Motilium for gastritis with high acidity: how to take
Motilium is a well-known drug that, as those who have tried it, helps reduce the symptoms of the disease and improve digestion. Motilium helps both adults and children with gastritis; it is also convenient that there are several forms of the drug, and each person can easily choose for himself what he likes best - suspension or tablets. Intestinal peristalsis is significantly enhanced, and the patient instantly feels a surge of strength and health. The website gastritinform.ru describes how to take Motilium for gastritis with high acidity.
Motilium®: A justified approach to the treatment of gastritis
Motilium® has proven itself to be an effective remedy in the complex treatment of gastritis with impaired motility. The use of the drug helps to eliminate symptoms associated with gastritis, such as a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium, early satiety, bloating, nausea, vomiting, belching, and a feeling of discomfort in the epigastric region.
After in the 80s. XX century The role of Helicobacter pylori in damaging the mucous membranes of the stomach was proven, gastroenterologists declared war on this bacterium. However, even defeating a pathogen will not bring relief if the unpleasant symptoms that accompany it are ignored. Typically, patients suffer from symptoms such as bloating and a feeling of heaviness after eating, belching, nausea, vomiting, caused by impaired motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Motilium: description of the drug
Motilium belongs to the group of second-generation prokinetic drugs that stimulate gastrointestinal motility. They are used to treat diseases of the upper digestive tract.
Motilium belongs to the group of second-generation prokinetic drugs that stimulate gastrointestinal motility
Prokinetics are often taken as antiemetics. The clinical and pharmacological group of the drug is a centrally acting antiemetic drug that blocks dopamine receptors.
The drug has 3 release forms, developed by the manufacturer JANSSEN-CILAG in France. The first includes film-coated tablets, which are washed down only with water and are more suitable for adult patients. This type of drug contains 10 mg of domperidone and is available in blisters of 10 or 30 pieces. On the cross section of the tablet there is a white core.
The suspensions are designed for use from the first day of a child’s life, but, according to the instructions, in order to avoid side effects, you should consult a doctor about the need to use Motilium in children. A dosing syringe is placed in a cardboard package of the suspension, allowing you to accurately measure the amount of medicine required for the child. In pharmacies, the product is sold in 100 ml bottles of dark glass.
The most convenient form of release is lingual tablets, designed for rapid resorption (within 2-3 seconds) and do not require washing down. Like coated tablets, lingual tablets can be purchased in quantities of 10 or 30 pieces. Supplied in blisters and cardboard boxes, the packaging bears the signature “Express”. Produced using Zydis technology.
After taking the drug, its absorption occurs quickly through the gastrointestinal tract. On an empty stomach, this process occurs faster, the maximum concentration of the active substance is achieved in a period of 30 minutes to an hour.
The convenient release form and method of application allow you to take Motilium anywhere; you just need to put the tablet on your tongue, wait until it is completely dissolved, and swallow the saliva and sediment
The drug is taken 15-30 minutes before meals.
Dosage of the drug Motilium
The method of application depends on the purpose of therapy and the age of the patient. Motilium suspensions are prescribed to children under 5 years of age, with a body weight above 35 kg - coated tablets. Adults and children over 5 years of age are advised to take lingual tablets.
The convenient release form and method of application allow you to take the prokinetic drug anywhere. To do this, just put the tablet on your tongue, wait until it is completely dissolved, and swallow the saliva and sediment. There is no need to take the tablets with water.
For nausea and vomiting, the drug is used as follows:
- adults and children over 12 years old - 20 mg 4 times a day;
- children from 5 to 12 years old - 10 mg (in the morning, afternoon, evening and before bedtime).
The suspension is prescribed in an amount of 5 ml per 10 kg of weight 4 times a day. The prokinetic agent is taken before meals, the maximum daily dose of the drug is 80 mg, which should not be exceeded. If it is necessary to use Motilium for functional disorders of the digestive system of a chronic type, then a different dosage calculation scheme is indicated.
Adults and children take 10 mg of medication 30 minutes before meals three times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to the permissible daily value, but for children under 12 years of age the dosage cannot be changed. Adults and children take the suspension 2.5 ml for every 10 kg. For children over 1 year of age, the dose is doubled if necessary, but not exceeding the maximum amount of medication.
Interaction with other drugs
Motilium is a stimulant of intestinal motility and is inappropriate for use in conjunction with antacid, antisecretory drugs to avoid reducing the absorption of Domperidone.
Macrolides, antibiotics, and antimycotics will help inhibit the initial metabolism of domperidone, although a maximum increase (almost 3 times) in AUC is observed in the plateau phase.
If Domperidone is taken in combination with Ketoconazole, the duration of the QT interval will be slightly increased.
It is acceptable to use Motilium with dopaminergic receptor agonists (Bromocript, Levodopa) and the therapeutic effect will not change. It is possible to reduce the bioavailability of Motilium when taken together or previously with sodium bicarbonate (Cimetidine).
Domperidone is metabolized mainly by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Other drugs that inhibit these enzymes may lead to increased plasma concentrations of domperidone.
These are antifungals (Fluconazole), antibiotics (Clarithromycin), protease inhibitors (Saquinavir), calcium antagonists (Amiodarone, Verapamil).
What we combine Motilium with - first of all:
- neuroleptics;
- dopamine receptor antagonists without affecting the vomiting center.
Alcohol compatibility
Thanks to the active component in the composition, Motilium quickly blocks neurotransmitter receptors, due to which the excitatory effect is transmitted to the vomiting center along the nerve endings.
This mechanism of action eliminates the connection between the vomiting center and the stomach, leading to the suppression of vomiting and nausea.
