Causes of splenic rupture
Damage to tissue or organ lining occurs in people regardless of age; the disease is equally dangerous for adults, children and adolescents.
Characterized by the formation of an extensive hematoma filled with blood clots, it is called subcapsular. Over time, the capsule breaks and opens, causing bleeding.
The most common cause is severe trauma to the peritoneum.
Less commonly, the cause is one of the following factors:
- Increased physical activity in the presence of diseases of the lymphatic organ;
- Infectious processes in the body, increasing the load on the spleen and the risk of injury;
- Pathological changes in the spleen itself, for example, its enlargement;
- High level of blood filling during fetal growth during late pregnancy;
- Damage to the capsule during pushing during rapid and/or difficult labor;
- Clonal disorders of the hematopoietic system;
- Metabolic disease;
- Benign or malignant neoplasms in the cells of the spleen;
- Inflammatory processes of neighboring organs - for example, tuberculosis, cirrhosis of the liver, hepatitis C and others;
- Vector-borne infectious diseases - for example, malaria.
Prognosis after spleen removal
Since the functions performed by the spleen are performed not only by it, after removal of this organ a person, thanks to correct and complete rehabilitation measures, can return to a normal lifestyle. But possible consequences:
- weakened immunity;
- changes in the blood;
- signs of dyspepsia (digestive disorders);
- the formation of large and small blood clots in the vessels of the liver;
- atelectasis of the lungs - collapse of some of their areas.
For the rest of his life, a person who has had his spleen removed must adhere to certain recommendations:
- beware of infectious diseases - to do this, get vaccinated in a timely manner during epidemics, avoid crowded places (queues, festive events, public transport), get vaccinated before traveling to exotic countries, carefully follow the rules of sanitation and hygiene;
- If you have a cold, do not self-medicate at home, but immediately consult a doctor;
- avoid countries where you can become infected with malaria;
- for the first two years, do a control ultrasound of the abdominal organs once a year, then, if there are no changes due to splenectomy, once every two years;
- Use all medications only as prescribed by a doctor or after consultation with him;
- engage in physical exercise (but not sports - the difference with physical exercise is the severity of physical activity); observe the correct regime of rest, work, nutrition, sex, quit smoking, do not use drugs, do not abuse alcohol (but reduce its use to a minimum) - that is , lead a healthy lifestyle.
If these simple rules are carefully followed, the patient with the spleen removed will not feel any changes in his general condition.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
15, total, today
( 195 votes, average: 4.58 out of 5)
Periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum): forms and treatment
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: symptoms and treatment
Related Posts
Signs and symptoms
A warning about damage to the tissues or capsule of the spleen is the following clinical picture:
- Acute, unbearable pain in the left hypochondrium, which radiates under the shoulder blade;
- Pain on palpation;
- Nausea with vomiting or urge;
- Instant feeling of weakness;
- Bloating of the anterior abdominal wall;
- Sharp paleness as a result of internal bleeding;
- Loss of strength and appetite;
- Rapid pulse;
- Reduced blood pressure;
- Dizziness, resulting in decreased visual acuity;
- Pain in the anus;
- Loss of orientation in space, sometimes fainting.
At the moment of rupture, a person feels an unusual internal push inside the sternum on the left side.
When done simultaneously, the listed symptoms appear immediately, within five to ten minutes. Two-stage is characterized by the appearance of symptoms only after final damage to the organ tissue.
Signs
Symptoms of splenic rupture are very varied, their intensity depends on the degree of rupture, the presence or absence of damage to other organs. It also matters how much time has passed since the injury.
Immediately after injury, the condition may be subacute or acute. In the second case, severe bleeding is observed without signs of peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum.
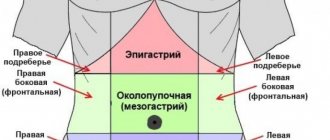
The leading symptom in adults in the first few hours is pain under the left rib and in the upper abdomen. About half of the patients complain that the pain radiates to the left shoulder and back in the projection of the spleen.
Almost all victims tend to take the fetal position - lying on their left side, they pull their knees to their stomach - or roll over onto their back. The abdomen does not move when breathing; it is usually tense, although in severe cases - with collapse or traumatic shock - it can be relaxed.
Some time after the injury, the tone of the intestinal muscles decreases significantly, and paresis, a condition close to paralysis, may develop. This is manifested by stool retention and flatulence.
