Why does the body feel bad?
There is a group of diseases that cause illness that impairs the quality of life. Common causes:
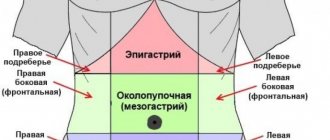
- Eating stale food. Pathogenic bacteria and pathogens cause intoxication of the body. The severity of the disease is proportional to the amount of toxins.
- Acute surgical pathologies - acute pancreatitis, attack of appendicitis, intestinal obstruction.
- Chronic inflammation of the digestive organs: stomach ulcers, gastritis, colitis, cholecystitis. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are considered the most common causes of discomfort.
- Neurological disease, brain pathology - concussion, intracranial pressure, migraine. Disturbance in the functioning of the brain and central nervous system harms the functioning of other systems.
If additional symptoms appear
Nausea can occur as an independent symptom or be accompanied by other conditions. Based on such combinations, one can draw conclusions about the causes of the attack and make a preliminary diagnosis .
If nausea occurs without vomiting and additional symptoms, then special attention should be paid to previous situations (the child was seasick in transport, the baby ate too much, etc.).
Association of nausea with additional symptoms:
- Fever (increased body temperature in combination with nausea can be a symptom of infectious diseases; the risk of infection affecting the child’s body increases if other symptoms are added to nausea and fever, for example, abdominal pain or diarrhea).
- Vomiting (nausea in most cases provokes vomiting; the cause of this condition can be external or internal factors; if nausea and vomiting occur once, then there may be no reason for serious concerns; frequent attacks indicate a malfunction of the internal systems of the child’s body).
- Diarrhea (nausea accompanied by diarrhea, in most cases indicates abnormalities in the digestive system, but in some cases such symptoms may indicate nervous overexertion in the child).
- Abdominal pain (nausea and pain in the abdominal area are caused by diseases of the digestive tract, as well as the consequences of food poisoning or foreign bodies entering the gastrointestinal tract).
- Dizziness (nausea in most cases is accompanied by general weakness of the body and dizziness, these symptoms are interrelated and rarely appear separately, the condition may indicate any of the provoking factors - infections, diseases of the digestive system, motion sickness, etc.).
Features of the course of the disease in children
The peculiarities of physical development and nervous regulation of the child’s body give reason to identify characteristic causes that are objective and subsequently gradually disappear.
Course of the disease in infants
Increased attention should be paid to infants. Establishing the functioning of the digestive system takes time. Developmental imbalance can be considered a natural phenomenon in the first year of life.
The causes of infant nausea are:
- Specific work of the gastrointestinal tract of a small child in the first months. Too active, “greedy” sucking, weak contact of the mother’s nipple contributes to the baby swallowing air. The consequence is regurgitation of food. The growth of the child eliminates the imbalance, the discomfort disappears, digestion is normalized, and the symptoms disappear.
- Premature introduction of complementary foods. The child’s stomach experiences difficulties with digestive adaptation. Different compositions of products result in regurgitation and intestinal upset. Parents must properly organize nutrition for 1 year of life and follow the schedule for introducing the new menu. Following the rules will help avoid problems.
- Teething causes infant nausea, accompanied by pain and copious amounts of saliva.
Course of the disease in preschool children
The causes of illness in preschool age are increased physical activity, curiosity, and expanding social circle. The child has increased sources of danger:
- Ingestion of a foreign body by a child.
- Infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (sore throat, flu). The virus releases toxins and ingests purulent discharge (tonsillitis).
- Helminthic infestations. A child exposed to pinworm infection, through contact, transmits the infection through toys and clothing. Poor health, loss of appetite, lethargy are the result of poisoning by helminth waste products.
- Poisoning with drugs and household chemicals. Gagging can be a lifesaver. The toxic substance will be eliminated naturally.
- Excessive afternoon activity disrupts the balance of gastric juice - alkali. It is necessary to delimit the alternation of outdoor games and food intake, and control the volume of food eaten.
Features of the disease at school age
School age is characterized by causes characterized by the consequences of physical and mental stress. Increased emotionality and lability of the nervous system result in stress.
- Psychogenic nausea is the result of adaptation of a growing organism and the increased demands of the children's team. A case of nervous tension in a teenager is a common occurrence. The skillful behavior of parents and the help of teachers will help restore the psychological background of the student, and nervous nausea will pass.
- Irregularity of food intake, non-compliance with the regime, quality of nutrition.
- Violation of the vestibular apparatus, “seasickness”. The center of balance in the inner ear is sometimes underdeveloped. “Seasickness” can disrupt the usual rhythm of a person’s life. Symptomatic treatment is necessary: restriction of food intake before the trip, the presence of a drug containing mint, valerian, mint leaf.
