Signs that may accompany acid burps
Depending on what triggered the symptom, additional manifestations may occur:
- pain and heaviness under the sternum, in the epigastric region;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing food);
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- burning in the chest (heartburn);
- hiccups;
- nausea;
- flatulence (bloating with increased gas production);
- diarrhea or constipation.
Sour belching is often combined with other symptoms - heartburn, pain in the epigastric region, heaviness in the stomach
Causes and factors for the development of symptoms
Trouble can be caused not only by pathological conditions of the stomach or other organs, but also by poor nutrition:
- habit of overeating;
- significant physical activity on a full stomach;
- addiction to sweet soda (especially after meals), strong coffee;
- eating in a hurry.
Video - Doctor explains in simple language the causes of acid belching
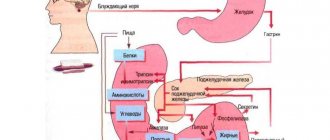
Most often, belching of air with acid, especially chronic, is caused by certain diseases. The main cause of the symptom and its faithful companion heartburn is gastroesophageal reflux disease, abbreviated as GERD. This condition is characterized by the passage of acidic fluid from the stomach into the esophagus (gastroesophageal reflux). Rejection occurs due to insufficiency (relaxation) of the lower esophageal constrictor muscle (cardiac sphincter) and disruption of the motor activity of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. The stomach contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin - they have a strong irritating effect. With duodeno-gastric reflux, bile and pancreatic enzymes also enter the stomach. Frequent reflux of acid into the esophagus provokes inflammation of its mucous membrane, and reflux esophagitis develops. GERD is always accompanied by strong sour belching and a painful burning sensation behind the sternum - heartburn. At the same time, other symptoms may be present: pain and rawness in the throat, behind the sternum, dry cough, hoarseness, attacks of nausea.
Gastroesophageal reflux occurs due to insufficiency of the cardiac sphincter
The development of this pathological phenomenon is facilitated by provocateur factors:
- some foods consumed in large quantities: tomatoes, citrus fruits, sweets, coffee, chocolate;
- Phentolamine, hormonal drugs, Eufillin and others;
- inactivity, chronic stress, constant overeating, especially while lying down, addiction to alcohol and tobacco.
Other causes of acid burping:
- gastritis with high acidity;
- ulcerative defect of the stomach or duodenum;
- pyloric stenosis or narrowing of the pylorus - the narrowest place at the exit from the stomach;
- hiatal hernia - partial displacement of the digestive organs through the esophageal opening of the diaphragm into the chest cavity;
- autoimmune pathology - scleroderma.
With these diseases, belching appears for the same reason as with GERD - due to the entry of stomach acid into the esophageal tube. In fact, GERD is a complication of all of the above diseases. Pathologies of the small intestine and biliary tract support inflammation in the stomach and can also become a provoking factor for belching.
Table - Acid Belching, Additional Symptoms and Possible Diagnosis
| Symptoms | Possible reason | What's happening |
| Hiatal hernia. | In case of injuries, congenital defects of the diaphragm, heavy loads, excess weight, endocrine disorders, during the period of bearing a child, the digestive organs are displaced from the abdominal cavity, peristalsis and normal functioning of the sphincters are disrupted, which leads to upward reflux of acid, heartburn and sour belching. |
| Scleroderma is a systemic pathology characterized by the replacement of healthy tissues of internal organs and skin with connective tissue. | Belching with acid is one of the manifestations of complications of the disease. The walls of the esophagus and constrictor muscles (sphincters) are affected with the growth of connective tissue in them, the peristalsis of the digestive organs is disrupted, and constant reflux of acid into the esophagus occurs. |
| Gastritis with hypersecretion of gastric juice | Inflammation of the mucous membrane is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which stimulates the secretory ability of the stomach. Dysfunction of the esophageal valve and an overly acidic environment in the stomach lead to regular upward reflux of acid. |
| Stomach ulcer | Pathology occurs for various reasons, one of which is high acidity in the stomach, which causes belching with acid. |
| Pyloric stenosis (can be caused by a tumor or adhesions, scars). | The process of food passing from one digestive section to another is disrupted, the stomach becomes full, and food stagnates. The lower valve of the esophagus cannot cope with the pressure in the overfilled stomach and acid reflux occurs. |
| Complex two-stage reflux: duodenogastric and gastroesophageal, which can be provoked by:
| If the motility of the digestive organs is impaired, there is strong pressure in the duodenum, or weakness of the pylorus, intestinal contents are thrown back into the stomach. With esophageal reflux, both stomach acid and bile enter the esophageal tube, causing heartburn and bitter-sour belching. |
Diseases
Sour belching after eating may indicate the presence of serious gastrointestinal diseases:
- Gastritis. Manifestations of gastritis are possible in two forms: chronic and acute. A characteristic accompanying symptom is excessive production of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is one of the components of gastric juice, which helps to break down and disinfect foods that enter the stomach (all food products must be disinfected with gastric juice and acid to avoid infection getting inside). When the level of stomach acid increases, a person experiences heartburn, nausea, or acid belching.