In addition to local symptoms, signs of increasing blood loss appear:
- pale skin;
- sticky cold sweat;
- drop in blood pressure;
- rapid heartbeat;
- increasing weakness;
- dyspnea;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
Somewhat later, apathy may be replaced by motor agitation, which alternates with fainting. At the same time, the pulse accelerates to 120 beats per minute and higher, the pressure drops below 70 mm Hg. Art.
Diagnosis at this stage presents some difficulties, since the clinical picture of splenic rupture does not have specific signs, except for pain in the left hypochondrium. The remaining symptoms are typical for any “acute abdomen”.
Diagnosis of splenic rupture
It is impossible not to notice the primary symptoms due to the sharp pain that a person feels. However, it is difficult to make a correct diagnosis, because the symptoms accompanying the pathology are also characteristic of other diseases in the abdominal cavity.
Only surgical intervention helps to definitively confirm the pathology; in other cases, establishing the correct diagnosis is possible with a probability of 12-14%.
If you suspect a splenic rupture, you must contact a specialist.
They will immediately prescribe a number of procedures necessary to determine an accurate diagnosis:
- Ultrasonography. The ruptures on the screen appear as anechoic (non-ultrasound-reflecting) formations of the edges and tissue of the spleen - this is due to the release of blood from the injury sites. Indicators of pathology on ultrasound are a decrease or complete absence of mobility of the diaphragm in the area of the left dome and an obvious displacement of the abdominal organs to the left. In certain cases, ultrasound examination is not possible due to pain when pressing on the skin;
- Laparoscopy. This surgical method allows you to determine the presence of damage, location and extent. Laparoscopy is a puncture of the abdominal cavity and insertion of a telescopic tube - a laparoscope - inside. In cases where laparoscopy cannot be performed due to contraindications, the doctor prescribes a similar surgical diagnostic method - laparocentesis. The soft tissues are pierced with a trocar and stylet and the fluid is removed;
- X-ray examination of the abdomen and chest. Sometimes it is impossible to see and evaluate the problem with plain radiography, so specialists prescribe a contrast study of the vascular network - antiography. It can be used to identify damage to blood vessels resulting from injury and assess the extent of blood loss.
Kinds
Splenic rupture is a pathological condition of this organ, which is classified according to the severity of the injury, as well as the presence of corresponding symptoms in adults and children.
The table below shows the main types of damage of this type:
| Types of splenic ruptures | Characteristics of the pathological state of the organ |
| Contusion | Contusion is the mildest degree of injury to the spleen. In this case, a small section of parenchyma ruptures, but the integrity of the main capsule of this organ is preserved. A patient with similar symptoms requires a surgical operation with minimal risk of complications associated with surgical intervention. After restoring the integrity of the spleen parenchyma, the patient is able to lead his previous lifestyle. If there is a contusion, there is no need to completely remove the organ. |
| Capsule rupture | Rupture of the splenic capsule most often occurs with abdominal injuries that occur due to contact of the surface of the left hypochondrium with sharp objects. In this case, the integrity of the protective shell of the organ is violated, but its parenchymal tissue remains undamaged. Rupture of the splenic capsule is a moderate injury. |
| Instantaneous rupture | Obtaining a one-stage rupture of the spleen involves a simultaneous violation of the integrity of the protective capsule of the organ and its parenchyma. This type of injury is dangerous to the health of the victim and requires urgent surgical procedures to stop internal bleeding. Simultaneous organ rupture is quite common in people with multiple body injuries who have experienced a fall from a great height. |
| Two-moment rupture | Two-stage rupture of the spleen is characterized by stages of damage to this organ. Initially, against the background of the injury, a rupture of parenchymal tissue occurs, and after a certain period of time, a subsequent violation of the integrity of the organ capsule occurs. The main danger of this type of injury is that secondary progression of the rupture can occur at any time. |
| Two-moment discontinuity of imaginary type | This type of splenic injury is also called simultaneous rupture of parenchymal tissue and the protective capsule with further tamponade of the damaged area. In this case, the area of the organ with compromised integrity is blocked by a dense blood clot even before the onset of symptoms characteristic of severe damage to the spleen. After a certain period of time, the formed blood clot is washed out, which entails the opening of extensive internal bleeding. The task of physicians who diagnose a patient with signs of a two-stage splenic rupture of an imaginary type is to promptly detect not only the presence of damage, but also the fact of organ tamponade through thrombosis. |
| Three-moment discontinuity of imaginary type | This type of violation of the integrity of the spleen is characterized by the presence of a two-stage rupture of the parenchyma and the protective capsule, which after a certain period of time begins to close with blood clots. In this case, the opening of internal bleeding occurs much later than usual. Three-stage rupture of the spleen is characterized by profuse blood loss, which begins suddenly and also threatens the patient’s life. |
In medical practice, the vast majority of spleen tissue injuries are instantaneous ruptures, the occurrence of which is accompanied by the immediate opening of internal bleeding into the abdominal cavity.
