The role of bile in the body
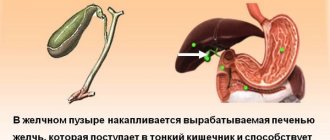
Full functioning of the digestive system is impossible without the participation of bile. Even a slight deviation from the norm leads to pathological changes and is reflected in a person’s well-being. Bile is produced by the liver by hepatocyte cells.
Initially, it fills the bile ducts, then the gallbladder and duodenum. The liver produces about 1500 ml of bile per day. The secretion accumulates in the gallbladder, and its release into the duodenum occurs 5 to 12 minutes after eating.
The role of bile in the body cannot be underestimated. It takes part in many enzymatic processes:
- promotes the production of hormones in the intestines;
- produces mucus and micelles;
- reduces the aggressiveness of pepsin;
- activates motility and tone of the small intestine;
- eliminates the adhesion of proteins to bacteria.
- takes part in metabolic processes;
- disinfects feces and has a moderate antiseptic effect;
- improves the absorption of water-soluble fatty acids, amino acids and vitamins.
All the positive properties of bile boil down to the fact that it helps in the digestion of food. The chemical composition of the secretion consists of enzymes, bilirubin, biliverdin, cholesterol, and also contains a small amount of vitamins and inorganic minerals. Due to the composition and properties of bile, the process of digesting food in the stomach is successfully completed in the intestines.
Causes of vomiting with bile
If bile is released during vomiting, this is a sign that the secretion has entered the stomach from the small intestine through the pyloric valve. Normally, it should close when semi-digested food, along with gastric secretions, enters the duodenum. When this process is disrupted, bile constantly enters the stomach, irritation of the receptors occurs, and the gag reflex itself does not bring any relief.
There are many causes of vomiting with bile, so before carrying out treatment measures, you need to identify the main cause, pay attention to the accompanying symptoms, and undergo the necessary research.
In any case, if repeated vomiting with bile occurs, the patient should not refuse hospitalization, since some diseases that cause this symptom can be life-threatening.
For cholelithiasis
Cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis) is a disease in which stones or sand are present in the bile ducts or bladder. This disease is considered one of the main causes of bile vomiting. The mechanism for the development of this symptom is the penetration of bile acids into the stomach.
The formations themselves consist of particles of bile exchange, which begin to stick together, forming stones. The size of such formations can range from several millimeters to several centimeters. The bile ducts are much smaller than the bladder itself, so when stones get into them, a blockage occurs. Symptoms in such cases are pronounced and are accompanied by:
- biliary or hepatic colic - acute pain in the right hypochondrium, which radiates to the lower back, scapula, sternum and other areas;
- nausea, vomiting with bile), which does not bring relief;
- yellowing of the skin;
- increased body temperature;
- bloating, diarrhea, or constipation;
- general weakness;
- bitterness in the mouth.
Treatment of gallstone disease includes removing stones from the body, normalizing the functioning of organs and systems that take part in the production and excretion of bile. The doctor may prescribe conservative or surgical treatment. It all depends on the size of the stones and the general condition of the patient.
Vomiting after gallbladder removal
After cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder), bile passes directly from the hepatic ducts into the small intestine. Most patients suffer from the following symptoms during the postoperative period:
- intestinal disorders;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- pain in the side;
- diarrhea;
- pale skin;
- increased fatigue;
- nausea and vomiting of bile.
All these ailments often appear due to overeating or failure to follow a diet that must be strictly adhered to for a long period, and sometimes throughout life. Correcting the nutritional diet will relieve the patient of such symptoms.
Vomiting with cholecystitis
The inflammatory process in the gallbladder leads to the development of cholecystitis. With this disease, there is an uneven release of bile into the intestines, which causes irritation of the receptors with the subsequent appearance of nausea and a gag reflex. In addition, the patient has:
- increased body temperature;
- bowel dysfunction;
- acute pain in the right side, which intensifies with the slightest turn of the body, coughing, radiates to the lumbar region, back.
Treatment depends on the form of cholecystitis and the stage of its development. Acute forms require hospitalization. For minor and chronic disorders, therapy can be carried out on an outpatient basis. It consists of following a strict diet, taking medications of different pharmacological groups to eliminate symptoms and the inflammatory process.
