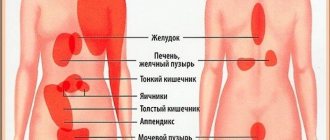
Heaviness in the lower abdomen in women can be caused by many factors. Among the causes that cause abdominal discomfort, there are both banal overeating and serious pathologies of internal organs. Pain in this area should not be ignored. A negligent attitude towards health triggers irreversible processes in the body and requires long-term treatment.
Heaviness in the lower abdomen in women
Etiology
Many organs are concentrated in the lower pelvis, among which the intestines, organs of the reproductive and urinary systems play a huge role in the functioning of the body. When discomfort appears in the lower part of the peritoneum, it is difficult to identify the source of its occurrence without qualified help. Disease of any organ located in this part of the abdomen can manifest itself with similar symptoms.
Among the most common are the following:
- dysmenorrhea;
- gynecological diseases;
- infections and inflammations of the genitourinary system.
While pregnant, a woman may also experience pain in the lower abdomen. Intestinal diseases and spinal pathologies often manifest themselves through pain in this part of the abdominal cavity.
Symptoms
A feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen is accompanied by various other symptoms that are associated with the primary source of development of the symptom:
- intestinal problems - decreased appetite and nausea;
- pathologies of the biliary system and liver - characterized by the appearance of a bitter taste in the oral cavity, headaches, discomfort in the liver area;
- infections of the pelvic organs - manifested by chills, high fever, a feeling of pressure in the rectum;
- disruption of the urinary system - characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, frequent and painful urination, and the presence of blood in the urine;
- problems during pregnancy - manifested in pale bloody or dark brown discharge from the genital tract, weakness in the body, pain during physical exertion.
Types of pain
Pain that occurs in the lower abdomen of women is divided into several types:
- sharp, cutting;
- dull;
- cramping;
- incessant;
- pulsating.
During the initial examination, doctors focus on the location of pain and the intensity of its manifestation.
Based on the characteristics of pain and presenting symptoms, a specific disease can be diagnosed.
Table 1. Symptoms and possible diseases
| Symptoms | Most likely disease |
| Dull pain accompanied by bloody discharge unrelated to menstruation | Inflammatory process of the genitourinary system |
| Prolonged pain, intense vaginal discharge and increased body temperature | Infectious diseases of the pelvic organs |
| Constant pain due to urinary problems | Urinary tract diseases |
| Cramping pain alternating with vomiting and lack of appetite | Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract |
| Periodically increasing pain lasting a long period of time and fever | Inflammation of the appendix |
Dysmenorrhea
Premenstrual syndrome is expressed through migraine attacks, nervousness, mood swings, weakness and pain in the lower abdomen. Manifestations of this kind both precede and accompany menstruation. These days, the stomach may increase in volume. If there is excessive production of a hormone that causes uterine contractions, the intensity of the pain increases.
Dysmenorrhea often causes heaviness in the lower abdomen
In nulliparous women, dysmenorrhea is considered primary. After the baby is born, the discomfort goes away and the cycle stabilizes. Representatives of the fair sex who have reached the age of 30 experience secondary dysmenorrhea. It is triggered by disruptions in the functioning of the uterus, operations or the formation of tumors.
Means to reduce heaviness in the lower abdomen in women
Since dysmenorrhea is a natural process occurring in the body, you can try to relieve the discomfort yourself. It is quite problematic to completely relieve the pain syndrome. It seems possible only to take measures aimed at reducing it. Folk remedies and special exercises successfully cope with this task.
A decoction of St. John's wort is an excellent remedy for heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen.
The following herbal decoctions will help cope with pain:
- Crushed leaves of St. John's wort, calendula and chamomile flowers brewed in equal parts.
- Dried dandelion roots, soaked for 20 minutes in a water bath.
- Pharmacy tincture of calendula.
- Green tea flavored with a pinch of mint and lavender.
