Diagnostics
Viral infections can independently infect the body and cause diarrhea, or they can begin against the background of an underlying disease.
The underlying pathology must be treated. Establishing the correct diagnosis and prescribing treatment is possible after a thorough diagnosis. The patient takes the necessary tests: blood, urine, feces. Blood is donated to monitor internal inflammation. In the blood of a patient with viral diarrhea, a reduced number of leukocytes is detected. In the urine, indications of the presence of protein and red blood cells are studied. When analyzing stool, the focus is on detecting undigested pieces of food, the presence of blood, and mucus.
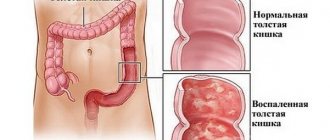
When diarrhea is viral, only the upper intestine is involved in the pathological process.
The large intestine is not susceptible to inflammation, so in case of a viral disease there should be no blood in the stool
It is important to determine the infectious nature of the disease; treatment depends on this. When studying biological material, an electron microscope is used
If necessary, analyze the vomit. More often this happens when intestinal flu is suspected. An X-ray examination of the peritoneum is possible. This method allows you to establish the exact picture and cause of diarrhea: virus, chronic illness, food poisoning.
Diagnostic features
As clinical experience shows, viral diarrhea can develop against the background of other respiratory intestinal infections or as an isolated disease. It is necessary to treat the underlying pathology.
A final diagnosis can only be made with available laboratory evidence and the exclusion of another cause of diarrhea.
Blood tests of patients with viral diarrhea reveal leukopenia (decreased white blood cell count) and lymphocytosis and monocytosis. Leukocytosis with a shift to the left indicates a bacterial infection.
If lymphocytosis and an increase in eosinophils (eosinophilia) are detected, then protozoa or helminths (giardia, chlamydia, E. coli) should be considered the “culprits” of the disease. In the urine, an increase in protein is detected, rarely red blood cells and hyaline casts.
The coprogram shows a significant amount of undigested fiber, starch grains, muscle fibers, and less commonly, leukocytes. Laboratory diagnostics consists of detecting and typing viruses in feces and antibodies in blood.
Methods used:
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA);
- diffuse precipitation reaction and latex agglutination;
- complement fixation reaction and indirect hemagglutination;
- polymerase chain reaction method;
- electron microscopy.
In formulating the diagnosis, the doctor must indicate the type of infection, severity, localization (gastroenteritis or enteritis), complications.
When diarrhea appears with a delay of several days after other symptoms of intoxication, the more likely cause is dysbiosis due to the treatment used, disturbances in the composition of digestive enzymes, or a nosocomial infection.
It is necessary to take into account the possibility of functional disorders of the intestines during ARVI and influenza associated with neurotoxicosis. The watery nature of the stool accompanies infection with Escherichia, acute bacterial intestinal infections caused by Klebsiella, Proteus, Clostridia, Salmonella.
By what features can one suspect diarrhea of viral etiology?
Diarrhea (diarrhea) in a bedridden patient: how to treat and how to stop
Viral diarrhea is associated with damage to the walls of the stomach and small intestine by pathogenic microorganisms. When they penetrate into the cavity of the digestive tract organs, their rapid reproduction begins, as a result of which dystrophic changes gradually develop, the epithelium is destroyed and the synthesis of disaccharidases is disrupted. The latter are enzymes, the deficiency of which causes sugar to accumulate in the intestinal cavity. This leads to increased pressure on the mucous membranes of the organ and impaired water absorption. Such processes together lead to the development of diarrhea.
The source of infection is a sick person or a carrier of infection. Some viral microorganisms can be transmitted from animals to humans. Also, sources of pathogenic flora can be products that cannot be processed at high temperatures, water, dirty hands, household and hygiene items.
Adeno, rota and enteroviruses are also transmitted by airborne droplets through coughing and sneezing from a sick person to a healthy person.
During a clinical study with viral diarrhea, mucus, blood, leukocytes and red blood cells were not detected in the biological material, which is associated with damage exclusively to the stomach and small intestine.
Causes of infection
Despite all caution, no one is safe from contracting a viral infection. The fact is that there are a huge number of reasons for infection with them. The most common of them are:
- Eating uncooked vegetables, berries and fruits from fruit trees that have not been washed.
- Using food products that have reached the end of their shelf life. In such food the number of harmful viruses is very high.
- Insufficient heat treatment of products. Live viruses may remain in undercooked meat or fish, as well as in other foods that have not been processed at high temperatures for long enough. Once in a favorable environment of the esophagus, stomach and intestines, even a small amount of them will begin to rapidly multiply and affect the condition of the body as a whole, as well as the gastrointestinal tract in particular.