By increasing the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter, alcohol has a blocking effect on dopamine antagonists and reduces the effect of Motilium itself.
Its use becomes simply impractical.
If a healthy person who does not suffer from a chronic disease drinks an excessive dose of alcohol, then a protective mechanism will work and the anti-nausea reflex will quickly remove excess poison from the body.
In the case of hangover syndrome and alcohol withdrawal, the development of chronic alcoholism in patients is possible. But it should not be confused with signs of ordinary intoxication due to an alcohol overdose. In the case of absystemic syndrome, metabolism begins to suffer.
To properly support the functionality of the brain during a hangover, the patient will want to drink another dose of alcohol in order to bring the functioning of the internal organs back to normal.
Failure to receive the next dose of alcohol will lead to headaches, hand tremors, increased nausea and vomiting. If you abruptly stop drinking, psychosis, delirium tremens, and alcoholic delirium may occur.
Withdrawal syndrome is treated with Motilium in order to minimize vomiting and nausea. The recommended dose is 20 mg up to 4 times a day shortly before meals. The maximum dose should not exceed 8 tablets per day.
Motilium instructions for use for children and adults
"Motilium" is the trade name of the drug "Domperidone". The product is produced by the Belgian company (Beerse). The instructions for use of Motilium recommend taking it to relieve the gag reflex.
The pharmaceutical product belongs to prokinetics - a group of medicinal substances that have a stimulating effect on the biomotor and bioelectrical activity of the gastrointestinal tract, and have antiemetic (reducing or suppressing the gag reflex) properties. The medicine has been on the pharmaceutical market for more than 20 years. The manufacturer offers the pharmaceutical drug in solid and liquid forms: tablets: in a protective coating and sublingual; suspension.
The absorption of the drug is accelerated in the absence of chyme. In people without organic changes in the digestive system, absorption increases if Motilium tablets are taken after meals, but in the presence of gastrointestinal pathologies, it must be administered 15 to 30 minutes before. before meals. With low acidity of gastric juice, the absorption of the drug worsens.
Motilium tablets for resorption and film-coated tablets for oral administration instructions for use
The therapeutic dose of Motilium for adults is 1 tablet of 10 mg administered 3 times a day; it is not recommended to take Motilium more than 3 tablets/day
Lingual Motilium is dispersed in the mouth. Lozenges are the optimal form for physical or mental difficulty in swallowing in adults. The dispersible form of the drug is also allowed to be used to treat children, provided that the patient’s body weight is equal to or greater than 35 kg.
The therapeutic dose for adults is 1 tablet (10 mg), administered 3 times a day. It is not recommended to take Motilium more than 3 tablets per day. For children in the age group 5 – 12 years, the recommended daily dose is 1 tablet 3 times a day. The product dissolves on the tongue and does not require drinking. Since the lingual form is very fragile, when removing it from the blister, it should not be pressed through the foil.
In the treatment of chronic dyspeptic phenomena, the recommended dose for adults is 10 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day. If the condition worsens, the amount of medicine can be doubled, but you should not use more than 8 tablets per day.
Nutrition for heartburn
If you have heartburn, it is important to adhere to a certain diet and nutrition regimen. Nutrition should be balanced, mechanically, chemically and thermally gentle.
If you have heartburn, you should eat:
- vegetables,
- bananas,
- sweet apples,
- lean boiled or baked meat,
- cereals,
- low fat dairy products,
- low-fat first and second courses.
It is recommended to exclude from the diet or minimize consumption of:
- citrus fruits,
- sour fruits and their juices,
- garlic,
- Luke,
- tomatoes,
- fatty and fried foods,
- dairy products with a high percentage of fat,
- seasonings, sauces,
- cream confectionery,
- fatty first courses,
- chocolate,
- coffee,
- strong tea,
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
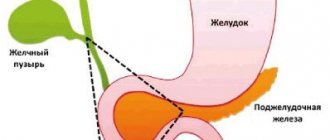
The drug Motilium for gastritis of the stomach
Motilium can be used for inflammatory diseases of the stomach, which are accompanied by impaired tone and peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract. This leads to food retention in the stomach and causes such unpleasant symptoms as a feeling of fullness in the stomach, pain, nausea and vomiting. Motilium helps improve the patient's condition.
Motilium for acute gastritis of the stomach
For the treatment of acute gastritis, medications are prescribed that stimulate the motor activity of the stomach, which promote the evacuation of food from the stomach and its movement through the gastrointestinal tract. These drugs include motilium, the mechanism of action of which is associated with blocking the transmission of the neurotransmitter dopamine to nerve cell receptors.
The main task of dopamine is to “deliver information” about the state of the stomach to the central nervous system (CNS), including the vomiting center. And if there is no information about trouble, the vomiting center does not cause phenomena such as nausea and vomiting - when motilium is prescribed, they are suppressed.
The use of Motilium during an exacerbation of chronic gastritis as part of complex treatment promotes the rapid disappearance of the main symptoms of the disease and accelerates the onset of remission
Motilium also causes an increase in tone and increased peristalsis of the smooth muscles of the stomach - the stomach quickly empties and food passes into the duodenum. This greatly alleviates the patient's condition.
Motilium for chronic gastritis
When treating chronic gastritis, a complex treatment is prescribed, the composition of which may vary depending on the type and stage of gastritis, and the patient’s condition. But an obligatory component in this case are prokinetic drugs that increase the tone and motor activity of the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract and promote the rapid evacuation of food from the stomach. Prokinetics are prescribed both during exacerbation and during remission as anti-relapse treatment.
