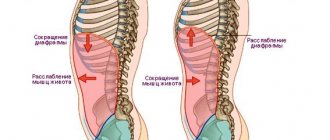
Pain in the stomach area, which appears after eating, sometimes occurs in completely healthy people. But more often it indicates the presence of certain problems associated with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Unlike hunger pains, “afternoon pains” are varied and have many causes.
Why does my stomach hurt after eating?
They do not necessarily occur immediately after the end of the meal. This group of pain sensations also includes those that appear an hour and a half after eating: when there is still food left in the stomach and the person has not had time to get hungry again.
They can occur after absolutely one type of meal, at the same time (for example, only after breakfast or only after dinner), after eating certain foods. Let's try to figure out why exactly this symptom occurs and how to get rid of it.
Stomach
Causes
Don't worry if this is a one-time occurrence and is definitely related to one of the reasons listed below. But it’s still worth reviewing your diet so that such episodes don’t happen again.
Provided there are no gastrointestinal pathologies, the stomach may hurt after eating due to:
- sprains due to overeating;
- a strong increase in the production of hydrochloric acid - when eating very fatty, heavy, spicy or sour foods;
- strong contraction of the stomach muscles.
Pain is one of the most common complaints in stomach diseases
There is no sharp pain, but what is more disturbing is aching pain combined with a feeling of heaviness
This symptom can be caused by individual intolerance to certain foods or food allergies. It is always associated with the use of a specific product or group of products. For example, lactose intolerance can be accompanied not only by bloating, rumbling and upset stools, but also by pain (appearing within an hour after drinking milk). Some other products work similarly. Which ones exactly can be identified if you try to remember everything you eat or keep a food diary.
Lactose and its intolerance
Comparison of normal digestion and lactose intolerance
Pain occurs in the presence of digestive diseases
- Chronic inflammatory disease of the esophagus, the stomach itself or the duodenum.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas.
- Acute infectious disease of the digestive system, food poisoning.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Tumor processes.
Tumor in the stomach
Pain after a moderate meal often occurs in those who are accustomed to washing down their meals with large amounts of liquid. At the same time, the volume of the stomach increases and the concentration of gastric juice decreases. Food takes longer to digest and stagnates in the stomach. Also, diluted gastric juice does not kill pathogenic bacteria that come from food. Because of this, an inflammatory process develops and diarrhea occurs.
Etiology
In gastroenterology, there are many predisposing factors for the appearance of stomach pain after eating, which is why they are usually divided into several large groups. The first of them is directly related to problems in the digestive system. Thus, the reasons may be:
- esophagitis - an inflammatory process in the mucous layer of the esophagus;
- gastritis of any nature;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum, stomach or esophagus. It is worth noting that if the first organ is affected, pain will appear several hours after finishing the meal, and in other cases – after about 15–30 minutes;
- appendicitis;
- GSD is a disease characterized by the formation of stones in the gallbladder or bile ducts;
- pylorospasm;
- pancreatitis and cholecystitis;
- gastroduodenitis;
- oncology;
- narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- pathologies of the spleen;
- chronic constipation and profuse diarrhea - in this situation, such manifestations act not only as a cause, but are also additional symptoms.
The second category of factors why the stomach hurts after eating includes those ailments that are not related to the gastrointestinal tract. These include:
- aortic aneurysm;
- a wide range of injuries, including fractures of the ribs or sternum;
- left-sided pleurisy;
- myocardial infarction.
The third group of reasons why stomach pain appears immediately or some time after eating includes physiological circumstances that are in no way related to the presence of a particular ailment. Among them:
- overeating - a large amount of food enters the stomach, which it cannot cope with;
- eating excessively cold or extremely hot foods;
- allergic reactions or intolerance to certain foods;
- poor nutrition – abuse of fatty, spicy and salty foods, as well as carbonated drinks and strong coffee;
- habit of drinking plenty of liquid with food;
- eating low-quality foods;
- eating a meal immediately before bed. Normally, the last meal should be at least two hours before bedtime;
- habit of taking a horizontal position after eating.