- Careless behavior in transport and public toilets. Remember that there can be much more microorganisms on door handles than on a toilet lid, because it is washed much less often. That being said, washing your hands when leaving a public restroom and when returning home from a trip around town can keep you healthy.
- Violation of personal hygiene rules. Sitting down at the table with dirty hands is not only indecent, but even dangerous both for the owner of the dirty fingers and for the family members sitting next to him.
- Use of one towel by all family members. By wiping our hands, we not only remove moisture from them, but also leave on the fabric the remains of microorganisms that were previously located on our body. It is very easy to transmit a disease that a person may not have, but is a carrier of, through such an object to all relatives.
- Inaccuracy and lack of careful control over the sterilization of instruments and technical equipment in medical institutions. This can lead to the fact that a person, for example, who comes to warm up the nasopharynx with a simple acute respiratory infection, receives an additional infection with an intestinal infection.
- Close communication with a sick person. The airborne route of direct infection from a sick person to a completely healthy person is no less effective than others. If you know for sure that you are sick, try not to get close to healthy people. If the carrier of the infection is someone else, then keep a maximum distance from him.
Development of the disease
Diarrhea (diarrhea) due to nervousness: can it happen, how to treat it
Viral diarrhea has three stages of development in both children and adults.
- Incubation stage.
- Stage of expanded manifestation.
- The recovery stage lasts up to 10 days.
The incubation period lasts from hours to 1 week. At this time, damage to the gastrointestinal tract and the urge to vomit after eating and drinking are observed. Mucus and food debris are found in the vomit. Vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea. Some people have a sore throat, cough, chills, weakness, and fever.
At the stage of developed manifestations, the reaction of each organism is different. Depends on the patient’s immunity and the type of infection affecting the intestines. The main symptom of this stage is diarrhea, which lasts throughout the duration of the full-blown manifestations. Duration from 2 to 7 days.
With residual manifestations of the third stage, both diarrhea and vomiting are observed, but not as intensely as during the second stage. Symptoms persist until pathogenic organisms are completely eliminated from the human digestive system.
What infections cause diarrhea?
The clinical picture of viral diarrhea depends on the pathogen that caused it.
Rotavirus infection
The incubation period takes 2-3 days, then the following symptoms appear:
- diarrhea – often light-colored stools, watery consistency, frequency 4-15 times a day;
- vomit;
- fever;
- the upper respiratory tract is often simultaneously affected, and this may appear before the gastrointestinal disorder;
- Complications are possible, most often dehydration.
Almost a third of children have rotavirus infection without symptoms. In adults, the possibility of such a course of the disease is even higher.
Norfolk virus
In most cases, the first place in symptoms is occupied by nausea and vomiting. Diarrhea occurs in less than half of patients. The frequency of stools rarely exceeds 4-8 times per day.
Adenovirus
The incubation period can reach 10 days. The main symptom is diarrhea, the frequency of which can reach 15 times per day. It can last 1-10 days. In addition to diarrhea, the disease may include nausea and fever, but such symptoms do not always occur.
Echoviruses
Echoviruses - diarrhea usually occurs moderately with a frequency of up to 5-6 times a day.
The disease begins with a rise in temperature, which lasts 1-2 days. Diarrhea usually occurs moderately with a frequency of up to 5-6 times a day. The disease begins with a rise in temperature, which lasts 1-2 days.
The following symptoms are also characteristic:
- stool is light or bright yellow in color, transparent mucus is present;
- a significant volume of bowel movements caused by gas bubbles;
- the respiratory tract is affected - usually the symptoms are mild, but the appearance of copious mucous discharge from the nose cannot be ruled out;
- In children, the liver often becomes enlarged and there is a high risk of complications – otitis media, pneumonia.
Coxsackie virus
The incubation period takes several days. In addition to diarrhea, the clinical picture is formed from the following signs:
- temperature rise to 39-40 degrees;
- repeated vomiting;
- rash - affects the face, chest, arms and legs;
- itching and swelling of areas with rashes;
- weakness;
- headache;
- damage to the mucous membrane of the pharynx and subsequent difficulties in eating.
If a newborn or a child under 2 years of age is infected with the Coxsackie virus, the disease is severe. Toxicosis and severe intestinal syndrome appear. Diarrhea occurs in the first days, the frequency of stools can reach 12-15 times a day. The feces are liquid and abundant, green in color, with lumps of undigested food visible in it. Clear mucus is also present.
Astroviruses
The incubation period takes 3-4 days. Usually the pathology is manifested by only one symptom – watery stools. It is observed for 2-3 days, but the virus continues to be excreted in feces for some time, but usually no more than 1.5 weeks.
Reoviruses
Bowel movements become more frequent up to 2-5 times a day. It is abundant and watery, there are no foreign impurities, and when it settles, three layers appear: foamy on top, liquid in the middle and slightly discolored gray-yellow feces at the bottom.
