Sometimes intestinal obstruction is confused with other forms of digestive tract disease. The appearance of sharp pain in the abdominal area is associated with many pathologies. However, the recurrence of discomfort after 20 minutes is accompanied by intussusception. The disease is characterized by the penetration of one site into another. As a result, obstruction occurs, divided into forms and types. When a diagnosis is made, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out. After this, conservative treatment is prescribed.
Intussusception: what is it?
Intussusception often occurs in infants. The disease refers to acquired obstruction of the digestive tract. In most cases, the disease is common in Asian countries. Historically, intussusception has been described in ancient times. The first surgical treatment and straightening of the segment was performed in the mid-19th century with a difference of 2 years. The incidence of insertion of one section of the intestine into another is comparable to the occurrence of congenital pyloric stenosis. Sometimes the disease is correlated with Meckel's diverticulum.
Forms, types and types of intussusception
The classification is divided into forms, types and types of the disease. Therefore, intussusception in children and adults is divided depending on the cause.
There are several types of the disease:
- primary;
- secondary.
In the primary type of intussusception, no clear cause is identified. When the secondary appearance of the disease occurs, additional factors precede this condition. Therefore, when it reoccurs, diagnostics reveals the presence of polyps or tumors.
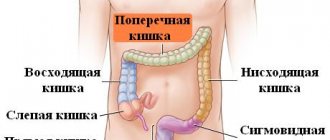
In addition to forms, there are types of intussusception. The disease is distinguished by location. The introduction of one site into another may be in the small intestine. In addition, there is intussusception of the large intestine and combined. Sometimes a section of the small intestine is inserted into the large intestine. Otherwise, the disease affects the entire intestines and stomach. Doctors distinguish a type when invagination of loops occurs through fistulas or stomas.
The classification of the disease is divided according to the type and direction of organ contraction. Therefore, they distinguish:
- isoperistaltic invagination (descending) - in the direction of contractile waves of the intestine;
- antiperistaltic invagination (ascending) - the introduction of one section of the intestine occurs in the opposite direction.
The disease can occur in a single case, or several intussusceptions are observed. In the simple type, a 3-cylinder integration is specified. During the course of a complex disease, more than 5 cylindrical intussusceptions are isolated. According to its form, intussusception is divided into acute and chronic.
Exacerbation occurs in 95% of the disease. Acute intussusception leads to disruption of the intestinal tract or a certain section. In addition, problems occur with the motor activity of the intestinal walls. Failure to provide timely assistance to a patient with an acute form of the disease leads to the death of the implanted area.
The chronic nature of intussusception is associated with the manifestation of symptoms after a certain period of time. Signs appear as in intestinal obstruction, but are not expressed. The recurrent form occurs in infants due to incompetence of the intestinal tract. Otherwise, he was treated for intussusception by straightening the implanted area.
In medicine, there are cases when the affected area heals on its own. This is called an abortive form of intussusception. The disease is characterized by compensation for the work of part of the intestine and manifests itself in aggravated symptoms.
Causes
The causes of volvulus can be different. Often, intussusception occurs due to indigestion, the formation of a tumor in the intestinal tract or fecal stones. In addition, the disease can be triggered by poor nutrition and excessive consumption of solid foods. This includes nuts and persimmons. Injuries to the abdominal area can cause volvulus. The cause of such injuries can be an accident, a severe bruise due to a fall from a height, or simply a blow to the stomach. Intussusception can also occur due to a variety of parasites living in the human body. These include: pinworms, opisthorchiasis, roundworms and worms. A large number of polyps can lead to volvulus. Tumors that obscure the intestinal lumen do not allow stool to pass normally and, thus, provoke intussusception. Poisons that can cause damage to the nervous system of the intestine will certainly cause volvulus.
Why does it happen?
If the primary type of intussusception occurs in adults and children, then the provoking factor is difficult to determine. The onset of the disease is accompanied by swelling of Peyre's plaques. The mesenteric lymph nodes are damaged due to a viral infection. The provoking factor is increased mobility of the cecum with a common mesentery.
Intussusception in children over 12 months of age is accompanied by anatomical disorders or changes in the organ.
Otherwise, the following reasons arise:
- polyps or Peutz-Jeghers syndrome;
- malignant formations in the form of lymphomas;
- benign tumors;
- duplications of the small intestine.
The disease can act as a sign of an underlying pathology.
Repeated intussusception occurs due to dysfunction of the pancreas. Sometimes it manifests itself against the background of diverticulosis and neoplasms of different etiologies (causes). There is a risk of implantation due to an improper rehabilitation period after surgery. Intussusception often occurs in people with a predisposition to food allergies. In addition, patients should monitor their diet and take preventive measures after infectious diseases.