One of the prokinetics is motilium, the mechanism of action of which is associated with blocking dopamine receptors. The use of Motilium during an exacerbation of chronic gastritis as part of complex treatment promotes the rapid disappearance of the main symptoms of the disease and accelerates the onset of remission. As an anti-relapse treatment, motilium can be used either alone or together with other medications that reduce the risk of exacerbations.
The course of treatment consists of taking film-coated tablets for oral administration or lingual tablets, one tablet three times a day, half an hour before meals. The duration of the course of treatment is determined by the doctor. Motilium for gastritis should be prescribed by a doctor.
Indications for use
Motilium perfectly eliminates belching, acid reflux, bloating, and a feeling of fullness in the stomach. If you are worried about nausea and vomiting, you can take a pill once or complete a full course of treatment.
It should be used with caution in patients with heart disease, as there is a high likelihood of side effects.
Nausea and vomiting, regardless of origin (infectious, organic, functional), can be caused by:
- diet violation;
- non-compliance with dosages during drug therapy;
- radiotherapy, chemotherapy.
The medicine quickly evacuates food into the duodenum and leads to muscle activation.
Indications for use:
- flatulence;
- vomit;
- epigastric pain;
- belching;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- dyspepsia in children;
- heartburn with stomach contents;
- nausea as Parkinson's disease progresses;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- slowness of gastric emptying;
- reflux esophagitis;
- congestion of the esophagus against the background of an inflammatory process;
- bloating;
- indigestion;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- digestive system failure;
- hypotension and atony;
- frequent regurgitation syndrome;
- cyclic vomiting in children;
- hiccups;
- atony, hypotension, peptic ulcer;
- paralytic ileus due to hernial intestinal obstruction;
- unspecified cholecystitis;
- esophageal ulcer;
- cholelithiasis;
- stones in the gallbladder ducts;
- abnormal movement of food, gastric contents through the esophagus in children or in the opposite direction.
Motilium eliminates gagging and heartburn when contents reflux into the esophagus. If a burning sensation occurs, then you should not resort to taking baking soda. It is enough to take a tablet of the drug, and your health will quickly return to normal.
Heartburn and diarrhea are common problems in overweight people who abuse medications, smoking and alcohol. If diarrhea is caused by an intestinal infection (salmonella), then the drug will relieve the problem and normalize your well-being.
Motilium for gastritis
The drug Motilium helps relieve the patient of severe symptoms of gastritis, which are associated with disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Indications for its use are the manifestation of the following signs of the disease:
When long-term therapy with Motilium is carried out, the patient must be under constant medical supervision
- changes in gastric motility, such as the gag reflex and gastroesophageal reflux;
- a state of nausea leading to vomiting, which is caused by dietary disturbances, the body’s reaction to certain medications, or infection of the body;
- dyspepsia (heartburn, belching, epigastric pain, bloating and vomiting) associated with gastroesophageal reflux.
The pharmacological effect of Motilium for gastritis is to stimulate intestinal motility. The active ingredient in this drug is domperidone, which is a dopamine antagonist and has the effects of certain antipsychotics. A medicine such as Motilium, used in the treatment of gastritis to relieve the patient of certain symptoms of the disease, is available in 3 forms - tablets, which are intended for resorption, regular film-coated tablets and suspension (syrup).
The main recommendation when using Motilium for the treatment of gastritis is that this drug, regardless of the release form, should be taken only before meals. Otherwise, the absorption of domperidone may be noticeably slower. In the case when tablets intended for resorption are prescribed, you should not wash them down with water, since they disintegrate on their own on the tongue within a few seconds.
If antisecretory or antacid medications are prescribed together with Motilium, they should be taken after meals to avoid combining these medications. The tablets should not be taken by patients with lactose intolerance, as they contain this substance. In case of liver failure, this drug is prescribed with caution due to the fact that it has a high degree of metabolism of domperidone in the liver. When long-term therapy with this drug is carried out, the patient should be under constant medical supervision.
Homeopathy for reflux esophagitis
Not everyone with GERD is suitable for synthetic medications, so treatment with complex homeopathy is prescribed. Advantages:
- normalization of the work of the National Assembly;
- stabilization of gastrointestinal motility;
- cytoprotective effect;
- protection of the esophageal mucosa from acid reflux;
- relief of extraesophageal symptoms of the disease;
- minimum side effects.
The new generation homeopathic medicine “Gastro-gran” is endowed with these properties. The medicine has a number of advantages:
- fights inflammation;
- choleretic;
- envelops;
- relieves pain and spasm;
- disinfects;
- accelerates regeneration.
Additional remedy:
- improves the condition of the liver, pancreas, and intestines;
- improves blood microcirculation;
- regulates the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- has a soft, calming effect;
- does not provoke side effects.
Shelf life of Motilium
Motilium is a medicine designed to relieve bloating, heaviness, nausea and other digestive disorders.
After opening the package, store for up to 1 year; do not take after the expiration date.
For children there is a suspension form. Other forms of the drug can only be used by adults.
The expiration date is indicated on the packaging. Should be stored out of the reach of children. The shelf life of film-coated tablets for oral administration is 5 years. Individually packaged tablets, once opened, can be stored until the expiration date. Store in a dark place at a temperature of +15…+30 °C. The shelf life of lozenges is 2 years. Store in original packaging, away from children, at temperatures up to 25 °C.
The shelf life of the oral suspension is 3 years. After opening, the bottle with liquid contents can be stored for up to 1 year. Store out of the reach of children at a temperature of +15…+30 °C. The shelf life of the Express suspension for oral administration is 2 years. Should be stored in the original packaging out of the reach of children, in a dry place at a temperature not exceeding +25 °C. After opening, store for up to 1 year. Do not take after expiration date.
