Stomach pain stops after eating
Stomach » Diseases » My stomach stops hurting after eating.
Dad has been complaining about stomach pain for many years. Or rather, he calls them abdominal pain. Mom and I have long suspected an ulcer, but dad calls it gastritis.
But dad says that when he is hungry, his stomach hurts very much, but when he eats, the pain goes away. Therefore, now it has come to the point that dad even sneaks in at night to eat. Including, he can cook something for himself at night - if he wants. And if he eats something wrong (and this happens because he is against diets), then the attacks are terrible.
I’m not talking about the fact that (already not being thin) dad began to gain weight and is having difficulty with it. But he doesn’t want to go to the hospital. What does it look like? So what should I do? Dad is 44 years old.
The symptom of “hunger pain” is characteristic of peptic ulcer of the duodenum or antrum of the stomach. When eating, the exposed (damaged) area of the stomach or duodenum is covered (enveloped) with food, thereby preventing gastric juice from irritating pain receptors.
To treat “hunger pains,” instead of eating, you can try to give your father some enveloping agents (they create a film over the exposed area of the stomach that protects against the aggressive environment of the stomach) such as “Almagel A,” “Phospholugel.” They can also be taken before bed.
Also, banal jelly will also do)).
The next drug is Omez or omeprozole. “Proton pump” blockers prevent the stomach from producing excess hydrochloric acid, which in turn is abundantly produced during gastritis or ulcers.
Meals are fractional 5-7 times a day, small in volume. Mostly porridge soups, even better if they are made with milk. No fried salty stuff.
Well, explain to your father, “It’s better to swallow a small hose (FGDS) once than to then swallow it almost every week during hospitalization.” If there is an ulcer, it can make a hole and then it will be BAD!
Often the ulcer is accompanied by a bacterial infection, Helicobacter pylori. this disease is contagious and is transmitted through utensils (spoons and forks). So be careful too!
Hunger pain in the stomach, the reasons for which they appear can be very diverse, but in any case it is a symptom of pathological changes in the digestive system of the body.
The occurrence of pain is associated with the appearance of a feeling of hunger, when you want to eat again. After eating, the pain goes away, even with a minimal amount of food.
In terms of intensity, the pain syndrome, if the cause is not eliminated and treatment is not carried out, intensifies, becoming almost permanent.
Characteristics of pain
Pain on an empty stomach is a characteristic sign of gastric or duodenal ulcer. Also, hunger pain can be a concern with gastritis with increased secretory function. Often the location of the pain syndrome is the upper abdomen, sometimes even with a sensation of irradiation to the left hypochondrium.
The nature of the pain in the stomach can be aching, throbbing, which subsides for a short time with a certain position of the body, but then returns again. Pain syndrome, which manifests itself on an empty stomach, is one of the pathological phenomena of the disease of the digestive system of the body. As a rule, this is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- belching with sour stomach contents;
- nausea and vomiting, bringing relief;
- bad breath;
- decreased appetite;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- weight loss;
- nagging pain localized in the stomach area;
- bloating;
- discomfort or pain in the left hypochondrium;
- sleep disturbance;
- intestinal disorder, with alternating constipation and loose stools.
Causes of hunger pains
Hunger pain in the stomach is the result of the aggressive action of hydrochloric acid on the affected mucous membrane of the digestive organ. The causes of hunger pain in the stomach, which results in changes in the mucous membrane, can be very diverse, namely:
- pathological changes in gastric motility;
- change in the normal secretory function of the organ towards increasing the acidity of gastric juice;
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa in the area of the ulcer or gastritis.
The development of gastritis with increased secretory function or the ulcerative process is facilitated by certain prerequisites in the form of:
- hereditary factors;
- bacterial damage to the gastric mucosa by the pathogen Helicobacter pillory;
- prolonged stressful situation;
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- errors in eating with frequent consumption of spicy and salty foods;
- long-term course of treatment with medications for concomitant diseases that irritate the gastric mucosa.
All these factors contribute to the development of inflammatory, erosive, ulcerative processes in the digestive system of the body.