The occurrence of intussusception of the ileum or cecum occurs due to infection. Infants are susceptible to these types of disease when complementary foods are introduced.
Who is at risk?
Intussusception occurs not only in children, but also in adults. Therefore, people who have had gastroenteritis, peritoneal tuberculosis and stomach diseases are at risk. The appearance of intussusception in a child is recorded in 80% of cases within several months of life. In most cases, the peak onset of the disease occurs at the age of six months. Pathology occurs during intrauterine development. However, boys are more likely to get sick than girls. Their ratio is 3:2.
Features of pathology in children
The clinical picture of intestinal obstruction has certain characteristics in children, especially at an early age.
They have a more pronounced intoxication syndrome - the temperature rises sharply, headaches, general weakness, and lethargy occur. The child behaves restlessly, constantly cries, rushes about, and refuses to eat. Be sure to read:
Intestinal colic in adults: how does it manifest itself and how to relieve pain?
Children are more likely to experience attacks of severe symptoms rather than constant pain. They can be accompanied not only by pain, but also by single or double vomiting.
Parents should feel the baby's tummy. If he has a dense formation that is localized in the lower abdomen, then it is necessary to suspect the presence of intestinal obstruction and consult a doctor. An unfavorable sign indicating the presence of pathology is also a prolonged absence of bowel movements.
Scheme of development of intussusception
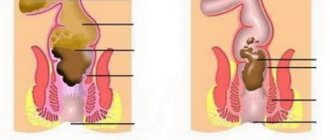
Regardless of the provoking factors, intussusception occurs due to a violation of the contractile function of the intestinal walls. The process is accompanied unevenly, and areas with spastic peristalsis are formed in the intestine. During this, a collision occurs between different parts of the intestine, which leads to the introduction of one into the other.
An irritant can be an allergen, drug or other factor that provokes convulsive contractions of the intestine. Because of this, intussusception occurs.
The disease progresses due to external factors. The invaded section of the intestine does not straighten out, but begins to be more strongly compressed by another area. In this case, during the diagnosis, the patient is observed to have swelling of nearby tissues. This occurs due to blood stagnation. A sufficient amount of oxygen ceases to flow into organs and tissues. The lack of necessary substances causes necrosis or death of the affected areas. If the arterial walls are damaged, the patient experiences bleeding in the digestive tract. Untimely treatment and seeking medical help leads to complications and unpleasant consequences. With prolonged course, intestinal obstruction develops.
How to recognize the disease?
The symptoms of intussusception in children and adults differ in the peculiarity of their manifestation at different stages and depend on the age of the patient. The clinical picture in infants is characterized by an acute onset.
Parents complain about the following changes in their child:
- anxiety;
- cry;
- knocking feet;
- loss of consciousness (not sleep);
- sweating;
- pale skin.
In addition, the baby is haunted by an attack of nausea. As a result, vomiting occurs. It looks like regurgitation in large quantities. However, the child continues to worry, which causes crying. Signs warn parents about pain syndrome in the baby. The discomfort does not last long and lasts up to 1 minute. When the attack of intussusception passes, the baby is able to fall asleep. After some time, the signs return.
The recurrence of intussusception symptoms becomes longer. The baby's condition is deteriorating. Prolonged course of the disease leads to stool disorder. Blood inclusions are observed in the stool.
Acute symptoms occur 12 hours after the first signs. When diagnosing a child, the affected area is detected by palpation. If the roundness of the abdomen is increased, then this becomes a sign of peritonitis. If help is not provided, after 24 hours, motor activity gives way to lethargy. The symptoms progress severely, and after 2 days complications arise. For children, the provoking factor is the incorrect introduction of complementary foods to infants.
Intussusception of the small intestine occurs in infants. Otherwise, the disease affects children over 3 years of age. The patient's condition worsens immediately after the first attack of pain. The symptoms do not subside over time and there is no remission. There are frequent attacks of vomiting. A small affected area is difficult to detect.
Intussusception of the cecum is accompanied by common symptoms. However, the affected area is located in the navel area. Blood in the stool is observed in the early development of the disease. If intussusception affects the colon or rectum, the disease is typical for adults. The discomfort is not acute, and the attacks continue for a long time.
Treatment
For successful recovery, treatment should begin in the first hours of intussusception. This is especially important in the acute form of the disease.
In any case, a positive result can only be predicted if competent and effective measures were taken within the first 24 hours.
Sometimes patients are given antispasmodics and painkillers at home, gastric lavage and cleansing enemas. This gives a short-term effect and the illusion of relief. But in the end they only aggravate the course of the disease and delay time. As a result, this threatens to worsen the prognosis for recovery.
