Description
Pain in the lower abdomen in women can have a different character. Every woman felt the nagging pain. It is usually a precursor to early menstruation.
This sensation in the lower abdomen is not acute, it is constant, aching, and not paroxysmal - the pain in women seems to be “pulling”, hence its name “pulling”.
The nagging pain is usually not short-term, but lasts about 40 minutes. You can tolerate it, unlike a strong acute one, but you shouldn’t do it.
If the feeling does not leave you for a long time, you need to pay attention to the symptom.
Why can the lower abdomen be pulled in a healthy person?
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
In women and girls of reproductive age, lingering pain in the lower third of the abdomen is a harbinger of the imminent onset of menstruation. Often, such a feeling in the lower abdomen is combined with aching pain in the lumbar region, and is also accompanied by irritability, tearfulness, a feeling of nausea, headache, heaviness and soreness of the mammary glands. All this allows the fair sex to understand that they will soon have to take out their calendar and mark the day the natural process begins. Nagging pain or pulling in the lower abdomen and lower back is caused by the fact that, under the influence of certain hormones - prostaglandins, the functional layer of the endometrium begins to recede, the thickness of which reached its peak during the period of ovulation so that a fertilized egg can easily implant into it. Since pregnancy has not occurred, the functional layer of the endometrium is shed by contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterus. The degree of pulling sensations is individual and each lady manifests itself with different intensity.
Ovulation period
Ovulation occurs approximately 2 weeks after menstruation. Natural pulling sensations in the lower abdomen occur due to the release of a mature egg from the follicle. Therefore, women and girls can feel the ovarian area, which indicates the activity of one or another ovary. In this case, the pulling sensation is accompanied by mucous discharge; there may be slight bloody inclusions, usually transparent or whitish in color. Such signs help a woman plan the day of conception.
Menopause
Nagging pain during menopause occurs in women from about 45 years of age, which is associated with the decline of the reproductive system and corresponding hormonal changes. Due to a decrease in the level of sex hormones, there is a decrease in the tone of the ligamentous apparatus of the reproductive organs, and hernias and prolapses may occur. During menopause, you need to be on guard, because many chronic diseases worsen, and some are disguised as menopausal symptoms.
After physical activity
After an abdominal workout, you may feel a tightening in your lower abdomen, which is also accompanied by muscle pain. Usually these symptoms completely go away after 3-4 days.
Factors
Factors that lead to nagging pain syndrome are divided into two categories - physiological and pathological.
With physiological ones everything is simple. This is pregnancy and the menstrual cycle, since discomfort in the lower abdomen often manifests itself in women before menstruation or at the onset of menstruation.
Pathological reasons:
- Gynecological diseases;
- Discomfort after sexual intercourse;
- Adhesive processes;
- Algodismenorrhea;
- Intestinal diseases;
- Spine pathologies;
- Diseases of the excretory system.
Nagging pain often occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle - around day 14-15.
The reason will be the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg - ovulation. Even minor bleeding may occur.
In this case, the pain syndrome is unilateral and lasts from a couple of hours to several days.
Many women experience characteristic pain during, before or after menstruation. In this case, the reason is the rhythmic contractions of the uterus.
If the receptors of the latter are very sensitive, the discomfort can be very strong. It can radiate to the lumbar area and other areas. But usually after menstruation this condition goes away.
If they are already over, but the nagging pain bothers you just as much, you need to go to the doctor to eliminate the risk of pathologies. Separately, it is worth mentioning about pregnant women.
During this period, the body spends maximum resources to ensure proper development of the fetus. The size of the uterus increases, it can put pressure on the intestines, bladder, and ovaries.
Previously, the abdominal muscles could be completely relaxed, but now the load is placed on them.
Expectant mothers may constantly want to go to the toilet , and the reason for this is increased pressure on the organs of the genitourinary system. An additional problem is constant constipation.
Despite the fact that some conditions cannot be eliminated until a certain period of time, constant discomfort should not be ignored.
If you notice bloody discharge, call an ambulance as soon as possible, as there is a risk of miscarriage.
