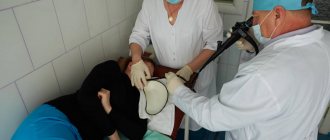
FGDS of the stomach (fibrogastroduodenoscopy or FGS - fibrogastroscopy) is considered a very unpleasant procedure. During gastroscopy, a special tube with a camera is inserted through the oral cavity into the stomach and intestines, which allows you to examine the mucous membrane from the inside. Every patient should know that not all food can be consumed before and after the study.
ESSENCE OF THE PROCEDURE
FGDS, also known as gastroscopy, is one of the most common types of diagnostics of internal organs - it can be used to identify pathologies in the esophagus, stomach and intestines. The essence of the study is the introduction of a special device, an endoscope/gastroscope through the oropharynx - this allows you to visually examine the insides and carry out simple procedures, such as a biopsy.
Harm during FGDS is unlikely, and discomfort is eliminated by anesthesia. However, sometimes the consequences of EGD can include pain.
Features of the development of complications
It should be understood that the invasive nature of gastroscopy, even if all necessary conditions are met, carries certain risks. The hardware installation allows you to visually assess the condition of the digestive tract from the oral cavity to the initial parts of the small intestine. Sometimes, multiple samples of material are taken for further histological examination (biopsy), which not only increases the duration of the procedure, but also increases the risk of complications, which may include abdominal pain.
The frequency and intensity of pain depends on the following factors:
- Anatomical and physiological characteristics of the body;
- The presence of concomitant diseases, especially the nervous system, blood and connective tissue;
- History of allergies, especially to the administration of medications;
- Endoscopist qualifications and skills;
- History of previous surgical interventions in this area;
- General condition of the patient;
- Emotional background and compliance (adherence to treatment);
- Correct fulfillment of all conditions of the preparatory stage;
- Compliance with recommendations after fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Bad habits (drinking alcohol or smoking on the eve of the procedure).
CAUSES OF STOMACH PAIN
The most common cause of pain after gastroscopy is quite simple and straightforward - the pain is provoked by the air that is pumped into the stomach. This is necessary to “smooth out” the mucous membrane. There is nothing wrong with this soreness; it usually goes away in a day or two without any treatment. Also, with such pain, quite active belching occurs, which is one of the most characteristic indicators that everything is in order.
Moreover, deliberate belching in this case will alleviate the condition somewhat, as it will release air from the body, so patients are often recommended to resort to it.
But the reason that your stomach hurts may be more dangerous. If the procedure was carried out incorrectly - or the patient did not allow it to be carried out correctly enough, for example, did not remain motionless. In this case, other quite dangerous options are possible, although there are not many of them:
- Traumatization of the walls of organs was carried out - the esophagus, stomach or rather thin areas of the upper stomach.
- The stomach or esophagus was perforated.
- There was an infection. In general, before FGS, the endoscope is processed in a special way using special saline solutions and using a certain technology. Also, patients are always checked for infections before the study. But if the doctor was sufficiently negligent or incompetent, then in very rare cases it is possible that the body was infected.
All measures are taken to ensure that this does not happen - therefore, cases when something similar happens during the procedure are isolated exceptions.
Why does my throat hurt?
Painful signs in the throat area appear for various reasons, because this part of the body is practically on the first flank of the battlefield when damage to pathogenic infections begins. At home, it is often difficult to notice deviations in health in a timely manner. Suddenly your throat suddenly starts to hurt - you always need to pay attention to this unpleasant factor and treat it with the right methods.
The question of why the throat hurts so much and it hurts to swallow is most often asked by people with a problematic immune system.
The body's protective resources decline mainly for the following reasons:
- chronic diseases, including viral and bacterial;
- overwork;
- poor nutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- undergoing hormonal or chemotherapy.
A sore throat that intensifies during swallowing, irritating sore throat, and a feeling of dryness are common reasons for turning to medical professionals. Or a good reason to start treating the disease at home.
Clinical manifestations of this type are inherent in a whole list of diseases that need to be treated in a timely manner.
Accordingly, before treatment at home is started, it is imperative to establish the correct diagnosis and undergo all the necessary examinations prescribed by the doctor.
If a sick person feels unwell, and understands that his throat hurts very much and it has become painful to swallow, what to do and how to treat it - the doctor will best tell you after conducting tests, as well as all the necessary diagnostic methods.