The patient must be urgently hospitalized in a medical facility.
The emergency physician can take preliminary emergency measures while the patient is being transported to the hospital. In particular: administer a solution of cordiamine subcutaneously (0.3 ml subcutaneously), a glucose solution intravenously, an analgin solution intramuscularly.
Treatment methods in a hospital are different. Their choice depends on the age and condition of the patient.
Often an effective remedy is reduction - an enema with air, barium or saline. In this case, to control the situation, ultrasound, pneumoirrigography or abdominal x-ray are also performed. In some cases, using an enema is permissible up to three times (but no more). According to statistics, in 75% of cases these measures help to avoid surgical intervention. Conservative treatment is more often used for children under one year of age and is usually effective when contacting a doctor early.
But using an enema is not always possible. If inflammation in the abdominal cavity, damage to the abdominal wall, sepsis, or peritonitis is diagnosed, then an enema can even be dangerous. With this option, the doctor decides on surgical intervention.
During the operation, an incision is made on the anterior wall of the peritoneum in the problem area. The sunken area is stretched, returning the intestine to its normal shape. In this case, the damaged areas are removed. During the operation, the appendix is usually removed (even if it is normal and not involved in the pathological process).
In severe cases - when a large area of the rectum is affected, infection or other related problems have arisen - an ileostomy is performed for a certain period. Ileostomy is a connection through the peritoneal wall of the lumen of the small intestine with a colostomy bag.
Next comes the postoperative period. At this time, drug treatment is carried out. Temperature is constantly monitored. If the patient is a small child, it is necessary to monitor his behavior, since he cannot yet say what is bothering him. Here, it is advisable to observe a pediatrician to help the surgeon.
Treatment with folk remedies in case of intussusception is ineffective and unacceptable.
The use of folk remedies can only be used in combination with the main treatment. It is aimed mainly at facilitating bowel function and bowel movements. The most commonly used are herbal decoctions and infusions. For example, flax seed, fennel, St. John's wort, and sandy sap are used. The use of beet infusion is widespread. In any case, such therapy should be agreed with the attending physician.
Establishing a diagnosis
Adults with intussusception should see a gastroenterologist or surgeon. First, the doctor collects complaints and conducts an initial examination. When palpation is carried out, the formation is felt during the period between attacks. The site is located in the right iliac region. For the patient, this process can be unpleasant if the symptoms of intussusception are pronounced.
If the patient was admitted to the hospital one day after the onset of attacks, then palpation of the affected area will be useless. Difficulties occur due to the development of disturbances in intestinal tone. If the affected area is located in the rectum, palpation is performed rectally. Sometimes the low location of the intussusception is accompanied by its prolapse.
To determine the exact location of a section of the intestine, additional diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- Doppler ultrasound examination;
- radiography of the peritoneum;
- CT scan;
- blood and stool tests.
Sometimes additional radiographic examination is performed using a barium enema. This helps to identify an obstruction in the path of the contrast agent. A severe course is determined by signs of intestinal bleeding. To do this, laboratory tests of blood and stool are performed. In case of intussusception, the results indicate the detection of mucus and blood in the patient's stool.
In what cases are additional diagnostics performed?
Additional diagnostics are used when polyps or neoplasms of various etiologies are detected in the intestines. Sometimes x-rays reveal a foreign body in the digestive tract. Otherwise, the patient's intussusception is accompanied by a large amount of parasitic microflora.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing intussusception is not always easy. Of all the symptoms, the most important for diagnosis are the sudden onset of the disease, sudden vomiting, bloody-mucous stools, and mainly palpation of an acutely developed intestinal tumor. It is especially important when the named symptoms are all present at the same time or appear quickly one after the other, since, of course, each of these symptoms by itself or a combination of only a few of them has no evidentiary value. For example, swelling, vomiting and constipation also occur with periappendicitis; on the other hand, tenesmus and mucous-bloody stools also occur with dysentery. The latter are also found with rectal polyps in children.
When one or other of the main symptoms is absent, the diagnosis can be extremely difficult. In this case, it is especially necessary to keep in mind other forms of intestinal obstruction, such as volvulus, internal strangulation, fecal stagnation (coprostasis), blockage of a swallowed foreign body, gallstone, compression of the intestine from the outside and intestinal tumors. It is especially difficult to recognize implantations with a gradual onset or a long time after the onset of the disease, when flatulence interferes with a thorough examination of the abdomen and tumors cannot be palpated through the rectum.
The diagnosis of intussusception is confirmed by ultrasound, radiography and CT.