Things are even more complicated with pathological causes . In a normal state, nagging pain after intimate intercourse should not occur, unless, of course, we are talking about the loss of virginity.
If this condition bothers you, and constantly, this may indicate the presence of an abnormal septum in the vagina of a congenital nature.
The size of the partner's genital organ also plays a role. If it is too large, there is a risk of damage.
Pain syndrome is a common consequence of the inflammatory process on the cervix and in it itself. White fluid may be discharged from the vagina.
Particular attention should be paid if it turns yellow or green. This indicates that a bacterial infection is possible, and you should not hesitate to visit a doctor.
Another pathological cause is algodismenorrhea. Pain during menstruation is a normal condition , but if it is tolerable and passes quickly.
With the same pathology, everything is more serious. More often, this trouble is provoked by hormonal or nervous disorders.
It can usually appear 1.5-2 years after the start of the cycle. Additionally, a woman may have a fever, vomiting and even fainting. Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs can provoke adhesions.
This is probably due to pathologies in the intestines, excretory and reproductive systems. If the diseases become chronic, then adhesions are a protective reaction against bleeding or the spread of inflammation.
Since they are not able to resolve themselves, they can gradually transform into chronic ones.
Detecting a tumor process in the genital area is quite difficult, especially in the initial stages. Often nagging pains indicate pathologies.
For example, it could be a cyst in the ovary. At first the sensations will be localized in one side. But if the formation becomes malignant, the pain will spread throughout the entire pelvic area.
The reason for this is that muscle peristalsis is disrupted in the affected area .
Diseases accompanied by the same symptoms, regardless of gender
There are diseases in which both men and women equally often complain of nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Chronic appendicitis
The disease develops when an acute attack is stopped independently and there is no surgery. In this case, the inflammation of the appendage of the cecum does not stop. A pronounced adhesive process occurs. This is the body's defense response to limit the spread.
Frequent nagging pain in the right area of the lower abdomen is sometimes the only sign of the disease. For a complete diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude the presence of diseases of the genital organs, urination, and intestines. If the diagnosis is confirmed, elective surgery is recommended. This is the only way to get rid of pain.
Chronic diverticulitis of the ileum
The disease is caused by inflammation of saccular protrusions on the wall of the ileum. They occur during the formation of the intestinal tube in the fetus or as an acquired pathology as a result of thinning of the wall.
Without inflammation, diverticula are not clinically apparent
The entry of intestinal microorganisms, retention of contents, and decay contribute to the inflammatory reaction.
It is clinically difficult to distinguish from an attack of appendicitis: nagging or bursting pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, fever. The transition of pain to throbbing is an unfavorable sign. It indicates the formation of an encysted abscess. Complications include peritonitis, bleeding and intestinal obstruction. Treatment is only surgical.
Intestinal obstruction
The pathology completely or partially disrupts the passage of contents through the intestinal tube. Possible due to:
- with mechanical blockage by adhesions, diverticula, tumor, fecal stones, foreign body;
- damage to intestinal motor function by eating too heavy a meal after fasting;
- diseases of inflammatory origin (pancreatitis, colitis, appendicitis);
- uncontrolled use of medications, drug addiction.
Abdominal pain increases gradually and becomes very strong, bursting, spreading in all directions. Stool is retained, gases do not pass, the abdomen is swollen in the upper intestines, repeated vomiting occurs, and a false urge to defecate occurs. For health reasons, urgent surgery is required.
Chronic sigmoiditis
The sigmoid colon is located in the left side of the abdomen, in the side and ileum. Due to physiological bends, the speed of movement of intestinal contents here is reduced. The location is convenient for supporting chronic inflammation. The process causes correspondingly nagging pain to the left of the pubis, radiating upward into the lower back.
Long-term disease leads to damage to the entire intestinal wall with surrounding tissues (perisigmoiditis) and lymph nodes. The pain becomes constant, intensifies with movements, after an enema, while walking. Treatment measures often come down to a lifelong diet and anti-inflammatory treatment.