The drug is not suitable for use if:
- the internal packaging is damaged;
- there is no marking or it is unclear;
- external physical properties have been changed;
Analogues of Motilium Ganaton; Itopra; Dimetpramide; Itomed; Metoclopramide; Melomida; Cerucal; Perinorm; Tseruglan.
What kind of drug
Motilium is a drug that improves intestinal motor function, has an antiemetic effect, it increases the tone of the sphincter of the lower part of the esophagus. It does not affect the activity of gastric juice and its production.
The active substance of the drug is domperidone (a substance that has antipsychotic properties, but does not have side effects). Taking the drug increases the production of prolactin.
Available in the form of tablets, lozenges and suspension. Each form has different dosages of the active substance and differs in the country of origin.
The most pronounced therapeutic effect is increased peristalsis, which helps accelerate the removal of food from the stomach and duodenum. With rapid evacuation, food does not rot or ferment in the digestive tract, which helps reduce heartburn, nausea and increased gas formation.
Motilium for heartburn, gastritis, constipation and other gastrointestinal diseases | mfarma.ru
Gastritis is the most common pathology of the digestive system among the adult population. It is caused by the lack of a proper diet, overeating and starvation diets, infection with Helicobacter, passion for fast food and canned foods, and stress. Motilium for gastritis is included in complex treatment if clinical signs of impaired evacuation of contents, stagnation, and fermentation in the intestines appear.
The indications can be formulated in more detail as follows:
- nausea and vomiting due to an increased reflex effect on the nervous regulation of the stomach,
- gastroesophageal reflux (tendency to reverse reflux of acidic chyme into the esophagus) with increased pressure in a distended stomach and insufficient tightness of the cardiac sphincter,
- the influence of various drugs on the transport function of the organ,
- damage to the gastrointestinal tract by toxins of pathogenic bacteria and viruses in food poisoning, gastroenteritis of infectious etiology,
- atony that occurs after chemotherapy and radiation therapy of tumors.
When prescribing Motilium, the doctor must take into account the type of gastritis, the presence of concomitant diseases, and the age of the patient.
Why does heartburn occur after eating?
Often, heartburn after eating occurs due to excessive release of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. This occurs when eating fatty, fried, spicy, smoked foods and marinades. Citrus fruits, fruits with high acidity and tomatoes, which promote increased production of gastric juice, can also trigger a burning sensation.
Under the influence of caffeine, the esophageal valve relaxes, and the contents of the stomach enter the esophagus, causing an unpleasant burning sensation, and carbonated drinks contribute to an increase in intragastric pressure, which also leads to the development of heartburn.
In addition to the above, mention should be made of cheese, avocado, peppermint, nuts, milk chocolate, chips and confectionery.
The benefits of Motilium for diseases and problems with the gastrointestinal tract
The pharmacological effect of Motilium is due to the content of domperidone. The synthetic substance blocks the transmission of impulses at the level of:
- endings of nerve fibers (receptors) in the muscle layer of hollow organs, transmitting information to the center with the participation of the dopamine type D2 mediator,
- vomiting center in the medulla oblongata.
The suppressive effect on the motility of the stomach (especially in the antrum), the upper part of the small intestine, and the esophagus is removed, and the tone of the cardiac sphincter is strengthened. Studies of electrical impulses propagating a peristaltic wave show an increase in its duration and strength. This promotes more intensive removal of gastric contents towards the duodenum and speeds up evacuation.
By activating the contractility of the muscular layer of the stomach:
- improves mixing and processing of food with acid and enzymes,
- the composition entering the intestine becomes more prepared for the subsequent action of enzymes,
- is expressed clinically in the disappearance of signs of digestive failure (belching, heartburn, heaviness after eating, pain, bloating).
The positive effect of Motilium is observed in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to stagnation and decreased muscle tone:
- gastritis,
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD),
- ulcer,
- reflux esophagitis,
- atony of the stomach.
The use of Motilium does not allow food to stagnate, there is no phenomenon of irritation of the gastric mucosa.
The use of the drug by a healthy person is not excluded if the accumulation and retention of contents is caused by overeating heavy meat and fried foods. An increase in internal pressure in the esophagus prevents reverse reflux. The patient's heartburn and sour belching disappear, and the sphincter function is restored.
The instructions indicate the positive effect of the drug on the treatment of atonic constipation, dull pain caused by it, and flatulence. Since older people are more likely to suffer, the medicine should be taken carefully in combination with other laxatives only on the basis of a doctor’s recommendation.
The activity of the vomiting center is stimulated by certain drugs (especially those prescribed for parkinsonism), toxic substances, and infection. The product helps with motion sickness in transport. A pronounced gag reflex interferes with medical procedures (insertion of a probe into the stomach, fibrogastroscopy). Preliminary use of Motilium prepares the patient for the procedure.
The inhibitory effect relieves nausea and vomiting in such cases.
You can purchase Motilium in the pharmacy chain in one of the forms. Pharmaceutical companies produce:
- tablets for lozenges and with a protective coating,
- suspension in vials.
Usually the first 2 types are used by adults and older children; the syrup suspension is intended for younger children, but does not exclude use at any age. The dosage of domperidone is important for the prescription: in tablets of 10 mg, in suspension 1 mg in 1 ml.
Pediatricians use Motilium in the treatment of cyclic vomiting, frequent regurgitation, and gastroesophageal reflux.
It is prohibited to use the drug during pregnancy and lactation. If necessary, other means are used.
