Hyperfunction and hypofunction of the pancreas, regardless of the cause, pose a health hazard.
Malfunctions are associated with a disorder of the secretory activity of the organ. Diabetes mellitus is especially difficult - a condition with impaired synthesis or production of insulin, which develops with hypofunction of the pancreas, leads to severe damage to many organs and systems, changes the patient’s lifestyle and takes a long time to be treated. During therapy, another disorder may occur when the amount of hormones produced increases sharply. With hyperfunction of the pancreas, a life-threatening condition often develops if the amount of synthesized hormonal substances becomes critically high. In such cases, emergency assistance is necessary.
Harbingers of pathological changes
As already mentioned, this scourge is diagnosed in isolated cases, but no one is immune from its occurrence. That is why you should know about the main manifestations indicating the development of pathology, which will help you not to miss the first warning signs and contact a specialist in a timely manner. This, in turn, will give the patient a chance for possible complete recovery of such a capricious and difficult-to-treat organ as the pancreas.
Gastroenterologists, in response to people’s questions about how pancreatic hyperfunction manifests itself, usually note that the very first manifestations that characterize pancreatic hypersecretion are nonspecific. Based on them, it is very difficult to suspect disturbances in the functioning of an organ, since these are signs of general disorders in the body - increased fatigue, weakness, malaise, constant drowsiness and apathy. Occasional loss of consciousness and convulsions are also observed. Only as the pathology progresses do more obvious symptoms appear, indicating that the gland is intensively producing hormones and enzymes:
- Morning loss of orientation, expressed in the occurrence of difficulties when communicating with others, as evidenced by stereotypical phrases and movements.
- Psychomotor tension is almost constantly present, reminiscent of moderate alcohol intoxication.
- The appearance of convulsive seizures similar to epileptic seizures, the characteristic difference of which is that they last longer.
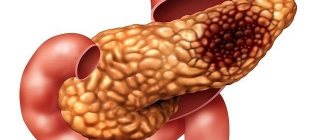
In the case when hyperfunction of the pancreas, associated in clinical practice with the very dangerous disease insulinoma, becomes malignant, a person develops signs of oncology - acute pain in the abdominal cavity, obesity, stool disorders. The transformation of this pathology into cancer occurs very often, and metastasis to the liver is always noted.
To treat gastrointestinal diseases, people successfully use Galina Savinova’s method. Read more >>>
The faster a person reacts to the fact that his pancreas has begun to produce excessive amounts of hormones and enzymes, the more effective the treatment will be. Otherwise they can be very serious, in most cases resulting in death.
Treatment
Acute attacks of the disease, as a rule, are neutralized by the administration of intravenous glucose. The patient has the right to refuse this method and begin taking any sources of glucose during a sharp deterioration of the condition. Hyperfunction of the pancreas can be accompanied by the appearance of tumors in this organ. In such a situation, treatment of the disease consists of surgery and removal of the tumor.
Sometimes, due to the individual characteristics of the patient, such surgical intervention is strictly contraindicated. Then the patient must follow a special diet, take special medications and strictly follow doctor’s orders.
But do not forget that such a conservative method of treatment is considered less effective, in contrast to timely removal of the tumor.
Identification and treatment of misfortune
As already mentioned, this pathological phenomenon is very important to identify at the initial stages of development. Only in this case can the success of the treatment course prescribed by a specialist be guaranteed. Diagnostic studies are carried out in several stages, at each of which the doctor receives certain information indicating the pathology of the pancreas condition. Typically, the following methods are used for diagnosis:
- step-by-step determination of blood levels of proinsulin, insulin and glucose;
- conducting a functional test, before taking which the patient must fast for a day;
- computed tomography performed on certain areas of the body.
If there is a suspicion of cancer, the blood is tested for the presence of tumor markers (proteins of a certain type that are produced by abnormal cells). The main task of diagnosis is not only to identify hyperfunction, due to which hormones in the digestive organ are produced in excessive quantities, but also to identify the factors that provoked such an imbalance. Only after this is it possible to prescribe adequate therapeutic measures that can eliminate the pathology.
Therapeutic measures
If an increased level of enzymes produced by the pancreas is detected in the body, therapeutic measures must be started at the earliest possible date. Only in this case is it possible to avoid very serious problems associated with the destruction of certain tissues and walls of blood vessels in the body. Such pathological changes can provoke the following misfortunes:
- cancerous tumors;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- gangrene;
- stroke.
