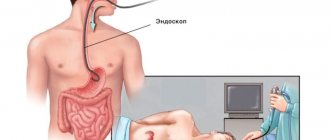
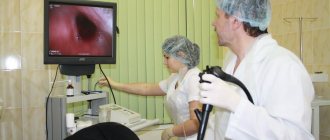
Indications
The FGDS procedure is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- painful sensations in the stomach immediately and 6 hours after eating;
- bloating;
- the presence of frequent heartburn or belching;
- regularity of nausea and vomiting;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysphagia (a disease associated with difficulty swallowing).
In addition, the procedure is prescribed as a preventive examination in the treatment of gastritis and ulcers, as well as before a number of surgical operations.
Indications and contraindications
The fibrogastroduodenoscopy procedure is prescribed by a gastroenterologist, therapist, surgeon or oncologist if the patient has:
- abdominal pain of unspecified nature;
- vomiting coffee grounds or blood;
- bloody stools;
- frequent belching with a sour smell;
- constant bloating, flatulence;
- discomfort and pain when swallowing;
- polyps;
- suspected tumor of the stomach or duodenum;
- bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
FGDS can also be prescribed to take biopsy material from pathological areas in the stomach and duodenum, to collect gastric juice and determine acidity, to assess the effectiveness of therapy, and in the diagnosis of pyloroduodenal organic or functional stenoses.
When you can’t perform FGDS of the stomach
Absolute contraindications to performing FGDS of the stomach include: agonal conditions, acute myocardial infarction and recent stroke, aortic aneurysm, as well as diseases in which it is impossible to insert an endoscope into the stomach (severe burn of the esophagus, severe cicatricial stricture of the esophagus).
Relative contraindications include:
- serious condition of the patient;
- post-stroke and post-infarction conditions;
- transient cerebrovascular accidents;
- the patient has a hypertensive crisis, exacerbation of asthma (bronchial asthma), mental illness, severe blood clotting disorders, severe diseases of the respiratory system, severe cardiovascular pathologies.
Possible diagnoses
The table below describes in detail the main pathologies that can be diagnosed using FGDS, their signs and the purpose of the study.
Table:
| Diseases | Symptoms | Procedure function |
| gastritis | pain on an empty stomach; vomiting and retching; “sour” belching; increased salivation; heartburn after eating | detection of pathology |
| stomach or duodenal ulcer | nausea after eating, which can lead to vomiting; feeling of heaviness in the stomach; heartburn | identification of pathology; stopping bleeding; administration of drugs |
| cholecystitis | pain in the right hypochondrium; weakness; increased gas formation; stool disorder | detection of pathology |
| inflammation of the esophageal mucosa | pain in the oral cavity; heartburn; nausea and vomiting; false feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the larynx | detection of pathology |
| inflammation of the gastric mucosa | loss of appetite; pain in the stomach; nausea and vomiting; belching; increased gas formation; weight loss | detection of pathology |
| inflammation of the intestinal mucosa | pain in the stomach; nausea and vomiting; increased gas formation; diarrhea | identification of pathology; taking a biopsy |
| inflammation of the duodenal mucosa | pain in the abdominal area; nausea and vomiting; unreasonable weakness | detection of pathology |
| bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract | vomiting and bloody stools; weakness; dizziness | identifying pathology and stopping bleeding |
| polyps | none | identification and removal of pathology |
| stomach cancer | decreased immunity; unreasonable weight loss; weakness |
How to do regular and capsule endoscopy and is it painful?
All the actions that the patient needs to do are not particularly complicated and the person himself only needs to listen carefully to the endoscopist’s commands and carry them out clearly so that the light bulb is swallowed correctly. Swallowing a probe to check the stomach is carried out as follows:
- Wear a special electronic vest on the body, the lining of which is equipped with many sensors, the purpose of which is to read information data transmitted by the capsule signal.
- Swallow the single-use capsule equipped with a video camera. Each device individually is sterile and its reuse for examining another person is not permitted.
- After entering the larynx, the probe passes through the esophagus, falls into the stomach, penetrates the duodenum, and from there, under the influence of reflex contractions of the gastrointestinal tract, moves further into the large and small intestines. Photo and video recording is carried out automatically with a frequency of at least 2 frames per 1 second.
Endoscopy of the rectum is the final stage in the examination. It is absolutely painless, and the most comfortable conditions are created for the patient. The duration of the diagnosis is within 8-9 hours. During this time, the person can lie quietly in the bed of their room, relax and rest while the endoscope moves through their digestive system.