The effectiveness of therapy is affected by interactions with various medications. It is reliably known that the results of use are reduced by:
- anticholinergic drugs (Atropine, Aprofen, Benactizine, Scopolamine, Cyclizine, Dicyclomine),
- Cimetidine,
- sodium bicarbonate.
The effect is enhanced when used:
- Ketoconazole.
- Fluconazole.
- Itraconazole.
- Coriconazole.
- Erythromycin.
- Clarithromycin.
- Amprenavir.
- Fosamprenavir.
- Atazanavir.
- Indinavir.
- Ritonavir.
- Nelfinavir.
- Saquinavir.
- Verapamil.
- Diltiazem.
- Amiodarone.
- Nefazodone.
- Aprepitant.
- Telithromycin.
And the combined administration of Motilium with Erythromycin and Ketoconazole affects the conductivity of the myocardium, which is manifested by arrhythmias, diagnosed by the ECG picture.
Treatment of GERD with medications
Reflux can be cured only with adequately selected medication correction in combination with diet and proper lifestyle. Subsequent maintenance treatment of GERD can significantly improve the condition by relieving symptoms, preventing the appearance of other diseases, and reducing the risk of multiple exacerbations.
The most reliable way to eliminate GERD is with pills, maintaining health in the future with proper nutrition and prevention with folk remedies.
Drug treatment of the disease
Treatment of reflux esophagitis with medications is based on the development of an individual regimen for taking a group of drugs:
- prokinetics;
- antisecretors;
- antacids;
- auxiliary means.
To treat reflux esophagitis, it is important:
- undergo a detailed course of examinations;
- strictly comply with the doctor’s requirements;
- Do not self-medicate or adjust therapy (especially for allergic rashes).
Below are the characteristics of the medications used on which the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease is based.
Antacids and alginates
Objectives of medications:
- acid neutralization;
- pepsin inactivation;
- adsorption of bile acids, lysolycetin;
- stimulation of the production of bicarbonates in protective mucus;
- cytoprotective effect;
- stimulation of esophageal self-cleaning with alkalization of the stomach;
- increased contractility of the lower cardia during the transition from the esophagus to the stomach.
For GERD, liquid forms of antacids are recommended, which can be of the following subtypes:
- non-systemic drugs synthesized on the basis of non-absorbable aluminum and magnesium: Maalox, Phosphalugel, Gastal, Rennie;
- effective drugs with ingredients that relieve flatulence and bloating: “Protab”, “Daigin”, “Gestid”.
The best of the best:
- "Maalox." Advantages: variety of pharmaceutical forms;
- the highest acid-neutralizing property;
- providing a cytoprotective effect by binding bile acids with cytotoxins and lysolecithin;
- the ability to initiate the production of prostaglandins and glycoproteins;
- an increase in the amount of bicarbonates and mucus produced;
- minimum side effects;
- pleasant aftertaste.
- III generation antacid alginates: Topalkan, Gaviscon. They are synthesized on the basis of a colloidal suspension and alginic acid, which: form a protective film over the surface of the gastric contents;
- absorb acidity;
- protect the esophagus from the adverse effects of acid reflux.
Take after a meal and before going to bed.
IPP
Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease is not complete without the use of powerful antisecretors. The most powerful are PPIs. Advantages:
- minimal number of side effects;
- work of the active ingredient relative to the parietal cell without deep absorption;
- effective inhibition of Na+/K±ATPase activity;
- rapid blockade of the last stage of hydrochloric acid production with its complete inhibition in the stomach.
The best effective PPIs are: Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Lanzoprazole, Rabeprazole (Pariet). A single dose of 40, 30, 40, 10 (20) mg, respectively, can completely block the synthesis of hydrochloric acid for 24 hours.
An analogue of Omeprazole is its modified subtype - Losek. Advantages:
- absence of allergic fillers (lactose, gelatin);
- smaller dragee size;
- special coating for easier swallowing;
- soluble in water for use through a nasopharyngeal tube.
Another effective remedy is “Nolpaza” - an antiulcer, acidity-reducing, generic pantoprazole. Nolpaza is recommended when taking other drugs simultaneously due to its 100% compatibility. Take 20 or 40 ml 1 time per day.
H2-histamine blockers
There are 5 generations:
- "Cimetidine";
- "Ranitidine";
- "Famotidine";
- "Nizatidine";
- "Roxatidine."
The second and third generations are most often prescribed:
- "Ranisan", "Zantac", "Ranitin";
- “Kvamatel”, “Ulfamid”, “Famosan”, “Gastrosidin”.
Their advantages:
- rapid decrease in acid production - night, day, basal, activated by drugs;
- slowing down the secretion of pepsins.
Famotidine has a number of advantages over analogues for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
But Famotidine has:
- fewer side effects;
- requires low dosages for long-lasting effects;
- better stimulates the protective functions of the mucous membrane, the synthesis of bicarbonates;
- improves blood supply and epithelial repair;
- The duration of action of the dose is 20 mg - 12 hours, 40 mg - 18 hours.
Prokinetics
Objectives of drug treatment for GERD:
- strengthening of antropyloric motor function;
- acceleration of evacuation of food bolus from the stomach;
- stimulation of the tone of the lower cardia during the transition from the esophagus to the stomach;
- reducing the number of reflux cycles, the time of aggressive interaction of acidic juice with the esophageal mucosa;
- initiation of esophageal self-cleaning.
Popular options:
- The Metoclopramide group (Cerucal, Reglan) is a dopamine blocker that can enhance motility and tone of the gastrointestinal tract with sphincters, have a positive effect on esophageal clearance and reduce the number of refluxes. But there are side effects (migraines, insomnia, impotence, nervous dysfunction), so long-term use is not recommended.