If a malignant insulinoma is detected, which provokes hyperfunctionality in the pancreas, experts recommend surgical intervention. If the tumor is small in size and local in nature, only it is excised. But in some cases, partial removal of the organ may be necessary.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease consists of several stages, which allows the doctor at each of them to obtain extensive information about the condition of a particular organ and the body as a whole. Diagnosis of the disease consists of:
- determining glucose levels;
- determining insulin levels;
- determining the level of proinsulin;
- functional test, which is taken after a daily fast;
- conducting computed tomography of specific areas of the patient’s body.
How to cure pancreatic hyperfunction?
Mirror image of pathology
The disease has a mirror image - it is a decrease in the functioning of this digestive organ. Hypofunction and hyperfunction of the pancreas are very serious pathological changes, and it is difficult to say which of them is more dangerous. But if we take it in comparison, we can say about hypofunction that it appears in people with inflammatory problems of the pancreas quite often. Its essence lies in the fact that the gland begins to produce hormones and enzymes in insufficient quantities, which also leads to the development of serious diseases, the most famous of which is diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms of chronic hypoglycemia
Periods of exacerbation are “diluted” with signs of chronic hypoglycemia. The following symptoms appear:
- paralysis of facial muscles;
- violation of tendon reflexes;
- loss of taste sensitivity;
- memory loss;
- deterioration of intellectual performance;
- loss of professional skills.
When malignant insulinoma develops, the patient suffers from diarrhea and severe abdominal pain.
Diabetes mellitus develops with hyperfunction of the pancreas
Causes
If the pancreas functions normally, then the blood contains an acceptable level of sugar, and the digestive tract copes well with processing BZHU. But if a malfunction occurs in the functioning of the organ, the following dangerous conditions may develop:
- hypofunction – a reduced level of insulin in the body, which provokes the development of diabetes mellitus;
- hyperfunction is an increased level of insulin in the body, provoking the development of hypoglycemia.
The main cause of pancreatic hypofunction is damage to the islets of Langerhans, a special cell group that produces hormones.
Decreased hormone synthesis can be caused by the following factors:
- obesity;
- infectious lesion;
- autoimmune reactions;
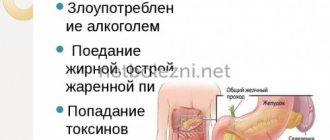
- intoxication of the body;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- psycho-emotional overstrain, stress.
Hyperfunction of the pancreas appears due to a deficiency of glucose in the blood, due to which the body intensively produces insulin. The following reasons can trigger the development of this condition:
- brain tumors;
- glucagonoma is a tumor that forms on the islets of Langerhans, which is predominantly malignant;
- insulinoma is a tumor that forms in the gastrointestinal tract, which enhances the production of insulin and is benign;
- improper administration of insulin in diabetes;
- increased acidity of gastric juice.
Increased synthesis of hormones is considered a rare phenomenon, which is usually diagnosed in females.
Location, size and structure of the pancreas.
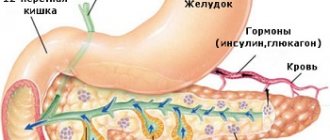
The pancreas is an organ of both external and internal secretion.
The endocrine part of the gland is represented by separate cell groups that form small islands in the mass of the rest of its tissue. These groups of cells are called islets of Langerhans. The number of islets is greatest in the caudal part of the gland. The size of one island is 0.1-0.3 mm, their number is from 200 thousand to 1.8 million. Some islands are separated from the surrounding tissues by a thin connective tissue membrane. There are four groups of cells in the islets of Langerhans: alpha, beta, y and gamma. They are colored differently and perform different functions. Beta cells are the most common (70%), approximately 20% of all cells are alpha cells, and approximately 5% each are yam and gamma cells.
Symptoms of pathology
Impaired functioning of the pancreas often has mild, nonspecific symptoms, resulting in difficulties in early diagnosis of the problem.
Hypofunction is accompanied by the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus, the first sign of which is unquenchable thirst, due to which the patient can drink about 10 liters of water per day. Due to the fact that such a large amount of fluid enters the body, polyuria syndrome occurs - frequent urination.
Also, reduced hormone synthesis can be suspected by the following signs:
- dry mouth;
- severe weakness;
- reduced performance;
- dehydration of the body;
- rapid weight loss even with constant overeating.
