The intestinal mucosa is a complete ecosystem inhabited by dozens of species of microorganisms. Their species composition depends on the age of the person, region of residence, diet and other factors. Conventionally, bacteria can be divided into beneficial ones, which are necessary for the full functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, neutral and conditionally pathogenic.
Potentially dangerous microbes can be present in the intestines of a healthy person in minimal quantities without causing disease. The balance between harmful and beneficial “inhabitants” of the intestinal environment is fundamental to digestion and overall health.
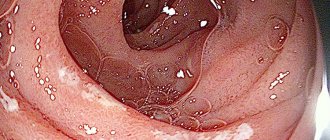
When the balance of microflora is disturbed, intestinal dysbiosis occurs. There are more “bad” microorganisms than “good” ones, which disrupts the absorption of nutrients, reduces the protective functions of the mucous membrane, and contributes to the development of serious diseases.
Symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis
The cause of pathological disorders of the intestinal environment can be treatment with antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, an infectious disease, food poisoning, or an improper diet. The imbalance in the species composition of organisms occurs against the background of helminthiases and gastrointestinal diseases. Also at risk are people who are addicted to too strict diets, uncontrollably taking enterosorbents, laxatives, and doing enemas to cleanse the intestines.
An imbalance in the intestinal environment can be suspected by the following signs:
- increased gas formation (flatulence);
Nausea and vomiting nausea and vomiting- pain;
- loss of appetite;
- hypersensitivity to certain products;
- bloating and rumbling in the stomach after eating;
- violation of bowel habits. Most patients complain of frequent loose stools, alternating diarrhea and constipation;
How to bring down a high temperature? temperature increase;- bad breath.
Intestinal dysbiosis negatively affects appearance and well-being. Due to nutritional deficiency, the patient experiences weakness and loss of strength, and becomes more irritable. A decrease in the protective functions of the intestines leads to the body being unable to cope with toxins. Patients complain about
Frequent migraines and headaches. Who to contact? headaches and other signs of intoxication.
Women note increased brittleness of nails and deterioration in hair growth and hair loss. Against the background of prolonged intestinal dysbiosis, anemia may develop, caused by a deficiency of vitamins and microelements. The skin on the body becomes dry, and on the face, on the contrary, more oily. When the pores are clogged on the face, it appears
What can cause a rash? rash.
The symptoms of intestinal microflora disorders are very extensive and similar to other diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, you need to contact a gastroenterologist and undergo an examination.
Main causes of dysbiosis
Important information: an imbalance of natural microflora never occurs on its own. This is a consequence of the manifestation of various endogenous or exogenous factors. Treatment requires an integrated approach with careful diagnosis.
There are many causes of dysbacteriosis, the main ones are:
- The use of any medications that may have a negative effect on the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. These can be antibiotics, antiviral, antibacterial, hormonal, sulfonamide drugs, as well as laxatives, histamine blockers, antacids, immunosuppressants.
- Surgical operations develop the iatrogenic stage of dysbiosis.
- Chaotic, unbalanced nutrition. Anyone who does not consume healthy foods and does not receive the required amount of components for the balanced functioning of the body falls into the risk group. Intestinal disease often occurs when there is a disruption in the usual diet, a sudden transition to a new diet, or the consumption of emulsifiers, additives, and dyes in food.
- Stressful situations and nervous strain can affect the normal functioning of the intestines. This is the so-called “stress dysbiosis”.
- Diseases of the digestive tract: pancreatitis, duodenal ulcer, stomach ulcer, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, gastritis with high acidity and others.
- Impaired metabolism.
- Intolerance to certain foods by the body.
- Acclimatization – disruptions occur throughout the body, including disruption of the normal microflora.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Impaired peristalsis.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Diabetes.
- The colonization of pathogenic microbes is facilitated by trichomoniasis, helminths, giardiasis and other parasitic infestations.
- Oncological disease.