This type of damage to this organ does not present any particular difficulties in diagnosis; it allows timely detection of pathology and taking measures to stop blood loss. Two-stage organ ruptures occur in 13% of all patients with such injuries.
The average duration of the time interval from the moment of damage to the spleen to the opening of internal bleeding can range from several hours to 2 weeks.
It all depends on the nature of the injury, the reasons that provoked it, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Types of splenic rupture
Organ ruptures are conventionally divided into single and multiple, and the latter, according to medical statistics, occur more often.
The full classification is as follows:
- Without damage to the outer shell - this condition is also called contusion;
- Rupture of the capsule without damaging the parenchyma (that is, functionally active epithelial cells);
- Simultaneous rupture of the capsule and shell;
- Damage to the parenchyma, followed after a while by rupture of the membrane - two-moment latent;
- Damage to the entire spleen with late bleeding.
When making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the full clinical picture: the patient’s complaints, pulse, appearance, blood pressure, results of a clinical blood and urine test.
The damage can only be treated surgically. You cannot get by with taking medications or using folk remedies.
If you have alarming symptoms, you need to call doctors, but you shouldn’t remain idle until they arrive. Correctly provided first aid will improve the patient’s well-being and shorten the recovery time after surgery.
Consequences and prognosis
A ruptured spleen has dangerous consequences. The risk of death depends on the general condition of the victim, the extent of the injury and the correctness of medical care. But even timely surgical treatment cannot completely return a person to their usual way of life. The operation only stops the bleeding and partially preserves the functions of the damaged organ. At the same time, the patient’s immune defense decreases, the number of platelets increases, and he begins to get sick more often and longer. Severe infections are complicated by serious processes. In the early postoperative period, secondary bleeding, peritonitis, pancreatic necrosis, and subphrenic abscess often occur. A little later, thrombocytosis, fulminant sepsis, decreased resistance to infection and oncopathology, and the development of asthenia develop. The body of newborns and elderly people is often unable to cope with severe pathology.
Damage in which the integrity of the outer shell of the organ and its parenchyma is disrupted is called splenic rupture. The main sign of the process is the dissociation and separation of the organ structure with the formation of a slit-like space. Closed injuries are diagnosed more often than open ones. A ruptured spleen is a medical emergency. Otherwise, the victim will die from massive bleeding and shock. You can live without a spleen. If the organ is completely removed, the liver takes over its functions. When an organ ruptures, the entire body suffers.
First aid for a ruptured spleen
Sequence of actions when providing first aid:
- Lay the victim with his back on a hard surface (couch, floor), and place a small cushion or rolled towel under his head;
- Using three fingers or the bottom of your palm, apply pressure in the middle of the chest - this will help stop internal bleeding;
- Repeat such pressure every 30-35 seconds until the victim is taken away in an ambulance;
- Apply a cold compress to the abdomen area - use a cold damp cloth, frozen food from the freezer, etc.
Diagnostics
Currently, due to the widespread use of endoscopic methods, laparoscopy is becoming increasingly important in the diagnosis of splenic ruptures.
At the initial stages of pathology development, blood tests are of little information. This is explained by the fact that due to the activation of compensation mechanisms, the composition of the blood can remain within normal limits for several hours.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to perform the following instrumental techniques:
- Radiography. Typically, x-rays are taken of two areas: the chest and abdomen. The technique allows you to identify a rupture of the spleen by the following signs: displacement of the left side of the colon, identification of homogeneous tissue on the left under the diaphragm, dilatation of the stomach, limited mobility of the spleen.
- Laparoscopy. The technique makes it possible to detect bleeding localized in the abdominal cavity within a short time. This is an endoscopic procedure that allows doctors to determine the source of the bleeding.