- body temperature rises to 38°C;
- there is tearfulness of the eyes;
- problems with nasal breathing;
- dryness and cough;
- feeling of body aches.
ARVI is becoming a common root cause, due to which you have to figure out what to do if your throat hurts and it hurts to swallow at home. Which methods should be used to treat the problem should be decided based on the diagnosis, age, condition of the patient and many other important factors. Additionally, ARVI is characterized by:
- severe weakness;
- general feeling of malaise;
- can “break” bones and hurt muscles.
The temperature rises in many patients on the second or third day after the first symptoms in the nasopharynx appear or when the throat hurts and it hurts to swallow. Body temperature at home increases in the absence of sufficient therapeutic measures and is accompanied by aches and heaviness in the body. It is necessary to be treated in a timely manner so that it does not worsen.
It is important to know that throat diseases occur not only due to viral and bacterial infections, but also due to fungal lesions and tumors.
In this case, when the throat is very sore, it hurts to swallow, rather than to treat it - the question becomes much more serious. Fungal infections are the result of active growth of fungi.
They can often manifest themselves as laryngitis, sore throat and pharyngitis, and this is quite difficult to treat.
Sore throat occurs in many cases due to:
- a chronic infectious focus, such a stage may already need to be treated with antibiotics, and not just with standard methods at home;
- when there is a sore throat - a similar phenomenon occurs with sinusitis, which is an inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses, they are close to the throat and microorganisms penetrate it, causing inflammation and that’s why it hurts;
- seasonal or year-round allergies can be another reason why your throat hurts and it hurts to swallow; in this case, you should try to avoid any irritants entering the respiratory system at home or on the street (regular dust, including house dust, pollen from flowers and etc.);
- with a tumor, the situation can also affect the throat and it can become painful; patients often complain that breathing is difficult and there is hoarseness in the voice, which cannot be treated with standard methods.
When the throat is very sore and it is painful to swallow, the patient is at risk for the following diseases:
- Sore throat is characterized by an extremely high increase in body temperature (up to 40°C), the sore throat is unbearable, the mucous membrane is inflamed and red, joint pain and migraines begin, the disease is treated with antibiotics.
- Pharyngitis - the distinctive signs are dryness and soreness, as well as pain, aggravated at the moment of swallowing, a feeling of heaviness in the throat, there may be plaque and inflammation on the mucous membranes, you can gargle with Iodinol, but without proper therapy the disease becomes protracted and becomes chronic .
These are just a few of the factors that can cause your throat to become inflamed and sore, and should be treated immediately.
We must not forget that throat diseases always develop quickly - even feeling completely healthy in the morning, you can barely speak from pain by lunchtime.
Viral symptoms tend to manifest gradually and therefore it can be difficult to begin treatment in a timely manner. But only a doctor can give a definite answer regarding the etiology of the disease.
What should you do if your throat hurts and it hurts to swallow? It is initially important to correctly determine the diagnosis before starting treatment.
Infections are characterized by already known signs: drowsiness, loss of strength, cough. Lymph nodes may also become enlarged and headaches may appear. It must be treated correctly according to the doctor’s recommendations.
For what other reasons can there be a sore throat and painful swallowing for a long time without fever:
- stomatitis or periodontitis - inflammation of the oral cavity, as well as similar gums, begin to develop due to the presence of microbes on the oral mucosa; in addition to pain, ulcers may appear and lymph nodes may enlarge;
- the presence of a foreign object - when the throat is very sore and it is painful to swallow, what you need to do first is to make sure that there are no small objects stuck in the throat, such as fish bones, chips from bones, etc.;
- suffered injuries - the damage may well be due to a burn or other damage to the mucous membrane; in this case, it is recommended to gargle with non-hot chamomile and suck on lozenges with an antiseptic effect.
Without a fever, a sore throat may be due to clogged sinuses for too long. When a person is forced to breathe through the mouth, the mucous membrane begins to dry out and irritation may occur. In this case, it is good to carry out inhalations and actions aimed at eliminating nasal congestion, which helps treat the disease.
Treatment for the throat will depend on the nature of the disease.
- If it is an infectious disease, such as an acute respiratory viral infection or an acute respiratory infection, then you should rinse with mild and safe means, such as a chamomile solution, and treat the disease thoroughly.