- Age-related changes - older people often have impaired functioning of the correct intestinal microflora.
If an absolutely healthy person falls ill with dysbacteriosis, the cause should be sought either in a change of place of residence or in the characteristics of professional activity.
How to collect stool for dysbacteriosis?
The coprogram allows you to diagnose diseases of the digestive system. Stool culture is carried out to identify the parasitic or infectious nature of the pathology. Before defecation, it is necessary to empty the bladder and carry out hygiene procedures. Cover the bottom of the toilet with paper or use a disposable plastic plate. Feces are collected in the morning or a maximum of 8 hours before delivery to the laboratory in a clean container.
3 days before collecting stool, stop taking antibiotics, laxatives, and iron supplements. 2 days in advance - exclude tomatoes, beets and other foods with a high content of coloring pigments, fatty and spicy foods from your diet. You cannot take the test during menstruation.
Treatment of intestinal dysbiosis
The first stage of treatment for intestinal dysbiosis is diet therapy. Diet adjustments are aimed at limiting or eliminating foods that create a favorable environment for pathogens, irritate the intestines and increase fermentation.
How to treat intestinal dysbiosis will be determined by a gastroenterologist after a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes laboratory tests, x-rays and ultrasound of the abdominal organs. After determining the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and identifying the composition of the microflora, the patient is prescribed the necessary medications. Their action is aimed at treating the disease that led to the imbalance and normalizing the intestinal environment.
Treatment
To restore microflora, both medicines (probiotics and prebiotics) and natural products are used - sources of beneficial microorganisms and a nutrient medium for them.
Probiotics are foods or medications that contain beneficial bacteria, while prebiotics create a suitable environment for the life of beneficial microorganisms.
Treatment includes three stages:
- Neutralization of pathogenic flora.
- Removing intoxication.
- Restoration of healthy intestinal microflora.
Medicines for the treatment of dysbiosis
Drug treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist. Approximate diagram:
- Proper nutrition.
- Taking medications that populate the intestines with beneficial bacteria. Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform, Acylact, Enterol, Biosporin, Biogaya and the like.
- Taking prebiotics - drugs that create a nutrient medium for beneficial microorganisms. Lysozyme, Lactulose, Hilak forte, Inulin and others.
- To improve digestive function, take enzyme preparations. Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon.
- Symptomatic treatment of constipation and diarrhea. Duphalac, Regulax, Bisacodyl, Imodium and others.
- If pathogenic flora is detected, you must first take a course of antibiotics or bacteriophages.
Treatment takes from 2 weeks to 2 months, sometimes longer. Taking medications must be agreed with your doctor. They all have different effects and only a doctor can assess what medications are needed in a particular case.
Treatment with folk remedies
In folk medicine, the treatment of dysbiosis is based on natural remedies that eliminate symptoms and remove the cause of the disease:
- Plants with antimicrobial effect. Coltsfoot, calamus, St. John's wort, sage, chamomile, rosehip, raspberry, cranberry. Beekeeping products also have a pronounced antimicrobial effect.
- Yarrow, oak bark, St. John's wort, chamomile, and calendula have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Flaxseed, elecampane, marshmallow, angelica, and oats have a protective enveloping effect.
- For diarrhea, oak bark, bird cherry, and burnet will help.
- Peppermint, fennel, dill, buckthorn, and aloe have a laxative effect.
The most popular means:
- Potentilla decoction. Has anti-inflammatory and astringent effects. Helps well with diarrhea.
- Oak bark decoction.
- For breakfast, eat steamed oatmeal with dried fruits.
- Take a collection of peppermint, dandelion root, chamomile, currant leaf, and burdock root.
- For 2 weeks, swallow a whole clove of garlic an hour before your first meal.
What is intestinal dysbiosis? How to treat dysbiosis?
Diet for dysbiosis
Compliance with nutritional recommendations is a prerequisite for successful treatment of dysbiosis. When planning your diet, avoid the following foods:
- sweets;
- fatty meat, smoked meats, canned food, spicy marinades;
- yeast bread and other products that increase gas formation.