For pancreatitis
Vomiting of bile is almost always present in acute pancreatitis. Inflammation of the pancreas causes disruption of the outflow of bile and poor digestion of food. Characteristic signs of the disease include:
- nausea, single or repeated vomiting with bile;
- pain in the left hypochondrium;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- temperature increase;
- general weakness and increased fatigue.
The development of pancreatitis with severe symptoms often manifests itself against the background of poor nutrition, alcohol consumption, or as a consequence of other gastrointestinal diseases. Treatment is carried out comprehensively, including following a diet and taking medications.
Pyloric stenosis
Pyloric stenosis (pyloric stenosis) develops as a complication of peptic ulcer disease. Accompanied by narrowing of the walls of the transition from the duodenum, decreased tone of the pyloric valve and muscle sphincter. All these pathological processes lead to the reflux of bile acids into the stomach, irritation of the mucous membrane, followed by vomiting. Pyloric stenosis is characterized by morning nausea and vomiting, pain and discomfort in the stomach after eating.
Other reasons
In addition to the main diseases and disorders that can lead to the appearance of vomiting with bile, there are others that may be associated with infectious diseases, be the result of intoxication of the body, or appear during exacerbation of certain diseases. Vomiting with bile exudate can result from:
- alcohol intoxication;
- toxicosis of pregnant women;
- disorders in the vestibular apparatus;
- brain tumors;
- helminthic infestations;
- brain injuries;
- abdominal injuries;
- kidney or adrenal disease;
- drug intolerance or overdose;
- diabetes;
- myocardial infarction.
Usually, vomiting of bile occurs during repeated cleansing of the stomach, when the urge to vomit is present, but the intestines have already been cleared of the contents. Sometimes it appears only in the morning, is not associated with food intake, and may contain an admixture of blood or particles of indigestible food.
If there is no relief after vomiting, such a symptom bothers the person systematically, there are other ailments, there is no need to delay visiting a doctor or self-medicate. The sooner a person seeks help from a doctor, the sooner the cause will be clear and the necessary treatment will be provided.
Treatment
For the treatment of belching, bitter taste in the mouth and in the presence of bile, the following drugs are prescribed:
- To protect the esophagus from the negative effects of bile, antacid medications are taken. They envelop the mucous membrane of organs, creating a protective layer. Pharmacies sell tablets and suspensions. Many of them relieve pain and help reduce acidity. Rennie, Almagel, Maalox.
- In order for the muscles of the lower sphincter to perform the main function and block the passage, Omez is taken.
- Often spasmodic phenomena occur due to stress. To relieve tension, take sedatives. Available in the form of tablets and drops. Valerian, Motherwort. You can take 10 drops per glass of water.
- To get rid of bile, choleretic drugs are taken, which help the easy outflow of digestive secretions. Doctors recommend not only medications, but also traditional medicine: teas, medicinal herbs. They are always available in pharmacies, formed into separate bags for greater convenience.
- During the period of illness, supporting the liver is very important to prevent further destruction. Galstena is prescribed, a plant-based drug. Take 1 tablet morning, afternoon and evening.
What does the color of bile mean?
Normally, bile is yellow, greenish or brown in color. If pathology is present, this indicator may change. The shade of liquid for different diseases is shown in the table:
| Color | Possible disruption of the gastrointestinal tract |
| Red | An admixture of blood from a disintegrating tumor, ulcer or other lesion of the biliary tract or intestines |
| Very dark | Stagnation |
| Faint color, white bile | Atrophy of the bladder mucosa |
| Dark yellow | Hemolytic jaundice |
| Pronounced green | Inflammation of the biliary tract. |
Of course, the color of bile does not provide grounds for making a final diagnosis. Its shade can only suggest one state or another. Next we need a more accurate diagnosis.
Who should I contact for help?
So what do you need to know about this? To deal with a problem, you must first determine what caused it. Belching of bile, the causes and treatment of which are discussed in our review, is evidence of a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract.
Therefore, you should contact the following doctors for help:
- The therapist conducts an oral interview with the patient and, based on the collected data, writes a referral for consultation with the right specialist.
- Gastroenterologist - deals with problems related to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. You can make an appointment with him without first visiting a therapist.
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor decides to prescribe additional laboratory tests to assess the patient’s condition and draw up a detailed clinical picture. As soon as the examination results are in hand, the most effective treatment is selected, which, as a rule, is based on taking medications.