Malignant neoplasms of the colon
At the beginning of the development of colorectal cancer, nagging pain in the lower abdomen is possible. The growth of the tumor, the disintegration and addition of inflammation cause severe pain in the iliac region on the left or right, in the lateral zone, bloating, constipation, and signs of intestinal bleeding.
To distinguish from other diseases, endoscopic colorectal examination with biopsy cytology is necessary. Treatment is only surgical.
In what cases can you cope with the problem at home?
If pain occurs before or during menstruation, then you don’t need to see a doctor. Typically, such sensations go away on their own as the cycle progresses.
You can take a painkiller or antispasmodic tablet or apply a heating pad.
Heavy lifting and vigorous activity should be avoided.
It’s better to rest and lie down, then the discomfort will go away faster.
Sometimes such pain during pregnancy is understandable, because the uterus grows, and organs shift because of this. But remember that during this period you are doubly responsible, and you should not ignore any deviations from the norm.
Nagging and aching pain in the abdomen as a result of a woman’s pregnancy
If such painful sensations occur together with a delay in menstruation, this may be pregnancy. Along with all the symptoms, the girl does not feel the same as before. Irritability, at times weakness and fatigue appear. The woman feels sleep-deprived and her mood often changes. Increased sensitivity and breast tenderness may occur.
Any woman experiencing such symptoms should consult a gynecologist. The doctor will confirm or deny a possible pregnancy and determine whether the symptoms in this case are normal.
When do you need a doctor?
If discomfort tormented you for a couple of hours and disappeared, no longer making itself felt, you can calm down.
But if the pain is constant and noticeable, consult a doctor. There can be many reasons for this condition, and usually a routine examination is not enough to determine a specific one.
The first doctor you should go to is a gynecologist.
He may order the following tests:
- General blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound and x-ray of the problem area;
- Culture and cytology to determine sexually transmitted infections;
- Hormonogram;
- Hysterosalpingography – evaluation of the fallopian tubes.
- Colposcopy is a detailed examination of the vaginal area.
Nagging pain along with discharge may indicate microflora disturbances or a bacterial infection.
However, if bloody fluid is released from a pregnant woman, there may be a high risk of miscarriage, vascular damage, or placental abruption.
If the right side of a woman’s lower abdomen is pulled, thoughts of appendicitis immediately appear, and the left side usually hurts in the case of chronic sigmoiditis, which involves inflammation in the place where the colon and rectum connect.
But only ultrasound and x-rays can confirm all these diagnoses.
A gynecologist can refer you to a gastroenterologist, surgeon, traumatologist, or rheumatologist.
After all, one of the popular reasons is a vertebral hernia in the lumbar region . It gives into the genitals, and not vice versa.
Read what are the causes of infertility in women, what should be its comprehensive treatment.
In our review you will find information about methods of conservative treatment of uterine fibroids! Is it possible to treat the disease without surgery?
Do you know which medications are effective for cystitis in women? Look for effective names here: .
Diagnostics
To find out why there is nagging pain in the lower abdomen you need to:
- lie on your back and palpate the abdomen;
- if the pain is sharp and severe, and not nagging, then you should not do this, so as not to damage the organs and provoke a rupture, here you just need to call an ambulance;
- Having established the exact location of the abdominal pain, suggest what may be causing it. If the cause is menstruation, menopause, pregnancy, and this is not the first time you have had this condition, then treatment can be carried out at home, without consulting a doctor;
- if you have established the physiological cause of the pain, take a position that is comfortable for you: sitting, lying on your back or on your side, drink an antispasmodic to relieve the feeling of tension;
- if the nagging feeling continues to torment you for more than several hours, then you need to immediately call an ambulance;
- if you do not see objective reasons for the occurrence of pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, then it is better to consult a doctor (to begin with, you can contact a therapist, and he will advise you of a specialist; women can immediately make an appointment with a gynecologist);
If you do go to the doctor, then be prepared to undergo an examination; for women this is a mandatory gynecological examination; men can be examined by a proctologist or urologist, if necessary.
You will definitely need to take the following tests and examinations:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- bacteriological culture of urine or vaginal discharge;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- X-ray examination;
- donating blood for hormones;
- for women, colposcopy (deep examination of the vagina) and hysterosalpinography (examination of the fallopian tubes).