If there is an imbalance in the intestinal environment, foods rich in fiber are beneficial. The diet should be based on porridge, fresh vegetables, dried fruits, lean meat, and dairy products. It is recommended to eat small portions several times a day, avoiding overeating and starvation. It is necessary to drink 1.5-2 liters of water per day and limit carbonated drinks, coffee and alcohol.
Causes of flatulence
The stomach and colon of healthy people contain a certain amount of gases, but in some cases increased gas formation is observed. The causes of flatulence can be different: treatment is not always required. Often the patient just needs to reconsider his lifestyle.
If you eat in a hurry, while running, you swallow large portions of air with food, which leads to bloating. A similar situation occurs in healthy people who abuse carbonated drinks, beer, kvass, and foods that enhance the fermentation process, for example, black bread, legumes, and cabbage. Treatment of flatulence in this case consists of normalizing the diet.
What is the cause of frequent flatulence?
Regular flatulence is a reason to be wary. Increased gas formation, which reminds you of itself after every meal, can be a sign of a number of diseases. These include intestinal dysbiosis, enzymatic deficiency, and impaired formation of bile acids. Abdominal bloating can be caused by a mechanical obstruction: a tumor or intestinal adhesion.
In patients with diseases of the liver and biliary tract, flatulence is accompanied by heaviness in the abdomen, nausea, discomfort in the right hypochondrium, and general weakness.
Flatulence occurs with infectious and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. These include colitis, pancreatitis, and intestinal infections. These diseases are dangerous due to their complications and require mandatory treatment in the gastroenterology department.
In people with lactose intolerance, consuming dairy products causes bloating. If increased gas formation occurs against the background of pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, treatment of flatulence is aimed at eliminating the main cause of its occurrence. The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor after diagnosis.
People with a healthy gastrointestinal tract can also suffer from bloating. Frequent stress and overexcitation lead to spasms of the smooth muscles of the intestines. This worsens peristasis, leads to the accumulation of gases and causes a feeling of fullness. To treat flatulence, which is of a psychogenic nature, it is necessary to normalize the psycho-emotional state.
Bloating in pregnant women is caused by an increase in the size of the uterus, which puts pressure on the intestinal walls. Also, the hormone progesterone, produced during pregnancy, causes relaxation of not only the uterus, but also the intestinal muscles, which leads to a slowdown in peristalsis and the accumulation of gases.
Symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis
The intensity and severity of symptoms of dysbiosis in children and adults depends both on the degree of imbalance and on the reproduction of which type of pathogenic microorganism has become predominant. Let's consider the general symptoms and features of dysbiosis:
- Allergy
Against the background of dysbacteriosis, children often develop allergic reactions to products that previously did not cause any disturbance - bronchospasm, urticaria, angioedema, skin rash and itching. As well as intestinal disorders - sharp abdominal pain, loose foamy stools, nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting, decreased blood pressure.
- Dyspepsia
In adults, intestinal dysbiosis can be accompanied by dyspeptic disorders - alternating constipation and diarrhea, possibly only diarrhea or persistent constipation, bloating, flatulence, belching, rumbling in the intestines, unpleasant taste in the mouth, dry mouth, bitterness in the mouth, lack of appetite. All this is due to the fact that opportunistic and pathogenic microbes destroy digestive enzymes in the small intestine, preventing normal digestion and absorption. Read more about dyspepsia.
- Hypovitaminosis
Impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestines, or the so-called malabsorption syndrome. This is manifested by hypovitaminosis, a deficiency of B vitamins, a lack of calcium becomes especially noticeable, iron deficiency anemia appears, protein-energy deficiency appears, and the ion balance is disturbed (see vitamin deficiency and hypovitaminosis).
- Decreased immunity
Against the background of long-term dysbacteriosis, a person’s immunity decreases, which is manifested by repeated acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, relapses of herpetic infections, fungal diseases (thrush in women, fungal stomatitis, etc.)