Diagnostics
As noted more than once in the article, you should definitely consult a doctor. At the initial stage, a thorough examination by a gastroenterologist is carried out. The specialist uses palpation and tapping to determine the location of intense pain, then conducts a survey of the patient about taking medications or nutrition. The doctor prescribes tests, ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder, and endoscopy to determine the exact cause of bile vomiting. If necessary, the gallbladder is additionally examined using MRI and CT.
You can read more about the procedures in the articles: Ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver MRI of the gallbladder and ducts CT scan of the liver: indications, contraindications, preparation for the study
Vomiting bile during pregnancy
During pregnancy, vomiting bile is no exception. It can appear in the early stages with toxicosis or in the late trimesters. In the first case, this condition is not dangerous, but if vomiting in the last trimester, this may be a sign of gestosis, which is extremely dangerous for both the woman and the fetus.
Bile acids during vomiting can also be present in chronic diseases: cholecystitis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, etc. In any case, it is important to determine the cause and, if necessary, treat.
What should you not do if you have bilious vomiting?
When helping yourself or a stranger, the main thing is not to overdo it, otherwise you can cause serious harm to the body.
When vomiting with bile secretions, it is prohibited:
- drink alcoholic beverages, potentially dangerous foods that can provoke an attack;
- actively engage in sports, drink a lot of fluids of questionable quality;
- take painkillers or diuretics;
- Trying to cure unpleasant symptoms on your own without specifying the cause of their appearance.
Vomiting of bile in children
In a child, vomiting of bile, just like in an adult, can be caused by various disorders and diseases. In infants it can appear due to congenital anomalies of the bile ducts, poor nutrition of the mother or a change in formula, and often occurs with fever.
Causes
Abnormalities in the functioning of the stomach can occur due to:
- intestinal infections;
- food poisoning;
- binge eating;
- appendicitis;
- brain concussion;
- helminthic infestations.
Symptoms
Attention should also be paid to accompanying symptoms. Most often this is abdominal pain, elevated body temperature, pale skin, lack of appetite, diarrhea, excessive sweating and other signs.
If you are vomiting repeatedly and there is a yellow or green substance present, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor. Examination of the child and the results of the examination will help to recognize the cause and, if necessary, carry out treatment.
Biliary vomiting in a child, causes
What to do if a child is vomiting bile? Vomiting in a child, especially if it contains bile, requires an immediate visit to the doctor. If it was caused by food poisoning, the baby is placed in a hospital, where measures are taken to gently restore the little patient’s health and his diet is monitored.
In addition, vomiting with bile inclusions can be caused by problems in the gallbladder or due to inflammation of the appendix. If signs of appendicitis appear, the child must be immediately taken to the nearest hospital or an ambulance must be called. It should be remembered that parents of a sick baby must remain calm so that anxiety and panic are not transmitted to the child. This can frighten him or cause nervousness and hysteria, interfering with the work of doctors.
Vomiting bile after drinking alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption leads to severe intoxication of the body, so vomiting with bile in this condition is not uncommon. If such a symptom appears once, there is nothing to worry about, it is the body being cleansed of harmful toxins. However, repeated vomiting is a clear sign of disruption of the biliary tract.
Vomiting bile during alcohol intoxication has its own characteristics. Vomit is green in color due to the mixing of ethanol, stomach contents and bile. Sometimes, against the background of prolonged alcohol consumption, an exacerbation of chronic intestinal diseases occurs, which can also lead to vomiting of bile acids.
If the vomiting does not stop, the person’s condition worsens and medical attention is required. In a hospital setting, detoxification measures will be carried out that will help cleanse the body of accumulated toxins, thereby improving the general condition.
For minor poisoning, treatment can be done at home. It will include taking sorbents, drinking plenty of fluids, bed rest and no alcohol.
Diagnostic methods
What are they and what are their features? So, you are belching bile, what should you do? The first thing you need to do is make an appointment with a therapist or gastroenterologist. It is especially not recommended to hesitate if there is a white or yellowish coating on the tongue, and there is also a bitter taste in the mouth. Patients are examined according to the following scheme:
A number of specialized laboratory tests may be required to obtain more detailed information. The most commonly prescribed are:
- EGDS or esophagogastroduodenoscopy is the study of the inner walls of the esophagus using a flexible hose with a video camera installed at the end. It is highly informative and provides the opportunity to visually assess the degree of damage to internal organs.