The classification of the causes of different age groups is due to the specific diversity of manifestations. Children and adults can get poisoned, swallow a foreign body, or get the flu.
Causes of frequent nausea without vomiting and other symptoms
Often the onset of nausea is observed in the morning, and other symptoms are added: weakness, sweating, dizziness and general malaise.
Nausea is not always accompanied by vomiting, fever and other symptoms. In this case, an analysis of the events preceding nausea will help determine the cause of this condition.
The main causes of nausea without vomiting:
- Hypertension. The development of this disease occurs precisely with this symptom. Constantly increased blood pressure leads to rapid wear and tear of blood vessels and thinning of arterial walls, so this condition cannot be ignored.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. With gastritis and ulcers, nausea begins after eating. Pancreatitis is characterized by the appearance of this symptom on an empty stomach. Other signs that should also alert you are: a burning sensation in the upper parts of the stomach, bloating, belching and heartburn.
- Kidney pathologies. Most often, the problem is inflammatory in nature; the appearance of nausea does not depend on the time of day or food intake. The color and smell of urine changes, there may be an increase in temperature and pain in the lumbar region.
- Heart failure. Constant nausea, general weakness and tachycardia are frequent harbingers of a stroke or heart attack. There may be a metallic taste in the mouth, and there is no noticeable relief when changing body position.
- Pathologies in the functioning of the gallbladder. Nausea in this case may also be accompanied by bitterness in the mouth, which intensifies after eating. This may be caused by obstruction of bile drainage, inflammation, or blockage of the bile ducts with stones.
- Thyroid dysfunction (hypothyroidism). Insufficient hormone production may also result in persistent nausea without vomiting. In addition, this condition is manifested by increased sweating, chills, and a feeling of increased fatigue.
- Pregnancy. In the early stages of pregnancy, a woman’s hormonal background changes at tremendous speed, so nausea is a frequent “companion” of this period. In some cases, toxicosis causes uncontrollable and frequent vomiting, but usually nausea appears in the morning and goes away after eating.
- Stress. Nervous tension and an unpleasant situation can cause severe nausea, even vomiting. The features of such a reaction are purely individual and are not related to age, gender or other characteristics.
- Problems in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Diseases of the middle ear, hereditary predisposition, and simply structural features can cause nausea. Most often this manifests itself when traveling in public transport, but sometimes it can also become motion sickness when performing ordinary actions, for example, a sudden change in body position, bending or turning the body.
- Intoxication of the body. Often food and alcohol poisoning is manifested by severe vomiting, indigestion and stomach pain, but in some cases the only symptom will be constant nausea.
- Taking certain medications. Side effects after taking many hormonal drugs, as well as other groups of drugs. They go away on their own when the dosage is stopped or reduced.
Brain injuries and concussions can also cause severe nausea, but in such cases, symptoms often include fever, dizziness and changes in the functioning of the eye system. If you experience nausea after a fall, bruises or illness, you should definitely get examined.
Most types of brain tumors in the early stages are accompanied by persistent nausea that does not end with vomiting, so you need to pay close attention to this symptom.
Among women
The peculiarity of the structure of the vestibular apparatus and the vomiting center in the brain in women suggests a greater tendency to nausea.
Representatives of the fair sex are also more likely to experience hormonal fluctuations, so it is not surprising that women experience nausea much more often than men.
There may be several reasons for this:
- The most pleasant and predictable is pregnancy. Despite the fact that toxicosis does not occur in all women, a feeling of nausea can accompany even the “lightest” pregnancy. Nausea can appear in the morning, on an empty stomach, with overeating and anxiety.
- Nausea during menstruation is also not uncommon. Many women feel the approach of menstruation in advance precisely because of this sign. Nausea can be regular or occur periodically. In general, this reaction of the body is considered normal; the alarm should be sounded when the intensity of attacks increases.
- Of course, the menopause period also often occurs with this very symptom. Hot flashes, pressure surges and nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting - all these are signs of hormonal instability, as well as cardinal “changes” in the body.
- Migraine attack. The causes of this disease have not been fully studied, but women are also more often susceptible to such attacks. Nausea, apathy and photophobia are common symptoms of this condition.
Women are more susceptible to manifestations of nausea “due to nervousness”, and the cause in this case may even be banal fatigue and lack of sleep. Typically, such problems do not require special treatment, but you should devote more time to rest, do what you love, or “switch” to more pleasant things.
The child has
The manifestation of nausea in children is a common occurrence, but this symptom can only be accurately “identified” in older children. Newborn babies often regurgitate undigested food, which is associated with the process of formation of the digestive system.