Why do you suffer from hunger pain until you eat? They are most often a sign of the presence of a peptic ulcer and appear at a specific time, that is, in the morning, at night, after meals, during the day at certain times.
This condition during hunger is relieved by taking milk or a small amount of food, as a result of which the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice, which irritates the area of the ulcer, decreases, and the pain then goes away. That is, in order to feel normal when hunger arises, you must definitely eat.
Important! The appearance of constant hunger pain in the stomach is a direct indication for examination by a gastroenterologist in order to exclude or confirm a gastric ulcer with the subsequent prescription of a course of treatment.
Diagnostics
If your stomach hurts in the morning, then this pathological phenomenon requires finding out the cause of its occurrence. To clarify the diagnosis, an objective examination of the patient, laboratory diagnostics and research using instrumental methods are carried out, which include:
- fibrogastroscopy of the stomach;
- radiography or fluoroscopy with barium;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI or CT – as an additional method for differential diagnosis;
- gastropanel;
- blood for hemoglobin, ESR, leukocytosis;
- according to indications - biochemical blood test;
- urine for general analysis;
- analysis of gastric juice for pH;
- bacterial culture for the presence of Helicobacter pillory.
After examination and clarification of the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment:
- antibacterial agents - in the presence of bacterial infection;
- antispasmodics – to relieve muscle spasms of the stomach;
- agents that regulate the acidity of gastric juice;
- painkillers;
- restorative medications, including vitamin therapy.
As a rule, after such an intensive course of treatment, pain in the upper abdomen should disappear and the patient's general condition will improve.
Success in treatment depends on compliance with the mandatory diet. The stomach stops hurting only if, in addition to drug therapy, you also follow a daily regimen that includes:
- fractional meals 5-6 times a day;
- eat in small portions, no more than 200 grams per meal;
- last meal three hours before bedtime;
- food processing is carried out by stewing or steaming;
- preference is given to puree soups, where all products are crushed to a mushy state;
- food must enter the stomach in ground form;
- complete cessation of smoking and drinking alcohol.
The following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- fatty meats and fish;
- confectionery;
- fresh white bread;
- smoked and canned products;
- butter;
- colored carbonated drinks, beer;
- strong black and green tea, coffee;
- all kinds of spices (onion, horseradish, garlic, mustard, pepper);
- citrus fruit;
- salted and pickled vegetables.
Following all the doctor’s recommendations for treatment with medications in combination with nutritional therapy ensures success in relieving pain caused by a disease of the body’s digestive system.
Treatment with traditional medicine
Treatment with medications of the underlying disease in order to relieve pain during hunger pain in the stomach can be supplemented with traditional medicine. Various herbal decoctions, teas, and mixtures can only be used after additional consultation with a doctor.
The course of herbal treatment lasts up to two months, subject to a strict diet. Regular use of the following recipes has a good effect on reducing hunger pains and normalizing stomach function:
- drinking 30 ml of freshly squeezed cucumber juice before meals;
- juice from plantain leaves – relieves pain during cramps;
- infusion of chamomile flowers - a tablespoon of dried flowers is brewed in a glass of boiling water, and then infused for two hours. You can take a glass instead of tea three times a day on an empty stomach and before meals during the day;
- dissolve cinnamon powder on the tip of a knife in water and use it as a remedy to relieve heartburn and help neutralize excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach;
- flax seeds - a tablespoon of seeds is brewed with a glass of boiling water, infused for one to two hours. After straining, take half a glass before meals. It has an enveloping and anti-inflammatory effect, protecting the gastric mucosa from the negative effects of hydrochloric acid;
- infusion of lemon balm and fireweed - equal proportions of dry herbs are brewed with a glass of boiling water, and the mixture is infused for two hours. Take half a glass three times a day, optionally adding a spoonful of honey to the infusion;
- oats - a glass of grain is filled with a liter of water at room temperature and infused for 8-12 hours, followed by boiling for half an hour. Take half a glass before breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Correct and comprehensive treatment on the recommendation of a doctor with subsequent dynamic observation gives good results in terms of health, ability to work and a positive prognosis.