- A collection of chamomile, mantle, rose petals, calendula and nettle.
- A mixture of oak bark and valerian.
Decoctions should be taken 3 times a day before meals. Herbs should be brewed at the rate of 20 g. for 1 glass of boiled water. Taking B vitamins, zinc, magnesium and calcium is also beneficial during this period.
In addition to traditional medicine, it is useful to do physical exercises aimed at improving the condition.
A combination of the following exercises provides significant pain relief:
- From a kneeling position, with your hands on the floor, rotate your pelvis in different directions. Recommended execution time is 5 to 7 minutes.
- Sitting on the mat, straighten your back and touch your heels. From this position, you need to try to raise your legs to your stomach about 25 times in a fast rhythm.
These simple movements help improve blood flow in the internal organs and reduce discomfort. If you have severe pain, you should visit a gynecologist.
Treatment
After the patient has been diagnosed and the exact source of the unpleasant symptom has been established, the physician can eliminate the feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. To quickly relieve discomfort, doctors recommend:
- do not drink too much water while eating;
- Chew or crush foods thoroughly before eating;
- do not overeat;
- choose natural and healthy products;
- engage in light physical activity;
- to walk outside;
- keep the house clean and tidy.
Further treatment is prescribed by doctors depending on the diagnosed provoking factor. If there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, the patient is recommended to follow a gentle diet and use special medications. Drug treatment for heaviness in the lower abdomen is prescribed not only for pathology of the stomach or intestines, but also for other ailments.
Quite often, to relieve painful attacks, patients need to take antispasmodics or painkillers. To eliminate the cause of the development of the symptom, doctors prescribe medications on an individual basis, based on the characteristics of the body and the course of the disease.
Gynecological diseases
In most situations, discomfort in this area of the peritoneum is caused by gynecological pathologies. The most common diseases include inflammatory processes of the reproductive system.
Fibroids often cause a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen
Table 2. Possible diseases
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Vaginitis | It is characterized by a feeling of heaviness both in the lower abdominal cavity and over the entire surface of the vagina. Accompanied by excessive vaginal discharge caused by exposure to fungal microorganisms and staphylococci. |
| Endometritis | Inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa. It manifests itself through increased body temperature, disruption of the vaginal microflora and heaviness in the peritoneum. Benign tumors also cause discomfort in this part of the abdomen. |
| Endometriosis | The growth of endometrial cells, which promotes the extension of tissue beyond the uterine area. Heaviness and discomfort in the affected organs is especially pronounced before the onset of menstruation. |
| Cysts | Despite the fact that the formation of cysts, as a rule, is asymptomatic, a “heavy” abdomen often serves as an alarm bell for an unpleasant disease. |
| Uterine fibroids | A benign tumor formed on the basis of connective tissue. Large-sized formations lead to excess pressure on neighboring organs, which provokes malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system. The painful sensations are not very pronounced. Pathology manifests itself through heaviness in the lower abdominal region. |
In addition, abnormalities of the reproductive system organs can cause discomfort.
What pathologies are characterized by discomfort in the pelvic area?
If we talk about the causes of heaviness in the lower abdomen in a theoretically healthy woman, then the first thing that should be remembered is the intestines, located directly from the navel down. Accordingly, severe discomfort in this area may directly indicate problems in the digestion process or a deterioration in the condition of the organ itself. The bladder and genitals also need to be taken into account. And if the severity shifts to the side, problems with the gallbladder, kidneys, and pancreas cannot be ruled out.
- Before the start of the menstrual cycle and in its first days, heaviness may be accompanied by a feeling of pain in the legs, pressure and the inability to move freely. This is blood pressure on the pelvic organs and/or a surge in estrogen, which usually does not indicate any serious pathologies if it is a temporary and short-term phenomenon.
- The severity accompanied by pain should already alert you, especially if vaginal discharge is added to it: symptoms characteristic of inflammatory processes of the genital organs, endometrial detachment, neoplasms in the uterus or ovaries.