A gynecologist, proctologist, urologist, traumatologist, surgeon, and rheumatologist can examine the patient. The choice of specialist will depend on what disease is suspected.
Preventive measures and additional recommendations
There is no universal remedy that could prevent discomfort in the lower abdomen, because too many reasons can lead to it.
But there are still measures that will help improve the condition and reduce the risk of discomfort:
- Strengthen your immune system, take vitamins;
- Maintain personal hygiene;
- Eat right;
- Lead an active lifestyle and be outdoors.
It is important to visit a gynecologist in a timely manner and undergo a comprehensive examination for prevention.
It is better to treat any problem at an early stage rather than in an advanced stage. Constantly monitoring your health will help identify any abnormalities.
What diseases in men cause nagging pain in the lower abdomen?
Closest to the lower abdomen is the pelvic zone, in which in men an important organ is located - the prostate gland with seminal vesicles.
Chronic prostatitis
If a man complains that “it hurts and pulls in the lower abdomen,” then first of all, suspicions of chronic prostatitis arise. Middle-aged men are more likely to get sick, especially with sedentary work (drivers, pilots). The pain is constant, radiating to the suprapubic area, coccyx, anus, groin and external genitalia.
Why does my lower abdomen hurt when lifting weights?
Itching in the anal area is typical; when straining, prostate secretion is released in drops through the urethra. Exacerbations of prostatitis are caused by hypothermia, alcohol consumption, and sexual excesses.
In addition to the characteristic pain, pain during urination, increased urination, retention of urine, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder are added. The man's temperature rises, dizziness, weakness, headaches, and insomnia appear. Character often changes; a tendency towards isolation and irritability over trifles is noticed in the family.
Benign tumor
Prostate adenoma is formed by overgrown glandular cells. The disease occurs more often in older men. An enlarged prostate puts pressure on the urethra. Therefore, in the early stages, symptoms indicate impaired urination: straining to push urine out, frequent urges without the feeling of complete emptying of the bladder.
A constant aching pain in the groin and above the pubis is excruciatingly endured by patients. Further increase leads to stagnation of urine and inflammation. In men, cystitis, prostatitis, and pyelonephritis are detected.
Adenoma is associated with hormonal disorders
Prostate cancer
A malignant tumor of the prostate gland occurs against the background of a long course of adenoma, inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs. The disease begins with nagging pain above the pubis and in the perineum, frequent urination, and the appearance of blood in the urine. Further development of the tumor is characterized by rapid metastasis, pain in the bones (legs, spine, ribs), loss of appetite, and weight loss.
What pathology causes nagging pain in women?
Menstrual function is a physiological phenomenon and in a healthy woman it should not cause any signs of illness. But some experience intense pain every month and their general condition is disrupted. This symptom is called algodismenorrhea.
Gynecologists identify secondary dysmenorrhea caused by pathological changes in the uterus, appendages, and impaired structure of the internal genital organs.
Adenomatosis
Nagging pain is combined with heavy uterine bleeding and prolonged brown discharge from the uterus. Women who have not given birth after 30 years and suffer from infertility are more likely to suffer. With adenomatosis (endometriosis of the uterus), the internal epithelium grows from the uterine cavity into the muscular layer, and “pockets” are formed.
With menstrual blood, the endothelial layer of the uterus is torn away, a mass of blood enters the “pockets”, they expand and put pressure on the surrounding tissues. This causes intense pain radiating to the back and groin.
Hormonal drugs are used in treatment. After conception and during pregnancy, obstetricians monitor the development of the fetus and prevent rejection. Women are observed by a doctor for a long time. The formation of cysts and foci of endometriosis in the pelvis and cervix is possible. It is believed that the pathology disappears after the onset of menopause.
Inflammatory diseases
Chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital area in women are often accompanied by nagging pain. Menstrual bleeding provokes the development of inflammation, since blood is considered a good environment for pathological microorganisms to live.
Adhesions in the tube become one of the causes of infertility and ectopic pregnancy
At the same time, the general condition worsens, the following appear:
- weakness;
- headache and dizziness;
- muscle pain;
- temperature increase.