Let's talk about one of the most common disorders: stomach pain. Is there anyone who has never suffered from this problem?
In the vast majority of cases, this is simply a malaise, but if the problem recurs and is associated with other symptoms, it should be a warning sign.
Let's look at what the possible causes of stomach pain may be and how to eliminate them.
Characteristics of stomach pain
Abdominal pain is a symptom that every person has encountered at least once in their life.
They often appear from trivial digestive problems or minor stomach illnesses, but sometimes, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, they can be a sign of more serious disorders.
Abdominal pain can affect people of any age, but it most often affects children and women of childbearing age.
Stomach pain can be divided into several types depending on the location, time of symptom onset and duration.
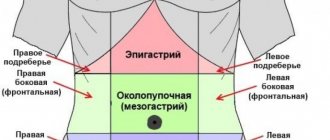
Depending on the anatomical position of the gastric pain, we have:
- Right-sided: typical for pathological processes in the pancreas and gall bladder.
- Left-sided: typical for pathological and non-pathological processes in the stomach and colon.
- Upper center (epigastric region): typical of pathological and non-pathological processes in the stomach, sphincter, gall bladder and even sometimes heart problems.
- Below (hypogastria): typical of pathological processes involving the first part of the small intestine, duodenum and gastroduodenal sphincter.
Depending on when it manifests itself, we may have the following types of stomach pain:
- Before meals: typical for diseases such as gastritis and non-pathological conditions such as excessive hunger.
- After eating: Typical for conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux and hiatal hernia, as well as non-pathological conditions such as slow and difficult digestion or excessive food intake.
- In the morning: may be caused by a feeling of hunger or acute and chronic gastritis or gastric ulcer.
- Evening: Abdominal pain that occurs in the evening or at night is typical of conditions such as acid reflux or hiatal hernia.
Source: https://moy-zheludok.ru/zabolevaniya/posle-priema-pishhi-perestaet-bolet-zheludok
Characteristics of pain
Pain on an empty stomach is a characteristic sign of gastric or duodenal ulcer. Also, hunger pain can be a concern with gastritis with increased secretory function. Often the location of the pain syndrome is the upper abdomen, sometimes even with a sensation of irradiation to the left hypochondrium.
The nature of the pain in the stomach can be aching, throbbing, which subsides for a short time with a certain position of the body, but then returns again. Pain syndrome, which manifests itself on an empty stomach, is one of the pathological phenomena of the disease of the digestive system of the body. As a rule, this is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- belching with sour stomach contents;
- nausea and vomiting, bringing relief;
- bad breath;
- decreased appetite;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- weight loss;
- nagging pain localized in the stomach area;
- bloating;
- discomfort or pain in the left hypochondrium;
- sleep disturbance;
- intestinal disorder, with alternating constipation and loose stools.
Hunger pain in the stomach: all causes, treatment, complications
Hunger pain in the stomach is a fairly common symptom that is often undeservedly ignored. Many patients confuse the discomfort in the pit of the stomach that occurs on an empty stomach with a normal feeling of hunger. But even when severe hunger pains appear in the upper abdomen, the situation does not change - the person simply “eats” them and continues to go about his business as if nothing had happened.
The insidiousness of hunger pains in the stomach is that they serve as the first signal of serious diseases of the upper digestive tract. How to cope with hunger, which has crossed all acceptable limits, we will talk in this article.
Causes of hungry stomach pain
The most common and most “harmless” cause of pain in the upper abdomen on an empty stomach is gastritis , or inflammation of the gastric mucosa.
Due to the dietary habits of the urban population, vulnerability to prolonged psycho-emotional stress and lack of time for regular preventive examinations, this disease occurs in almost every third person.