- Ultrasound - it can be used to detect tumors and neoplasms in the early stages. It can be carried out both detailed and complex.
- Colonoscopy is a visual examination and assessment of the condition of the intestines.
- Probing the stomach - taking juice for analysis to determine acidity and the presence of certain enzymes. The essence of the study is that a long tube with a probe is inserted into the patient’s stomach and liquid is taken with its help. The procedure is carried out over several days on an empty stomach in a hospital setting.
- Liver examination is mandatory. This is due to the fact that belching of bile is most often associated with a disruption in the normal functioning of this internal organ, so at the examination stage it is important to make sure that there are no pathologies.
The doctor decides which laboratory test methods will be prescribed based on the information received from the patient and the symptoms present. After receiving the results and making an accurate diagnosis, the most effective and safe treatment program is selected. As a rule, a course of medication is prescribed in combination with a special diet. This will be discussed in more detail below.
What to do if you are vomiting bile
A single vomiting of bile does not mean the development of pathology. This reaction may be associated with the consumption of low-quality food, heavy foods. However, it cannot be ignored, especially if such a symptom appears periodically and is accompanied by other clinical signs. First aid for a patient who is vomiting bile is as follows:
Drinking regime
Drink as much liquid as possible: herbal tea with chamomile, still mineral water. This will help prevent dehydration and cleanse the intestines of food debris and bile acids. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5 liters per day. liquids.
Normalize nutrition
If there is no appetite, do not force the patient to eat; heavy, fatty and spicy foods should also be excluded from the diet.
As soon as the patient feels better and wants to eat, the diet should include porridge with water with a small amount of butter, a protein omelet, light vegetable soup without frying, low-fat mashed potatoes, mashed lean meat dishes, steamed.
It is also good to include berry jelly in your diet, which gently envelops the walls of the stomach, and bananas. It is better not to eat other fresh fruits yet. Eat bread dried.
Fractional meals
Portions should be small, the frequency of eating 5 - 6 times a day, small portions.
Medicines
Sorbents and choleretic agents will help improve the condition, but they must be taken according to the instructions for use. If, in addition to vomiting with bile, other symptoms are present, the patient’s condition does not improve, you should consult a doctor. A comprehensive examination, examination and history will help determine the cause, make a diagnosis, and prescribe the necessary treatment.
What not to do when vomiting bile
There are several rules that cannot be applied if a person has vomited masses of a yellow or green hue:
- rinse the stomach with potassium permanganate;
- forcefully give food or drink;
- take strong analgesics;
- place a heating pad on your stomach if there is a risk of bleeding;
- drink kefir or milk.
All these actions will only worsen the patient’s general condition, and taking analgesics will blur the clinical picture, which will complicate the diagnosis.
Treatment of vomiting with bile
Therapy for vomiting with bile, first of all, should be aimed at eliminating the cause itself. Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor selects the necessary treatment regimen. It will include taking systemic and symptomatic medications, which must be administered intravenously or orally (by mouth).
- With repeated vomiting, it is important to restore water and electrolyte balance. For this purpose, Regidron powder is prescribed. In a hospital setting, medications are administered intravenously to prevent dehydration.
- Adsorbents are prescribed for food or alcohol poisoning: “Activated carbon”, “Atoxil”, “Sorbex” - help remove harmful toxic substances from the body.
- Drugs from the group of antacids. Allows you to normalize the level of acid juice, eliminate heartburn, bitterness in the mouth: “Maalox”, “Almagel”.
- Selective prokinetics. Strengthen the tone of the intestinal sphincter, reduce the risk of bile in the stomach: Motilium, Cisapride.
- Benzodiazepine tranquilizers: Betahistine, Metoclopramide - help reduce the urge to vomit.
Depending on the cause of vomiting, the patient may be prescribed choleretic preparations, antibiotics (for intestinal infections) and other drugs. In any case, therapy must be agreed upon with a doctor, who will prescribe the dose and duration of any medication.
During treatment, important attention should be paid to nutrition. The diet should not contain spicy, fatty or fried foods, and you should also completely avoid alcohol. To normalize intestinal function and eliminate the urge to vomit, doctors prescribe dietary table No. 5, which is suitable for people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How long treatment will take and what prognosis awaits a person depends on the root cause, stage of the disease, age and characteristics of the body. A timely visit to a doctor will help increase the chances of a quick and successful recovery.