In addition to diarrhea, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- acute onset of illness:
- low-grade fever, may remain normal;
- bloating, pain;
- a third of patients have pale pink spots - the rash affects the face, neck, torso, appears on the 2-3rd day, and disappears within a day without a trace.
Calcivirus infection
The incubation period is 1-2 days. Diarrhea is one of the main symptoms of the disease. It manifests itself simultaneously with vomiting and cramping abdominal pain.
Cytomegalovirus
With cytomegalovirus diarrhea in patients with AIDS, in addition to stool disturbances, abdominal pain and fever occur. The person is losing weight, and anorexia is possible. Endoscopy reveals a detailed picture of colitis:
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
- areas of swelling;
- erosion;
- ulcers.
Diarrhea caused by cytomegalovirus may be accompanied by complications - bleeding, perforation of the intestinal walls. The disease can also affect the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine.
Herpes
When men with AIDS are affected by the herpes simplex virus, the clinical picture of ulcerative proctitis and anitis may appear. In addition to diarrhea, the following symptoms occur:
- severe pain in the anorectal area;
- tenesmus;
- secretion from the rectum, in which blood impurities are observed.
There is no diagnosis of viral diarrhea. Its specific name will depend on the virus that causes the diarrhea. After a general definition, the doctor will make clarification.
Fever, aches, abdominal pain, headache - what to do?
- You can afford a little painkiller - Nurofen or paracetamol. In large doses, drugs have a bad effect on the stomach.
- Never give children aspirin or analgin - there are a lot of side effects. Analgin, also known as metamizole sodium, is banned in Europe, America and 40 other countries.
Diarrhea in the morning with jvp
After 12-24 hours, you can gradually begin to eat. For starters, crackers, bagels, rice porridge with water, bananas, and mashed potatoes are suitable. You need to eat in small portions. For a while you will have to give up fried, fatty, spicy foods. And also exclude milk, alcohol, coffee, and fast food from your diet.
You are already better... It will take time to improve the functioning of the stomach, intestines, liver and pancreas. Some people cannot do without the help of pills.
- Enveloping agents (phospholugel, maalox, almagel) will protect the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines: take 1 hour after meals and at night 3 times a day - 5-10 days.
- Enzymes (Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin, Abomin) for better digestion of food: take with meals - 7-14 days.
You can get the stomach flu again and again. Some people get sick 2-3 times a year.
Take care of yourself, Your Diagnostician.
Thank you, dear commentators. A lot of interesting. And most importantly - from life.
Viral diarrhea can be caused by rotavirus, enterovirus, norovirus, coronavirus, astrovirus, adenovirus, and reovirus infections. It occurs with a pronounced clinical picture, which is characterized by vomiting, nausea, and weakness. For therapeutic purposes, antiviral drugs, sorbents, and rehydration solutions are prescribed
During treatment, an important place is occupied by a special diet that will help restore the functioning of the digestive tract.
Infections causing diarrhea treatment with tablets
If diarrhea of viral origin is severe or prolonged, symptomatic treatment is necessary. Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Loperamide;
- Imodium;
- Lopedium;
- Diasorb;
- Enterol;
- Diarol;
- Bizmat;
- Desmol.
Diarrhea caused by an adenovirus may require rehydration. This measure is necessary for any type of diarrhea, if it is prolonged or its frequency per day is too high. In these cases, the water-electrolyte balance is disturbed. Glucose-saline solutions are used for rehydration. Glucose in them is needed for the absorption of salts and normalization of metabolic processes. More often they resort to Regidron, Glucosalan, Oralit, Humana Electrolyte. You can prepare a glucose-salt solution yourself by mixing 1 tsp in 1 liter of boiled water. Salt, 0.5 tsp. soda and 8 tsp. Sahara.
In the first 4-6 hours, the rehydration solution should be taken at a rate of 50-80 ml per 1 kg of weight - this allows you to replenish the losses that occurred before the start of treatment. Further therapy is supportive. You need to take 80-100 ml of rehydration solution per 1 kg of weight per day.
For diarrhea due to the Coxsackie virus, rehydration is also carried out, and measures are taken to relieve the symptoms of the disease. Rehydration therapy is carried out until fluid loss stops, that is, until the stool frequency normalizes. For rotavirus diarrhea, immunoglobulins are used. For children, a combination of alpha-2-interferon and vitamin E is effective. This combination is administered rectally as microenemas. The dosage is determined by age; a doctor should prescribe therapy.
If diarrhea is caused by cytomegalovirus colitis, then Ganciclovir is prescribed. The drug is administered intravenously three times a day. The dosage is calculated based on the patient’s weight - 2.5-5 mg per kilogram. This treatment is carried out for 3 weeks. Then maintenance therapy is required for another 5 days. During this period, the drug is administered once a day, 5 mg per kilogram of weight.