- Angiography. This procedure requires a significant amount of time, and therefore is used extremely rarely in modern diagnostics of splenic ruptures. In addition, it is very difficult to find good equipment and experienced specialists.
- Laparocentesis. It is performed if the specialist does not have endoscopic equipment to carry out diagnostics. It involves puncturing the anterior abdominal wall with a special hollow instrument through which a catheter is inserted to perform aspiration (suction) of the contents of the abdominal cavity. Although this technique allows you to identify the presence of bleeding in the abdominal cavity, it is not informative enough to determine its source.
Surgical treatment of splenic rupture
The purpose of surgery is to stop internal bleeding, which leads to death. Before surgery, resuscitators stabilize hemodynamics by transfusion of blood or blood substitutes.
In cases where the patient is in critical condition and delay can end tragically, specialists perform an emergency operation to stitch or remove, while continuing the transfusion.
Previously, twenty to thirty years ago, one method of treatment was used in medicine - removal of the entire organ (splenectomy).
Today, splenectomy is indicated only in the following cases:
- Inability to close the wound;
- Separation of the spleen from the pedicle;
- Lacerated and through knife or gunshot wounds;
- Cracks and breaks directed towards the organ gates;
- Cutting seams.
In other situations, after the operation, the organ remains completely or partially.
Treatment methods
Before starting the operation, doctors try to stabilize the victim’s condition as much as possible, transfuse blood and blood substitutes, and restore blood pressure to the required levels. If it is impossible to do this, the operation is performed in any case, but then the patient’s body is supported with the help of special devices.
A stay in the intensive care unit may take up to 10 days, and full recovery may take one to two months.
If previously the spleen was removed, now it is possible to sutured the parenchyma and restore the blood supply to the organ. Unfortunately, successful operations are performed only in one percent of cases, and in case of extensive damage, there is no point in suturing the parenchyma, because the edges of the organ diverge due to significant pressure in it.
Therefore, in case of large injuries, they resort to splenectomy - removal of the spleen. After the operation, infusions of blood substitutes or blood are continued for some time, trying to stabilize the patient’s condition.
Conservative treatment methods are used quite rarely.
Splenic rupture is a dangerous injury, and an incorrectly selected technique can lead to significant blood loss.
Therefore, the risks of conservative treatment are high, and complications can lurk everywhere. The injury is treated conservatively only if the pathology does not progress, blood counts are stable for two days, there is no need for a transfusion, and the patient is young enough (up to 55 years). Such patients are monitored especially carefully.
Recovery after surgery
In order to soften the blow to the immune system, immunostimulating drugs and vitamin-mineral complexes are prescribed, which a person takes for the rest of his life.
Recovery in adults and children after surgery lasts three to four months, but despite such a short period, it is difficult. During this period, they adhere to bed rest, take medications prescribed by a doctor - antibiotics and painkillers, and follow a strict diet.
The patient's diet consists of the following dishes:
- Non-rich, low-fat meat, fish and vegetable broths;
- Porridge from brown rice, green buckwheat, millet, pearl barley, oatmeal;
- Boiled or stewed red fish;
- Stewed or steamed vegetables: potatoes, zucchini, all types of cabbage, bell peppers, etc.
To restore the body, you need to absorb 2000-2100 kilocalories per day.
Smoking and drinking alcohol in any form is prohibited.
Patients after splenectomy are advised to avoid hypothermia to prevent a decrease in immunity.
Emergency surgery as the only treatment option
The only effective way to stop internal bleeding when the spleen ruptures is emergency surgery. It must be carried out as soon as possible, since in the case of intra-abdominal bleeding, death can quickly occur.
Small hematomas or breaks in the parenchyma are opened and sutured without removing the organ. But if the degree of damage is significant, then the spleen is completely removed. This operation is called splenectomy.
At the moment, doctors give preference to organ-saving operations and try to preserve the spleen. But if this is not possible, splenectomy is the only way to save the victim’s life.
Before the operation, blood transfusion is performed, since a person, as a rule, loses a large amount of blood.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed additional treatment, which is aimed at preventing complications, reducing pain and replenishing blood loss in the body.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- antibiotics (to prevent bacterial complications);
- antispasmodics and painkillers;
- transfusion of plasma and blood replacement components.
What is a splenic contusion?