Types of pain
If there is an inflammatory process, the feeling of heaviness is not necessarily associated with overeating: even a small amount of food can cause irritation of the receptor apparatus of the gastric mucosa and submucosa. Sometimes the pain is strong and sharp - in this case the patient may be afraid of a serious illness. Based on the nature and time of pain, the possible cause of its occurrence can be determined.
| Feel | Possible reason |
| Sudden sharp pain that occurs within 30 minutes. | Indicates the presence of acute or chronic inflammation in the acute stage, cholecystitis, pancreatitis |
| Severe pain, burning sensation. | Chemical or thermal burn of the mucous membrane, food infection |
| Penetrating. | Indicates a perforation of the ulcer. Usually accompanied by other symptoms |
| Pain that resembles a burning sensation. | Gastritis, gastroduodenitis, ulcer |
| It's a dull pain. | Chronic gastritis |
| Spasmodic pain. | Duodenitis, ulcer |
| Constant aching, low-intensity pain. | Polyps, tumors, including cancer |
| Acute short-term pain (attack from a few seconds to a couple of minutes). | Diaphragm spasm |
| Cramping pain takes the form of short attacks. | Food infection |
| Pain that started in the upper part of the stomach, but after a few days went down. | Colitis |
For diagnosis, it is important to know exactly where it hurts. Diseases of the esophagus and gastritis of the upper part of the stomach radiate to the chest. The lower part of the stomach (above the navel) occurs with pyloritis, duodenitis, as well as with gastritis of the fundus of the stomach.
Video: 7 types of abdominal pain
Prevention and prognosis
To date, there are no specially designed preventive measures to prevent abdominal pain after breakfast or other food consumption.
The likelihood of illness can be reduced by following these simple rules:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- constant increase in immune resistance;
- body weight control;
- avoiding emotional exhaustion;
- taking medications strictly as prescribed by the clinician;
- early identification and treatment of any disorders that may lead to pain.
Do not forget about regular preventive examinations in a medical institution with visits not only to a gastroenterologist, but also to other doctors at least 2 times a year.
Abdominal pain after a meal can easily be treated with conservative therapy; patients often have a favorable prognosis. Ignoring or eliminating pain on your own can aggravate the problem, and refusing medical help will inevitably cause the progression of the underlying disease. The combination of such oversights is dangerous with negative consequences, even death.
What does the localization of pain and the timing of its onset indicate?
Chronic gastritis is the cause of pain during or in the first minutes after finishing a meal. The lower the painful inflamed area, the later the pain appears. Additional symptoms in these cases: belching sour ( gastritis ) or rotten ( duodenitis ), heartburn, heaviness, nausea, bloating.
Belching is a symptom of gastritis or duodenitis
A stomach ulcer makes itself felt approximately 30-60 minutes after eating. The earlier the pain appears, the closer to the esophagus the ulcerative damage is located. A duodenal ulcer signals itself with pain after an hour and a half after eating. Light foods cause pain almost immediately. Heavier ones (meat, baked goods, fatty foods) provoke pain a little later.
Stomach ulcer
Associated symptoms
Pain is often accompanied by:
- feeling of heaviness;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- bowel dysfunction;
- lack of appetite.
Lack of appetite
If at least 2-3 of them are observed, a disease of the digestive system can be suspected with a high probability.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Pain in the upper abdomen is not always associated with ailments of the stomach itself. Sensations in diseases of the pancreas and gall bladder are projected into this area.
Food poisoning
Acute pain appears suddenly and is often spastic in nature. Signs of poisoning appear either immediately (an hour and a half) or within 48 hours.
Food poisoning
Even mild poisoning is usually accompanied by nausea, belching, and heartburn. In more serious forms, vomiting occurs and there is a high fever. Usually, after vomiting, there is short-term relief, the pain decreases, but soon returns again - until the stomach is cleared of food and pathogenic bacteria.
Gastritis
The pain occurs immediately. Often this condition is accompanied by belching with the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus (reflux), which causes an additional burning sensation and nausea. With chronic gastritis, the pain may subside over time. Too spicy, sour, and heavy foods usually provoke discomfort.
Gastritis
During an exacerbation, pain can appear absolutely after every meal, regardless of its nature. Antacids help relieve pain.
