One of the many causes of chronic diarrhea, not accompanied by blood in the stool, but with abdominal pain, is microscopic colitis. This is a collective diagnosis that includes inflammatory diseases of the colon that do not have obvious symptoms during endoscopy and x-ray examination. The diagnosis is confirmed by microscopy of the histological sample. Microscopic colitis includes lymphocytic and collagenous colitis. This is a fairly rare pathology and the cause is not reliably clear. Lymphocytic and collagenous colitis may be observed in patients with Sjögren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, and diabetes mellitus. Nowadays, such forms of colitis are detected more often, but this is due to more advanced diagnostics. According to A. Trom (2005), if in patients with chronic diarrhea no changes are detected during colonoscopy, then the biopsy shows microscopic colitis in 11.7% of cases.
Lymphocytic colitis
Normally, in humans, per 100 epithelial cells there are about 5 lymphocytes, immune cells located in the submucosal layer. According to G.Adler, with lymphocytic colitis there are more than 24 lymphocytes per 100 epithelial cells. The strongest infiltration of immune cells is observed in the cecum and ascending colon.
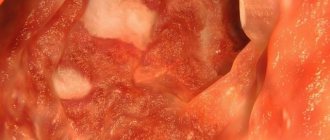
Microscopy reveals lymphocytic infiltration. Photo by Andreas Munch (Andreas Munch, USA)
The disease most often develops in people over 50 years of age. Women get sick 2-4 times more often than men. The disease manifests itself in frequent (up to 4-6 times a day) and loose stools, accompanied by cramping pain in the abdomen. Lymphocytic colitis usually has a benign course. Diarrhea occurs periodically, and quite long asymptomatic periods are possible. Diagnostics. Laboratory tests may not show significant abnormalities. Most often, there is a slight increase in ESR and C-reactive protein. Endoscopy and x-ray revealed nothing. Diagnosis is made by biopsy. Sometimes, over time, lymphocytic colitis can turn into collagenous colitis.
Prevention
In most cases, the symptoms of catarrhal colitis are a consequence of poor personal hygiene or poor nutrition. Eliminating these factors helps reduce the risk of inflammation. Products that are intended for fresh consumption (vegetables, fruits, berries) must be fully processed to remove contamination. Regular quick snacks can disrupt the functional state of the digestive tract and provoke the onset of colitis.
Other preventive measures:
- strengthening the body’s immune system (taking vitamins, eating healthy foods, healthy lifestyle);
- regular examination by a gastroenterologist (especially if there are signs of abnormalities in the digestive tract);
- avoiding uncontrolled use of medications that can have a negative effect on the digestive tract and intestinal microflora.
Collagen colitis
This disease is characterized by deposition of the fibrous protein collagen in the submucosal layer of the large intestine. Normally, the collagen layer has a thickness of 2-5 microns. In case of illness, this figure increases by 2-100 times. approx.
Collagen is a fibrillar protein involved in the formation of fibers of tendons, muscles, and bones. Forms a three-dimensional “mesh” of internal organs (stroma), determining its shape and density. It is the most abundant protein in our body, accounting for 25-35% of our mass. By the way, it is the submucosal layer in the intestines that is the strongest, thanks to this collagen layer. Therefore, when applying an intestinal suture, surgeons always grab it. There are 28 known types of this protein. Normally, the stroma in the submucosal layer of the intestine consists of type 4 collagen. With collagenous colitis, another, type 3, accumulates. This is important for diagnosis.
Clusters of collagen are visible. The thickness of the layer in a pathological process can reach 10 mm! (usually 1-3 mm). Photo by: Andreas Munch (Andreas Munch,USA)
The causes of collagenous colitis are unclear. There are suggestions that the synthesis of type 3 collagen, which is usually detected in regenerating tissues, is a defense against an unknown irritant.
Moreover, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be such an irritant. The development of symptoms of collagenous colitis is sometimes observed after long-term (at least 5 years) use of NSAIDs. What happens? Aspirin, which has been shown to reduce the risk of colon cancer with long-term use, may provoke another problem... Research in this direction continues. Moreover, long-term use of NSAIDs is usually typical for patients with other chronic diseases, including rheumatic diseases. Therefore, whether NSAIDs are to blame for this remains to be seen. An increased incidence has been reported with long-term use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), the majority of modern antidepressants. The most likely cause is thought to be of autoimmune origin. This is supported by the frequent combination of autoimmune thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes mellitus. In addition, antinuclear antibodies are detected. Symptoms . The main symptom is watery diarrhea, with stool volume reaching 4 liters per day. This occurs due to the release of a large amount of fluid and salts into the intestinal lumen. Of course, the symptoms of cholera are far from being seen, when fluid losses can reach 15-20 liters, but still, many patients experience exhaustion quite quickly. They lose body weight. Dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain) are also common. Diagnostics . Almost the same as with lymphocytic colitis. The tests may show a slight increase in ESR. The diagnosis is confirmed histologically. Moreover, it is best to take a biopsy in the right parts of the colon, since thickening of the collagen layer may not be observed in the rectum and sigmoid colon. Treatment . If NSAIDs are being taken, they are discontinued (it is assumed that they may be the cause). Nutritional adjustments are made, foods that stimulate peristalsis are excluded (for example, coffee, alcohol, dairy products. Antidiarrheal drugs are used, for example, loperamide (Imodium). There are studies on the use of the drug cholestyramine , which binds bile acids (bile stimulates peristalsis). In some cases, clinical the effect was achieved by taking antibiotics ( metronidazole ), which may lead to the idea that some kind of bacteria may be the etiological factor.In more severe cases, sulfasalazine budesonide is the best recommended ).