A change in discharge is characteristic: an unpleasant odor due to the admixture of pus. Typical neurological complaints are insomnia, stabbing pain in the heart, and irritability. The examination reveals a sexually transmitted infection in 60% of cases; therefore, the diagnosis must take into account the woman’s sexual behavior.
The risk of inflammation increases significantly in the following cases:
- undergone diagnostic curettage, abortion;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- refusal and untimely termination of therapy for an acute disease.
For congenital anomalies, disruption of the structure of the uterus
Nagging pain occurs in a girl with a congenital anomaly during her first menstruation. If the defect is a clogging of the vagina or cervix, then the blood is not released, but accumulates and significantly expands the vagina and uterine cavity.
Teenage girls with painful menstruation should be shown to a gynecologist and examined. In women who have given birth, adhesions (synechias) may form in the uterine cavity as a result of the use of intrauterine contraceptives, a previous abortion, or endometritis. A delay in the outflow of blood is caused by retrodeviation of the uterus (bend).
The cause of the bend is heavy physical work, improper management in the postpartum period, sudden weight loss
Primary algodismenorrhea
It is distinguished by the lack of connection with gynecological diseases. The pain syndrome is explained by functional disorders due to pathology of the endocrine and nervous systems, a tendency for the body to increase the synthesis of prostaglandins that contract the uterus, and an increase in the level of estrogen. It is typical for girls with overload at school, at work, low mobility, poor nutrition, and increased emotional perception.
In 2/3 of cases, a diagnosis of premenstrual syndrome is made. Nagging pain occurs in the lower abdomen several days before the scheduled start of menstruation. Most intense on the first day. There is a combination with headache, nausea, fainting, vomiting, and pain in the mammary glands.
Tumors of the internal genital organs
Benign tumors of the ovaries and uterus (cysts, fibroids) with their growth stretch the organ and contribute to nagging pain. At the same time, the ligamentous apparatus is connected to the process. The clinical picture is necessarily complemented by severe uterine bleeding.
Malignant ovarian tumors are characterized by bilateral pain, since they affect both organs. Pain syndrome is expressed at stages II–III of cancer. There are other signs:
- loss of appetite;
- weakness;
- weight loss;
- nausea;
- hormonal disorders;
- metastases to the stomach.
Pain in the lower abdomen on one side occurs due to cancer of the fallopian tube. Its early manifestation is considered to be periodic heavy watery discharge. The pain itself in this case is caused by impaired peristalsis of the tube.
The early stages of uterine sarcoma are accompanied by uterine bleeding, rapid tumor growth, intense pain, and metastases. For an experienced doctor, the significance of nagging pain in the lower abdomen is important for assessing a person’s condition and making a diagnosis. Patients with such symptoms should be examined and specific causes identified.
Possible cancer
Constant abdominal pain may be a consequence of the development of cancer of one of the abdominal organs. The nature and strength of the pain syndrome depends on the stage of the disease that appears. Sometimes you can feel bulging formations in the patient's abdomen. With such damage to the abdominal organs, patients often experience a loss of strength and weakness . An important sign in the diagnosis of cancer is inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin area .
Possible problems with the urinary organs
Pain in the suprapubic region usually indicates inflammation of the bladder. Possibly difficulty urinating . In this case, the shade of urine becomes cloudy and darker .
If, in addition to the suprapubic region, pain is felt in the lumbar back , radiating to the sides of the abdominal cavity, there may be a possibility of kidney inflammation. Urolithiasis of the kidneys can also cause pain in the hypochondrium.
If the pain is acute, this may be a sign of stone blockage in the urinary tract. Severe and sharp painful spasms may indicate urinary retention. A similar situation can be caused by blockage of the urinary tract with a stone or cancer.
Drawing in the lower abdomen
If the lower abdomen is tight, the reasons can be explained by natural physiological processes, but can also be harbingers of serious diseases. In addition, each person has his own pain threshold and for one this symptom will be a feeling of discomfort, and for another it will be a dull or aching pain.