A bruise of the spleen is a closed injury to the tissues of an organ without changing its shape and structure, which is a consequence of injuries in the abdominal area - blows, falls, car accidents, gunshot or knife wounds.
Injury to the spleen can lead to:
- contusion, characterized by damage to the splenic parenchyma against the background of the integrity of the organ capsule;
- damage to the splenic capsule without compromising the integrity of the parenchyma;
- immediate rupture of an organ, accompanied by simultaneous damage to all its layers;
- two-stage rupture of an organ, characterized by sequential tissue damage - deformation of the parenchyma with a violation of the integrity of the capsule (the time interval between these phenomena can range from 10 hours to 3 days);
- a two-component rupture complicated by tamponade - blocking of arteries with blood clots.
A hematoma due to a bruise of the spleen can be either open or closed. In the first case, a bruise appears on the injured site, in the second, a subcapsular hematoma forms.
Attention! A splenic hematoma cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Depending on the nature of the prevalence of the pathological process, bruises are divided into isolated and multiple. In the first case, only the spleen is injured, in the second, other organs located in the abdominal cavity are also affected.
How to live with a sewn-up spleen?
If the organ has been preserved, further therapy involves taking good care of your health. It will be necessary to exclude or minimize traumatic situations fraught with contusion of the spleen. Heavy loads on the abdominal area are contraindicated. The slightest suspicion of relapse should prompt a medical examination.
A healthy diet and a moderately active lifestyle will help avoid diseases that will cause a pathogenic environment to attack the blood and, consequently, the spleen.
When is it necessary to remove the spleen?
The bleeding that accompanies a ruptured spleen is life-threatening, so the goal of surgery is to stop the bleeding.
A safe and effective way to stop this is to remove the organ. After all, during the work, the spleen is constantly filled with blood, and such pressure can tear the sutures placed during the operation.
Lacerated, through wounds, multiple ruptures and cracks in the spleen, which are not compatible with the normal functioning of the organ in the future, serve as an indication for splenectomy (the so-called operation to remove the spleen). The organ will also be removed if it is torn from the vascular pedicle on which the splenic vein and artery are located.
Serious soft tissue hematomas of the spleen pose the risk of sudden rupture, so this is also a reason for resection.
Getting rid of an organ is a reliable method, but not the only one.
Splenic rupture: first aid
Among injuries to the abdominal organs, this injury occurs in approximately thirty percent of cases. It is accompanied by pain, which is first localized in the left side of the abdomen, and then spreads to its entire area.
The rupture will be accompanied by bleeding, and only a specialist knows how to stop it, so the first thing to do is call a doctor!
If internal bleeding is not stopped in time, death will occur. Death from splenic rupture is possible with a loss of two to five liters of blood. The rate of flow depends on the size of the wound and the intensity of the process.
Sometimes a loss of three hundred milliliters of blood is enough for anoxia (oxygen deficiency) to occur and death to occur.
While waiting for professional help, urgent measures need to be taken:
- Place the victim carefully, without sudden movements, on his back and ask him not to move so that the bleeding does not increase.
- Apply an ice pack to the area where the pain is felt.
- You can press and hold the solar plexus area firmly until emergency services arrive, this will compress the abdominal aorta and reduce blood loss.
Possible complications
One of the most dangerous complications is secondary bleeding. Sometimes even a sutured spleen can cause bleeding because the blood pressure in the organ is too high. Sometimes, under significant stress, such a spleen simply bursts.
After surgery, complications such as secondary immunodeficiency, especially in children, and post-splenectomy sepsis may also develop.
What should you do if you have to remove your spleen due to a rupture? Is it possible to live without her?
One of the most dangerous complications is secondary bleeding. Sometimes even a sutured spleen can cause bleeding because the blood pressure in the organ is too high. Sometimes, under significant stress, such a spleen simply bursts.
Complications such as secondary immunodeficiency, especially in children, and post-splenectomy sepsis may also develop after surgery.
What should you do if you have to remove your spleen due to a rupture? Is it possible to live without her?
No one is immune from accidents. This is why abdominal injuries, including bruises to the spleen, are quite common. Damage to this vital organ can result in large blood loss, so you need to know how to recognize the symptoms of a bruise and provide assistance.