- The Motilium group (Domperidone) is a peripheral dopamine blocker. Advantages: no side effects due to non-systemic effects. Can be used in combination with other medications (except antacids, which work in an acidic environment) or monotherapy.
Tablets for GERD have different effects and can be combined.
- The Prepulsid groups (Cisapride, Coordinax, Peristil) are gastrointestinal prokinetics. They have an indirect cholinergic effect on the neuromuscular apparatus of the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the tone and amplitude of esophageal peristalsis, accelerating the evacuation abilities of the gastric lumen. They do not change the level of digestive juice production, so it is better to combine them with antisecretors.
- The new prokinetic drug "Ganaton" is a dopamine and acetylcholinesterase blocker with minimal ability to penetrate the central nervous system. Advantages: completely relieved symptoms in 7-9 days;
- complete epithelization of erosive changes in 25 days;
- satisfactory drug interactions;
- no side effects.
"Ganaton" should be taken before meals, 1-2 tablets 3 times a day, but not more than 150 mg/day.
Cytoprotectors
Medications for GERD are necessary to increase the protective function and resistance of digestive mucus to the influence of adverse factors (for example, high acidity, taking NSAIDs). GERD is treated with the following medications:
When treating the affected esophageal mucosa, it is important to take care of restoring its protective properties.
- "Misoprostol" ("Cytotec", "Cytotec") - has broad protective properties: influencing the acidity of digestive juice by suppressing the synthesis of acid with pepsin, reducing the diffusion of hydrogen ions;
- enhancing the synthesis of bicarbonates in mucus, which increases its self-defense;
- accelerating blood supply to the tissues of the esophagus.
- "Venter" (Sucralfate) - accelerates the healing of erosions and ulcers on the mucous membrane by creating a protective film on the surface of defects. Has an astringent effect. Taken for GERD between snacks, separately from antacids.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid (“Ursofalk”), if GERD is caused by reflux of the duodenal alkaline environment with bile impurities into the esophagus. When reflux is combined with cholelithiasis, the drug (maximum dose - 250 mg) is combined with Coordinax or Cholestyramine to bind bile acids.
Symptomatic treatment
If other gastrointestinal pathologies are associated with GERD or reflux was caused by one of them, the disease is treated symptomatically, according to the type of underlying disease:
- Stress or neurosis as the root cause of reflux esophagitis. Prescription of sedatives (valerian, motherwort) and consultation with a psychotherapist are required.
- Peptic ulcer disease. De-Nol should be additionally prescribed. For bacterial ulcers, antibiotics are taken.
- Weak immunity with low tissue regeneration. It is recommended to take immunostimulants.
Homeopathy for reflux esophagitis
Not everyone with GERD is suitable for synthetic medications, so treatment with complex homeopathy is prescribed. Advantages:
- normalization of the work of the National Assembly;
- stabilization of gastrointestinal motility;
- cytoprotective effect;
- protection of the esophageal mucosa from acid reflux;
- relief of extraesophageal symptoms of the disease;
- minimum side effects.
The new generation homeopathic medicine “Gastro-gran” is endowed with these properties. The medicine has a number of advantages:
- fights inflammation;
- choleretic;
- envelops;
- relieves pain and spasm;
- disinfects;
- accelerates regeneration.
Additional remedy:
- improves the condition of the liver, pancreas, and intestines;
- improves blood microcirculation;
- regulates the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- has a soft, calming effect;
- does not provoke side effects.
Multivitamins
When treating GERD, it is important to fill your diet with multivitamins and minerals. This is important in maintaining and restoring immunity, improving the quality and accelerating the regeneration of damaged tissues. Since only 20% of the daily norm of nutrients enters the body with food, it is necessary to ensure their influx from the outside through multivitamin complexes.
The drug of choice for GERD is Orthomol Immun. The drug is taken orally in a course of 1 month. Vitamins (B2, B1, B6, B3, E and C), micro- and macroelements allow you to:
- better resist illness and stress;
- restore immunity;
- prevent secondary infection of a weakened body;
- prevent relapses;
- get a boost of vivacity and energy.
"Orthomol Immun" has a positive effect and treats a number of organs and systems:
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- spleen;
- circulatory system;
- Bone marrow;
- endocrine system.
Treatment for GERD is prescribed only by a doctor.
Approaches
Depending on the severity of reflux, morphological, secretory and microcirculatory changes in GERD, the use of one of several medicinal methods is proposed:
Step-by-step intensification of treatment with the prescription of medications of different strengths and their combinations:
- antacids, diet, changes in habits;
- prokinetics/H2 blockers;
- PPIs or H2-blockers with prokinetics, in severe stages - PPIs with prokinetics.
Today, many effective methods for complex restoration of the esophagus with tablets have been developed.
A gradual reduction in the therapeutic effect with the initial use of PPI tablets and the transition to blockers with prokinetics after obtaining the required effect. The regimen is justified when using relatively severe cases of GERD with deep ulcerative-erosive damage to the esophageal mucosa.
- According to Grigoriev, it involves prescribing medications in accordance with the stage and form of the disease: For reflux without esophagitis, Motilium/Cisapride 10 mg 3 times a day is prescribed. course 10 days. If you additionally drink antacids - 4 rubles/day. 15 ml every 60 minutes. after meals and before bed.
- For stage I with superficial esophagitis - H2 blockers, for example, Ranitidine/Famotidine, 150/20 mg, respectively, 2 times a day. with a break of 12 hours. Course - 6 weeks.