Chronic gastritis is so widespread that even some doctors treat it not as a disease, but as something completely natural and harmless. This is a deep misconception : without proper treatment, gastritis can lead to a number of complications, including:
- gastric ulcer , which always occurs against the background of an inflammatory process;
- iron deficiency anemia due to slight bleeding from erosions (small superficial ulcerations of the mucous membrane) over a period of months or even years;
- B12 deficiency anemia , which may well result in severe damage to the spinal cord (funicular myelosis);
- increased vulnerability to intestinal infections and the occurrence of food allergies ;
- high risk of developing stomach cancer , and so on.
The mentioned peptic ulcer is another common cause of hunger pain in the stomach. This symptom is more typical for the localization of an ulcer in the duodenum; it is known that in this case, eating food significantly alleviates the condition of patients, in contrast to patients with stomach ulcers - food often only makes them worse.
Other, more rare causes of abdominal pain on an empty stomach include:
- chronic pancreatitis, or inflammation of the pancreas (pain may shift to the left side);
- biliary dyskinesia (displacement to the right side);
- anxiety spectrum disorders;
- bulimia, etc.
It should be remembered that hunger pain can also be caused by completely natural reasons - for example, after very spicy food or drinking too much water.
Associated symptoms
The mechanism of development of hunger pain in the epigastrium has long been known. Under the influence of the reasons described above, gastric peristalsis (that is, contraction of its walls) increases significantly, which stimulates impulses in the medulla oblongata.
Which nerve centers are activated is one of the key differences between hunger pain and true hunger - in the second case, the hypothalamus is stimulated.
Painful sensations can occur at different times of the day. So, with a duodenal ulcer, especially intense hunger pains begin closer to the night , which is why patients are literally drawn to the refrigerator. Fasting only increases the severity of painful sensations, so with this disease there may be pain in the morning .
With chronic gastritis, there is no pattern in the occurrence of discomfort - it can occur at any time .
Patients often note a number of additional symptoms:
- a feeling of rapid satiety, regardless of the intensity of hunger (sometimes one piece of bread can help even in cases where a person thinks that he can eat an elephant);
- nausea , which increases the degree of discomfort ;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- belching of air and regurgitation , or "regurgitation" of small amounts of gastric contents after eating (due to increased gastric motility, especially in gastroesophageal reflux disease);
- heartburn (due to the reflux of acidic gastric juice into the esophagus);
- flatulence , or bloating with excess gas formation in the intestines (with reduced secretion of hydrochloric acid, or hypochlorhydria, fermentation processes intensify in the small and large intestines);
- weight loss or uneven fat deposition (for example, an increase in waist size with thin arms and legs) due to impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestines;
- diarrhea and other stool disorders.
Help at home
If a person experiences hunger pain in his stomach, do not torment him - let him eat . The choice of food is yours, but it is better to refrain from fatty, spicy, fried and smoked foods.
It is best to cook slimy porridge in milk (for example, oatmeal or rolled oatmeal) - it will not only satisfy hunger, but also form a protective film on the gastric mucosa that will prevent the action of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice.
Low-fat soups, steamed cutlets and boiled vegetables will also be useful.
If it is not possible to eat, but you have access to a first aid kit, you can take any antacid drug in the form of an emulsion - Phosphalugel, Almagel or Gaviscon. These medications protect the gastric mucosa from an aggressive acidic environment and act for 3-4 hours. If antacids do not help, then it is very likely that you are simply faced with severe hunger.
What not to do when you have stomach pain when you are hungry:
- “Wash down” the pain with water - the liquid will quickly pass into the duodenum, enhancing gastric motility. As a result, the malaise will only intensify.
- Smoking . Nicotine increases the secretion of hydrochloric acid and stimulates peristalsis, and tobacco tar has an extremely negative effect on the condition of the mucous membrane. In fairness, it should be noted that for some people, smoking dulls, rather than provokes, hunger.
- To drink coffee . The caffeine and aromatic compounds contained in coffee are an enormous burden for a hungry stomach. Of course, during the first 30-60 minutes the pain will subside, but then it will resume with the same force. Remember that coffee itself can cause severe abdominal discomfort.