If, in addition to these signs, nausea and vomiting, confusion and unbearable weakness are observed, then this indicates the development of a diabetic coma. If such symptomatic manifestations appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. The main symptom of pancreatic hyperfunction is hypoglycemia syndrome, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- low blood sugar in the morning or after physical stress;
- loss of consciousness during prolonged fasting;
- dizziness;
- hyperhidrosis;
- trembling in the body;
- causeless anxiety, fear;
- nausea, vomiting;
- fatigue, weakness;
- arrhythmia, tachycardia.
The patient constantly feels brutal hunger, may behave inappropriately towards food, and try to take it away from another person. The condition is normalized and the symptoms go away if the patient is given a dose of glucose. Lack of therapy leads to the following neurological disorders:
- disorientation in the morning (repetition of words and movements, answers out of place);
- psychomotor agitation, the person is in an “intoxicated” state;
- disorientation in the area;
- inability to concentrate;
- absent-mindedness;
- apathy;
- prolonged convulsive attacks similar to epileptic seizures;
- disturbance of consciousness, up to coma.
At first, the signs are such that the patient takes it for overwork and does not see a doctor.
As the pathology progresses, the symptoms intensify, are expressed more clearly, and vegetative attacks appear. During an exacerbation of hypoglycemia, the patient may experience a moving gaze, double vision, and trembling throughout the body. Chronic hypoglycemia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- deterioration of memory and mental abilities;
- loss of professional skills;
- violation of taste;
- dysphagia;
- constant drowsiness;
- headache.
If there is no treatment for pancreatic hyperfunction, irreversible mental changes occur and severe complications arise.
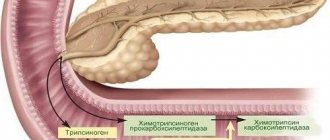
Pancreatic hormones.
The islets of Langerhans produce three hormones: insulin, glucagon and lipocaine.
The importance of insulin was discovered back in 1889, when researchers Mehring and Minkowski, having removed a dog's pancreas, discovered sugar in its urine. From this they concluded that the pancreas regulates the amount of sugar in the body. The Russian scientist L.V. Sobolev showed in 1902 that the pancreas, along with the exocrine gland, also performs an endocrine function. He tied up the excretory duct of the pancreas, after which he noted the death of cells in which the secretion is formed, released into the duodenum, while the islet tissue did not undergo changes and there were no disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism. In 1921, scientists Bantig and Best isolated a hormone from the islets, which they called insulin (insula - islet).
Currently, the structure of insulin has been fully studied and it is artificially synthesized. The insulin molecule consists of two chains: A and B. Chain A includes 21 amino acid residues, and chain B includes 13-30. It has been established that insulin is produced in beta cells. Zinc is required for its binding to the granule protein and subsequent release. Insulin stimulates the synthesis of glycogen in the liver and muscles, inhibits its conversion into sugar and promotes the oxidation of sugar in the muscles. Therefore, after turning off the function of the islets of Langerhans (there are drugs that selectively damage them), the sugar content in the blood increases sharply, which is called hyperglycemia, and it begins to appear in the urine. The presence of sugar in the urine is called glucosuria. When insulin is administered, the amount of sugar in the blood sharply decreases from 80-120 to 30-45 mg%. A decrease in blood sugar is called hypoglycemia.
Glucagon is produced in alpha cells, consists of 29 amino acid residues and acts opposite to insulin. It causes hyperglycemia and reduces glycogen content in the liver.
Lipocaine promotes the release of fats from the liver, their oxidation in it and inhibits the conversion of carbohydrates into fats. The secretion of hormones by the islets of Langerhans is regulated by blood sugar. Alpha and beta cells sense changes in blood sugar concentrations, and the activity of these cells changes according to the principle of negative feedback. Hyperglycemia activates beta cells and inhibits alpha cells, and hypoglycemia activates alpha cells and inhibits beta cells.
Diagnostic methods
Symptoms of hypofunction and hyperfunction of the pancreas in the early stages of development are mild and nonspecific, which makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. As a result, diagnosis is difficult, and the patient is often misdiagnosed.
To correctly diagnose the problem, after a detailed survey and examination, the doctor should prescribe the following examinations:
- Blood analysis. First of all, the doctor prescribes a blood test to detect the levels of insulin, proinsulin and glucose. Blood sampling for testing is carried out on an empty stomach.
- Functional tests. If at the time of the blood test the patient has no signs of hypoglycemia, then a functional test with fasting is performed. To do this, you refuse to eat for 2-3 days. To confirm the diagnosis of hypoglycemia, another test may be prescribed, in which the patient is given an injection of insulin, after which the blood is examined.