- GERD. This disease is characterized by impaired motor function of the stomach. Stagnant processes occur in the body, which provokes unpleasant belching.
- Chronic pancreatitis. In chronic pancreatitis, enzymatic production is disrupted (which affects digestion and absorption of foods).
- Various disorders in other parts of the body.
- Depressed state of the protective function of the immune system.
Diagnosis of diseases that can cause acid belching
If you have complaints about acid belching, you should contact a gastroenterologist. The doctor will examine the patient, assess the condition of the skin, determine the location of the pain (if any) by palpation, ask the patient how often and at what time the belching appears, whether it is associated only with food or happens at night, will clarify the nature of the belching - it has a slight sour taste , bitterness, or there is a large reflux of acidic liquid into the oral cavity. It is imperative to clarify whether the patient has chronic diseases of the digestive organs.
To establish a diagnosis, the gastroenterologist interviews the patient, examines, palpates and prescribes laboratory and instrumental examinations.
To make a diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental examinations are required.
Lab tests:
- In a clinical blood test, attention is paid to ESR, leukocytes, and hemoglobin. In acute inflammatory processes, as well as in scleroderma, the number of leukocytes and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increase, and hemoglobin may be reduced.
- Blood biochemistry makes it possible to evaluate the functioning of the pancreas, liver, and gall bladder.
- Feces for coprogram, occult blood, helminth eggs are given to determine the enzymatic capacity of the pancreas, exclude internal bleeding and the presence of helminths in the body.
Instrumental methods:
- contrast radiography is needed to identify the incorrect location of the digestive organs, their displacement from the abdominal to the chest cavity, which is typical for a hernia; the method is also used to identify gastric ulcers or narrowing of the pylorus;
- intraesophageal pH-metry is prescribed to identify reflux and determine the level of acidity of the liquid that is thrown into the esophagus;
- intragastric pH-metry is used to assess the acidity of gastric juice;
- esophagomanometry is performed to assess esophageal peristalsis;
- endoscopic examination of the esophagus is necessary to examine its walls;
- gastroduodenoscopy is necessary to visualize pathological phenomena on the gastric mucosa, ulcers, erosions, narrowing of the pylorus; sometimes during the procedure a biopsy is performed followed by histological and microbiological examination of the material;
- cholecystography and ultrasound of the gallbladder and biliary tract are performed if the patient’s complaints, in addition to acid belching, include pain in the right side, under the ribs, nausea, and bitterness in the mouth.
Endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum is one of the main methods for diagnosing the causes of sour belching
Table - Differential diagnosis of diseases causing symptoms
| Disease | Diagnostic methods | What is shown |
| Gastritis | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy | The mucous membrane is red, swollen, has minor hemorrhages and erosions. |
| Intragastal pH-metry | Increased acidity. | |
| Blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori | Positive indicator. | |
| Hiatal hernia | X-ray with contrast | Displacement of organs. |
| Intraesophageal pH-metry | There are refluxes into the esophagus. | |
| Esophagomanometry | Violation of esophageal peristalsis. | |
| Esophagoscopy | Inflamed mucous membrane of the esophagus. | |
| GERD | Intraesophageal pH-metry with determination of acidity level | Stomach acid reflux. |
| Esophagoscopy | Inflammation of the esophageal mucosa. | |
| Stomach ulcer | X-ray with contrast agent | On an x-ray, the ulcer appears as a niche. |
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy | Ulcerative defect; examination of the material taken during the biopsy shows the presence of Helicobacter pylori. | |
| Intragastric pH-metry | High acidity in the stomach. | |
| Pyloric stenosis | Gastroduodenoscopy | Severe narrowing or blockage of the pylorus, adhesions, swelling. |
| Contrast fluoroscopy | Impaired motor ability of the stomach, narrowing of the pylorus, the stomach is enlarged. | |
| Duodenitis | Duodenoscopy | Inflammation of the duodenal mucosa. |
| Scleroderma | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy | Sclerotic changes in the walls of the esophagus and stomach. |
| Duodenostasis (stagnation in the duodenum due to a violation of its patency) | Contrast fluoroscopy | Intestinal motility is impaired. |
| Duodenal sounding | Inflammation of the walls of the duodenum, the presence of erosions, tumors, ulcers, helminths, foreign bodies, adhesions | |
| Computed tomography or MRI | Used if it is not possible to find out the cause of duodenostasis using the endoscopic method. | |
| Gallbladder diseases | Ultrasound | Irregular shape and location of the organ, thickening of the walls. |
| Cholecystography (x-ray examination with contrast) | Disorders of the secretory and motor function of the gallbladder. |
Treatment
Therapeutic tactics depend entirely on the identified pathology, the manifestation of which is acid regurgitation. Treatment necessarily includes medications, dietary nutrition, and sometimes surgery. Surgery may be required for pyloric stenosis or hiatal hernia.
General recommendations
Along with prescribing medications, the doctor gives the patient recommendations:
- lifestyle correction: quitting smoking and alcohol;
- moderate physical activity;
- therapeutic diet with the exclusion of certain dishes, hot and cold drinks;
- relaxing cardiac sphincter: antidepressants;
- potassium compounds;
Medicines
Medicines prescribed for acid regurgitation:
- for reflux disease, gastritis or ulcers: antacid drugs: Phosphalugel, Almagel, Gastratcid, Maalox, Gaviscon;
- Omepprazole, Famotidine, Lansoprazole (Lancid);
- Domperidone, Metoclopramide (Reglan, Cerucal);
- Novobismol, Sucralfate, Misoprostol, bismuth subnitrate;
- Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin, Levofloxacin, Metronidazole;
- enzyme agents: Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon, Panzinorm;
- antacids;
- No-shpa, Papaverine;
For scleroderma, immunosuppressants, hormonal drugs, antisecretory and antacid agents, and prokinetics are prescribed.
In case of hernia and pyloric stenosis, surgery may be indicated to restore the physiological position of the organs and the patency between them. Surgical treatment may also be required to eliminate duodenostasis in the case of a neoplasm of the stomach or duodenum, or the presence of adhesions in the intestine.
Photo gallery - Drugs for the treatment of pathologies that cause sour belching
Almagel is an antacid drug that is used to bind stomach acid in gastritis or ulcers. Cholenzym is a choleretic agent, it is prescribed for diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Gaviscon effectively eliminates the symptoms of GERD, gastritis and peptic ulcers - heartburn and sour belching Mezim forte - an enzyme preparation, prescribed for pancreatic insufficiency Cerucal is an antiemetic and prokinetic agent that normalizes gastric motility Omeprazole suppresses the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach Metronidazole is one of the antibacterial drugs that are prescribed when the bacterial nature of an ulcer or gastritis is confirmed
Diet food
Without following a diet, it is almost impossible to get rid of sour belching. The following foods should be removed from the patient’s diet:
- coffee;
- chocolate, sweets, baked goods;
- sour fruits, citrus fruits;
- cabbage, eggplant, tomatoes;
- mushrooms;
- fatty, fried foods;
- smoked meats;
- marinades, sauces, seasonings;
- horseradish, garlic, pepper;
- pearl barley, millet groats;
- soda;
- canned food;
- fermented milk products - sour cream, kefir, whole milk.