- Problems with the pelvic vessels also often make themselves felt by heaviness, pain, and a feeling of paralysis of the lower extremities. Increased discomfort is observed after active walking, physical activity, and maintaining a stationary (especially sitting) position.
Pregnancy
In most cases, pain in the lower abdomen is physiological in nature. There may be several reasons for discomfort during pregnancy:
- natural stretching of the uterus during fetal development;
- pressure from the enlarged uterus on neighboring organs;
- stretching of the ligaments supporting the uterus.
Pregnancy is often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen
Unpleasant sensations in the abdomen vary depending on the phase of pregnancy. Already from the first weeks after conception, the uterus begins to grow. In the early stages, severity is caused by internal changes in the body. Attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus is accompanied by a slight nagging pain.
In later stages, heaviness in the lower abdomen is caused by the uterus pressing on the bladder and intestines. Discomfort in the last weeks of gestation is caused by stretching of the abdominal muscles, which do not have time to adapt to the rapid growth of the child.
If heaviness in the peritoneum is accompanied by severe pain, these may be the consequences:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- early placental abruption.
Unpleasant symptoms of pregnancy failure also include dark brown spotting, severe weakness, and increased pain with minor physical exertion.
If the placenta detaches prematurely, discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen are inevitable.
Failed miscarriages are especially dangerous. The embryo remains in the uterus and is saturated with blood, which leads to cramping pain in the lower abdominal cavity. The condition requires immediate surgical intervention.
To reduce pain during pregnancy, the expectant mother needs frequent walks in the fresh air and a well-planned diet.
Pain due to disorders in the genital area
Gynecologists divide lower abdominal pain in patients into functional (physiological) and organic. Functional reasons are caused by temporary underdevelopment of the genital organs in girls, associated with menstruation, pregnancy. They are associated with excitement, hypothermia, and the onset of sexual activity.
Organic causes always manifest themselves in acute or chronic pathology of the uterus and appendages. The pain varies in nature and may be accompanied by uterine bleeding and vaginal discharge.
Differences between physiological pain and organic pain:
- lack of a clear connection with the previous action, spontaneous onset and disappearance;
- short-term nature;
- moderate intensity;
- relatively satisfactory health.
Secondary dysmenorrhea, which depends on the pathology of the uterus and appendages, must be distinguished from physiological causes.
Physiological pain in women
To figure out why a girl’s lower abdomen hurts before and during each menstruation, gynecologists will need to study the patient’s hormonal levels and regimen. Primary algodismenorrhea is associated with functional disorders caused by underdevelopment of the endocrine and nervous systems.
In girls, the production of prostaglandins and estrogens increases, which increase uterine contractions. It is often observed with overload in studies, little physical activity, poor diet (coffee, sandwiches, chips), and emotional stress.
In 75% of cases, the diagnosis is defined as “premenstrual syndrome”. In addition to pain, a few days before menstruation, the following occur:
- headache and nausea;
- dizziness and fainting;
- vomit;
- The mammary glands swell and hurt.
During pregnancy, pain is caused by stretching of the ligamentous apparatus. Most often they bother primiparous women over the age of 25 with poor physical fitness.
It is impossible to exclude the occurrence of an acute disease or an exacerbation of a chronic disease during pregnancy, therefore every expectant mother is obliged to closely monitor her well-being and inform the doctor about any changes.
Ovulation pain occurs on days 14–15 of the normal menstrual cycle. Lasts for several hours or days. Women experience regular nagging pain in the lower abdomen that intensifies during sexual intercourse. They are caused by hormonal changes with increased blood supply to the ovary. Usually one-sided. Women require observation by a gynecologist.
Pain due to pathology of the genital organs in women
Organic pain, depending on pathological changes in the uterus and appendages, is provoked by: hypothermia, heavy physical work, sports, increased nervous tension, and the use of intrauterine contraceptives.