- CT. Allows you to detect a pancreatic tumor at an early stage, study in detail the structure of the formation and the nature of its growth. Tomography is also used to track the condition of the organ throughout treatment.
- Angiography. Helps detect changes in the pancreas, identify a tumor, determine its location and size.
If a malfunction of the pancreas is suspected, a urine test is also prescribed. If necessary, other diagnostic measures and consultations with various specialists may be prescribed.
Diagnostics
When a patient suspects this condition, they should go to a place where proper diagnostic procedures are performed. Provincial public hospitals usually lack the required equipment and specialists. Therefore, you first need to find the nearest clinic that offers the necessary services. Procedures that are advisable to perform on a patient include:
- Radioimmunological blood test. The most important parameters include insulin levels, as well as C-peptide data;
- Angiographic examination - x-ray with a contrast agent, it is carried out to detect incipient tumors and determine the stage of their development;
- Computed tomography to study the condition of the digestive system;
- Study of blood glucose levels. The procedure must be carried out on an empty stomach: you cannot eat on the day of the procedure, the day before - eating is allowed no later than 18 pm. A reading below 2-3 mmol per liter indicates hyperfunction of the gland in question and excessive insulin production;
To detect the content of immunoreactive insulin, the patient has a portal vein catheterized.
To prevent glandular diseases, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle
Functional test - checking the reaction to glucose. Before the procedure, the patient must avoid eating for 15-20 hours. During this time, the blood glucose level has time to drop significantly compared to the routine level, and if there is excessive pancreatic function, the patient will experience signs of a hypoglycemic attack. The patient's blood sugar is measured, and then a glucose solution is administered intravenously.
Possible complications
Hypofunction and hyperfunction of the pancreas are dangerous conditions that, if left untreated, lead to the development of serious consequences. With reduced hormone synthesis due to high concentrations of glucose in the blood, destruction of the vascular system and tissues may begin.
This provokes the development of pathological conditions:
- stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- gangrene;
- loss of vision.
In this condition, the body’s defense reactions decrease, resulting in frequent infectious and pustular diseases. A severe complication of pancreatic hypofunction is diabetic coma, which, in the absence of timely assistance, can cause death.
Enhanced hormone synthesis is a more dangerous condition that can seriously harm human health.
Hyperfunction of the pancreas threatens the development of complications:
- heart pathologies;
- convulsions;
- epilepsy;
- hallucinations;
- mental disorder;
- paresthesia of the limbs;
- impotence;
- muscle atrophy;
- obesity.
This disease can lead to insulin shock, loss of consciousness, and coma. Often patients quickly recover from a comatose state, but with frequent repetitions of attacks, coma can lead to death. You can avoid such dangerous complications if you consult a doctor in time and start treatment.
Hyperfunction of the gland
Causes
The disease occurs much more often in women than in men.
Determining the root cause of hyperfunction will become the basis for further treatment. Pancreatic hyperfunction occurs when glucose levels decrease. The body responds to this with a sharp increase in insulin production (which it subsequently cannot neutralize).
The increased function can be distributed according to gender: in women the disease is much more common than in men. The reason for this is the differentiation of the hormonal system, as well as the distinctive characteristics of the female body (the disease progresses on a large scale with a shorter time interval).
To track the first manifestations of the disease, you should pay special attention to:
- diet;
- blood glucose levels;
- general condition of the body.
Symptoms
The symptoms are not pronounced. It is for this reason that patients do not notice changes in the usual rhythm of life, ignoring a visit to the doctor. The initial symptoms of increased glucose levels are more similar to typical fatigue or nervous feelings. Basic symptoms include:
- fatigue, weakness of the body;
- high degree of fatigue, which is not justified;
- drowsiness;
- apathetic state;
- cramps in the limbs;
- loss of consciousness.
The faster you respond to the manifestation of symptoms due to pancreatic hyperfunction, the more effective and efficient the treatment will be. If timely treatment is not started, the consequences can be irreparable, even death.
Over time, the symptoms will become more pronounced and cause great discomfort to the patient, thereby disrupting his usual routine.
Advice: take care of your own health and undergo routine examinations by specialists, which include an additional list of tests. This way you can increase your chances of a speedy recovery.
Diagnostics
CT scan.