- You can also gargle with salted water; it is better to use table sea salt.
- Lemon juice diluted in warm water, as well as a solution of iodine and soda, are good for rinsing.
Is gastroscopy harmful?
Negative consequences after FGDS are a rare phenomenon. This diagnostic procedure has been worked out to the smallest detail, so even novice specialists do not make fatal mistakes that could lead to life-threatening consequences for the patient. Doctors are allowed to perform gastroscopy on “living patients” only after completing a special training course and passing an exam.
No matter how strange it may sound, the main danger of gastroscopy is the patient’s inappropriate behavior during the examination. Gastroenterologists and endoscopists note that those most susceptible to violating behavioral recommendations are those who, before diagnosis, are very worried about whether it is harmful to do an FGDS of the stomach. As a result of anxiety, they may forget how to breathe properly and resist, which increases the likelihood of injury.
Important! Diagnostic and therapeutic gastroscopy, during which the doctor and patient follow a set of standard rules, does not cause harm to health. This method is approved for use even in infants, which indicates the absolute safety of FGDS.
Technique
The appearance of stomach pain after FGDS is directly related to the features of this procedure. First of all, it should be carried out only according to the indications of the attending physician, who can properly assess the person’s health status and give individual recommendations. Gastroscopy itself is widely used not only for diagnostic purposes. In many cases, right during the procedure, the doctor can detect the source of bleeding (ulcer, polyp). FGDS allows you to immediately stop it, eliminating the need for radical surgical intervention.
Endoscopic techniques are being intensively improved, so the development of unpleasant sensations during fibrogastroduodenoscopy is gradually reduced to a minimum. This is possible thanks to the use of modern flexible gastroscopes of various lengths and diameters. It is selected for each patient individually, taking into account the goals of the study.
The entire procedure takes no more than 10 minutes if the patient listens carefully to the doctor and follows all his instructions.
The preparatory stage is also important. Very often, the appearance of stomach pain after gastroscopy occurs due to the patient ignoring such rules.
Nutrition after FGDS
“What should I eat after gastroscopy?” - patients often ask. Most people have no desire to eat after gastroscopy. Your doctor will tell you how long and what you can use.
You need to eat like this after gastroscopy:
- a light snack of boiled porridge or yogurt is allowed;
- You can drink weak tea or unsweetened juice;
- for several days it is advisable not to eat fatty or smoked foods, as well as fast food;
- If after the procedure you feel a burning sensation, a stomach ache or discomfort in the throat, it is advised to drink several glasses of clean water at once.
Many patients immediately after the study begin to eat the same as before, but this is not advisable. Each person’s body adapts differently after gastroscopy. If the patient ate heavy food, then after the procedure you should not immediately return to it. It is better to consult on this issue with the specialist who conducted the study. He will tell you what foods to watch out for. Following the recommendations will prevent the development of possible complications.
Diarrhea
Theoretically, gastroscopy cannot provoke diarrhea. But the wrong way out of short-term fasting, which is necessary for proper preparation, often leads to bowel problems. Taking special medications and adjusting your diet will help eliminate diarrhea.
Complications after gastroscopy are not that common. This depends on a number of factors:
- individual characteristics of the patient’s body;
- doctor's qualifications;
- accuracy in the actions of a specialist;
- correct adherence to all recommendations before, during and after gastroscopy;
- a list of procedures performed on the patient;
- the presence of diseases that the subject was silent about;
- an allergy to an anesthetic that was not disclosed by the patient or that was not checked by the physician before the examination.
That is, pain in the throat and abdominal area, as the most common complications, can occur due to the fault of the doctor and the patient himself to the same extent.
In addition to the fact that a person feels pain in the stomach and mouth (throat), other consequences may occur:
- heart rhythm is disturbed (this happens during the procedure of swallowing the probe);
- the lungs become inflamed due to aspiration;
- laryngotracheitis develops as a result of tube trauma;
- the walls of internal organs are injured;
- the endoscope touches and damages the trachea;
- an allergic reaction occurs to the anesthesia used;
- the jaw is damaged (mainly in those patients who had loose, diseased teeth);
- in the neck area there is a feeling of squeezing due to the inserted tube;
- The stomach swells, belching constantly occurs, etc.