Antacids
Duodenitis
Pain occurs after about half an hour, when the partially digested bolus of food moves towards the intestines. Nausea, often leading to vomiting, belching, heartburn, and stool disorders are accompanying symptoms.
Treatment of duodenitis
Peptic ulcer
It is characterized by hunger pains, but there are cases when they appear after eating - especially when overeating or breaking the diet. The pain is usually aching. An acute attack may indicate perforation of the wall of the stomach or duodenum .
Video - Peptic ulcer
Pancreatitis
Pain after eating food, especially after fatty and heavy food. An attack can last a long time - up to 8-12 hours (with severe overeating), and often radiates to the lower back. Additional symptoms include fever, nausea, and increased heart rate.
Pancreatitis
Cholelithiasis
The upper abdomen on the right side hurts, often radiating to the arm or shoulder. Occurs after eating foods that stimulate intense bile production. An attack of pain may result in vomiting mixed with bile.
Cholelithiasis
Polyps
Like benign formations, polyps cause irritation and spasm of the stomach walls. Hence the unpleasant symptoms. The feeling of fullness occurs even with small amounts of food and lasts a long time. The clinical picture is characterized by the same symptoms as in most gastrointestinal diseases.
Polyps in the stomach
Video - Polyps in the stomach
Stomach cancer
This disease is characterized by mild pain in the stomach after each meal, a feeling of heaviness combined with a sharp general weight loss against the background of an increase in abdominal volume. Vomiting with blood often occurs. In this case, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, since stomach cancer is a rapidly developing disease.
Factors predisposing to stomach cancer
Intestinal obstruction
The pain is moderate and occurs immediately or within the first 30 minutes after eating. Vomiting with the smell of feces is the main symptom by which obstruction can be distinguished from most gastrointestinal pathologies.
Intestinal obstruction
Localization of stomach pain
True pain in the stomach is localized in the iliac region and hypochondrium. However, after eating, pain can occur not only in the stomach itself. Often it radiates down the abdomen, into the hypochondrium, and into the back. Based on the location of unpleasant sensations, one can judge the presence of various diseases.
Pain in the middle of the upper abdomen and around the navel
It is a symptom of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. It can appear immediately, when eating certain foods, or 1.5-2 hours after eating.
Pain in the iliac region extending to the right hypochondrium
Characteristic of cholelithiasis, inflammation of the biliary tract and gallbladder. With these pathologies, discomfort in the stomach appears approximately 0.5-1.5 hours after eating food (sweet, fatty and fried).
Pain in internal organs is not only the stomach, there are many other vital organs under the right rib, find out more if you have pain in your right side under the ribs.
Do you constantly suffer from headaches in the back of your head? That way
Constant sharp pain in the solar plexus is not a very positive sign. You can find out all the information about symptoms here.
Pain in the pit of the stomach and in the left hypochondrium, in the upper abdomen in the midline
It is noted for peptic ulcer of the duodenum and stomach. It can be retrosternal, encircling, or radiate to the back. With a stomach ulcer it appears 1-1.5 hours after eating, with a duodenal ulcer - after 1.5-2 hours. It can be of almost any nature and be accompanied by a number of additional symptoms.
Dull or cutting constant pain high in the pit of the stomach and in the right or left hypochondrium
It is a symptom of pancreatitis. As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies, the pain becomes acute, can cause shock, and becomes girdling.
Suspicions of cancer of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
In the first stages of the disease, the patient does not experience any pain.
As the tumor develops, the pain becomes more pronounced, often accompanied by several of the following symptoms: loss of appetite and weight, persistent discomfort in the upper central abdominal area and a feeling of fullness, indigestion, heartburn, nausea and vomiting (sometimes with blood), enlargement belly sizes and others.
Early pain (immediately or within 1 hour after eating) is caused by diseases of the esophagus and stomach, late pain (after 1.5-2 hours) indicates problems with the intestines. Pain that appears an hour and a half after eating is most often stomach pain.
Additional symptoms
Based on the presence or absence of additional symptoms, one can judge the causes of stomach pain after eating:
- Heaviness, mild nausea, bloating - poor nutrition, insufficient production of gastric juice.
- Heartburn and burning, sour or belching with an unpleasant odor, together with nausea, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence can worsen gastritis.