- For II - the same medications, 300 or 40 mg, respectively, 2 times a day. An alternative is Omeprazole 20 mg after lunch (at 14-15:00). Course - 6 weeks.
- For III - “Omeprazole” or “Omez” 20 mg 2 times a day. with an interval of 12 hours. Course - 4 weeks. Continue to take the same drug (30 mg 2 times a day) or another PPI. Course - 8 weeks. Next, a histamine blocker is prescribed in a minimum dose for a period of 12 months.
- For IV - Omeprazole 20 mg 2 times a day. with an interval of 12 hours. Course - 8 weeks. An alternative is another inhibitor (30 mg 2 times a day). At the calm stage - constant use of histamine blockers. Additionally, Sucralfate (Venter, Sukratgel) tablets (1 g) 4 times a day are prescribed (for the treatment of refractory manifestations). half an hour before meals. Course - 1 month.
Mild forms of esophageal damage are recommended to be eliminated using the Tytgat technique.
- According to Tytgat: superficial esophagitis (stage 0-I) - treatment with a regimented diet, antacids or H2-blockers for a short course;
- Stage II - lifelong diet therapy and regimen, long-term use of blockers with prokinetics, or a course of PPI tablets;
- III degree - a combination of blockers with PPIs or maximum doses of blockers with prokinetics;
- If there is no effect - surgery.
When attacks of anxiety or depression occur, the following are additionally prescribed to improve the prognosis:
- "Eglonil" (50 mg 3 times/day);
- "Grandaxin" (50 mg 2 times/day) with "Teralen" (25 mg 2 times/day).
Maintenance therapy
The outcome of the disease with properly selected treatment is favorable, but the risk of relapse is high. Therefore, after the main therapeutic course, it is necessary to prescribe maintenance treatment against exacerbations. Without a maintenance course, six-month remission occurs in only 20% of patients. Most patients take PPIs long-term or for life, which prolongs remission and reduces the risk of developing esophageal strictures and Barrett's disease. H2 blockers and prokinetics are ineffective in maintaining a stable condition in GERD, so PPIs are prescribed.
To prevent recurrence or complications of GERD, preventive treatment is necessary.
Pregnancy and GERD
Many medications are unsafe during pregnancy, so the basis of treatment is a proper diet, traditional recipes and lifestyle changes. Since reflux disease is always accompanied by heartburn, non-systemic antacids are prescribed to relieve symptoms, for example, Maalox, Phosphalugel, Sucralfate (but it causes constipation). Ranitidine or Famotidine are less commonly prescribed for refractory disease.
Nizatidine is prohibited during pregnancy. Taking Omeprazole, Omez, Metoclopramide, Cisapride is advisable only in extreme cases, when the benefit outweighs the possible harm to mother and baby. Traditional methods of treatment are used more often.
Children
Young patients are a special group, the treatment of which requires a careful approach. Many medications are contraindicated at certain ages, so treatment methods for GERD vary.
Early age
Treatment approach:
- Postural therapy with feeding the baby while sitting or at an angle of 45-60° and maintaining this position for half an hour after eating. Then the child is placed on his back with his head elevated at 30°.
- Correction of the diet with a decrease in the amount of food per meal and an increase in the number of feedings. When feeding breast milk, it is important for the mother to drink a thickener. Artificial babies should be fed mixtures with gum (Nutrilon AR, Nutrilak AR, Humana AR) or rice starch (Enfamil AR).
- Taking prokinetics (Motilak, Cerucal), antacids (Phosphalugel) and antisecretors (Losec). The dosage is selected by the doctor.
Older age
Treatment option:
- nutrition correction;
- sleep with the head of the bed raised by 15 cm;
- taking antacids in the form of suspensions or gels (Almagel, Phosphalugel, Maalox, Gaviscon), prokinetics (Motilak, Cerucal);
- traditional methods of treatment.
The selection of the medication, its dose and course of treatment is carried out by the doctor.
Conclusion
Medicines are the main step in the treatment of GERD. Properly selected medications can increase remission periods and prevent relapses. For long-term maintenance therapy, it is better to use PPIs. Currently, new non-systemic drugs with minimal side effects are being developed that can be used for long-term treatment of the disease in all groups of adult patients, including children and pregnant women.
proizjogu.ru
Admission rules with diagrams
The difference in the additional composition of the tablet form of Motilium allows you to choose a convenient application:
- a regular tablet is dense in consistency, it must be swallowed whole, without chewing or crushing into powder, washed down with a small amount of water,
- The lozenge should be carefully removed from the blister, since it is fragile and brittle, placed on the tongue and waited 1-3 minutes until it dissolves with saliva; it is not necessary to wash it down.
The drug should be drunk 15-30 minutes before starting to eat. If necessary (night heartburn, reflux when lying down), Motilium is prescribed three times a day and a fourth - before bedtime.
The main indication for the use of the suspension: the child’s age is up to 5 years and weight is less than 35 kg. In such cases, tablets are not used.
Average dosage:
- for adults - 2 tablets 3-4 times a day,
- for children 5-12 years old - one 4 times a day.
The maximum per day that an adult and a teenager can take is 80 mg, and a child over 5 years old can take 2.4 mg per kg of body weight (but not more than 80 mg).
For younger children, the dosage is calculated at 2.5 ml per 10 kg of body weight. The daily dose is divided into 3-4 doses. Syrup is also given to babies 15-30 minutes before feeding, if necessary additionally at night. For up to 12 months, Motilium is prescribed strictly under the supervision of a doctor, mainly for hospital treatment. This is due to the increased sensitivity of the nervous system of infants to the drug, insufficient barrier function of the meninges, and possible negative manifestations.