If the spleen is damaged, serious complications can arise, but at the same time, removing it entirely does not significantly change the performance of the body
The spleen is an organ located in the upper left part of the abdominal cavity (near the stomach), changing its size depending on the filling with blood and having a vertically elongated, horizontally elongated or obliquely elongated shape. The normal weight of the spleen is 150-200 grams, its length does not exceed 16, its width is six, and its thickness is two centimeters.
The main functions of the body are:
- Protective. The spleen is a natural filter of the human body, preventing toxins and pathogenic bacteria from entering the blood. The spleen produces lymphocytes - immune cells. That is why the removal of this organ leads to a sharp decrease in immunity.
- Control of blood cell functions. When old red blood cells and platelets are detected, the organ destroys them, after which the hemoglobin from the red blood cells turns into bilirubin and hemosiderin.
- Participation in immune processes. The spleen takes part in the production of immunoglobulin and produces antibodies to antigens that have entered the body.
- Participation in iron production processes.
- Production of white blood cells and red blood cells during pregnancy. After childbirth, these functions are taken over by the bone marrow.
The spleen is a vital organ of the human body, and therefore its damage can lead to irreversible consequences, and in some cases, death.
The severity of the consequences of bruises for the body is determined both by the degree of damage to organ tissue and by the quality and timeliness of medical care provided.
The most common complication of splenic contusion is internal bleeding, which in some cases is prone to recurrence.
In addition, it is possible:
- splenomegaly (increase in organ size);
- the formation of cysts and other neoplasms in the abdominal space (they can be either malignant or benign);
- necrotic damage to nearby organs;
- development of septic reactions.
As for surgical removal of the spleen, it can lead to the following complications:
- bleeding;
- infection of the wound surface;
- violation of the integrity of nearby tissues and organs;
- the appearance of blood clots or blood clots;
- the formation of a hernia in the area where instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity;
- change in blood formula;
- development of sepsis;
- disorders of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
These disorders can develop within two years after surgery.
A sign of complications with a bruised spleen may be severe bloating and lack of urge to defecate.
Subsequently, people who have had a splenectomy may experience:
- pancreatitis;
- decreased immunity and susceptibility to certain diseases;
- formation of blood clots in the vessels of the liver;
- Atelectasis of the lungs - collapse or airlessness of their alveoli.
The likelihood of these complications can be reduced by:
- preventive examinations and ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract;
- blood and urine tests taken on a regular basis;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition;
- avoidance of taking medications without a doctor’s prescription and indications;
- dieting.
People who have had their spleen removed should be alert to the following symptoms:
- sharp pain in the abdominal area;
- increased body temperature;
- dyspnea;
- increased sweating;
- dizziness, nausea, vomiting;
- prolonged diarrhea of unknown origin;
- long-lasting cough;
- increased heart rate;
- blood, pus, or inflammation in the surgical incision areas.
If any of these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor - this will help avoid the development of postoperative complications.
If a person whose spleen has ruptured does not promptly go to a hospital for help, he will have to face very dangerous complications:
- against the background of bleeding, anemia will begin to develop;
- intestinal paresis may occur;
- collapse will occur;
- a state of shock will develop;
- the functionality of other organs will be impaired;
- death.
The greatest threat to the patient’s life is rupture of the spleen with its subsequent crushing.
In this case, the person develops a traumatic state of shock, which modern medicine classifies as follows:
- Lung. The person experiences lethargy, the skin begins to turn pale, shortness of breath appears, and the pulse quickens. There is a decrease in reflexes, but consciousness is not impaired.
- Average. The patient becomes lethargic, the pulse rate reaches 140 beats per minute.
- Heavy. The skin becomes gray in color. Cold sweat appears, and acrocyanosis develops. The pulse rate reaches 160 beats per minute.
- Extremely difficult. The person is unconscious and the pulse cannot be felt.
Why does the spleen rupture?
- The main, but not the only cause of organ damage is a concussion or bruise due to a blow to the peritoneum or ribs, as a result of a fall from a height, a transport accident and other traumatic factors.
- Infections and inflammations in the body are a common cause of splenic rupture because they increase the size of the organ, which is extremely unfavorable for its tissues. Tuberculosis, hepatitis, pyelonephritis, and liver diseases pose great dangers.
- Excessive tension of the peritoneum during heavy lifting or during intense labor is dangerous for the spleen.
- During pregnancy, the volume of blood in a woman’s body increases, and this is also a threatening factor for organ tissue.