Diagnosing a disease consists of several stages, each of which provides the doctor with extensive information about the state of the body and a specific organ. Diagnostics consists of:
- determination of glucose content;
- determination of insulin content;
- determination of proinsulin content;
- functional test, which is taken by the method of daily fasting;
- conducting computed tomography of certain areas of the body.
Treatment
Attacks of the disease can be neutralized by intravenous administration of glucose or glucose solutions. The patient can refuse intravenous administration and take any sources of glucose when he feels a sharp deterioration in his condition. Increased function is accompanied by the formation of a tumor in a specific organ. Treatment of the disease consists of surgical removal of the tumor.
In some cases (due to the individual characteristics of the patient), such surgical intervention is prohibited. The patient should adhere to a special diet, take special medications and strictly follow medical instructions.
Please note: the conservative method is less effective than timely tumor removal.
Prevention
The method of preventing hypofunction and hyperfunction of the pancreas is proper nutrition, which implies adherence to fractional meals and regular intake of carbohydrate foods. The best diet for this purpose is diet table No. 5 according to Pevzner. You can prevent the development of the problem if you adhere to the following preventive measures:
- to live an active lifestyle;
- quit smoking;
- avoid intoxication of the body;
- when treating diabetes mellitus, follow all doctor’s recommendations;
- strengthen the immune system;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress and stressful situations;
- do not self-medicate with medications;
- Avoid strict diets and fasting.
Impaired functioning of the pancreas can occur as a result of various pathologies, so it is necessary to periodically undergo a preventive medical examination and, if any problem is identified, begin its treatment immediately.
It is extremely important to check your blood glucose levels regularly.
Hypofunction of the pancreas, like its hyperfunction, is a serious pathology that requires careful examination and treatment. Increased production of hormones usually indicates deadly diseases. Insufficient secretion leads to the appearance of diabetes mellitus, a severe but correctable condition. Each type of functional malfunction of the gland should be considered separately.
The pancreas is an organ that performs exocrine and intrasecretory functions.
The pancreas is an organ that performs exocrine and intrasecretory functions.
Symptoms of hypofunction
It is worth remembering that the symptoms of this disease are entirely individual in nature and may vary depending on the patient’s condition. Reduced pancreatic function is manifested by the following main symptoms:
- constant feeling of thirst, dehydration;
- feeling of dryness and discomfort in the mouth;
- frequent urination (polyuria);
- fast and dramatic weight loss;
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
- painful sensations localized in the abdomen;
- fatigue and weakness;
- confusion.
Such symptoms can lead to diabetic coma. If you notice the presence of the above symptoms and a deterioration in your general condition, immediately seek help from a specialist.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that high levels of glucose in the blood can lead to the destruction of some tissues and blood vessels. Sometimes these processes can lead to gangrene, blindness, cardiovascular disorders and strokes. In order to prevent such manifestations of the disease, it is necessary to monitor your health and go for medical examinations more often.
Hyperfunction
Increased production of pancreatic hormones is most often a symptom of the presence of hormone-producing tumors. They develop on the tissues of the glandular apparatus and are named depending on the type of hormone they synthesize: glucogonoma, gastrinoma, VIPoma. The most common type of neoplasm is insulinoma, a tumor that affects the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans. In addition to the above, hyperfunction develops as a result of oncological processes in the brain (regulatory centers of the gland) and increased acidity of gastric juice. In the latter case, the violation is of a purely functional nature.
Hypofunction
Diabetes mellitus is the most common manifestation of pancreatic hypofunction
The main disease that occurs when pancreatic secretion decreases is diabetes mellitus. The pathology is caused by an insufficient level of glucose utilization by somatic cells, which leads to an increase in its concentration in the blood.
Insulin deficiency develops when:
- obesity;
- autoimmune reactions;
- infections;
- toxic effects;
- thyrotoxicosis.
One of the first symptoms of diabetes is thirst. The patient can drink up to 10 liters of water per day. Diuresis naturally increases, which is the second symptom of the disease. Patients with diabetes are prone to overeating, but even after eating large amounts of food they continue to lose weight.
As the disease progresses, patients experience damage to the vascular intima, which causes many clinical signs (retinopathy, trophic ulcers, lameness, malfunction of internal organs). There is a decrease in the intensity of the body's defense reactions. Patients suffer from pustular diseases, and they more often develop infections of the upper respiratory tract. With a significant increase in blood glucose, a person falls into a hyperglycemic coma.