To ensure that gastroscopy does not entail a number of unpleasant and potentially dangerous consequences, it is necessary to carefully monitor the patient’s condition while swallowing the probe and when removing him from medicinal sleep. Among all the side effects, the most common after gastroscopy is a sore throat, less often – the stomach area.
If your stomach hurts after a gastroscopy and the pain does not subside within 1 to 2 days, this is a cause for concern. There is no need to panic, but you cannot continue to ignore the symptoms. When your throat just hurts after gastroscopy, many people ignore the symptoms and believe that this is the norm. Yes, pain may be felt throughout the day.
- Most often, patients find it painful to swallow. The reason for this is mechanical irritation caused by the tube.
- The camera probe enters through the larynx, travels down the esophagus, enters the stomach, and is sometimes directed toward the beginning of the small intestine, depending on the area of the patient being examined.
- As it moves, the tube may touch the internal walls and surfaces of organs, causing minor damage.
- When sensitive mucous membranes are affected, pain occurs, but lasts literally 1 day. For more severe damage, discomfort may subside within 2 to 4 days;
- The strongest sensations are observed immediately after the procedure. Then the pain should subside.
- If the symptoms appear progressively, gradually intensifying, an error was made during the procedure.
- In this case, we are talking about the beginning of inflammatory processes. An infection penetrates the damaged area, gradually worsening the patient’s condition.
- Often, if performed incorrectly, gastroscopy ends in a sore throat, the temperature rises, and the patient can easily get sick. At the same time, as a sore throat develops, a constant sore throat is felt, the throat is red, and there is swelling. Typically, 2–3 days pass from infection to the onset of illness.
- Pain in the stomach is most often caused by excess air, which is pumped in during gastroscopy for better passage of the probe. There is nothing dangerous here, the symptoms will gradually go away on their own.
- Pain also occurs when gastric tissue samples are taken for biopsy. This is also the norm, so there is no need to worry. The discomfort will go away in 2–4 days.
- It is extremely rare that due to the negligence of the doctor or sudden movements of the patient during the procedure, the probe can touch the walls of the stomach and damage them. Complications are rare, but if the pain does not subside within 3 to 5 days and gets worse, be sure to consult a doctor. He will decide what to do and check the extent of damage to internal organs.
As you understand, the presence of pain after gastroscopy is considered normal. This is due to the physiology of the human body and the unnaturalness of the presence of foreign objects inside. But if the discomfort persists for more than 4 days and the pain intensifies, contact your doctor immediately and consult with him. Ignoring symptoms can lead to serious complications, disease and other side effects.
PREPARATION FOR THE PROCEDURE
Even if there are no contraindications, the consequences of gastroscopy can be negative if you prepare for it incorrectly - including possible pain. Here are the preparations for FGDS that are mandatory:
- The last meal should be at least 7 hours before the procedure. In the morning before the procedure, you should even refrain from drinking water.
- If the patient is taking any medications, for example, anticoagulants, non-steroidal drugs, etc., it is necessary to discuss with the doctor the possibility of stopping them for at least a few days.
- A few days before the procedure, you must stop drinking alcohol and spicy foods, and you must also stop smoking.
Recommendations
Most often, people are interested in what to do if their stomach hurts after gastroscopy. The following recommendations have been developed on this issue:
If pain persists, self-medication is strictly prohibited. In order not to miss a serious complication that requires timely surgical intervention, you must immediately consult a doctor.
FGDS of the stomach (fibrogastroduodenoscopy or FGS - fibrogastroscopy) is considered a very unpleasant procedure. During gastroscopy, a special tube with a camera is inserted through the oral cavity into the stomach and intestines, which allows you to examine the mucous membrane from the inside. Every patient should know that not all food can be consumed before and after the study.
LET'S SUM IT UP
In the overwhelming majority of cases, when a patient has a stomach ache after an FGDS, this is nothing more than exposure to the air inside it. In this case, everything goes away on its own. Other cases, such as damage to internal organs, occur much less frequently, in isolated cases, but if they occur, they must be responded to immediately, the patient’s health directly depends on this, and in some more serious cases, his life.
SOURCES: https://bolvkishkah.com/obsledovanie/posle-fgds.html https://diagnozpro.ru/skopiya/gastroscopy/posle-fgds https://proskopiyu.ru/gastroskopiya/posle-fgds-bolit-zheludok. html