For diarrhea caused by the herpes simplex virus in an AIDS patient, Acyclovir is prescribed. 10-30 mg of the drug is needed per day for each kilogram of weight. This dosage is divided into 3 doses, the medicine is administered intravenously. Treatment is continued for 1.5-2 weeks. If diarrhea is accompanied by flatulence and pronounced fermentation processes, then enterosorbents or defoamers are included in the treatment. More often they resort to Smecta, Espumisan, Disflatil.
Young children with diarrhea of any origin should not be given enzymatic preparations containing ox bile. This applies to Festal, Panolez, Digestal and other medications in this group. This treatment may make your diarrhea worse.
Symptoms of diarrhea
In children under one year of age who feed only from the breast, the normal frequency of bowel movements should be about 5 times per bowel movement. Typically, the stool is yellowish in color, mushy, homogeneous, and free of pathological impurities (streaked with blood, mucus). If a one-year-old baby is bottle-fed, the stool happens two to four times a day, in some cases it has a brown tint.
As a result of the predisposition of the child’s digestive system, they are more likely to suffer from disorders, they experience diarrhea and other symptoms of the disease. If a baby has severe diarrhea, the volume of stool passed is more than ten grams per kilogram of the baby’s weight, then this is a clinical picture. In this case, diet will no longer help, the child must be urgently shown to a doctor, regardless of whether he is 5 years old or younger.
Gastrointestinal disorders occur in the presence of a viral or bacterial infection, and symptoms may occur as a complication of antibiotic treatment. But not only an intestinal infection can cause such a pathology; it is chronic, when a 4-year-old child has stool more than three times for more than three weeks.
For a mother who is breastfeeding, such manifestations indicate the presence of dysentery
In this case, it doesn’t matter how old the baby is, one year old or 4-5 years old, the main thing is to start timely treatment. It is necessary to eliminate the symptoms of the disease, since dysentery leads to dehydration and death
Symptoms
Symptoms of damage to the body by a viral intestinal infection are pronounced. The main one is viral diarrhea. In this case, it is usually accompanied by:
- sharp, sharp pain in the peritoneum;
- vomiting spasms;
- severe fever, which can last until the turning point in the disease or almost until recovery;
- weakness;
- muscle discomfort, turning into body aches;
- heat;
- cough;
- mucus discharge in the sinuses;
- pain and sore throat.
With a viral infection of the intestines, the urge to visit the restroom is very frequent, sometimes their number reaches up to 15 times during the day. In this case, diarrhea with water is complemented by the formation of foam and a strong, unpleasant odor. The stool has a yellow-green color.
Vomiting in patients occurs very often. During vomiting, not only the remains of undigested food, but also the mucus secreted by the stomach are abundantly expelled from the body.
Other symptoms of a viral infection with diarrhea may appear depending on which virus the patient was infected with. In some diseases of this group of infections, dysfunction and changes in the size of the spleen are observed. The liver may also undergo similar changes. Some viruses cause the formation of a white coating on the tongue. The other irritates the throat, causing pain and causing the tonsils to enlarge. In most cases, a process of intoxication of the body is observed.
What viruses cause diarrhea, properties and differences
In terms of the frequency of damage to people, rotavirus diarrhea is in first place (70% of all cases of diarrhea in children), intestinal adenoviruses are in second place, the number being half of the number of rotavirus infections.
On its way to the intestines, rotavirus causes severe intoxication
The remaining group includes:
- reoviruses;
- enteroviruses;
- Coxsackievirus A, B, R, Norfok;
- coronaviruses;
- astroviruses;
- caliciviruses.
All of them are quite persistent in the external environment (especially adeno- and enteroviruses). For example, water is a good habitat for enteroviruses; poor control of prevalence in tap water is a common cause of disease outbreaks.
The pathogens are resistant to ether and chloroform (the cause of infection during mask anesthesia), to acids, and easily bypass the stomach (adenoviruses are the least acid-resistant). They are distinguished by long-term preservation at low temperatures and freezing of products in the refrigerator.
Not all viruses are disinfected by chlorine-containing solutions, which are used when treating foci of intestinal infection. Thus, rotaviruses are resistant to hypochloride and are destroyed only by solutions of formaldehyde, ethyl and methyl alcohol.
Principles of therapy
Treatment can be carried out both in a hospital and on an outpatient basis. It all depends on the patient’s condition, as well as the severity of the disease.
The goal of treatment is to prevent dehydration. It is this complication that is the most serious, and if you have to deal with an advanced disease, the condition can even be life-threatening.
For any intestinal disorders, you need to drink as much water as possible. Mineral is best.