The capsule comes out naturally during bowel movements. It is quite possible to track this fact on your own at home.
All information recorded by the device is read by sensors installed on the vest and is also transmitted to the gastroenterologist’s computer monitor. The doctor can review the footage at any time for a more accurate diagnosis.
Preparation for FGDS
In order for diagnosis and possible treatment during the procedure to be effective, it is necessary to use the recommendations.
They are as follows:
- following a diet that includes proper nutrition and avoidance of nuts, seeds and chocolate;
- exclusion of food intake 12 hours in advance and medications on the day of the procedure;
- prohibition on brushing teeth and smoking on the day of FGDS;
- possibility of replacing breakfast with a glass of water.
Before the procedure, medical personnel should be warned about existing diseases and drug intolerances. It is preferable to wear clothes that will not restrict movement.
Even with a strong desire, it is better to adhere to the smoking ban.
Otherwise, diagnosis may take longer, and the urge to vomit will be stronger. It is also recommended to remove dentures and glasses during the procedure. To avoid the inconvenience associated with increased salivation, you need to take a small towel and diaper with you.
How to prepare for FGDS of the stomach
Preparation for FGDS of the stomach is divided into general and local. The patient is prepared by an endoscopist who will perform FGDS. The doctor who referred the patient for examination (gastroenterologist, surgeon, oncologist) can also provide additional advice.
For reference. Poor preparation can significantly complicate or make it impossible to conduct an FGDS, so it is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
General preparation includes three stages:
- Conducting psychological preparation of the patient. The doctor explains to the patient the goals and objectives of the upcoming study, argues for the need to conduct an FGDS of the stomach, and explains why this study will be more informative than other methods. The doctor also explains how the procedure will be performed. Patients with increased emotional lability may be prescribed mild sedatives, sleeping pills or tranquilizers.
- Detection and correction of blood clotting disorders, diseases of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory organs. This stage is especially important, since diseases such as angina pectoris, asthma, arrhythmia, severe respiratory failure, heart failure, and arterial hypertension require special drug correction several days before the study.
- Identification of diseases that may affect the choice of drugs used in preparation for EGD of the stomach. This stage includes identifying individual intolerance to drugs used in endoscopic examinations (intolerance to some local anesthetics), the presence of glaucoma (atropine is contraindicated in such patients), gallstones (salt laxatives are contraindicated in patients). In women, it is also necessary to exclude pregnancy, since most drugs are contraindicated for pregnant women.
Methods of pain relief
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a study that usually brings the patient extremely uncomfortable, but not painful sensations. Therefore, in Russia and the CIS, it is more often performed without anesthesia. This is due to the fact that during the procedure the patient only feels discomfort associated with breathing, belching, lacrimation and gagging.
However, the use of both local and general anesthesia is acceptable. Local anesthesia is performed by spraying a special composition onto the root of the tongue, which prevents the appearance of gagging. The product takes effect within a few seconds. The patient feels numbness in the throat during anesthesia.
Advantages of this anesthesia:
- safety in the absence of individual intolerance to the components of the composition;
- does not require special skills or equipment to use;
- The effect of the anesthetic lasts no more than 20 minutes and does not imply the presence of consequences in the form of drowsiness and confusion.
However, this method of pain relief also has disadvantages. One of them is the possibility of a spasm in the larynx. In addition, before using anesthesia, it is necessary to test for an allergic reaction. Therefore, if urgent diagnostics are necessary, this method of pain relief will not work.
In addition, due to the presence of a short limit of action, such anesthesia is not performed on patients undergoing fibrogastroduodenoscopy for the purpose of administering medications and removing tumors. In the presence of certain indications, as well as for highly impressionable people, intravenous or endotracheal anesthesia is used. This method requires certain equipment.
In addition, after the procedure, patients experience drowsiness and decreased quality of motor coordination.
Complications such as brief memory loss or deterioration may also occur. However, by the end of the day the symptoms disappear. The main advantage of this method of pain relief is the absence of all the unpleasant sensations that a patient may experience during fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
FGDS (gastroscopy). How it is carried out, methods of preparation.
Gastroscopy with biopsy allows you to take samples of the juice of the digestive organs and mucous membranes for analysis. This collection helps to identify abnormalities that were not noticed with x-rays and ultrasound.
What should a specialist know about the patient in advance?