Destruction of the islets of Langerhans and associated pancreatic hypofunction is an incurable disease. Therapy is carried out in a maintenance mode. The patient is forced to receive a synthetic hormone in injection form throughout his life. Today's technologies make it possible to deliver insulin using a pump - a special device that delivers the drug constantly, in small portions.
On a note! In the history of medicine, there are experiments in treating diabetes by transplanting sections of the pancreas. Unfortunately, these attempts were not effective enough to be put into practice.
Hypo and hyperfunction of the pancreas requires mandatory examination and treatment by an endocrinologist. Traditional medicine recipes are not applicable here. Therefore, at the first signs of the disease, it is recommended to undergo a full examination and begin a course of therapy indicated for the identified disease.
Hyperfunction and hypofunction of the pancreas: what are the probable causes of the syndrome?
Hypo- and hyperfunction of the pancreas are serious diseases that can lead to death in the absence of appropriate therapy. Please note: hyperfunction is quite rare.
The appearance of such a disease is associated with disturbances in the functional activity of the nervous system, hypoglycemia (a condition of the body in which the glucose level decreases to a minimum).
For this disease, glucose is administered intravenously, which helps stabilize the patient’s condition and blocks the symptoms of the disease.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Even a “neglected” gastrointestinal tract can be cured at home, without surgery or hospitals. Just read what Galina Savina says and read the recommendation.
Hypofunction of the pancreas leads to diabetes mellitus. In this case, the patient is advised to take insulin to maintain normal functioning. Timely treatment will help cope with hyperfunction and hypofunction of the pancreas and increase the chances of a speedy recovery.
Main harbingers
It can be determined that a patient is developing increased gland function by the following signs:
- Weakness, fatigue, decreased performance;
- Sharp weight gain without changing diet;
- Limb spasms;
- Drowsiness;
- Absent-mindedness, impaired concentration;
- Loss, confusion.
Many of these symptoms, especially if the person’s condition is not accompanied by disturbances of consciousness, are usually attributed to overwork and stress. Because of this, the patient may delay visiting the doctor.
To alleviate the disease, injectable glucagon is administered
Pancreas structure
The pancreas plays a vital role in the functioning of the body. It weighs no more than 70 grams, and its size varies from 16 to 22 cm. This elongated organ, “hiding” behind the stomach, consists of a body, head and tail.
The triangular body of the gland has an anterior, posterior, and inferior surface. The cone-shaped tail reaches to the spleen. The head is located on the bend of the duodenum.
Inside the organ are the islets of Langerhans. Their cells are intertwined with blood capillaries and autonomously equipped with nerve fibers. The islands contain:
Insulin production occurs in beta cells.
Answers on questions
What complications can develop with hypoglycemia?
The brain is the first to suffer from prolonged glucose deficiency. Therefore, the most dangerous consequence of hypoglycemia is stroke.
If the blood sugar level drops below 2.2 mmol/l, then irreversible processes may begin that provoke the development of:
- epilepsy;
- dementia and mental disorders;
- parkinsonism;
- encephalopathy.
A decrease in sugar levels below 2.0 mmol/l leads to glycemic coma, during which certain areas of the brain may die. Without timely medical care, death is inevitable.
What symptoms indicate pancreatic hyperfunction in young children?
Newborn children whose mothers had diabetes or suffered from other pancreatic pathologies during pregnancy are closely monitored. The presence of hypoglycemia in a child may be indicated by severe pallor, excessive agitation, or, conversely, inhibition of reactions. Children often develop chills in a warm room, accompanied by tremors of the limbs. Severe tachycardia is observed.
Parents should also be aware that impaired consciousness and mental development can also be a consequence of pancreatic hyperfunction due to insufficient supply of glucose to the brain.
Exacerbation of the disease
The clinical manifestation of pancreatic hyperfunction is a consequence of hypoglycemia. During an exacerbation of the disease, symptoms become more pronounced.
After waking up, a person experiences difficulties with orientation in time and space. He performs the same movement several times and answers questions vaguely.
Psychomotor agitation is very pronounced. The patient's behavior is in many ways similar to the reactions of a heavily drunk person. Neurovegetative disorders begin to develop. They are characterized by heart rhythm disturbances, increased sweating, and redness of the facial skin. Sharp pressure fluctuations are observed.
The most severe degree of impairment of consciousness is hypoglycemic coma. Sometimes the patient is in a “dream-like” state. He moves unconsciously, and after “awakening” he cannot understand how he ended up there. This condition is called retrograde amnesia.