The package contains a measuring syringe. With its help, the required amount of the drug is collected and poured into a spoon, glass or directly into the child’s open mouth. The frequency of dosing is recommended, as when using tablets. If the suspension must be prescribed to an adult or adolescent, then use 10-20 ml up to four times a day. The maximum you can drink per day is 80 ml.
The doctor decides how much treatment is required for a particular patient.
Gastritis therapy
Gastroenterologists believe that the inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa begins with a hyperacid state. Irritating factors stimulate increased acid secretion by parietal cells. According to the depth of the lesion, the process reaches the muscle layer, affecting individual areas or the entire stomach.
When treating hyperacid erosive gastritis, medications are prescribed to reduce the acidity of gastric juice (antacids). These are drugs such as Rennie, Almagel, Phosphalugel, Maalox. In addition, histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine, famotidine) are often used.
You cannot take medications with Motilium at the same time; they reduce its effect. Therefore, it is better to use the following regimen: Motilium as prescribed - before meals, antacids - after finishing the meal.
With a long chronic course of the disease, blood circulation is disrupted, the functions of the epithelium are depleted, the walls become atrophic, thin, and are easily injured. The effectiveness of domperidone in such conditions is reduced because the nerve receptors through which the drug acts partially disappear. Motilium should be prescribed with caution for atrophic gastritis. An artificial increase in contractility can cause additional trauma to the stomach.
Side effects
Exceeding the permissible dosage of taking Motilium provokes side effects, namely:
- drowsiness throughout the day;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- nervousness and irritability for no apparent reason;
- tremor of the limbs;
- with significant drug poisoning, convulsions occur throughout the body.
To reduce the negative consequences, you should take activated carbon and antihistamines. In severe cases, call an ambulance. Before the team arrives, monitor the patient’s condition and provide the necessary assistance depending on the symptoms.
Advice. To avoid negative effects from treating digestive problems, consult your doctor before use. The time spent visiting the office is fully justified with proper treatment.
Conditions and diseases when Motilium is prohibited or taken with caution
Motilium is not suitable for the treatment of any vomiting or nausea. For example, anesthesiologists and surgeons do not recommend using the drug to relieve vomiting in the post-anesthesia period. Especially if the operation was performed on the digestive organs. Excessive motor stimulation can cause suture dehiscence and bleeding.
The shell form of the tablets contains the obligatory component lactose. It is contraindicated for people with congenital intolerance and impaired intestinal absorption function. Therefore, the use of the drug is undesirable.
Aspartame is included in the lozenges; it is prohibited for persons with hyperphenylalaninemia (hereditary fermentopathy).
If vomiting is caused by renal failure, then doctors increase the interval between subsequent doses of the drug, reduce the frequency to 1-2 times a day, but do not reduce the daily dose. If the tests worsen, the dosage has to be reduced.
Caution is required when using Motilium to treat patients with liver failure. Domperidone is metabolized in liver cells and can increase the load. Monitoring of biochemical tests will be required.
The official annotation defines contraindications:
- intestinal obstruction,
- increased levels of the hormone prolactin in the blood and a tumor of the pituitary gland (prolactinoma),
- bleeding from the stomach or intestines caused by various diseases,
- signs of rupture of the stomach or intestines (for example, with an ulcer),
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug,
- period of pregnancy and lactation,
- body weight less than 35 kg (if tablets are prescribed).
In addition, domperidone does not produce the same effect with all drugs. You cannot use Motilium on your own without precise indications.
Contraindications
It is forbidden to take Motilium, as follows from the instructions for use, if you have the following diseases and conditions:
- intestinal obstruction;
- lactation period;
- lactose intolerance (for coated tablets);
- renal failure;
- perforation of any part of the intestine;
- increased levels of prolactin in the blood;
- pituitary tumor;
- liver diseases;
- postoperative vomiting;
- pregnancy;
- bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Motilium should only be used during pregnancy if absolutely necessary.
Individual intolerance to the components of Motilium excludes the use of the drug.
If you are taking medications that contain telithromycin, voriconazole, erythromycin, amiodarone, fluconazole, clarithromycin or ketonazole, you should not take the drug.
Important! It is worth noting that children weighing less than 35 kg are allowed to use only the suspension. And for children under one year of age, the suspension is prescribed with extreme caution.
Motilium®: gastritis does not come alone
Chronic gastritis is a long-term recurrent lesion of the gastric mucosa, occurring with its structural restructuring and disruption of its secretory (acid- and pepsin-forming), motor and endocrine (synthesis of gastrointestinal hormones) functions of the stomach. Despite the fact that in a large proportion of cases of chronic gastritis of the stomach, the etiological factors remain unidentified, Helicobacter pylori is increasingly suspected in the development of this disease, since its role in damage to the mucous membrane is no longer in doubt. This bacterium causes antral gastritis and pangastritis [1], therefore, certain groups of drugs, including antibiotics, are used to treat gastritis of bacterial etiology. Unfortunately, eradication of Helicobacter pylori does not always lead to relief of symptoms accompanying gastritis. One of the problems in the treatment of gastritis is that the efforts of doctors are primarily aimed at combating bacterial infection, while the need to eliminate the symptoms of impaired motility is often forgotten [2]. Symptoms include a feeling of bloating and heaviness in the abdomen after eating. In addition, upper gastrointestinal motility disorders are often accompanied by nausea and, less commonly, vomiting. To eliminate such symptoms, a separate drug with a different principle of action is needed, which will help normalize gastric motility. What do professionals recommend to eliminate the discomfort that may accompany gastritis?