- Sour or rotten belching are symptoms of gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis.
- Constipation or diarrhea, vomiting, weakness, fever, may be symptoms of food poisoning or an infectious disease.
Other diseases that cause stomach pain
Stomach pain can occur against a background of nervous exhaustion , neurosis , and anxiety . Also, some diseases can create the feeling that your stomach hurts. For example, moderate heart pain due to angina pectoris and heart failure can easily be confused with stomach pain, especially if the attack occurs after eating. With an acute heart attack, you may also experience a sensation of sharp pain in the stomach (some patients with ulcers may mistake the heart attack for a perforated ulcer).
Pylorospasm is a spasm of the pylorus, located between the stomach and duodenum; it is not based on gastric pathology. This condition occurs as a reaction to severe stress, with neuroses . Pain appears 20-30 minutes after eating - when food reaches the duodenum. After vomiting and complete emptying of the stomach, the pain stops until the next meal. In this case, the patient requires neurological and psychotherapeutic assistance.
Manifestations of neuroses - one of the causes of stomach pain
Symptoms
Due to the fact that pain in the stomach after eating food in the vast majority of cases is formed against the background of the presence of pathology, it is natural that pain syndrome will not be the only clinical manifestation.
Associated clinical manifestations are considered to be:
- constant heaviness in the stomach after eating and a feeling of fullness;
- bloating;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- nausea with frequent vomiting;
- increased gas formation;
- bowel dysfunction, which is expressed in alternating constipation and diarrhea or the predominance of one of these symptoms;
- heartburn and burning in the chest area;
- belching with a sour smell that does not stop for two hours;
- spread of pain throughout the abdomen, as well as in the back and upper body - chest, shoulder blades, neck and arms;
- temperature increase;
- weight loss;
- the appearance of blood impurities in stool or vomit;
- pale skin;
- weakness and malaise, which leads to decreased performance.
These are just the main signs that can complement the main symptom. If they occur, you should consult a gastroenterologist as soon as possible.
After eating, my stomach hurts. What to do?
This condition should not be tolerated, hoping that it will go away on its own, especially if the attacks of pain return and other digestive disorders are present. Also, you should not try to cope with the problem using traditional methods - they are only good if they are used as an auxiliary treatment if there is a clear diagnosis. Painkillers are not the answer: by masking the pain, you only make your condition worse. In addition, many painkillers additionally irritate the gastric mucosa and can cause inflammation.
"No-shpa" - a drug for stomach pain due to gastritis
Who should I contact?
A gastroenterologist treats diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and associated stomach pain . You should contact him first. He will conduct an examination and interview, and, if necessary, prescribe an additional examination or refer you to another specialist. You should not ignore the recommendations of a gastroenterologist regarding additional consultation with another specialist: for example, stomach pain is often associated with stress and occurs against the background of neurosis , in this case a consultation with a neurologist or psychotherapist will help. If a patient has problems with teeth, and pain occurs due to poorly chewed food, examination and treatment by a dentist cannot be avoided.
A gastroenterologist treats diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and associated stomach pain.
Diet recommendations
It is advisable for any person, even completely healthy ones, to build their diet in accordance with standard requirements. To reduce the risk of pathologies of the digestive system and, as a result, abdominal pain, it is important to eat the right foods and minimize the amount of junk food in the daily menu. All food should be rich in vitamins and valuable microelements. This is necessary to prevent hypovitaminosis and more serious diseases associated with a total deficiency of a particular substance.
Acute colic in the stomach indicates the possible development of gastritis or ulcers. For these diseases, special attention is paid to such a method of treatment as diet therapy. It is recommended to add more light soups and slimy porridges to the daily menu. Such food envelops the walls of the organ, relieves those that have already occurred and prevents possible pain in the stomach and diarrhea.
If the patient does not follow the doctor's advice regarding their diet, treatment may not be effective. The presence of a constant irritant in the abdomen provokes new attacks and worsening of ulcerative-inflammatory lesions. Pain after eating food indicates that it was of poor quality, too fatty, spicy, salty. Prohibited products include:
- fast food;
- smoked meats;
- alcohol;
- onion garlic;
- coffee;
- fried foods;
- dough products;
- sour fruits and vegetables.
