositories, suspensions.
- Antibacterial agents (for infection): Tienam, Nevigramon, Meronem, Furazolidone, Kanamycin sulfate, Negram, Ercefuril, Ciprofloxacin, Rifampicin, Ceftazidime.
- Enzyme preparations: Panzinorm forte, Festal, Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin, Pankurmen, Digestal.
- Antispasmodics: Drotaverine, Papaverine, Spasmomen.
Diet
The speed of recovery depends on the baby’s diet, so diet therapy is an important component of treatment. Rules:
- It is necessary to limit the amount of food consumed (at any age).
- Allowed: viscous oatmeal and rice porridge, light vegetable and meat broths, crackers, biscuits, hard-boiled eggs. It is permissible to give bananas, apples, and persimmons baked.
- Prohibited: pickles, marinades, mushrooms, fatty meats, dairy products, soda, smoked foods, sweets, legumes, bread.
Diets are followed for the first 3 days. Then other foods are gradually introduced.
How to prevent dehydration?
When the body dehydrates, all beneficial substances and water itself are washed out, so fluid replenishment is necessary. For this purpose, salt solutions are used: Glucosan, Regidron, Tsitroglucosolan, Oralit, Enterodes, Gastrolit. After recovery, vitamin and mineral premixes are necessary.
Folk remedies
Used primarily as an adjuvant therapy. What is allowed in childhood:
- Brew oak bark in the standard way. Give the baby 2 tbsp. l. decoction during meals.
- From the age of 2, children can be given strong black tea.
- Combine sage, chamomile and St. John's wort in equal proportions. Separate 1 tbsp. l., pour a glass of boiling water. Let it brew, strain. Take 50 ml three times a day after meals.
- Boil blueberries and bird cherry (fruit – 2 parts, water – 3 parts). Boil for 15 minutes, take 50 ml 3 times a day.
- Prepare jelly at home from natural ingredients. Drink in unlimited quantities.
- It is useful to give liquid after boiling rice.
Treatment
In uncomplicated cases, you can try to stop diarrhea in a three-year-old child on your own. To do this, take the following steps:
- ensuring optimal drinking and nutritional regimen;
- prevention of dehydration;
- detoxification of the gastrointestinal tract;
- restoration of intestinal microflora.
Nutrition and water regime
When diarrhea occurs, it is very important to follow your diet and nutrition regimen. Drinking plenty of fluids will help restore fluid loss in the body. You should try to maintain a “hunger break” during the first 8-10 hours after the onset of diarrhea. When a child feels nauseous, he will most likely refuse to eat, but if an appetite appears on the first day, you can give dry cookies or wheat bread crackers.
In the next 2-3 days, the baby should be fed rice porridge cooked in water, dietary puree soup, and for 4-5 days - give up fiber-rich fruits.
Detoxification
Treatment of diarrhea in children under 3 years of age and older is accompanied by the use of sorbents that absorb toxins and waste products of pathogenic bacteria.
Effective absorbent anti-diarrhea agents:
- Smecta - suitable even for infants, it removes toxins perfectly. The drug can be given to a child by mixing it with food. For children 3 years old, 2 packets per day are enough to achieve a therapeutic effect.
- Enterosgel is a unique product that removes toxins while repelling water, salts, and minerals, envelops the gastrointestinal mucosa, relieving irritation.
- Activated carbon – absorbs toxins and helps thicken stool.
These drugs are not used if bleeding in the digestive tract is suspected, and they are not taken simultaneously with other medications.
Preventing dehydration
If you have to treat loose stools in a 3-year-old child at home, the following is used to replace lost fluid:
- Rehydron - the contents of the package are dissolved in one liter of water and the baby is given a drink, offering him 1-2 tablespoons of solution every 10 minutes.
- Gastrolit - in the first 4 hours of the disease, give the baby 50 ml of a solution of this drug, then 10 ml after each loose stool.
If there are no medications with a similar effect, you need to give the babies saline solution. To do this, dissolve 30 g of sugar and 5 g of salt in one liter of water.
Why is watery diarrhea dangerous in a child?
The main danger of watery diarrhea is complete dehydration of the body, which can be fatal. In addition, the following complications may occur:
- disturbance of electrolyte metabolism;
- hypovitaminosis;
- lack of calcium;
- deficiency of potassium and other minerals;
- exhaustion;
- growth retardation;
- convulsions;
- poisoning of the body due to infectious etiology;
- renal failure;
- chronic diarrhea;
- acidosis;
- shock.
Treatment of childhood diarrhea
Parents need to understand how to properly stop diarrhea and when it is better not to do so. The reason for the development of diarrhea will influence what measures should be taken and why it is better to abstain.
The table below shows treatment recommendations depending on the factors that provoked the disorder.
| Causes of diarrhea | Principles of treatment |
| Intestinal infections | You should not use medications to stop diarrhea. You can take a sorbent such as “Activated carbon”. To properly treat intestinal flu, it is better to consult with your child. He will select suitable antiviral agents. |
| Food poisoning | Sorbents are used. The use of drugs that stop diarrhea, such as Loperamide or Levomycetin, is permissible only in case of severe watery diarrhea. It is important to provide the child with plenty of fluids and limit food intake. |
| Helminthiasis | It is important to consult a doctor to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. Treatment consists of eliminating the parasite. Treatment of diarrhea is symptomatic. It is important to restore the water-salt balance. |
| Drug-induced diarrhea | Stop all laxatives and other drugs that have side effects that weaken the intestines. If diarrhea develops after antibiotics, the use of bifido and lacto bacteria is recommended. |
| Gastrointestinal diseases | Self-medication is highly undesirable. A full examination and adequate treatment is needed. |
We recommend: What to do if a baby has diarrhea?
When treating diarrhea, it is important to stay hydrated. This is the most basic complication caused by diarrhea. When there are disorders, the intestines actively throw out water, trying to get rid of toxic compounds. As a result, the body loses a lot of water. And for small children this is a very dangerous condition.
Prevention measures
To prevent excessively loose stools, you must adhere to the following rules:
- monitor baby’s hand hygiene;
- thoroughly wash fresh fruits, vegetables, berries;
- thermally process dishes;
- disinfect rattles and other toys that the baby may put in his mouth;
- wash baby dishes with boiled hot water and then dry thoroughly;
- monitor the diet of the baby and mother while breastfeeding.
If your child develops watery diarrhea, contact the clinic immediately, because this may indicate the development of serious pathological disorders in the body. There is no need to rely on chance that everything will go away on its own. Remember, not only the future health of the baby, but also his life depends on this.
Previous Post How to use chamomile to treat diarrhea?
Next post How to treat diarrhea in guinea pigs?