If microscopic colitis does not respond to a course of therapy in severe conditions of the patient, surgical intervention is performed - a stoma is performed in order to turn off the function of the affected part. When the intestine is switched off from the intestinal passage, regression of pathological changes is observed in it (when the passage is restored, characteristic microscopic changes appear again). There is still something in the intestinal contents...
In general, microscopic colitis has a favorable course, and long-term remission is often observed even without treatment.
Symptoms
If you have several symptoms of catarrhal colitis, you should consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. The danger of the disease lies in the rapid transition from the acute to the chronic phase. The severity of pain during inflammation depends on the general clinical picture of the patient’s health.
A significant deterioration in the condition of the body is observed with diffuse colitis (each intestinal calving occurs).
Other possible symptoms:
- sudden mood changes and insomnia;
- pain in the digestive system;
- pain in the intestines that subsides after defecation;
- increased gas formation;
- belching and bitter taste in the mouth;
- causeless bouts of vomiting and regular nausea;
- general weakness of the body;
- increased body temperature combined with chills;
- bad breath;
- impurities of blood or mucus in the stool;
- disturbances in the process of bowel movement (diarrhea or constipation);
- signs of intoxication of the body.
Treatment
Treatment of this disease is aimed at eliminating the acute stage of lymphocytic infiltration and lengthening the duration of remission intervals. Therapy for this pathology is nonspecific. High therapeutic effectiveness is observed when prescribing antimalarial medications (Hydroxychloroquine, Chloroquine) and anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin) after preliminary treatment of concomitant pathologies of the digestive tract. If the state of the gastrointestinal system allows, enterosorbents are used. Locally, the use of hormonal corticosteroid ointments and creams, as well as injection blockade of skin rashes with Betamethasone and Triamcinolone, is indicated.
If there is resistance to the treatment, plasmapheresis is added (up to 10 sessions). Therapy of the digestive system with lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of the intestines and stomach is closely related to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, inflammatory process in the large intestine, etc., which can be characterized by damage to the mucous membranes. To identify them, the patient must undergo appropriate diagnostics and therapy, which consists of taking antidiarrheal, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory medications, as well as following a diet (small meals, avoidance of foods that provoke fermentation, smoked, spicy and fatty foods).
According to this information, it becomes clear that leukocyte infiltration of the cervix is a condition that develops in the presence of an inflammatory process in the tissues. Most often found in cervicitis and vaginitis.
The diagnosis of leukocyte infiltration is made to women who have had a smear taken during a gynecological examination. The resulting material is sent to the laboratory for examination under a microscope. A smear is obtained using a Volkmann spoon after inserting a speculum into the vagina.
Where does the research material come from? The doctor takes tissue from the places where he sees pathological changes. The resulting material is applied to a glass slide and dried, only then the smear is checked in the laboratory.
Preparation
Only a comprehensive examination will allow us to detect the cause of leukocyte infiltration and cure the changes occurring in the cervix. An increased number of leukocytes is treated with antiseptic and antibiotic drugs, as well as lactobacteria and bifidobacteria.
Treatment of leukocyte infiltration also depends on the cause itself. Having gotten rid of the disease, the level of leukocytes in the epithelium of the cervix will be restored. It is possible to be sexually active in this condition if additional tests do not reveal a specific infection.
Lymphocytic gastritis is a rare type of ordinary chronic gastritis of unknown origin. The disease is characterized by nonspecific clinical manifestations and endoscopic signs. It most often affects older people after 60-65 years of age, but sometimes infants up to 1 year of age. Adult women get sick 3 times more often than representatives of the stronger sex.
The disease manifests itself in severe infiltration of the gastric epithelium. In this condition, small lymphocytes (or T-lymphocytes) are located in the gastric pits on the surface of the mucosa and there is infiltration of the membrane with plasma cells. Lymphocytic gastritis, if left untreated, in most cases leads to serious complications.