If diarrhea occurs more than 15 times a day, is watery and profuse, you should call an ambulance. A group of doctors knows which anti-diarrhea drugs should be administered to a person to protect his life.
We recommend: What to do if you have pain in the right side and diarrhea?
It is important to adjust your diet. The table below shows foods that you can eat when you have diarrhea, and which ones you should avoid.
| Recommended Products | Prohibited Products |
| Crackers | Milk |
| Whole grain cereals | Baking |
| Stewed fruits and vegetables | Sweets |
| Low fat kefir | Bold |
| Dried fruits | Raw vegetables and fruits |
To normalize microflora and restore intestinal enzyme balance, it is recommended:
- "Linex";
- "Mezim";
- "Hilak-forte";
- "Pancreatin".
You can reduce the frequency of bowel movements and cleanse the intestines by taking enterosorbents. Activated carbon, Smecta and Atoxil help well.
Your doctor may prescribe antiviral drugs. The use of antibiotics is prohibited.
Prevention will help prevent infection and transmission to other family members:
- frequent hand washing;
- careful handling of dishes and products;
- use only boiled or filtered water.
Diagnosis of the disease
Viral diarrhea of various forms is recognized by laboratory diagnostics:
- The protein level in the urine increases, and single red blood cells are detected.
- A blood test for a viral infection will show lymphocytosis, leukopenia.
- Undigested fiber and an increased number of leukocytes are found in the stool.
In laboratory conditions, the patient’s stool is examined, identifying viral antigens using immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and serological reactions.
Mild viral diarrhea in adults is usually treated at home. The main therapy is aimed at stopping intoxication of the body, restoring intestinal function and water-salt balance.
The recommended therapy will depend on how long the diarrhea lasts and how serious the symptoms of intoxication are. In case of severe dehydration, the patient is sent to a boxed department under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment with antibiotics for viral diarrhea is not carried out; such drugs are contraindicated for the reason that they, on the contrary, increase dysbiosis and intoxication of the body.
Antidiarrheal drugs and sorbents will help stop diarrhea:
- Smecta;
- Enterosgel;
- Atoksil and others.
Treatment of diarrhea should be accompanied by restoration of water-salt losses; for this, the patient is given Regidron or Glucosolan. In case of severe dehydration in a hospital setting, polyionic drugs - Lactosol, Trisol, Kvartasol - are administered intravenously.
A special diet and bacterial preparations will help normalize the intestinal microflora:
- Bifiform;
- Lactobacterin;
- Bifidumbacterin.
In parallel with this, the patient is prescribed multienzyme drugs - Festal, Mezim, Pancreatin.
Important! Viral diarrhea is a serious disease and treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor. Diet is of particular importance: in case of viral diarrhea, foods that can cause fermentation in the intestines and increase peristalsis are excluded from the diet
Fatty types of meat, fish, saturated broths are excluded, and the amount of food rich in carbohydrates is reduced. Diet 4b recommends fermented milk products that help eliminate dysbiosis
Diet is of particular importance: in case of viral diarrhea, foods that can cause fermentation in the intestines and increase peristalsis are excluded from the diet. Fatty types of meat, fish, saturated broths are excluded, and the amount of food rich in carbohydrates is reduced. Diet 4b recommends fermented milk products that help eliminate dysbiosis.
The disease in adults usually goes away within two weeks, but sticking to a gentle diet, regardless of how long the diarrhea lasted, is better even longer - up to a month.
An indication of how serious the disease is is that children who have suffered rotavirus infection are observed by an infectious disease specialist for six months after recovery. Therefore, it is better to avoid the disease.
Vaccination against rotavirus infection is carried out abroad, but in our country prevention consists of:
- control of rotavirus carriers;
- isolation of sick children from being in a group;
- processing of premises.
Rotavirus is resistant to the external environment, it can survive in feces for more than a week, tolerates heat and cold, and dies only at 100 o C.
Therefore, in order not to become infected, you need to avoid contact with a sick person - the virus is transmitted through food and household items.
The usual rules of hygiene will help you not find out what diarrhea is, you just need:
- Wash your hands after going outside or using the toilet.
- Do not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits.
- Do not use other people's utensils.
- Do not eat or drink in unfamiliar places.
These simple rules will preserve your health and the health of your loved ones. Avoid contact with sick potential carriers of the virus; disinfect the premises if the sick person is in your home.
The increased incidence of viral diarrhea most often occurs in the summer. The main role here is played by climatic conditions, increased consumption of fruits and vegetables, swimming in rivers and reservoirs, and so on. The main causative agents of the disease are the following common viruses:
- Rotavirus;
- Norfolk;
- Hawaii;
- Astrovirus;
- Adenovirus;
- Coronavirus;
- Enterovirus;
- Astrovirus.