Pulling in the lower abdomen - problems with the digestive system
Diseases associated with problems in the intestines: intestinal obstruction and constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, colitis, diverticulosis, ulcers, cancer. Similar symptoms may be harbingers of severe pain caused by appendicitis.
Pulling in the lower abdomen - problems with the urinary system
Hypothermia weakens the immune system, and then a sign of incipient cystitis becomes a tugging sensation in the lower abdomen.
Hypothermia weakens the immune system and then a sign of incipient cystitis becomes something that pulls in the lower abdomen
If the pain extends to the lumbar region, you should immediately consult a doctor for further examination and exclusion (or confirmation) of diseases such as urethritis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis and oncology.
Pulling in the lower abdomen - problems of the circulatory system
More often affects women of reproductive age than men. Varicose veins of the pelvis are also the reason why the lower abdomen is pulled, but rarely does anyone associate this symptom with the veins. When a menstrual cycle disorder occurs with pronounced pain, increased sensitivity of the vagina, problems with urination, frequent inflammatory processes, the patient sounds the alarm.
Pulling in the lower abdomen - hernia
Umbilical, inguinal, herniated discs are often the source of nagging pain in the lower abdomen. The presence of an intervertebral hernia is indicated by a sharp shooting pain in the lumbar region, radiating to the groin or buttock. Inguinal and umbilical hernias can be accompanied by severe pain, vomiting and nausea.
Pulling in the lower abdomen - infections
One of the most common causes of uncomfortable pulling sensations is infections caused by pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa). At the initial stage, you may also experience itching, burning, difficulty urinating, pain, and discharge.
What kind of pain is called nagging?
The pain can be localized in the lower abdomen, above the pubis, lower right side or left. The nagging pain is usually aching, lasts at least half an hour, moderately strong, but not sharp or cramping. It brings significant discomfort to the person; if you take a comfortable position, the pain may ease, but there will still be a pulling sensation. This pain usually lasts for some time, then subsides and returns again.
Tugging sensations often bother women more than men. This is due to the fact that in addition to the general causes of nagging pain, women experience these sensations for a number of physiological reasons related to gynecology.
What does heaviness in the lower abdomen indicate during pregnancy?
Pregnant women should definitely listen out for abdominal pain of unknown origin, because it can harm two lives at once. In addition to the relatively harmless flatulence and stool disorders that we described above, heaviness in the abdomen can be accompanied by contractions and serious pathologies of pregnancy.
Threat of placental abruption
A real threat to the life of the fetus is premature placental abruption, a pathology that most often manifests itself in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. The placenta performs a protective function, providing the baby in the womb with everything necessary. If it is completely detached, the fetus may die.
Classic symptoms of this complication:
- internal or external bleeding,
- severe and dull pain in the groin area,
- hypertonicity of the uterus;
- heartbeat disturbances in the fetus.
Premature placental abruption during pregnancy can be triggered by abdominal trauma or the presence of the following in the mother:
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs);
- iron deficiency anemia;
- autoimmune diseases;
- allergies to certain types of drugs;
- changes in the uterine epithelium (occurs in women who have had a large number of births);
- sudden changes in blood pressure.
Training contractions
At the end of the second trimester, pregnant women may feel cramping pain and tension in the abdomen several times a day, during which the uterus becomes as if “stone-like.” These are training contractions that prepare the body for future childbirth.
There is no need to be afraid of them, but if the intensity of the pain increases, it is better to consult a gynecologist to eliminate the threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
In the last weeks of pregnancy, similar sensations can be caused by the onset of labor pains.
Divergence of the pelvic bones
Pain in the pubic, groin or pelvic area in a pregnant woman, which intensifies when walking and changing body position, often indicates a divergence of the bones of the pubic symphysis - symphysitis. This pathology usually manifests itself in the third trimester and requires close monitoring by a doctor until birth. In some cases, the pregnant woman even requires hospitalization.
Fetal kicks
Starting from the middle of pregnancy (16-24 weeks), pain in the lower abdomen can also occur due to the movements and kicks of the growing baby. And, although they are often quite painful, they are completely natural and safe.