- Take NSAIDs such as Analgin, Nurofen, Ketorol and so on. These drugs have a detrimental effect on the condition of the gastric mucosa and themselves provoke the formation of ulcers. For abdominal cramps, it is best to take No-Shpu.
- Be patient and think that everything will go away on its own. If hunger pain is caused by an ulcer, then increased contraction of the stomach walls will only worsen the condition.
Conclusion: If you often suffer from hunger pangs and have no access to home-cooked food, always have at least a candy bar or a packet of cookies with you.
Treatment under medical supervision
If you experience frequent abdominal pain on an empty stomach, you need to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist and have a gastroscopy. A thorough diagnosis will help identify the cause of discomfort and prescribe adequate therapy.
Drug treatment for hunger pain in the stomach depends on the underlying disease. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- Antacids (described above).
- Antiulcer drugs of various groups aimed at suppressing the secretion of hydrochloric acid (omeprazole, pantoprazole, esomeprazole, ranitidine and others).
- Antibiotics if gastroscopy results confirm Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Prokinetics that normalize gastrointestinal motility. These drugs also have an antiemetic effect (Cerucal, Motilium).
- Antidepressants and anxiolytics , if it is proven that the discomfort is due to depression or anxiety disorders.
Some patients self-prescribe treatment for hunger pain in the stomach using folk remedies. For this purpose, a wide variety of recipes are used, including daily consumption of cucumber juice on an empty stomach and a decoction of St. John's wort, whose components can cause persistent disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Practice shows that treatment with traditional medicine methods does not alleviate the condition, but only contributes to the worsening of the disease.
During drug treatment, you should follow a special diet appropriate to the diagnosed disease. Otherwise, the therapy will be ineffective.
You may also like
Source: https://zhivotu.net/golodnye-boli-v-zheludke/
Diagnostics
Only a gastroenterologist can find out the causes of pain after eating in a child or adult and prescribe the most effective treatment.
Given the existence of a wide variety of predisposing factors, the process of making a correct diagnosis should only take an integrated approach. The first stage of diagnosis consists of manipulations that are performed directly by the clinician:
- familiarization with the medical history - to determine the influence of the pathological factor;
- study of life history - to clarify the impact of predisposing sources that have a physiological basis;
- deep palpation and tapping of the anterior wall of the peritoneum;
- measuring temperature and pulse, heart rate and blood tone;
- a detailed survey of the patient will enable the doctor to draw up a complete symptomatic picture, determine the location and nature of the pain, which may indicate an underlying disease.
- general clinical blood test;
- microscopic examination of feces;
- bacterial tests;
- immunological tests;
- PCR diagnostics;
- blood biochemistry.
Abdominal pain goes away after eating
Hunger pain in the stomach, the reasons for which they appear can be very diverse, but in any case it is a symptom of pathological changes in the digestive system of the body.
The occurrence of pain is associated with the appearance of a feeling of hunger, when you want to eat again. After eating, the pain goes away, even with a minimal amount of food.
In terms of intensity, the pain syndrome, if the cause is not eliminated and treatment is not carried out, intensifies, becoming almost permanent.
What to do if your stomach hurts
If the pain is on the left side, under the ribs, the stomach is most likely to blame. It can make itself felt for a number of reasons - both safe and not so safe.
But there are often cases when pain signals problems with completely different organs.
When to see a doctor immediately
Call an ambulance if the pain in the stomach area is severe and accompanied by the following symptoms:
- you experience discomfort and tightness in your chest;
- you suspect that the pain may be related to a recent blow to the stomach;
- your temperature is above 38 °C;
- there is constant vomiting or vomiting of blood;
- the skin on the body has turned yellow;
- you are experiencing breathing problems;
- You are pregnant.
An ambulance is not needed, but try to get an appointment with a therapist as soon as possible if:
- the pain is not severe, but lasts 2–3 hours or longer;
- the stomach is sensitive to touch;
- in addition to the pain, you notice that you need to go to the toilet more often than usual, or the pain intensifies when you urinate.
If there are no alarming symptoms, relax.
Most pain in the stomach area is not dangerous and, most likely, this is your case.