Older children will be able to truly describe the symptoms of nausea, so parents of children should be wary of other signs. These include refusal to eat, lethargy, capriciousness of the child, as well as bloating, pale skin with cold hands and feet.
The following factors may cause nausea in a child:
- Food poisoning. This is not always accompanied by vomiting, especially if toxins enter the body in small doses.
- Infectious diseases. In this case, the causative agent of the disease also provokes digestive disorders, fever and general weakness in the baby.
- Diseases of the central nervous system. Ailments such as meningitis and encephalitis in the initial stages are accompanied by severe nausea, often ending in vomiting.
- Surgical pathologies. Inflammation of the appendix and acute abdomen syndrome is characterized by severe abdominal pain, fever and nausea.
- Foreign body in the esophagus. Swallowing small parts is a popular “fun” for kids who actively explore the world around them. In this case, there may be nausea, non-productive cough and even suffocation, so help must be urgent.
- Nervous overexcitation. The reason could be active play, a trip on public transport, a change of scenery, or even a long-awaited toy. The main thing here is to distract the baby by providing a calm environment.
- Parasitic infection. Infection with different types of parasites can also cause nausea.
Any alarming symptoms of illness in a child is a reason to visit a doctor. Many life-threatening illnesses begin with nausea, and in young children they can progress very quickly.
This is why self-medication will never be justified, especially if an infection or surgical pathology is suspected. A timely visit to a doctor can save a life, so in this matter it is better to be safe than to waste precious time.
How not to miss the onset of the disease
Many people experience nausea for no reason. The human body is a complex mechanism of interaction between internal organs and systems. Deviations in the operation of the mechanism are the result of various reasons. The parents’ task is to objectively assess the situation, weigh the clinical picture and complaints.
Diagnosing the condition of a preschooler is difficult. With nausea, it is difficult for a baby to describe the sensations. Parents should pay attention to appearance, absence, increased appetite, and behavior changes. Nausea occurs without fever, without vomiting, and stops after eliminating the sources of origin (ate, rest, calm down). It is enough to feed in a balanced manner, exclude colds, and create a favorable psychological environment.
Danger signals
The child feels nauseous, has a constant high temperature, vomits, and has regular abdominal attacks—complicating the symptoms requires the help of a specialist.
- It is possible to determine the deterioration of health when the child begins to vomit. Frequent vomiting causes dehydration. Irreversible changes in the kidneys and brain occur, followed by convulsions, renal coma, and death.
- You should pay attention to what time of day the child vomits. If it is morning, there is an increase in intracranial blood pressure. A diagnosis from a neurologist is required.
- The child has vomited, mobility decreases, there is a desire to lie down and immobilize the body - a dangerous signal of an acute surgical illness.
- Are the symptoms complicated by lethargy, weakness, lack of appetite, drooling, convulsions, clouding of consciousness? An ambulance must be called immediately.
What treatment is needed
Temporary deterioration allows you to continue playing, watching TV, walking - the prognosis is good. Relatives should urgently become a “doctor”. First aid is recommended. What you have to do is: put the baby in a lateral position. It is important to prevent clogging of the respiratory tract with undigested food. Vomiting will help clear your stomach. The disappearance of malaise and normalization of general well-being will allow you to gradually resume your usual daily routine.
After vomiting, it is recommended to help restore fluid balance by taking plenty of fluids throughout the day. Usually clean warm boiled water. An infant needs to drink more often: give water every 3-5 minutes; starting from 2-3 years - every 5-10 minutes. The fluid intake regimen is determined by the ratio “body weight – amount of water drunk.” 1 kg. body weight requires 100-150 ml. drinking.
The rehydration solution perfectly restores strength - Regidron compensates for the loss of mineral salts and glucose. Rehydron can be easily replaced with a similar homemade solution. Dissolve 0.5 teaspoon of salt, a little soda, and 4 teaspoons of sugar in 0.5 liters of warm boiled water.
Within 12 hours after the onset of the disease, it is useful to give enterosorbents: activated carbon, Enterosgel, Polysorb, which have a high level of absorption. Dyspeptic symptoms are eliminated by the drug Motilium. Mint tea, lemon balm, lemon, and a decoction of dill seeds will give a calming effect due to their antispasmodic effect and dilation of blood vessels.
Doctors advise taking bifidobacteria. The use of stomach and potent drugs is contraindicated; it is forbidden to induce vomiting or administer injections. Acute surgical disease requires surgical intervention. Every parent should know: self-medication is dangerous because it wastes time and worsens the condition of the little patient. Delay costs lives. It must be said: immediate hospitalization is the only correct decision. The doctor will determine the cause, prescribe an examination, appropriate treatment, and prescribe surgery.