Causes of pain
Pain is always a signal of problems in the body. It would be incorrect to say that pain is a variant of the norm. The appearance of any discomfort is a reason to listen carefully to your feelings and find their cause. Even if pain is not associated with serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, it indicates one or another malfunction in the functioning of the human body.
Functional reasons
This group includes conditions that are not associated with organic damage to the structures of the pelvis or abdominal cavity, but are caused by a malfunction in their functioning:
- Menstruation. A nagging pain over the womb that occurs 1-2 days before menstruation and persists throughout the entire period of monthly discharge is not considered normal, but occurs so often that it cannot clearly indicate pathology. In gynecology, the appearance of mild or moderate pain during menstruation is allowed, provided that such sensations do not interfere with the woman’s normal lifestyle and are not accompanied by other negative symptoms: heavy discharge, vaginal itching, high body temperature, etc. The severity of pain is determined by individual sensitivity.
- Ovulation. Pain that occurs in the middle of the cycle on one or both sides can be caused by the release of a mature egg into the abdominal cavity and overstretching of the ovarian capsule. Discomfort persists for up to 36-48 hours, after which all unpleasant sensations disappear. The likelihood of pain increases when ovulation is stimulated with medications.
- Pregnancy. In anticipation of the baby, the muscles and ligaments of the pelvis are stretched, which leads to the appearance of a weak nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. The pain should not be severe. Increased discomfort, as well as the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract, is a sign of a threatening or incipient miscarriage.
- Errors in nutrition. Eating spicy, fried, fatty or spicy foods, overeating - all this leads to disruption of the intestines and the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen. The pain is most often localized on the right or left, accompanied by bloating and flatulence. Negative symptoms go away on their own within a few hours and do not require treatment.
- Taking medications. Pain in the lower abdomen can be a side effect of some medications, which is usually written about in the instructions. Symptoms go away after completing the course of therapy and stopping the drug.
Be sure to read: Why and what causes your stomach to growl, what to do?
Organic causes
This group includes conditions associated with damage to internal organs: the uterus and appendages, intestines, and bladder. The pathology that occurs in women during pregnancy also deserves special attention.
- Diseases of the reproductive organs: uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Pain in the lower abdomen occurs with inflammatory changes, hyperplastic processes, tumors, and congenital malformations. The pain can be nagging, aching, or in acute situations – cutting, cramping. May be accompanied by bloody vaginal discharge, itching and burning in the genital tract, and increased body temperature. Some gynecological diseases accompany infertility.
- Obstetric conditions. In the early stages of pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen indicates an impending miscarriage, and in combination with spotting, an incipient abortion. In later stages, pain syndrome occurs when premature or timely labor begins, placental abruption and other conditions. It is also important to exclude ectopic pregnancy.
- Diseases of the digestive tract. Drawing, aching and cramping pain in the lower abdomen (left or right, center) is associated with pathology of the colon. These can be inflammatory changes and neoplasms. Intestinal diseases are accompanied by flatulence, bloating, diarrhea or constipation.
- Surgical pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Appendicitis and other similar conditions are included in a separate group as potentially life-threatening. Pain during surgical pathology is usually acute, sudden, and severe. Possible disturbance of stool up to intestinal obstruction.
- Pathology of the urinary system. Pain above the womb is caused by cystitis - inflammation of the bladder. The disease is accompanied by frequent urination, burning and pain when passing urine, and often an increase in body temperature.
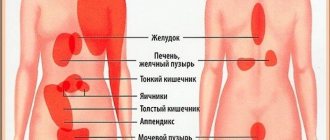
Relationship between pathology and localization of pain in the lower abdomen
When looking for the cause of pain, it is important to pay attention to its nature, time of occurrence and connection with various provoking factors (eating, intimacy, physical activity, taking medications). It is necessary to determine the exact location of the pain in order to quickly make a diagnosis (see further in the table).
| Localization of pain | Possible reasons |
| Lower abdomen on the right |
|
| Lower left abdomen |
|
| Centered above the womb |
|
Be sure to read:
Intestinal colitis: symptoms and treatment in adults