People who smoke in the morning before meals are more likely than others to suffer from stomach pain. Nicotine irritates the receptors of the mucous membrane, and in the presence of inflammatory processes, aggravates their course. The culture of eating should be observed. Meals should be taken in small portions, but more often. While eating, chew large pieces thoroughly and avoid talking at the table.
Pain radiating to the back often demonstrates a pre-infarction state. People with cardiovascular diseases, no less than others, should adhere to a special diet. It is not advisable to eat store-bought semi-finished products. It is quite difficult to find a truly high-quality product, so it is better to prepare all the desired dishes yourself.
Localization of pain in the navel area clearly indicates inflammation of the appendix, in which it is better to abstain from food. And during the recovery process you will have to follow the rules of the diet. Sometimes it is useful to arrange a fasting day, which will help cope with general weakness and cleanse the body. This gives the organ a chance to heal on its own without the help of auxiliary aids.
The occurrence of abdominal pain is directly related to the patient’s lifestyle and errors in diet. In order to eliminate the risk of repeated relapses, you need to eat right, walk daily and protect yourself from emotional disorders.
Diagnostics
To determine whether stomach pain after eating is the cause of gastrointestinal pathology, you need to undergo several diagnostic measures.
A general blood test will help identify the presence of an inflammatory process, and will also give the doctor more detailed information about your condition. Based on this test, the doctor can recommend more specialized ones - those that will help identify problems in the digestive organs.
General blood analysis
FGDS ( fibrogastroduodenoscopy ) is a study of the condition of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a probe with a video camera at the end. This method allows the doctor to look inside the patient, assess the condition of the mucous membrane, and see possible foci of inflammation, ulcers, erosion, and neoplasms. Usually, during the procedure, a fragment of the mucous membrane is taken for examination. This helps determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection and the likelihood of cell degeneration.
Ultrasound of the stomach is another additional method that will help evaluate its functioning.
Ultrasound of the stomach
CT scans and x-rays of the stomach help identify the presence of benign or malignant tumors.
It is important to properly prepare for a visit to a gastroenterologist. The more accurate and complete your answers to the doctor’s questions, the faster he will be able to make a diagnosis and relieve you of stomach pain.
The most common questions at a gastroenterologist’s appointment regarding abdominal pain
- When exactly does the pain occur (while still eating, immediately after it, after some time - after 15-20 minutes, after an hour or more)?
- At what time of day is the pain worse?
- In what part of the abdomen is the pain localized?
- Does the pain symptom appear at other times - on an empty stomach, at night, in the morning?
- After what foods does the pain almost always occur/is more severe?
- Are you taking any medications? Did the pain appear when you started taking them or much earlier/later?
Stomach ache
Other questions for a gastroenterologist include the following:
- What additional symptoms are there? Describe even those that, in your opinion, are not even related to the digestive system;
- diet of the last days;
- What diseases or changes in condition do you have or have recently had?
Medical history
The doctor will also palpate the abdomen and prescribe additional examination.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor uses data from several examination methods. Only in this case will the diagnosis be as reliable as possible and the treatment effective.
Treatment
After the examination and confirmation of the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed individual therapy depending on the disease to treat stomach pain after eating.
Treatment options usually include:
- drug therapy;
- diet therapy;
- folk remedies.
From the material presented, it is clear that there are many diseases that can cause stomach pain, and to eliminate them you may need drugs with the opposite effect. Therefore, it is recommended to use medications to relieve an attack if the patient has already been examined, knows the cause of the disease and knows how to cope with it.
If you are not completely sure of what is happening, it is better not to take risks, not to select medications on your own, but to consult a doctor first.
If pain is severe, do not use anti-inflammatory or painkillers. These drugs distort the clinical picture. You can take a medicine that relieves spasms of smooth muscles, for example No-shpu.
A doctor also prescribes a diet appropriate for each disease, but while there are no recommendations, you can rely on the following lists.
You can't eat:
- all fresh vegetable, fruit or berry dishes;
- fresh baked goods;
- any types of smoked meats;
- sauces;
- pickles;
- chocolate and ice cream desserts;
- carbonated drinks, coffee, tea;
- unleavened milk;
- no cold, very hot, hard, fried, fatty or spicy foods.