The disease is quite common throughout the world and a large number of children suffer from it every year. The routes of transmission of viral diarrhea can be as follows:
- a sick man;
- animals;
- Food;
- drinking water;
- Houseware;
- toys.
The virus can also be transmitted by airborne droplets.
Causes
Viral diarrhea is a complex disease characterized by several modes of transmission and a number of organisms that cause the disease. During diagnosis, an important aspect is the accurate determination of the virus for more effective development of a further treatment strategy.
Forms of infection
Viral diarrhea is caused by:
- reoviruses (group includes rotaviruses);
- adenoviruses (serotypes 30, 40 and 41);
- enteroviruses (Coxsackie B (types 1,2,5));
- coronaviruses;
- astroviruses;
- caliciviruses (Norfok).
Diarrhea due to rotavirus is a clear sign of the disease; in addition, this virus occurs in 70% of cases of infection in children.
Viruses are resistant to prolonged exposure to water and treatment with various chemicals.
Transmission routes
Medicine identifies two main ways of transmitting viral intestinal infections:
- Fecal-oral route.
- Airborne.
To become infected through the airborne route, a person must be in close contact with a previously infected patient, while the fecal-oral route involves a significantly larger number of transmission mechanisms.
Mechanisms of spread of infection through the fecal-oral route:
- food products (without timely temperature treatment);
- dishes prepared outside of sanitary requirements (without temperature treatment, in violation of the sanitary conditions of the kitchen area);
- water;
- violation of hygiene rules before eating (insufficient cleanliness of hands, dishes, dining area).
The signs and course of viral diarrhea can vary significantly depending on the type of virus and the level of a person's defenses. Nevertheless, even with high immunity, one should be vigilant and pay sufficient attention to the conditions for preparing and consuming food and drink. Since this can lead to the introduction of a virus unknown to the immune system.
Treatment of viral diarrhea
Infection of the body with a virus does not always mean rapid development of the disease. Some of them negatively affect the body solely against the background of another pathology. To get rid of viral diarrhea in adults in such cases, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment to rid the body of the disease indicated by the viral infection.
It is impossible to choose the right treatment without conducting comprehensive research. For a thorough diagnosis, the patient needs to go to the laboratory and have various physiological materials tested, such as feces, urine, and blood.
The presence of viral diarrhea will show a reduced number of leukocytes in the blood. Studying urine will allow you to evaluate the presence of red blood cells and protein compounds in it. A stool analysis will allow specialists to detect the degree of digestion of food, as well as the presence of blood and mucus.
If intestinal flu is suspected, vomit is analyzed. In this case, it is possible to conduct radiographic examinations of the abdominal cavity. This will allow you to choose correctly how to treat viral diarrhea.
If the viral infection with diarrhea is mild, there is no need to hospitalize the patient. Treatment can be carried out at home. To do this, it is extremely necessary to provide the patient with plenty of fluids, high-quality food and a number of drugs containing enzymes that will help restore the digestion process.
If the disease is acute, the patient is admitted to the hospital. The fact is that acute viral diarrhea is an extremely life-threatening disease. The patient must be under the supervision of medical personnel at all times.
Young children with signs of viral diarrhea are admitted to hospital, regardless of whether it is acute or not. When a child defecates frequently with liquid feces, a child's body quickly loses water, which leads to a serious form of dehydration. As a result of changes, body tissues can begin irreversible processes that lead to death. In this regard, remember that if the child becomes ill, do not waste time, but call an ambulance without delay.
You can get rid of a viral infection with diarrhea either with medication or with the use of folk remedies. The main thing is to know what you are treating.
Medicines
The medical treatment of viral diarrhea in adults involves an integrated approach. To bring the body back to normal, medications are used that can rid the body of pathogenic flora, normalize and improve the activity of all affected gastrointestinal organs. Pharmaceuticals necessary for treatment belong to the following groups:
- antidiarrheal drugs;
- absorbents;
- probiotics;
- saline solutions that are used to restore water and electrolyte balance.
Each of these groups has its own tasks. Medicines of the first group act on the intestines themselves, eliminating dysfunction and stimulating the restoration of the correct rhythm of muscle contractions. Sorbents remove toxic compounds from the body. Probiotics restore normal intestinal microflora.
When the temperature rises above 38.5 0, patients are prescribed the use of antipyretic drugs. If spasms and pain are felt in the body, the patient is given painkillers and analgesics. Antibiotics are not prescribed for viral diarrhea in adults, since they cannot cope with viruses.
Folk remedies
A virus accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea can be treated not only with pharmacological drugs. If, after conducting research, the doctor reveals that you have a viral form of diarrhea that is not burdened by other diseases, you can get rid of it using the following methods:
- Strong tea. Brew a strong, thick tea infusion and let it cool slightly. Then drink tea, restoring moisture and strengthening the intestines. Even better - take half a spoon of dry tea leaves into your mouth, chew and drink 2-3 sips of water.