Video - Harmful foods that cause burping
For gastritis and ulcers, it is preferable to boil, bake or steam cook food.
It is recommended to include in the diet:
- boiled and stewed vegetables - pumpkin, carrots, potatoes, zucchini;
- slimy soups with unrich broths;
- porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice);
- yesterday's bread, wheat crackers;
- steamed and baked dishes from dietary meat - turkey, rabbit, veal, and lean fish;
- eggs in the form of an omelet;
- bananas, baked apples.
In the acute period of a gastric disease, it is very useful to eat mucous porridges or soups with water that envelop the walls of the stomach
You need to eat small portions at least 4 times a day.
Folk remedies
It is worth noting that it is unlikely that it will be possible to cure the symptom with folk remedies alone. It is necessary to eliminate the root cause of this phenomenon, for which you need to take medications prescribed by your doctor and follow a diet. However, folk remedies can be a good help in the complex treatment of the underlying pathology that causes acid belching.
To reduce the acidity of gastric juice and improve the digestive system, traditional healers recommend the following remedies:
- infusion of flaxseed: pour a teaspoon of raw material with half a glass of boiling water, leave for at least 2-3 hours, drink the infusion in the morning on an empty stomach;
- infusion of medicinal chamomile: pour 2 large spoons into 300 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour, strain, drink half a glass three times a day;
- infusion of fennel and anise seeds: pour 2 teaspoons of the mixture with boiling water (1 glass), leave for 40–60 minutes, drink a tablespoon 4 times a day half an hour before meals;
- oat infusion: grind the oats along with the peel, steam a large spoon of the raw material with boiling water (350 ml), leave for 3-4 hours, preferably in a thermos, strain thoroughly and take 2 large spoons 10-15 minutes before meals and before bed;
- fresh potato juice: grate peeled potatoes, squeeze the juice through cheesecloth, drink immediately (you need to prepare at least half a glass of juice), drink the product three times a day, half an hour before meals.
Fresh potato juice effectively relieves acid burps and heartburn
Baking soda is a very popular remedy for sour belching and heartburn. In fact, using this method, you can not only not get rid of unpleasant symptoms, but also make the situation even worse. Sodium bicarbonate is an alkaline that quickly neutralizes stomach acid. However, during the chemical reaction, a large amount of carbon dioxide is released, which has a strong irritating effect on the stomach, as a result of which hydrochloric acid begins to be released in even greater quantities, another high reflux of acidic gastric contents into the esophagus occurs and heartburn with belching only intensifies.
Video - How to get rid of burping
ethnoscience
Nature's pharmacy contains the necessary herbs, plants, berries and other ingredients needed to help a person with sour burping. Unlike drug treatment, traditional medicine helps the body cope with the disease without side effects and without harm to other organs not involved in the process. First aid at home after a sour dish: quickly drink milk.
1 recipe
Fresh goat milk helps regulate the function of the digestive organs and a person gets rid of belching. You need to drink 3 glasses a day every day for two to three months. The period of admission depends on the speed of health restoration.
2 recipe
Physical exercise has a beneficial effect on the human body. Health problems arise when physical activity decreases while constantly sitting in one place. The tone of the internal organs decreases, and malfunctions occur.
Lying on your back, raise your straight legs 45 degrees and hold for 2 minutes, then gently lower. Repeat several times. At first, the belching will increase, but gradually the symptoms will begin to weaken and stop completely.
This recipe is not a way to treat a disease, but a method of quick relief for an acidic taste in the mouth. In any case, you should consult a doctor to get an accurate diagnosis.
3 recipe
Flax seeds will 100% help in the process of getting rid of burping. Constant use of the medicine will give lasting and noticeable results. The preparation is easy: 1 tablespoon of seeds per glass of boiling water. Let it sit for half an hour. For the first dose of liquid in the form of mucus, drink one-fourth of a glass, the rest for subsequent doses. The course is designed for 3 weeks, 3 times a day.
Source
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis for relief from a symptom depends entirely on the underlying disease. Timely treatment of gastritis, ulcers, gastroduodenitis ends successfully. Duodenostasis and pyloric stenosis caused by a tumor require surgical treatment and have a relatively favorable prognosis. Sour belching, which occurs as a complication of scleroderma, can be eliminated with symptomatic treatment, however, it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease.
Today, pharmacology offers many drugs that, when used correctly, can effectively eliminate the symptom.
In case of untimely examination, self-medication, or failure to comply with medical prescriptions, diseases that cause belching can be complicated by:
- GERD - esophagitis with ulceration of the walls of the esophagus;
- gastritis - erosions, ulcerative defects;
- ulcer - perforation (perforation) with the threat of internal bleeding, as well as pyloric stenosis;
- pyloric stenosis - gastrointestinal obstruction, gastrogenic tetany;
- hiatal hernia - erosive or ulcerative reflux esophagitis, esophageal ulcer, esophageal bleeding in case of perforation, strangulated hernia.
If gastroesophageal reflux, which causes sour belching, is not treated, complications may develop in the form of an esophageal ulcer.
Prevention
To ensure that the symptom never bothers you, you must maintain food hygiene:
- limit heavy animal fats, too spicy, sour, peppery dishes in the diet;
- give up alcoholic beverages, strong coffee, soda;
- eat food in fractional portions, do not overeat;
- do not eat before bedtime;
- quit smoking.
Addiction to fast food is a quick way to get stomach disease, heartburn and belching.
Belching with acidic gastric contents can signal serious pathologies of the digestive organs, so do not postpone a visit to the gastroenterologist. It is necessary to find out the cause of the unpleasant symptom and get rid of the disease in a timely manner to avoid complications. Be healthy!
How to get rid
Almost every person at least once in his life has wondered how to get rid of heartburn. These days, there are several ways to combat illness. The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the symptoms.
Taking medications
Self-administration of medications for heartburn is possible only in one case - if you experience heartburn due to eating foods unusual for your diet or overeating.
Under these circumstances, you can use proven and popular pharmaceutical drugs, including:
- "Renny";
- Gaviscon;
- "Phosphalugel";
- "Maalox";
- "Gastal";
- "Omez";
- "Almagel";
- "Mezim";
- "Vicair";
- "Bellalgin."
By taking these medications according to the instructions, it is easy to cope with the unpleasant sensations of heartburn and belching.
If air belching and heartburn appear twice a week or more often, and are also accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, this is a serious reason to check your health. It is not recommended to take heartburn medications before visiting a specialist.
The gastroenterologist will conduct an appropriate examination, based on the results of which, using palpation, the doctor will determine the presence of serious diseases accompanied by belching. After this, he may prescribe laboratory tests and instrumental examination of the gastrointestinal tract (endoscopy, ultrasound, etc.).
Based on the results of the examination and research, the specialist will easily make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of medications for heartburn and belching, a special diet and regular consultations with a doctor.
Interesting! Burning sensation in the right hypochondrium: causes and what to do
Traditional methods
Over the course of its existence, humanity has come up with several ways to combat illness, for example, for heartburn and belching, it is recommended:
- Chew a small handful of sunflower seeds;
- Eat a medium-sized apple or carrot;
- Use a teaspoon of any vegetable oil;
- Drink warm milk.
Traditional medicine recipes
However, natural remedies are much more reliable in the fight against heartburn. Traditional recipes are based on the correct use of the properties of medicinal plants. Herbs for heartburn have shown effectiveness and are popular; they have virtually no side effects.
To overcome unpleasant sensations, decoctions of the following plants are widely used:
- Yarrow;
- St. John's wort;
- Common dill;
- Pharmaceutical camomile;
- Mint;
- Anise;
- Bobovnik.
Often in folk medicine, freshly prepared potato juice is used for heartburn and belching.
An infusion of flax seeds also has enormous benefits; it is prepared in advance and consumed in the morning.
Calamus root is also an effective remedy. A pinch of the crushed product is dissolved in a glass of warm water and consumed before meals.