The severity of manifestations of dysbacteriosis depending on the type of pathogen
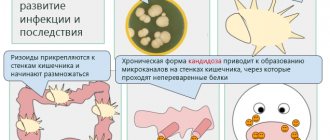
With fungal dysbacteriosis, the symptoms of microflora disturbance are characterized by more foamy stool, they are often in the form of lumps, with films. Severe septic forms are recorded extremely rarely. This dysbiosis is usually accompanied by candidiasis of the vagina and oral cavity, accompanied by itching and burning, redness and white deposits on the mucous membranes. Intestinal candidiasis often provokes the onset or exacerbation of existing atopic dermatitis or bronchial asthma, both in children and adults.
Staphylococcal dysbacteriosis often occurs as a generalized form with the development of sepsis. Even with a mild form, a low-grade fever occurs, and with severe and moderate severity of the process it is accompanied by high fever, cramping pain, vomiting, nausea, traces of blood in the feces (see Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella in infants).
Escherichia and Pseudomonas intestinal dysbiosis - such forms of the disease are periodic, erased in nature. It manifests itself as signs of dyspepsia, stool with mucus, and dull pain in the sigmoid colon.
Proteus - accompanied by dyspepsia, as well as prolonged low-grade fever; hypochodriac, astheno-neurotic manifestations are also possible.
Degrees of intestinal dysbiosis
Like many other diseases, a violation of the intestinal microflora can occur with minimal symptoms, have a sluggish nature, or, conversely, be accompanied by severe manifestations and consequences. There are several degrees of severity of dysbiosis:
- Latent form of dysbacteriosis
Or a compensated form, in which the amount of Escherichia coli slightly decreases or increases, while bifidoflora and lactoflora remain normal, with no significant intestinal dysfunction. With this form, a person experiences brittle nails, fragility and hair loss, cheilitis, glossitis, and also possible food allergies, a lack of B vitamins, constipation, and frequent ARVI.
- Subcompensated form
Against the background of a slight decrease in the number of bifidobacteria, the qualitative and quantitative indicators of Escherichia change, as well as an increase in the level of opportunistic bacteria, candida, and pseudomonads.
- Moderate severity
With this form, the number of bifidobacteria decreases slightly, and the opportunistic flora becomes larger than normal. At this degree, in addition to hypovitaminosis, anemia appears caused by iron deficiency, and calcium deficiency is also detected, appetite decreases, dull pain in the abdomen appears, nausea, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, rumbling, belching of air or bitter, a feeling of fullness, alternating diarrhea with constipation, low-grade fever, mucus in stool, changes in psychosomatic character - fatigue, irritability, depression.
- Severe degree
A severe degree of dysbacteriosis is expressed by frequent bowel movements, more than 5 times a day, increased body temperature (not always, enterocolitis can occur without an increase in body temperature), and significant weight loss. In addition to gastrointestinal dysfunction, destructive changes in the intestinal walls, as well as sepsis, can occur, since general and local immunity is significantly reduced and the effect of opportunistic bacteria is enhanced. Foamy, bright golden stool that turns green when standing and smells like cheap perfume. A large amount of mucus in the stool. Stools are frequent up to 20 times a day with severe enterocolitis. Dehydration increases rapidly, especially in infants. Klebsiella produces yellow-orange stool with a lot of blood. The frequency of stool depends on the severity of the process.
How to treat flatulence at home?
The main way to treat increased gas formation at home is diet therapy. Avoid legumes, beer, kvass, baked goods, limit the consumption of apples and cabbage. All these products cause fermentation. It will be useful to include crumbly cereals, boiled vegetables, and fermented milk products in your diet.
In the absence of individual intolerance, home therapy can be supplemented with herbal decoctions. Teas based on mint, chamomile, dried ginger, and cumin seeds help relieve increased accumulation of gases. Young children can make dill tea.