- Rice. This cereal has proven itself well as a binding product. Just boil it and collect the entire decoction, which you need to drink half a glass every 2-4 hours until the diarrhea subsides. This is very effective when it comes to curing diarrhea due to a viral infection in children.
- Pomegranate. Brew 2 tablespoons of finely chopped skin of this fruit in a glass of water and take about 20 minutes before eating normal food.
- A very simple way is starch. Pour half a glass of water into a container with 1 teaspoon of starch, stir and drink.
- Soak a dry piece of rye bread or crouton in water, and after 15 minutes you can drink a little of this excellent remedy.
- For adults, you can use a radical remedy: 80 ml of vodka and 1/3 tsp. drink salt in one gulp.
Infections that cause diarrhea
When loose stools appear, some begin to think that this is banal poisoning. Others are too worried about this, suggesting the presence of a serious illness. But you need to find a middle ground, because if an infection gets into the intestines, loose stools are guaranteed in the same way as with an eating disorder. But it will bring more consequences and danger than with mild poisoning.
At the same time, infections can be treated quickly and effectively if you do not hesitate and take the necessary measures on time. Several types of infection that lead to diarrhea should be distinguished.
Bacterial pathogens (salmonella, staphylococci, E. coli, etc.) enter most often through poorly treated drinking water, poor-quality food, and dirty hands. But viral ones can be infected by airborne droplets, just like ARVI. The risk of contracting viral diarrhea often depends on the person’s age and immune system.
The course, nature and treatment of infectious viral diarrhea in adults directly depends on determining the etiology (origin) of the microbial or viral pathogen. A specific pathogen can only be detected in laboratory conditions.
Once in the human body, infections multiply, provoke the growth of bacteria and cause infection of cells and tissues
Causes of viral diarrhea
Viral strains that can cause vomiting or diarrhea are highly contagious and easily transmitted through dirty hands. Shared drinks and utensils, food of questionable quality can also pave the way for microorganisms to reach your stomach.
People who managed to bypass the acute phase of viral diarrhea, as well as those who suffered a mild form of intestinal disorder without significant symptoms, can sometimes become carriers of the virus and spread the infection that causes diarrhea to others.
To prevent viral diarrhea, the same recommendations apply as for preventing bacterial infection: washing your hands, observing basic hygiene rules when cooking, following common sense, which will certainly help you protect yourself and your family from pathogenic microbes.
If viral diarrhea has overtaken you or a loved one, try to isolate the patient, as far as circumstances allow, and avoid unnecessary contacts. Separate cutlery and dishes are the first thing you should take care of when wanting to reduce the likelihood of contracting infectious diarrhea. It is better to protect yourself, since you can never know for sure which pathogen caused diarrhea - viral strains or bacteria. They often give a very similar clinical picture. In any case, uncomplicated viral diarrhea usually goes away on its own within two to three days.
Treatment
Treatment of viral diarrhea in adults is carried out on an outpatient basis. Treatment of children with viral diarrhea during the acute period is recommended to be carried out in a hospital setting, since a small organism is not able to fully resist the infection on its own.
Drug therapy
To suppress the activity and destroy the viral infection, antiviral drugs with interferon (Interferon, Viferon, Genferon) and umifenovir (Arbidol) are used. When the body temperature is more than 38C, it is recommended to take Paracetamol.
During the treatment of diarrhea of viral etiology, it is important to prevent the development of dehydration. For this purpose, rehydration solutions are prescribed for oral administration (Regidron, Gidrovit, Gastrolit). In severe cases, medications (Trisol, Chlosol, Acesol) are administered intravenously.
To remove toxic compounds and improve the general condition of the patient with diarrhea of a viral nature, sorbents are prescribed. Smecta, Enterosgel, Hilak Forte are absorbents that are approved for the treatment of viral diarrhea in children from birth and in adults. Adults and children over 5 years old can take Activated Carbon, Polysorb to speed up the healing process.
To restore the natural environment of the intestine during diarrhea of viral origin, it is recommended to take probiotics: Linex, Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform. To improve the production of enzymes, adults are prescribed Creon, Mezim or Pancreatin. For children, these drugs are prescribed only by a doctor; the dosage is calculated based on the body weight of the small patient.
During the treatment of viral diarrhea, antibacterial drugs are not prescribed, since they do not affect the vital activity of pathogenic flora.
The course of treatment for acute viral diarrhea lasts from 5 to 14 days. If necessary, a repeat course of antiviral drugs may be prescribed.
Diet
On the first day after the onset of viral disorders and the accompanying clinical picture, it is recommended to refuse to eat. During this period, it is important to ensure that you drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. For this purpose, boiled water, tea, compotes, herbal infusions, and still mineral water are suitable.
Starting from the second day of viral diarrhea, the patient is prescribed treatment table No. 4b, according to which the consumption of light and low-fat foods (chicken or vegetable broth, boiled chicken, mucous cereals) is allowed. During treatment and during the recovery period, it is important to exclude foods that increase intestinal motility, such as milk, coffee, and fats. Sweets and bakery yeast products are also prohibited. Vegetables and fruits are recommended to be consumed in processed form. Eggs can be included in the diet on days 3-5, but no more than 2 pieces. per day.
From dairy products, a week after the onset of diarrhea, you can gradually introduce kefir, tan, and ayran. For infants, the best diet is breast milk.
Treatment of viral diarrhea
Mild cases of the disease can be treated at home
It is important to ensure that the patient receives nutritious food, plenty of fluids, and enzyme-containing medications to improve the digestion process. In acute cases of the disease, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting
The acute nature of the disease is life-threatening. It is also better for young children to be treated in a hospital. The child is at great risk if he has frequent bowel movements. A child's body becomes dehydrated very quickly, the consequences can be very serious, even fatal. If there is a sharp deterioration in the child’s condition, you should immediately call an ambulance!
There are several ways to cure diarrhea caused by viruses:
- Medication.
- Using medicinal herbs.
- Properly selected therapeutic diet.
Drug treatment
For diarrhea caused by viruses, it is necessary to take drugs orally that can cure it, improve the functioning of the digestive system, and eliminate the causes of the disease. Such medications include:
- Sorbents.
- Antidiarrheal agents.
- Probiotics.
- Solutions for normalizing fluid and salt levels.
Viral diarrhea with frequent bowel movements and vomiting dehydrates. If the functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted, you will need to take multienzyme drugs that improve food digestion. Sorbents are used to remove toxins.
With diarrhea, the intestinal microflora is disrupted. Probiotics are prescribed to restore damaged microflora.
If viral diarrhea is accompanied by a fever of more than 38.5 degrees, it is better to take antipyretic drugs. If there are spasms, use analgesics or broad-spectrum painkillers.
For viral diarrhea, there is no point in taking antibiotics, since they do not act on viruses. But if the patient has a mixed type of infection, then antibiotic therapy is possible.
Diet
With prolonged diarrhea, maintaining proper nutrition is the basis of treatment. In the first days of illness, it is better to refuse to eat at all. It is necessary to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. Various liquids are suitable: water (boiled only), tea, compote, herbal infusions, still mineral water.
After some time, it is permissible to take light broth or low-fat soup. You should not eat spicy, fatty, fried foods during viral diarrhea. The load on weakened gastrointestinal organs will be too high, and additional irritation of the mucous membrane and aggravation of the disease may occur.
It is allowed to take chamomile decoctions, which have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and soothing effects.
The best diet for a breastfed baby is breast milk.
Kefir is recommended for older children.
For adults with viral diarrhea, table No. 46 is indicated. This means eliminating foods that enhance intestinal motility, avoiding fats and foods that enhance fermentation.
Prevention
Early detection and isolation of patients, wet cleaning and ventilation of premises. It is advisable to wear gauze masks by health workers interacting with patients.
Bibliography:
Zhdanov V.M., Gavrilov V.I. and Muzhenkova N.P. On the etiology of viral gastroenteritis, Zhurn., mikr., epid, and immun., No. 6, p. 78, 1955; Carpenter S. et al. Clinical and physiological observations during an epidemic outbreak of non-vibrio cholera-like disease in Calcutta, Bull. WHO, vol. 33, no. 5, p. 695, 1965; Mashilov V.P. Epidemic gastroenteritis and its recognition, in the book: Relevant, issue. epidemiological and infectious diseases, ed. V. I. Pokrovsky, part 1, p. 132, M., 1975; Mashilov V. P. et al. Functional state of the small intestine in patients with epidemic gastroenteritis, in the book; Relevant, issue, epid., ed. V. I. Pokrovsky, V. 3, p. 281, M., 1973; Plankina E. A. On the epidemiology of viral gastroenteritis, Zhurn, mikr., epid, i immun., No. 6, p. 86, 1955; A d- 1 e g JL a. Z i with k 1 R. Winter vomiting disease, J. infect. Dis., v. 119, p. 668, 1969; A gus SG ao Increased jejunal Jg, a synthesis in vitro during acute infections nonbacterial gastroenteritis, Amer. J. dig. Dis., v. 19, p. 127, 1974; Black-low NR ao Acute infections nonbacterial gastroenteritis, etiology and pathogenesis, Ann. intern. Med., v 76, p. 993, 1972, bibliogr.
V. P. Mashilov.