Before examination with an endoscope, the patient is required to report recent operations or treatment of the gastrointestinal tract with medications. In such cases, the mucous membrane may become very vulnerable to external irritants and a recovery period is first indicated before the examination.
The choice of anesthetic is greatly influenced by pregnancy, so this should also be reported to the doctor. During the procedure, Lidocaine is usually used in the form of a spray. It is safe even for pregnant women and the fetus, but if a person is intolerant to it, the session is carried out without an anesthetic at all.
The doctor must be informed about the presence of a heart valve, defibrillator, or pacemaker. The patient should report dental crowns (if he has them), a tendency to bleed after injury, and poor blood clotting. The doctor must be notified if a person has previously had endocarditis.
How to prepare for the procedure?
How to prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach? The examination is performed only on an empty stomach. The last meal is allowed 12 hours before the procedure. If a person is tormented by severe thirst, then you can only drink water in small quantities. A few hours before the procedure, brush your teeth, prohibit smoking, spraying cologne or perfume.
Morning preparation for examination
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach begins in the morning by avoiding taking any medications. This is agreed upon with the doctor in advance. In case of internal bleeding, gastric lavage is performed. If the session is scheduled for the morning, it means that food intake stops in the evening.
Preparation for inspection in the 2nd half of the day
If the study will be carried out in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed. You can only eat until 6:00. For breakfast, you are allowed to eat low-fat yogurt with a piece of bread. For drinks, you can allow tea or mineral water, but stop taking liquids 3 hours before the process.
You must arrive 10-15 minutes in advance for the procedure, as some preparation is required. If a person is very nervous, he is given a sedative. After examination, it is not recommended to eat or drink for 30 minutes until sensitivity returns to the mucous membrane.
Diet features
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach necessarily includes a mandatory diet. The diet is adjusted 3 days before the session. The procedure is done only on an empty stomach. Eating ends 12 hours before the examination. Fasting almost eliminates the digestive organs’ rejection of the endoscope and the occurrence of vomiting. The diet changes three days before the examination. During this period, the gastrointestinal tract is completely cleansed.
General recommendations for the diet:
- 5 meals a day;
- food is consumed in small portions;
- Dishes that cause increased gas formation are excluded from the diet;
- You need to drink at least 2 liters of plain water per day.
If a person is prone to flatulence, then for 3 days before gastroscopy one should take medications prescribed by the doctor. After the biopsy, a strict diet is followed for a day.
It is formulated in such a way as to spare the mucous membranes of the digestive organs as much as possible. Any mechanical, chemical, thermal effects on the gastrointestinal tract are excluded. You can only eat and drink non-acidic fruit juices, pureed soups, and milk. Spicy, hot food is prohibited. Any rough food is completely excluded.
What and when can you drink before FGDS?
Before the study, you can only allow weak tea, plain or mineral still water. For 8-10 hours, it is advisable to completely abandon liquids. In case of severe thirst, you can drink only half a glass, the last time - 3 hours before the start of the procedure. If a person takes pills and it is not recommended to skip them, then the medicine is washed down with plain water, but in a couple of sips.
What and when can you eat before FGDS?
During the preparation period, one day before the examination, the following is allowed:
- white poultry meat;
- compotes;
- dietary vegetable soups;
- green or other weak tea;
- boiled fish;
- skim cheese;
- fruits and vegetables (baked);
- still mineral water.
It is necessary to reduce sweet, flour products, and salt to a minimum. If the patient is not recommended to fast, then within 12 hours (at most, within an hour you can eat some white crackers, buckwheat porridge, stewed vegetables or apples baked in the oven.
Methodology for conducting FGDS
FGDS is mainly carried out in the morning, before lunch. Immediately before the procedure, dental crowns and glasses are removed in the office. The belt does not need to be removed if it does not compress the stomach. The person lies on his side on the couch, facing the apparatus. The doctor treats the patient's throat and mouth with an anesthetic. Most often, Lidocaine is used for these purposes in the form of a spray.
This anesthetic dulls the discomfort from insertion of the probe and reduces nausea. A mouthpiece is placed in the mouth, then a thin hose is inserted through the esophagus, at the end of which there is a mini-camera. It drops first to the middle. Then it is slowly pushed into the stomach. Its walls are examined within a few minutes.
The image from the camera is sent to a computer monitor, which immediately allows you to assess the condition of the organ being examined. If necessary, samples of the internal fluid are taken. The duration of such a study takes only a couple of minutes. To avoid unpleasant sensations and to minimize the urge to feel sick, the patient must completely relax.