The cause of bloating and increased accumulation of gases in the intestines may be a pathological process or infection. Treatment of flatulence includes taking medications prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Normal intestinal microflora
Clinical studies show that more than 600 species of microorganisms make up the adult gut microbiota. A sharp increase in the number of bacteria is observed in the distal parts of the small and large intestine. The accompanying microflora is represented by anaerobic microorganisms (enterococci, non-pathogenic Escherichia coli, etc.). In a smaller number, the microbiota consists of staphylococci, clostridia, proteas, and fungi.
Lifestyle, diet, and age can affect the predominance of certain microorganisms in the intestines. The determining role in the formation of the species composition of the microbiota is assigned to genetic factors. The importance of normal intestinal microflora:
- protection against colonization of the digestive tract by pathogenic bacteria;
- active participation in the processes of digestion and absorption;
- ensuring the synthesis of vitamins B and K;
- neutralization of toxic substances.
How to treat intestinal flatulence?
First of all, it is necessary to determine what causes flatulence. Based on the diagnostic results, a treatment regimen is determined. If gas formation is caused by excessive swallowing of air, avoid chewing gum, soda, and snacks on the go. If the culprits of bloating are foods that enhance fermentation, their consumption will have to be limited or eliminated.
To prevent bloating, healthy people are advised to avoid too hot or cold foods, drinking large amounts of coffee, soda, sweets, yeast products, and snacks. Limit vegetables and fruits to radishes, green and onions, cabbage, and apples. The cause of heaving can be oats and products made from them, including muesli and quick cereal-based breakfasts. Some people experience rumbling and bloating after eating fried meat or high-fat foods.
Treatment for flatulence due to pancreatitis includes taking medications that replenish the lack of pancreatic enzymes. If the cause of increased gas accumulation is a tumor or adhesions, surgical treatment is prescribed. Flatulence due to dysbiosis goes away after the intestinal microflora is restored.
How long does dysbacteriosis last after antibiotics?
It is difficult to say how long the manifestations of the symptom complex continue. The duration of dysbiosis will depend on factors:
- severity of the disease;
- duration of treatment with antimicrobial drugs;
- type of antibiotics;
- state of the immune system;
- age and individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Dysbiosis can manifest itself at the beginning of a course of antibiotic therapy or after its completion, in an acute or sluggish form. Continue for 2-3 days and do not require treatment, or last more than a month and without treatment will end in failure. There is information about the development of pseudomembranous enterocolitis against the background of intestinal dysbiosis, and in the acute course of the disease, death is possible.
Therapy for dysbiosis can be several times longer than the duration of antibiotic treatment; restoring the balance of microflora can take from several days to several months.
It is important not to self-medicate, but to seek the help of a specialist. Treatment of a malfunction in the microbial composition of the intestine begins with diagnostics, which will help identify missing strains of bacteria, identify species that exceed the conditional norm of their content, and prescribe the necessary medications to normalize the flora.
In newborn babies, there is a temporary imbalance of intestinal microflora, which is not associated with taking medications. Physiological dysbacteriosis can last from 1 to 6 months, in most cases it does not require special therapy. But if medication has been taken, any medication that affects the inhibition of the body’s protective function can cause an imbalance in the baby’s microflora. And the recovery period can take from several days to several weeks.
Breastfed babies are less susceptible to manifestations of dysbiosis than bottle-fed babies.
How to treat flatulence during pregnancy?
Flatulence in pregnant women is not dangerous, but can lead to muscle spasms and cause nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Treatment is usually not required; it is enough to adjust the diet by eliminating foods that cause increased gas formation. It is recommended to eat food often (5-6 times a day), but little by little and slowly. Decoctions of chamomile, mint, weak ginger and dill teas help against flatulence.
Dysbacteriosis is not an independent disease, but a consequence of poor nutrition or disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. The success of treatment directly depends on correct diagnosis and following the doctor’s recommendations.