Adenomatosis (endometriosis) is caused by the proliferation of epithelium from the inner layer of the uterus into the muscular layer. The most affected are nulliparous women over 30 years of age and those suffering from infertility. Symptoms are associated with constant nagging pain above the pubis, prolonged menstrual bleeding, and brown vaginal discharge.
The epithelium forms “pockets”. Menstrual blood gets into them and puts pressure on the surrounding tissue. Therefore, during menstruation, the pain intensifies, radiating to the groin and lower back.
Hormonal drugs are used for therapy.
During pregnancy, a woman with endometriosis is constantly monitored to exclude placental rejection.
Inflammatory diseases (endometritis, adnexitis) are accompanied by bursting or cramping constant pain. With adnexitis (inflammation of the ovary), the pain is one-sided. Irradiation to the sacrum and lower back is observed, and the general condition worsens.
The risk of inflammation is highest in women:
- who have undergone diagnostic curettage and abortion;
- refusing long-term therapy.
Additional signs include:
- weakness, dizziness;
- muscle pain;
- temperature increase;
- unpleasant odor from vaginal discharge due to an admixture of pus;
- insomnia;
- irritability.
In 60% of women, inflammation is caused by a sexually transmitted infection. Treatment must include a temporary cessation of sexual intercourse and examination of the partner.
Congenital and acquired anomalies - in girls they are detected during a painful first menstruation (contamination of the vagina, cervix). The accumulation of blood in the cavity causes expansion and constant pain. In adult women, blood retention is facilitated by the curvature of the uterus (retrodeviation) and fusions in the cavity (synechia).
Girls need to be shown to a gynecologist and examined urgently. Special exercises are selected for women, and if the situation cannot be corrected, surgery is performed.
Tumors of the genital organs in women have benign growth and a malignant course. Benign ones include cysts and fibroids. As they grow, they stretch the organ and cause bursting pain. At the same time, stretching of ligaments and adhesions (in case of chronic inflammation) takes part in the mechanism.
Manifestations can be an acute attack due to cyst torsion or rupture. In this case, the pain is one-sided, accompanied by dizziness and nausea, and shock is possible. With fibroids, the pain is accompanied by severe uterine bleeding and signs of anemia.
Malignant tumors of the appendages are accompanied by bilateral localization, intensity in stages II–III. Signs of cancer intoxication appear:
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- hormonal disorders;
- weakness.
Unilateral pain is caused by fallopian tube cancer. Early symptoms include intermittent, profuse, watery discharge. Uterine sarcoma is detected during examination for uterine bleeding. The tumor is characterized by rapid growth, increased pain and metastasis.
Tubal pregnancy with rupture - accompanied by sudden pain on one side of the abdomen, severe dizziness, and possible loss of consciousness caused by internal bleeding. A woman has a delay in menstruation, secondary signs of pregnancy.
Inflammation of the urinary system
The urinary system consists of the bladder, urethra, kidneys and ureters. Among the most common pathologies of these organs are infectious diseases.
Anatomically, the urinary tract is closely related to the reproductive organs
Ascending urinary tract infections are especially common in women. This is due to the physiological characteristics of the urethra. It is smaller and wider in size compared to the male organ. Harmful bacteria easily penetrate the bladder and travel further through the ureters into the renal pelvis. Most often, such diseases are chronic and do not have pronounced symptoms.
Table 3. Diseases of the urinary system
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Cystitis | Inflammation of the bladder, accompanied by acute, cutting pain in the lower abdomen. The process of urination is difficult and causes discomfort. |
| Urethritis | A urinary tract infection caused by exposure to fungi, parasites or viruses. Often transmitted sexually. |
| Pyelonephritis | Inflammation of the kidney parenchyma. Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and staphylococcus provoke the development of the disease. |
Bacteriuria is also classified as a urinary tract infection. It is characterized by the presence of bacteria in urine that contribute to the formation of an inflammatory process.
Causes of bacteriuria
Why does the lower abdomen hurt in women on the right and left?
The causes of pain in women can be divided into 2 groups: organic and functional.
Organic reasons:
- diseases of the female genital organs (adnexitis, endometritis, endometriosis, ovarian apoplexy, ovarian cyst, torsion of the peduncle of an ovarian cyst, uterine fibroids);
- use of an intrauterine device;
- acute surgical pathology, pathology of the urinary system, gall bladder (appendicitis, cystitis, cholecystitis, pyelonephritis);
- the woman’s health condition related to pregnancy (symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, threat of miscarriage, premature placental abruption, pain after a medical abortion).
Functional reasons:
- menstrual irregularities - algomenorrhea (see causes of painful periods) and dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- pain associated with ovulation (see also transparent, stretchy mucous discharge);
- stagnation of menstrual blood (bending of the uterus, hematometer).
Pain in the lower abdomen can have a different character and can be either sharp, cutting or stabbing, or dull, aching.
Inflammatory processes in the appendages and uterus
The inflammatory process in the uterus or appendages, as a rule, begins acutely, with an increase in temperature, the appearance of symptoms of intoxication and pain in the lower abdomen. With salpingo-oophoritis (adnexitis), the left or right side of the lower abdomen hurts, and with endometritis, the lower abdomen hurts in the middle. During a vaginal examination, with inflammation of the appendages, pasty and sharply painful appendages are determined, and with endometritis, an enlarged, softened uterus is palpated, painful on palpation and displaced behind the cervix. Chronic salpingoophoritis and endometritis occurs with aching, dull pain in the lower abdomen. In the area of the appendages, heaviness is determined, and the uterus is palpated as a dense and sensitive formation.
Treatment for inflammatory diseases of the genital organs consists of prescribing antibiotics, infusion therapy, vitamins, anti-inflammatory suppositories in gynecology for adnexitis.
Endometriosis
Genital endometriosis can affect the uterus, appendages and the retrocervical space. Endometriosis is the spread of cells similar in structure to the endometrium outside the uterus. Pain appears before menstruation and increases during it. With endometriosis of the uterus, pain is localized in the middle of the lower abdomen, with endometriosis of the appendages in the groin areas, with retrocervical endometriosis behind the pubis (see endometriosis of the uterus - treatment and symptoms). A significant adhesive process in the pelvis with this disease aggravates the pain syndrome. In addition to pain, a woman is worried about menstrual irregularities, changes in the nature of menstrual flow and female infertility (see uterus for infertility).
Treatment of endometriosis is hormonal; in some cases, surgery is indicated.
Ovarian apoplexy
Apoplexy or hemorrhage in the ovarian tissue occurs during the intermenstrual period (in the middle of the cycle) and is associated with ovulation. When the main follicle ruptures, the vessels of the ovary are damaged and bleeding begins in the tissue of the organ and the abdominal cavity. Apoplexy can be provoked by sexual intercourse or physical activity. Intra-abdominal bleeding is accompanied by intense pain in the lower abdomen, localized at the site of the damaged ovary and symptoms of posthemorrhagic anemia (pallor of the skin, drop in blood pressure, loss of consciousness). Emergency surgery is indicated.
Uterine fibroids
The lower abdomen hurts in women with uterine fibroids, with large tumor sizes and compression of neighboring organs, and with the birth of a submucosal myomatous node. The pain syndrome with large fibroids is aching, pressing or dull in nature. At the birth of a myomatous node, the pain is cramping, severe and accompanied by intense bleeding. In both cases, surgical intervention is indicated (see uterine fibroids - symptoms and treatment)
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst
The pedicle of an ovarian cyst can become twisted during bending, sharp turns, or physical work. If the leg is twisted 90 degrees, the venous outflow in it is disrupted, the cyst swells, and the pain is aching. With a 360-degree torsion, arterial blood does not flow to the cyst and a picture of an “acute” abdomen develops: cramping, severe pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst, signs of intoxication (nausea, vomiting), positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation, increased temperature, forced positioning of the patient’s body. Emergency treatment - removal of the ovarian cyst, while the leg does not untwist (see ovarian cyst - symptoms and treatment).