The endoscope easily slides into the esophagus during a sigh. Then the person being examined needs to breathe exclusively through the nose. In some cases, gastroscopy can be performed under local or general anesthesia. For example, with severe bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. The total duration of the procedure from the moment the probe enters the esophagus until its removal is from 5 to 15 minutes. This time may increase slightly if the person is under anesthesia.
What should you take with you?
Clothes should not restrict movement, be loose and light. This preparation will help the subject to relax. Be sure to bring napkins (without alcohol) or a collar for clothes.
During the procedure, the patient experiences strong salivation and severe belching, so clothing must be covered. If the person being examined is insulin dependent or takes antihypertensive drugs, then they may be useful after the end of the process. Additionally, you need to have a 0.5 bottle of still water with you.
The process of gastroscopy of the stomach is completely safe. It is performed only by doctors of certain qualifications. It is not recommended to be nervous during the procedure; you need to relax. FGDS is an unpleasant study, but necessary for a correct diagnosis.
Description of the procedure
The patient is greeted by a nurse who offers to cover the couch with a diaper and wrap the pillow with a towel. If anesthesia is planned, it is used at this stage. It should be noted that you should not be afraid to undergo the procedure without pain relief. The diameter of the endoscope tube does not exceed 1 cm.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a safe procedure. What this is can be seen in the photo.
During FGDS, the patient does not feel pain, but only experiences discomfort.
The nurse suggests lying on your left side and placing a special ring between your teeth to prevent the device from pinching. The doctor inserts an endoscope into the patient’s mouth, which at this moment must be attempted to swallow. When the device reaches the stomach, the compressor straightens the walls of the organ by pumping air.
At this moment, an electric suction is switched on, which cleanses the stomach of bile and juice. Next, the doctor examines the condition of the organs and mucous membranes and removes the endoscope. After the procedure, the patient is not recommended to eat food for 2 hours. If general anesthesia is used, this period of time should be doubled.
Procedure for conducting FGDS
Fears about the procedure are unfounded; they remain from the use of old endoscopes, which were quite thick and inflexible.
Modern equipment is free of these shortcomings. If you behave correctly during the examination, there is discomfort, but it is minimal. It’s not difficult to tune in to the procedure; just read the reviews on the forums. All the “horror stories” are a thing of the past. The only thing that may bother you during the procedure is drooling. All that is required of the patient is to strictly follow the nurse’s instructions and leave thoughts for later. The duration of the procedure is from 2 to 5 minutes, so everything goes quickly.
The diameter of the endoscope is much smaller than the diameter of the esophagus, not to mention the stomach, so the device can move in and out freely without causing any harm.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- The patient sits on a chair and begins to breathe evenly and deeply. You need to focus on breathing, constantly maintaining an even rhythm. It's best to focus on breathing - it's a good distraction. The endoscope does not interfere with breathing, since these are two different systems: the device is inserted into the esophagus, and air enters the trachea. The nurse always reminds you of this, you just need to listen to her explanations.
- The throat is treated with a spray containing an anesthetic. This is done in order to suppress the natural gag reflex. When the medicine takes effect, touching the back of the throat does not cause any trouble.
- You need to lie on your left side and slightly pull your legs towards your stomach. The nurse will help you lie down and position yourself correctly.
- You need to take a mouthpiece into your mouth through which the probe will be inserted. You need to firmly clamp it with your teeth. It is advisable to place a towel under your cheek to absorb saliva. Actually, that's all. Next, the doctor inserts the device into the mouthpiece and asks you to help him with swallowing movements. The patient is required to breathe evenly, which helps to deeply relax, and swallow at the doctor’s command. Some devices fit well under gravity, and no assistance with swallowing movements is required.
- After the examination, the doctor removes the probe, then you can release the mouthpiece. Then you can stand up, the procedure is over.
The maximum duration of the entire process is about 20 minutes.
Although the examination is gentle, the digestive canal is still slightly irritated by a foreign object. Usually there is no appetite immediately after the procedure, but you can eat at any time if you wish. There are no special restrictions on food. It is advisable in the first days after the study to limit heavy foods - fatty, fried, smoked. On the day of the procedure, it is better to eat well-cooked porridge, kefir, and yogurt. Be sure to read:
What is anoscopy and how is it performed?