Why is it so bitter in your mouth?
Bitterness in the mouth does not appear from bitter food, but from bile, which, during the proper digestion process, is released from the liver into the duodenum for further migration to the rectum. This liquid is necessary for the complete breakdown of fragments of products that have not been processed in the stomach, and has an important function. In the absence of local pathology, bile does not enter the stomach, because there is a valve (pylorus) in the way. Nature has provided such a structure, because bile is necessary only for processes occurring in the intestines.
Any ingredients are absorbed by the body only in the form of liquid (water). For example, fats cannot independently go into this state and be absorbed into the intestinal walls. The acidic environment of bile prepares fat for such a substance, which can be influenced by digestive enzymes.
If each liquid performs its function in the right place, then in the intestines the process of converting any products into the substance necessary for absorption is completed.
The picture changes when damage occurs at the junction of the liver, duodenum and stomach, which occurs under different circumstances:
- Congenital pathology - belching of bile occurs even in infants.
- Pregnancy , especially late in pregnancy, when the fetus gains weight and begins to put pressure on the internal organs of the mother’s abdominal cavity.
- External factors (injuries, bruises, heavy physical activity) deform the intestinal walls and the function of the valve. Bile under high pressure is freely thrown into the stomach.
- Any neoplasms that compress the intestinal walls, violating the diameter of the hole through which bile should leave the liver into the intestine.
- Surgery that weakens muscle tone, which disrupts their function.
- Taking medications that have antispasmodic properties. Long-term use disrupts the function of the sphincter, bile passes freely into the stomach.
- Chronic inflammation , swelling in the duodenum, which in medicine is defined as a chronic form of duodenitis.
The reasons for the entry of bile into the stomach include banal overeating, which provokes the release of a larger volume of acidic liquid than is acceptable. The gallbladder cannot retain the excess, so it literally “pouring” in different directions, including into the stomach. If a heavy meal occurs in the late evening, shortly before bedtime, then the horizontal position further aggravates the correct outflow of bile.
A person cannot understand that disturbances have occurred in the digestive system and considers belching to be a common occurrence.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies should be chosen in cases where vomiting with bile is not dangerous and does not threaten serious health problems.
Chamomile tea
It relieves hidden inflammatory processes from the gastrointestinal mucosa, restores stool, and gently stimulates digestive functions. You can read how to properly brew and drink chamomile tea here.
Green tea
Green tea also helps. Drink it not very strong during the day. You can add a little lemon to your tea.
Valerian root decoction
The crushed root of the plant (about 3 grams) is poured into one glass of water and brewed for about 15 minutes. After straining, take the decoction warm, one tablespoon at a time.
Oat decoction in water
To prepare it, take 200 g of grains (well washed, you can pre-soak them for an hour), pour them with a liter of water and put them to boil on the stove, tightly covering them with a lid. As soon as the water boils, reduce the heat and let the broth simmer for 15-30 minutes.
After the broth has cooled, strain and consume warm on an empty stomach or a few hours after meals, depending on how you feel and your health status. You can read more about everything here.
Ginger tea
To prepare, add chopped ginger to a glass of warm water at the tip of a teaspoon and mix thoroughly. You should not drink this tea during the acute stage of gastritis or ulcers.
Tea with mint
Tea with mint can stop the gag reflex, normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and is also a sedative. Brew mint leaves in a glass of boiling water and leave for no more than 15 minutes. Drink tea in small sips.
We invite you to watch the video “A Man Vomits Bile. Help with Eastern medicine."
Prevention
In order to prevent disruptions in the functioning of our gastrointestinal tract, we must pay attention, as mentioned above, to our nutrition. You need to give up alcohol, thermally unprocessed vegetables, fatty foods, smoked meats and canned food. Mushrooms and soups based on them, sweets and baked goods made with yeast are undesirable. And, of course, you need to monitor the expiration dates of products and not eat expired products.
If nausea occurs against the background of constant psycho-emotional stress, from which there is no way to get rid of it, the use of sedatives is allowed. Only light herbal dietary supplements can be used without a prescription.
Health to you and your loved ones!
You may be interested in the following articles: Bitterness in the mouth after removal of the gallbladder Diet for cholecystitis: basic principles of nutrition Diet for gallstones Diet and nutrition after removal of the gallbladder