Appendicitis
Symptoms of appendicitis in adults begin with a low-grade fever, pain that is felt first in the epigastrium, then shifts to the right iliac region, signs of intoxication and weakness. Possible loss of appetite, upset stool, vomiting. In the absence of emergency surgical treatment, appendicitis can develop into diffuse peritonitis and be fatal.
Example from practice: At night, a young woman comes to the emergency room with complaints of pain in the lower (more on the right) abdomen. First, she is examined by a surgeon who categorically denies the presence of his pathology. Then they call the gynecologist (me). I also deny mine. But my stomach hurts. The surgeon and I almost quarreled over whose patient it was. And since I am a young doctor, and he is experienced, and also the head. department, we agreed that this belly is mine and together we go for an exploratory laparotomy. The appendages are normal, but the appendix is weak (phlegmonous appendicitis). We perform an appendectomy as required. Yes, it’s not without reason that they say that appendicitis is the monkey of all diseases. In this case, there was an atypical location of the process, which misled the surgeon.
Cholecystitis
The inflammatory process in the gallbladder is more common when there are stones in it. The disease is acute, with fever, nausea and vomiting, itching of the skin due to high bilirubin, pain in the right hypochondrium and pain in the lower abdomen. The pain radiates to the back, lower back and subclavian region and intensifies after eating. Treatment consists of prescribing a diet and medications that improve the flow of bile; for large stones, surgery.
Cystitis, pyelonephritis
Inflammation of the bladder is accompanied by sharp, cutting pain in the suprapubic region, which intensifies with urination. Pyelonephritis is characterized by pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen. Inflammation of the bladder and kidneys occurs against the background of an increase in temperature with problems with urination and inflammatory urine tests (see symptoms of cystitis in women). Both diseases are treated with antibiotics and nitrofurans.
Ectopic pregnancy
A serious gynecological disease that involves the implantation of a fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity (in the tube, ovary, abdominal cavity). The disease during tubal abortion is characterized by periodic paroxysmal pain in the groin area or sharp, acute pain when the tube ruptures. The pain radiates to the vagina, rectum and supraclavicular area. Ectopic pregnancy occurs with severe intra-abdominal bleeding and requires immediate surgical intervention. Distinctive signs of the disease are delayed menstruation, a positive pregnancy test and possible spotting during an attack.
Other reasons
A feeling of heaviness can be a symptom not only of gynecological diseases and infections of the genitourinary system. In some cases, it is a harbinger of osteochondrosis of the lumbar or thoracic spine. There is an aching pain that causes discomfort both while walking and in a lying position.
Inflammation of the appendix is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and sharp pain in the abdomen
Table 4. Pathologies related to pulling sensations in the abdomen
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | Neurotic disorder. Accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the abdominal area and periodic stool upset. |
| Purulent appendicitis | The process of death of the nerve endings of this process does not always occur against the background of acute pain and swelling of the peritoneum. Often the alarm bell is nagging pain. |
Varicose veins can also cause heaviness in the abdomen.
First steps for pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen
If discomfort in this area is observed for a long time, you should undergo a comprehensive examination. To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe several types of body tests:
- urine and stool analysis;
- general and detailed blood test;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, liver and kidneys;
- a smear taken from the vagina and cervical canal;
- CTG.
Gastrointestinal diseases have similar symptoms, so the disease can only be detected using special equipment
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. The use of traditional medicine can temporarily brighten up unpleasant symptoms, but at the same time erase the overall picture of the disease. Treatment should only be prescribed by the attending physician. It is important to strictly adhere to the agreed recommendations and prevent complications from occurring or the disease becoming chronic.