Biopsy during FGDS
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a study that makes it possible to perform a biopsy. It is necessary for additional study of the tissues taken as a sample. With its help, you can make a more accurate diagnosis and even identify the cause of the pathology. This research method is highly informative. The procedure is performed during fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
The doctor, using an additional umbrella, collects cells from the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum . In this case, the patient does not experience additional discomfort or pain. More often than not, the patient does not notice how this process occurs. The biopsy requires abstinence from food for 5 hours after diagnosis.
Carrying out the procedure
Gastroscopy is carried out according to strictly established rules.
Gastroscopy must be carried out according to strictly established rules, which will ensure its high efficiency. Initially, the doctor administers anesthesia to the root of the tongue.
For this purpose, a spray or a special anesthetic solution can be used. The patient needs to lie on the couch on the left side.
Next, the doctor inserts a mouthpiece into the patient’s mouth. It helps protect the patient's teeth from injury. This device also protects the endoscope from biting.
A special gel is applied to the tip of the endoscope. Next, it is carefully introduced into the patient’s esophagus through the oral cavity. To move the endoscope through the digestive tract, the patient must take a sip.
During gastroscopy, patients, as a rule, do not have problems with swallowing a medical instrument. The patient's breathing remains smooth. To avoid negative consequences during endoscopy, a person is strictly prohibited from swallowing movements.
If saliva accumulates in the patient’s mouth during the examination, the nurse removes it with a special suction. The doctor slowly moves the endoscope through the digestive system.
Using an eyepiece and a monitor, the mucous membranes of the digestive tract are assessed. If it is impossible to see the walls, then water or air is supplied to the digestive system. For this purpose, a special channel of the endoscopic tube is used. Excess air and water are removed using suction.
The endoscope is characterized by the presence of a mini-camera, which is used to record the examination process. After the diagnosis, the doctor evaluates all the footage. Gastroscopy is a universal method for examining the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. If the patient swallows the probe correctly, the procedure will be completely painless.
Rules of patient behavior
It is possible to reduce discomfort during the procedure.
To do this, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Comply with all doctor's requests . An attempt to resist the process can only lead to its prolongation. In addition, the purpose of fibrogastroduodenoscopy, namely diagnosis, may be inaccurate.
- Watch your breathing . You should breathe slowly, it is better if a large amount of air enters through the mouth.
- Do not be embarrassed if there is excessive flow of saliva or belching . Such situations are absolutely normal during this procedure.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is an unpleasant diagnostic method. All of the above points urge the patient not to panic. After all, such a procedure lasts no more than 2 minutes.
If you have been prescribed FGS... Preparing for the examination
Some people literally panic when they are prescribed this procedure. They can’t even imagine how they can do this to the body, because everyone is familiar with the concept of “gag reflex.” But doctors are people too, and they understand perfectly well that FGS causes severe discomfort. Therefore, some rules are followed to reduce it.
The first and not very difficult condition is not to eat for at least 8-10 hours before the procedure. Your doctor will warn you about this. Complying with his instructions is not just important - it is in your interests. If the stomach is full during the procedure, this will lead to two troubles:
- Vomiting will most likely occur.
- The doctor will not be able to correctly assess the condition of the stomach, because the food in it will interfere with vision.
As a result, you will suffer, and the FGS will still have to be rescheduled to another day.
The second condition is necessary to ensure that no force majeure arises in the process: the doctor will ask about allergies and your body’s reactions to medications. Don't miss a thing. It is also necessary to report diabetes mellitus, if any.
The procedure itself is carried out in a specially equipped room. The tubes used today cause minimal discomfort. The gag reflex will be insignificant, but there will be no pain at all.
The procedure usually lasts about a minute. Among the negative consequences, one can highlight only unpleasant sensations in the throat in the next 24-48 hours. Side effects occur in 1% of all cases - as a rule, this is caused by the inexperience of the doctor when the wall of the stomach or esophagus is damaged. Such problems are resolved quite quickly.
Feelings after FGDS
After the procedure, the following manifestations are possible:
- discomfort in the stomach;
- feeling of nausea;
- a sore throat.
The last point is due to the fact that during FGDS, slight trauma to the tonsils is possible, so the patient may feel the same as during a sore throat. To quickly get rid of an unpleasant symptom, you need to eat soft food, eat a small amount of honey before going to bed at night and use lollipops.
In case of severe discomfort, it is recommended to drink a teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil before eating. It should be noted that the use of general anesthesia entails additional symptoms.
Complications after the procedure
For reference. FGDS of the stomach is a safe procedure. Complications after the procedure are extremely rare and do not pose a threat to the patient’s health or life.
The main complications are sore throat and discomfort after removing the endoscope. There may also be discomfort in the abdomen due to the entry of air. After belching air, the discomfort disappears.
When a biopsy is taken, slight swelling and discomfort in the epigastric region may be observed for several days.
More serious complications are rare. Minor bleeding may be due to damage to the esophageal mucosa by the endoscope.
Perforation of the wall of a hollow organ (esophagus, stomach, duodenum) can be observed in patients with large ulcers of the mucous membrane and gastrointestinal tract.
Bleeding may also occur after endoscopic removal of polyps. Most often, bleeding stops on its own, or after drug or endoscopic hemostasis.
Decoding the results
Only a doctor can correctly decipher the result and accurately determine the diagnosis. And only he, taking into account all the nuances identified during FGDS, will prescribe effective treatment. Therefore, as in other similar cases, you should trust professionals and not make an independent diagnosis. The most common study finding is gastritis.
This disease is found in almost any patient over 20 years of age. Another pathology that is often detected during fibrogastroduodenoscopy is an ulcer. This disease carries the possibility of serious complications, among which bleeding should be noted.
The most unpleasant diagnosis is the detection of a tumor, including polyps. In this case, a biopsy would be warranted. If necessary, polyps can be removed during the procedure.
Complications
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a relatively safe study that has a minimal risk of complications. However, about 1% of patients still encounter them. Some of them happen in the process itself.
This may include:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- an unpleasant sensation due to the presence of air forced by the compress in the abdomen;
- infection with infectious diseases;
- damage to organ walls.
It should be noted that coping with the first symptom on your own is quite simple. To do this, you need to burp, and relief will come immediately.
It is important to pay special attention to the fact that there is a list of certain indications that require urgent medical attention.
These should include symptoms that should not appear the very next day after the FGDS procedure:
- increased body temperature, which reached 38 degrees;
- cramps and pain in the abdominal area;
- vomiting with blood;
- liquid black stool.
It must be taken into account that the presence of even one of the above points is a sign of a dangerous complication.
Contraindications
The doctor makes decisions about the safety of the FGDS procedure.
However, there are general contraindications, these include:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- increase in goiter;
- high blood pressure;
- decreased blood clotting;
- the presence of pathologies leading to difficulty breathing (for example, asthma).
In addition to all of the above, this research method is not suitable for patients who have recently suffered a stroke or heart attack.
Alternative
For certain categories of patients, this research method is not possible, or it carries certain risks. Therefore, there are alternative diagnostic methods.
Among them it is necessary to note:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray with contrast;
- endoscopy using a video capsule;
- tomography.
Each of the above alternative methods should be considered in more detail. Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is an ineffective method. It is possible to suspect the presence of gastritis or a tumor, but an accurate diagnosis in this case is difficult to establish. This is due to the fact that using such a device it is difficult to assess the condition of the mucous membranes.
Contrast x-rays are the most popular. The risk of misdiagnosis is about 15%.
Using this method, the following list of pathologies can be identified:
- gastritis;
- ulcer;
- tumor.
Sometimes double contrast is used for greater information.
The video capsule allows you to completely replace fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This endoscopic research method involves the advancement of a special capsule that contains a microvideo camera through the gastrointestinal tract. The patient is asked to stroke it, after which an image appears on the monitor. Endoscopy using a video capsule is an absolute alternative to FGDS.
Tomography involves two ways to replace fibrogastroduodenoscopy. One of them, computed tomography, produces many images of the organ in layers. To make the picture clearer, contrasts are used. They are administered orally or intravenously.
It must be borne in mind that this research method is prohibited for children and pregnant women. MRI is suitable for such patients. However, this method does not diagnose all diseases. Usually it is resorted to in particularly difficult cases.
Cost of the procedure
The price for conducting an FGDS study varies from 1,000 to 9,000 rubles. This discrepancy in cost is explained not only by the regional affiliation of the clinic. It is important to consider that the use of pain relief and other additional services will lead to increased prices. But this procedure can be performed absolutely free.
To do this, if you find indications, take a referral from a doctor. Fear of fibrogastroduodenoscopy makes many people refuse the procedure. This attitude towards your body can lead to adverse consequences. Therefore, you should use modern medicine and find out the diagnosis in time. After all, health is important.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky