Establishing the correct diagnosis for diseases of the digestive tract is the main task of a specialist. To perform this, additional examination is carried out. Given the variability of the pathology, there is a need for differential diagnosis.
The problem is especially relevant if a stomach tumor is suspected. In this case, they decide on the advisability of performing special measures that show the true picture of the condition. Patients often ask: which method is the most informative and is it possible to check the stomach using MRI without a referral from a gastroenterologist? Such research is carried out in private clinics and government institutions on the written recommendation of a doctor and by prior appointment.
Do they do MRI of the stomach?
In order to diagnose pathology of the abdominal cavity, including parenchymal organs, a complex examination is often prescribed.
Layer-by-layer examination helps determine the type of tumor, location and extent of damage to the pancreas, larynx, esophagus and intestines. For a long time, the question remained open: is it possible to do an MRI of the stomach? Today, the diagnostic significance of the method is growing, especially when examining children, as well as patients with the third and fourth stages of cancer.
Why is gastroscopy needed?
Gastroscopy is prescribed for additional assessment of the condition of the stomach or diagnosis of pathologies of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Thanks to the examination, it is possible to identify a number of diseases:
- tumors;
- polyps;
- stomach or intestinal ulcer;
- gastritis;
- inflammation of the esophagus;
- stomach cancer;
- pancreatitis;
- gallstone pathologies.
Indications can be very different, from a routine check to monitor the treatment process to regular heartburn or stomach pain. After gastroscopy, additional studies are often prescribed if the specialist notices a problem with a specific organ.
What does an MRI of the stomach show?
Specialists resort to additional examination with layer-by-layer visualization in cases where standard methods do not provide a complete picture of the disease. MRI of the stomach shows the following parameters:
- the lesion and its size;
- prevalence of the process;
- the structure of the departments and the thickness of the walls of the organ;
- presence of metastatic changes;
- the condition of neighboring organs, including the liver, duodenum;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes due to malignant neoplasms;
- pathological accumulation of gas in the abdominal cavity.
The essence of the diagnostic method
Modern diagnostics is aimed at obtaining sufficient information with minimal invasive intervention when examining the gastrointestinal tract. MRI of the stomach is a relatively safe procedure that provides an accurate image of the organ in various projections. Visualization on electronic or printed media is achieved by exposing the area of interest to nuclear magnetic resonance. Taking into account the different degrees of tissue density, you can see a certain picture. As a result, many sections of the abdominal cavity are displayed on the monitor.
How to do an MRI of the stomach
The examination is carried out in a treatment room using a special device. Before the examination, the laboratory assistant introduces the patient to how the examination is done. Diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach. The following points follow:
- The medical professional clarifies the data on the presence of contraindications for MRI of the stomach.
- Personal belongings and metal objects - earrings, watches, belts and other jewelry - are left in a separate room. A woman needs to remove her makeup because cosmetics may contain metal particles.
- The person is placed on a table that automatically moves into the device tunnel.
Important! It is necessary to remain still for some time to obtain an accurate image. The duration of the procedure ranges from 20 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the process.
- During an MRI scan, a laboratory technician monitors the patient's condition. If the patient is bothered by noise, he is reassured or offered earplugs to reduce unpleasant sound sensations.
Premedication using an anesthetic aid is carried out for adults according to indications, if it is impossible to obtain data in another way. Specialists study the results and make a conclusion about the condition of the stomach and abdominal organs.
Applying Contrast
The study is rarely performed without drug preparation. The stomach is a hollow organ, so for good visualization it is better to give it a permanent shape. Immediately before diagnosis, the patient is given up to 250 ml of iron solution to drink.
In most cases, clarification of the localization of the pathology and structural changes in tissue is required. Therefore, an MRI of the stomach is done with contrast. To do this, a few minutes before the procedure, an intravenous catheter is installed through which an iodine-containing agent or gadolinium-based drug is administered. The medicinal substance, penetrating into the layers of the organ, accumulates in the affected area, which makes it possible to draw accurate conclusions about the pathology.
How is it carried out?
Fluoroscopy begins with the use of a contrast agent. Next, a vertical study , which allows one to evaluate the passage of barium suspension through the stomach and its distribution in the folds. After this, the patient is asked to take a horizontal position in order to study the pneumorelief and the duodenal bulb. To study the stomach under conditions of complete filling, the doctor asks you to drink barium sulfate in one gulp.
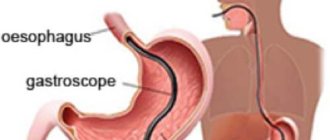
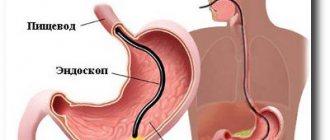
When performing an FGDS, the patient swallows a special flexible endoscope and lies on his left side. With the help of swallowing movements, the probe is advanced to the stomach, after which air is pumped to straighten the walls of the stomach. After removing excess mucus, an examination of the entire mucous membrane of the walls, as well as the duodenum, begins.
Important Lidocaine is used to reduce the gag reflex and reduce sensitivity. This is the only drug that can cause allergies.
How to prepare for research
If you plan to conduct a complex study, you should carefully prepare for it. Diagnosis is performed on an empty stomach. Therefore, it is recommended to refrain from eating 5-6 hours before. During the examination, the specialist additionally examines other organs of the digestive system. You need to follow a special diet the day before. You can eat easily digestible foods that do not cause gas formation in the intestines. Avoid full-fat milk, legumes, yeast products, thermally unprocessed vegetables and fruits. To prevent flatulence, simethicone preparations and sorbents are prescribed. Preparation for an MRI of the stomach under general anesthesia includes limiting drinking 3-4 hours before the diagnosis.
Indications
A gastroenterologist prescribes special diagnostic methods in exceptional cases. MRI of the stomach is performed according to indications when the following situations occur:
- the likelihood of organ damage by a malignant tumor;
- to determine the location of cancer;
- to detect metastases in the intestines, larynx, esophagus, pancreas or lymph nodes;
- for verification of various forms of neoplasms;
- differential diagnosis of cancer and peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- suspicion of a diaphragmatic hernia.
Is stomach MRI done for children?
The use of nuclear magnetic resonance for diagnosing diseases in childhood remains a controversial issue. However, in recent years, the method has become more widespread in developed countries due to its advantages. These include safety and high information content.
However, performing an MRI of the stomach and abdominal cavity is more difficult for a child than for an adult. This is due to the need to conduct the study under general anesthesia, especially in children. Because a small patient cannot remain in a motionless position for a long time. At the same time, indications for complex examinations in children are limited by the age-specific characteristics of gastrointestinal pathology. Therefore, it is rarely prescribed.
For whom is MRI of the stomach contraindicated?
Considering the features of the method, the study is allowed to be prescribed to most patients. However, there are contraindications to MRI. They are presented in the following options:
- presence of a cochlear implant, artificial pacemaker, neurostimulator, artificial valve;
- permanent or temporary implantation of metal plates and pins for the purpose of osteosynthesis;
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- intolerance to iodine or gadolinium.
Attention! If you have a history of epileptic seizures before the procedure, you must obtain permission from a neurologist to perform the procedure and recommendations for taking anticonvulsants.
What are the similarities between FGDS and X-ray of the stomach?
The main and main similarity of these research methods is that they allow you to visually assess the condition of the internal organ . However, there are many differences between them, and therefore, these studies are prescribed if only a certain list of diseases is suspected or in addition to each other.
Reviews
Many patients obtain important information from the opinions of others. You can find the following reviews from those who had an MRI of the stomach:
Lyudmila, 53 years old
“The doctor prescribed me an MRI of the stomach to clarify the diagnosis. A completely painless procedure. It is only unpleasant when installing a catheter. True, the constant knocking of the device was a little frightening. However, everything was fine - it passes. The results were released the next day on disk and paper.”
Alexander, 67 years old
“I suffer from stomach cancer. The question was about treatment, which is related to the stage of the disease. That's how the doctor explained it. The examination has already been carried out several times. The first time I noticed discomfort when I was placed in the tunnel, but I got used to it. I consider the high cost of the examination to be a significant drawback.”
Galina, 32 years old
“The doctor recommended that my baby have an MRI of the gastrointestinal tract and abdominal cavity - they are the same thing. I was worried because I was very afraid of anesthesia for the child. However, they reassured me and told me about the procedure. The day before, an intravenous catheter was installed and contrast was administered. The study itself lasted up to 30 minutes, the child slept after the administration of anesthesia. We waited almost a day for the results, but everything turned out okay.”
Which is better MRI or CT
Radiological methods include two main options that are used in the diagnosis of abdominal diseases. Patients are often interested in what is better: MRI or CT scan of the stomach. They cannot be called equivalent, because the studies have their own criteria and features, which are presented in the table.
Table 1. Comparative characteristics of MRI and CT
| Magnetic resonance imaging | CT scan |
| Electromagnetic radiation | X-ray radiation |
| Can be done several times a year | The number of studies is limited by the accumulated radiation dose |
| Cannot be done with implants or other built-in mechanisms | Can be carried out regardless of the number of implants and other built-in mechanisms |
| It is given to pregnant women in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters | Contraindicated for pregnant women |
| Informative for identifying soft tissue pathology, determining cancer at stages 3 and 4 | Informative for bone diseases, suspected lung tumors, malignant neoplasms in the initial stages |
MRI of the stomach or FGDS
To establish a diagnosis, patients may be prescribed several research methods, including FGS. Some people think you can get an MRI instead of swallowing a tube. However, radiological examination is often adjunct. Features of diagnostic directions are presented in the table.
Table 2. Distinctive features of MRI and FGS
| MRI of the stomach | FGDS of the stomach |
| Painless procedure | There is discomfort during and after the procedure |
| Insufficient information content to clarify the state of the epithelium | Good visualization of the mucous membrane |
| Duration 20-60 minutes | Duration 3-5 minutes |
| There is no possibility of histological diagnosis and treatment | A biopsy and therapeutic measures are performed |
MRI is an additional method that expands the diagnostic capabilities of the doctor to provide timely assistance to the patient.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
FGDS or fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a method of visual examination of the anatomical structure of the stomach and duodenum, as well as the condition of their mucous membranes. This procedure is carried out orally using a device such as a gastroscope , which is a tube with a fiber-optic system and a small camera at its end. The image captured by the camera is transmitted to a computer and can then be printed.