Nevertheless, it is worth understanding what exactly causes discomfort in the upper left part of the abdomen, so as not to miss dangerous “bells”.
Why does my stomach hurt?
Here are some of the most common reasons.
You swallowed air
This often happens, for example, with those who like to chew gum. Excess air in the stomach can cause muscle spasms and pain.
What to do about it
Wait it out. Pain due to stomach spasms is usually not severe and quickly goes away on its own. If they recur regularly, be sure to consult a physician or gastroenterologist. He will find out why air gets into the stomach and tell you what to do about it. For example, he will suggest giving up chewing gum, changing your diet, or taking medicine that reduces the amount of gas.
You have stomach (intestinal) flu
This is the colloquial name for gastroenteritis - an inflammatory process in the stomach. As a rule, its causative agents are viral infections. Stomach flu, in addition to abdominal discomfort, is accompanied by diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and fever - sometimes slight.
What to do about it
If the stomach flu is caused by a virus, it is treated only symptomatically: do not allow dehydration, and prescribe antiemetic drugs. However, only a doctor can diagnose viral gastroenteritis and prescribe treatment. Don’t try to do anything on your own - you could make a mistake and worsen your condition.
You ate something wrong
In addition to viral gastroenteritis, bacterial gastroenteritis is also common. In this case, the inflammatory process in the stomach is caused by bacteria that enter it with food - the same salmonella.
There are other ways to get gastroenteritis:
- take a sip of water from a dirty pond full of parasitic microorganisms;
- drink or eat something that contains heavy metals - arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury;
- get too carried away with sour foods - citrus fruits or tomatoes;
- take certain medications - certain antibiotics, antacids (stomach acid reducers), laxatives, chemotherapy drugs.
What to do about it
Let us repeat: if you have symptoms of gastroenteritis, be sure to consult a physician. The bacterial form of the disease is treated only with antibiotics. Other types require their own treatment strategies. Only a qualified physician can accurately establish a diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy.
You have indigestion (dyspepsia)
This is the name for the feeling of fullness and discomfort that occurs in the stomach after eating. This is a common problem, and it is often impossible to immediately determine its causes. And they can be different:
- binge eating;
- poorly chewed food;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- chronic constipation;
- smoking;
- stress, fatigue;
- taking medications - the popular aspirin and some other painkillers, birth control pills, some types of antibiotics, steroids, thyroid medications;
- a condition known as irritable bowel syndrome;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- diabetes;
- stomach cancer.
What to do about it
As you can see, indigestion can have dangerous causes, so it should not be ignored. If dyspepsia recurs regularly, be sure to consult a gastroenterologist.
You have heartburn
It is also known as gastroesophageal reflux. This is the name for a condition in which the contents of the stomach, along with acidic gastric juice, enter the esophagus. In addition to discomfort in the stomach area, a person feels a burning sensation in the middle of the chest.
Most often, heartburn depends on the diet: for example, it appears after drinking coffee, carbonated drinks, fatty and spicy foods. But sometimes it is the first symptom of serious diseases - stomach or esophageal ulcers, cancer and even heart attack.
What to do about it
If heartburn is a one-time occurrence, there is no need to worry. But if it recurs, and is also accompanied by other symptoms - nausea, loss of appetite, difficulty swallowing, consultation with a gastroenterologist is required.
You have gastritis or a stomach ulcer
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining. In the initial stages, it is accompanied by the same symptoms as indigestion, heartburn or stomach flu, so only a physician can diagnose gastritis itself. Noticeable pain appears only if the mucous membrane is already severely damaged or gastritis has developed into a stomach ulcer.
What to do about it
Go to a gastroenterologist with complaints. The doctor will send you for tests that will help establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. You should not delay this in case of gastritis, as it increases the risk of developing stomach cancer.
You have stomach cancer
It is difficult to diagnose this most dangerous disease in the early stages. Like gastritis, cancer hides behind innocent symptoms, including:
- frequent and prolonged heartburn;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating, as with dyspepsia;
- nausea, slight drooling;
- loss of appetite.