You can eat:
- dried bread;
- semi-liquid, puree or slimy soups and porridges made from white rice, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- well-cooked beef, chicken, turkey, rabbit meat (after removing all the fat and the skin from the bird);
- a small amount of butter or vegetable oil;
- from vegetables - boiled potatoes, stewed cabbage, beets, carrots.
Dishes should be warm, unsalted or contain a small amount of salt. You need to eat in small portions, but often.
Some folk recipes
Olive oil. Effective fast-acting remedies include the use of olive oil. To relieve an attack, it is enough to take 1 dessert spoon orally. To treat gastritis or ulcers, you need to drink 1 dessert spoon of oil in the morning before meals for a month. It has a healing and analgesic effect.
Sea buckthorn oil. Recommendations for use are similar to olive oil.
Propolis . They can cure gastritis and ulcers by eating the therapeutic norm of 6 g daily on an empty stomach. The duration of treatment is 3 weeks.
Water infusion of cumin . Preparation: Pour boiling water over 2 tablespoons of seeds, leave for about half an hour, strain. Drink the solution warm during the day before meals. Relieves inflammation and soothes soreness.
Diet
If your stomach hurts after eating, you must first determine which foods cause this reaction. Some foods may cause moderate pain, while others may cause very severe pain. The following have an irritating effect:
- fatty meat , fried foods – increases the production of gastric juice and bile. Difficult to digest with a lack of pancreatic enzymes;
- spicy and sour foods, coffee And strong tea – irritate the mucous membrane, increase the secretion of gastric juice;
Strong tea
- sweets , baked goods - provoke fermentation, especially against the background of low acidity.
- roughage can injure irritated and inflamed mucous membranes.
Avoid Rough Foods
- alcohol – causes vasospasm, stimulates the production of gastric juice.
To reduce the likelihood of pain, you need to consume only approved dietary products - low-fat broths and soups , cereals , boiled vegetables , baked fruits , lean meat and fish , dairy products - only if the body accepts them well.
You need to eat in small portions, 5-6 times a day, drink enough water , and do not wash down your food .
Eating small portions
If unpleasant sensations occur daily or at least 3-4 times a week, you should seek medical help.
Causes of pain
It is no exception that cutting pain in the stomach is not associated with a specific pathology. In this regard, the nature of the pain, its relationship with food intake, localization and intensity, as well as duration are important. These indicators will help in determining the causes of pain in the stomach. Stitching sensations can be single and constant, weak and pronounced, long-term and short-term.
The causes of pain in the stomach can be divided into 2 groups: functional and pathological. The first are caused by a temporary disorder in the functioning of the digestive organs. The second group of causes of stabbing pain in the stomach combines various diseases that may be accompanied by such a symptom.
Acute pain in the stomach area can be caused by overeating. This is a physiological reason. When a person cannot stop eating, the stomach gradually becomes full and becomes unable to properly digest the incoming food. There is heaviness, bloating and pain. This is the result of overstrain of the abdominal wall muscles.
The connection between psycho-emotional stress and the normal functioning of the stomach has been proven for a long time. In stressful situations, excessive production of hydrochloric acid occurs, which can corrode the mucous membrane of the organ walls. Alcohol and smoking also have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the entire digestive system and on the condition of the stomach in particular.
Forty-proof alcohol destroys the walls of the digestive tract, disrupting the established process, causing a feeling of discomfort in the epigastrium. As a result of smoking, toxic substances accumulate in a person’s mouth, and when a person chews food, smoking products are absorbed along with saliva.
In addition, people who smoke are more likely to feel hungry, and gastric juice is produced regardless of food intake. As a result, this leads to the appearance of spasms.
Worm infestation also often causes abdominal pain. Its peculiarity is that it is localized in the navel area. The larvae of worms, while in the stomach, produce toxins, which are what cause spasms. But this is not the most common cause of stabbing pain in the stomach.
Often women suffer from exacerbation of diseases of the digestive system during pregnancy. Discomfort and stabbing pain in the stomach during pregnancy may be associated with pressure from the growing uterus on nearby organs. In this case, such symptoms will disappear after delivery.
The cause of stomach pain is dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract