Signs and symptoms
The onset of the disease is indicated, first of all, by a sharp increase or decrease in appetite, as well as night hunger pains.
As the disease progresses, the list of symptoms expands:
- heartburn and aching pain in the left hypochondrium;
- black stool is a sign of gastric and/or intestinal bleeding (optional symptom);
- “sour belching” (this symptom can also occur with low acidity);
- nausea, usually on an empty stomach;
- vomiting, which occurs when a person has consumed a large portion of sour/fermented milk products;
- a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood provokes dizziness, weakness, shortness of breath, increased heart rate, and sometimes loss of consciousness.
- gas formation, frequent bloating;
- Constipation.
General symptoms of hyperacid gastritis
The main symptoms of gastritis with high acidity are as follows:
- pain of a pulling nature (sometimes a burning sensation in the abdomen) in the abdomen and left hypochondrium, they can become cutting or become paroxysmal;
- heartburn - this symptom is considered a specific sign of this type of gastritis;
- sour belching - the reflux of air and stomach contents into the oral cavity - indicates the presence of increased gastric secretion (while rotten belching is inherent in gastritis with low acidity);
- white coating on the tongue, bad breath;
- nausea, possibly with vomiting. Nausea can occur during long intervals between meals, and vomiting occurs in the presence of erosion, when the patient abuses acidic foods; sometimes vomiting occurs with streaks of blood, mucus or bile. After vomiting, pain may be relieved;
- increased gas formation, rumbling, bloating, which arise as a result of fermentation in the stomach;
- lack and loss of appetite;
- indigestion (diarrhea or constipation);
- night or hunger pain with an empty stomach.
Additional symptoms of this type of gastritis are:
- severe weakness;
- increased sweating at times;
- dizziness;
- palpitations and pressure lability;
- increased salivation;
- heartache.
With severe damage to the middle part of the stomach and increased acidity, signs of iron deficiency, pernicious, and folate deficiency anemia are noticed.
When a patient has chronic gastritis with high acidity, the symptoms of the disease are not so pronounced and appear with provoking factors, such as:
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- binge eating;
- food poisoning or eating food that irritates the stomach - fried, spicy, very cold or hot food;
- severe stress;
- smoking.
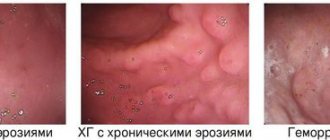
Exacerbation of hyperacid gastritis usually occurs in spring and autumn. With a prolonged course of hyperacid gastritis, in the absence of treatment, erosions form on the mucous membrane, followed by development into a gastric ulcer. Prolonged injury to the mucous membrane can lead to atrophy and the development of atrophic gastritis, which can then lead to organ cancer.
How to treat gastritis with high acidity
Gastritis is a disease that is treated by a gastroenterologist and nutritionist. The tandem of these two specialists must study in detail the patient’s medical history, physiological characteristics of the body, chronic diseases, including the gastrointestinal tract. Based on the diagnostic data obtained, doctors determine the type, form, stage of the disease, acidity level, and then prescribe the optimal treatment.
It is worth noting that for gastritis it is important to use several treatment methods. For example, a combination of folk remedies and drug therapy. However, following the diet prescribed in the individual diet is a prerequisite for the patient’s recovery.
Treatment of the disease involves the use of medications. However, today doctors, when selecting medications for therapy, are guided not by the level of stomach acidity, but by the condition of the mucous membrane.
Often, medications are first prescribed to relieve pain symptoms. The second task of such drugs is to reduce inflammatory processes. These painkillers include: No-shpa, Drotaverine, Metacin, Gastrocepin.
Treatment then continues with medications aimed at neutralizing the increased acidity. Such medications are called antacids. They contain a high concentration of magnesium and aluminum, which have the desired long-lasting effect.
Such antacids include: Gasterin, Almagel, Maalox, Altacid, Topalkan, Gastal, Rutacid, Gevixon, Palmagel. Treatment of the disease may also include taking blocker drugs that reduce the secretion of gastric glands, for example, Omeprazole, Rabeprazole. It is important to follow the dosage of the drug agreed with your doctor.
Gastritis - what is it?
The disease gastritis manifests itself in the form of an inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa. This type of inflammation reduces the normal functioning of the organ and leads to weakened human well-being.
Gastritis can disrupt the normal level of microflora and very often contributes to an increase in the level of hydrochloric acid, which leads to the formation of erosion and unpleasant symptoms.
Gastritis can take several forms:
- Initial – during which the patient does not feel strong symptoms, and the disease most often goes away on its own;
- Acute gastritis - symptoms manifest as severe pain and interfere with the digestion process;
- Chronic – the disease tends to arise and disappear on its own. Most often, this type cannot be treated.
In the absence of the necessary type of treatment, the disease can develop into more complex types of diseases and pose a threat to human life.
Rules of a therapeutic diet
The basic rule of the diet when treating gastritis with high acidity is frequent intake of warm food in small quantities.
The diet should be balanced, fortified and fractional. Prohibited foods include all spicy, salty, fried, fatty foods, sour foods and dishes, and alcohol.
Below is a table of prohibited and recommended foods, indicating the correct method for preparing them.
| Products/dishes | Allowed | Prohibited |
| Cereals, pasta | Buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, semolina, vermicelli. | Corn, wheat, beans, pearl barley. |
| First (liquid) | Vegetable and meat low-fat broths, milk soups, puree soups. | Rich borscht and soups, mushroom broths, okroshka. |
| Meat | Beef, rabbit, turkey, chicken in the form of cutlets, meatballs, meatballs, soufflé, meatballs and zraz. Cook in a steamer or slow cooker. Boiled tongue and liver. | Goose, duck, pork, fatty and stringy types of meat. Smoked sausage, frankfurters. |
| Fish | River (pike perch, cheek); sea (cod, pollock, hake) boiled. | Salted (salmon, salmon, trout) and canned. |
| Flour | Rusks, dried wheat, biscuits, savory buns and cheesecakes. | Rye bread, freshly baked puff pastry and yeast dough. |
| Vegetables and greens | Potatoes, carrots, cauliflower, steamed. Dill and parsley. | White cabbage, mushrooms, onions, spinach. Canned, pickled, pickled cucumbers, etc. form. |
| Fruits | All berries and fruits are pureed, baked or boiled. | Sour and citrus. |
| Milk products | Milk, kefir, yogurt, sour cream, cottage cheese. | Fatty and spicy cheeses. |
| Spices and seasonings | Cinnamon, vanilla in moderation. | Mayonnaise, ketchup, marinades, sauces, ginger, etc. |
| Beverages | Rosehip/rowan decoction, weak green tea, freshly squeezed juice, lightly carbonated mineral water. | Carbonated drinks, lemonades, citrus juices, strong black coffee/tea. |
Physiotherapeutic treatments
Treatment using procedures will be effective only in combination with other methods. Physiotherapeutic method is used to enhance the effect of medications. It is carried out on an outpatient basis in medical centers, inpatiently in physiotherapy departments of hospitals, and in sanatoriums.
The main supporting procedures are:
- Electrophoresis with antispasmodics (at home, you can replace it with heating pads applied to the stomach area).
- Magnetic therapy and hydrotherapy are aimed at accelerating the healing of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Usually used in periods between exacerbations of a chronic disease.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of gastritis with high acidity is infection with Helicobacter pylori. Repeated studies have proven a direct connection between the severity of inflammation of the gastric mucosa with hyperproduction of hydrochloric acid and the degree of bacterial invasion.
Helicobacter pylori is a bacteria unique in its properties, capable of not only surviving, but also actively reproducing in the stomach environment, which is aggressive for other microorganisms. They create an alkaline (ammonia) shell around themselves, which protects them from acidic gastric contents. At the same time, ammonia irritates the gastric mucosa, causing a decrease in somatostatin levels and an increase in gastrin secretion. As a result, the production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells increases and the overall acidity of gastric juice increases. In addition, Helicobacter pylori directly affects the epithelial cells of the stomach, thereby triggering the inflammatory process.
Exacerbation of Helicobacter pylori infection can be provoked by:
- unhealthy diet (abuse of fried, fatty, spicy foods, dishes rich in extractive substances);
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- food allergies;
- caffeineism (dependence on coffee, strong tea);
- taking certain medications (glucocorticoids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- exposure to ionizing radiation;
- severe stress.
Improper nutrition can provoke exacerbation of gastritis with high acidity
In addition to external ones, there are also a number of internal factors that provoke the development of gastritis with high acidity. These include:
- metabolic disorders (gout, thyroid disease, diabetes);
- severe chronic infectious and somatic diseases;
- hypoxia.
Gastritis with high acidity is often observed in young people, adolescents and children.
Gastritis with high acidity often develops against the background of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract due to reflex and direct pathological effects. For example, with gastroduodenal reflux, the contents of the duodenum are thrown through the pylorus into the stomach. The bile it contains damages the gastric mucosa and contributes to the onset of inflammation.
The body has a powerful defense system that prevents damage to the mucous membrane by aggressive gastric contents. However, there are a number of factors that weaken this protective mechanism and thereby contribute to the development of gastritis with high acidity:
- hereditary predisposition;
- prolonged physical or mental fatigue;
- weakening of the body's defenses;
- occupational hazards.
Folk remedies
Treatment of stomach inflammation can be supplemented with non-traditional methods that use folk remedies. Basically, the main ingredients for preparing decoctions and infusions are herbs, less often vegetables.
Below are the most popular folk recipes for the treatment of gastritis with high acidity:
- Herbal decoction of mint leaves, watchwort, yarrow, St. John's wort (proportions 1:1.5:1:2).
- A mixture of celandine herbs, chamomile, St. John's wort (1:3:3).
- A one-component infusion can consist of herbs or mint/linden/plantain leaves.
The preparation scheme for all of the above decoctions is identical.
The natural components of each recipe must be crushed, mixed until smooth and poured with boiling water.
Infuse the resulting preparation for at least 3-6 hours, be sure to strain. Use equal parts at least 3 times a day 30-60 minutes before meals.
Little-known folk remedies for the treatment of gastritis of the stomach:
- Drink 3/4 glass of potato juice on an empty stomach every day for 10 days.
- 150 g of warm honey solution daily for 30-40 days.
General principles of treatment
When gastritis occurs, the following treatment principles are most often used:
- reduction of pain symptoms in patients;
- reducing the process of inflammation in the stomach;
- restoration of gastric microflora;
- eliminating the causes of the disease;
- an integrated approach to the process of eliminating gastritis;
- maintaining proper nutrition.
During the treatment of gastritis, it is recommended to follow a certain type of diet and increase the intake of vitamins and minerals.
Gastritis in children
Most often, the disease manifests itself at the age of 6 years, when the child begins to actively develop. The reasons may be various factors.
For children, they most often use:
- Smecta - used as prescribed by a doctor. Has a sorbing effect on the body. Price 50 rubles per sachet;
- Famotidine - used for acute symptoms of the disease. Affects the secretion of the stomach, due to which there is less secretion of gastric juice. Price 70 rubles ;
- Festal - refers to enzymatic types of drugs. Reduce unpleasant symptoms and improve the digestion process. Price 210 rubles .
Smecta
Famotidine
Festal
To treat children, it is necessary to follow a dietary diet that normalizes the natural processes of regeneration of the digestive organs. You should also saturate your body with useful minerals and vitamins.