What to do about it
Understand that any regular symptoms cannot be ignored. If you have discomfort and pain in the stomach area (even if they do not seem serious to you), be sure to consult a doctor.
You have problems with other organs
The left hypochondrium contains not only the stomach. The pancreas, bile ducts, spleen, left lobe of the liver can hurt...
In addition, the organs in the abdominal cavity are closely connected: pain in one radiates to the other. Therefore, if there are strong cutting, stabbing sensations in the left side, it could be:
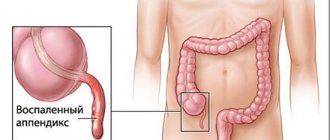
- appendicitis;
- pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
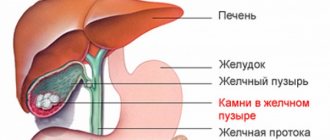
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts of the liver);
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder);
- duodenal ulcer;
- kidney stone disease;
- colitis and other pathologies of the large intestine...
What to do about it
Don't tolerate it. Any acute pain in the stomach area, especially if it recurs or lasts longer than a couple of hours, fading and reappearing, is a reason to visit a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. Your life may depend on this visit. Don't take risks.
Source: https://Lifehacker.ru/bolit-zheludok/
Symptoms associated with stomach pain
Stomach pain may be associated with certain symptoms, which can guide the doctor towards a correct understanding of the cause and then towards the correct diagnosis, which will become the basis for planning effective treatment.
Among the symptoms that may accompany abdominal pain we have:
- Diarrhea: Often occurs when stomach pain is caused by stress, anxiety, or gastroenteritis.
- Cough: A cough can be a consequence of esophagitis or nervousness, in which case it is called a nervous cough.
- Vomiting and nausea: Often present in cases of gastroenteritis, but also appears in stress gastritis.
- Burning: This is a typical symptom of acute gastritis, erosive gastritis, gastric ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux and hiatal hernia. It can also occur in case of prolonged fasting or anxiety and stress.
- Blood in the stool: this symptom is closely related to the presence of erosive gastritis and stomach ulcers.
- Belching: Occurs in cases of gastroesophageal reflux and hiatal hernia.
- Tachycardia: In case of stressful stomach pain, a rapid heartbeat may occur.
- Fatigue: If you are suffering from extreme fatigue and stomach pain at the same time, it is possible that stomach erosion is leading to blood loss and decreased hemoglobin concentration, which is the reason for feeling tired and tired.
- Fever: Fever is associated with abdominal pain in all cases of gastroenteritis.
- Back pain: If stomach pain is associated with back pain at the level of the kidneys, the cause may be problems with the gallbladder or pancreas.
- Chest pain: When you have both chest pain and stomach pain, this is an indication to seek emergency help, as it could be a heart attack.
Causes of hungry stomach pain, diagnosis and treatment
Hunger pain in the stomach, the reasons for which they appear can be very diverse, but in any case it is a symptom of pathological changes in the digestive system of the body.
The occurrence of pain is associated with the appearance of a feeling of hunger, when you want to eat again. After eating, the pain goes away, even with a minimal amount of food.
In terms of intensity, the pain syndrome, if the cause is not eliminated and treatment is not carried out, intensifies, becoming almost permanent.
Prevention and prognosis
To date, there are no specially designed preventive measures to prevent abdominal pain after breakfast or other food consumption.
The likelihood of illness can be reduced by following these simple rules:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- constant increase in immune resistance;
- body weight control;
- avoiding emotional exhaustion;
- taking medications strictly as prescribed by the clinician;
- early identification and treatment of any disorders that may lead to pain.
Do not forget about regular preventive examinations in a medical institution with visits not only to a gastroenterologist, but also to other doctors at least 2 times a year.
Abdominal pain after a meal can easily be treated with conservative therapy; patients often have a favorable prognosis. Ignoring or eliminating pain on your own can aggravate the problem, and refusing medical help will inevitably cause the progression of the underlying disease. The combination of such oversights is dangerous with negative consequences, even death.
Source