How to protect your stomach?
Antibiotics are universal means of combating infection and preventing the processes that accompany an infectious disease. But, despite the versatility of such drugs, they require use in combination with other medications, since they have a negative effect on the digestive tract.
The use of antibiotics without auxiliary therapy is fraught with serious disorders of the digestive system. Side effects such as pain in the epigastric region, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and flatulence are noted. To protect against negative effects, a whole range of methods is used: medicinal protection, traditional methods and diet correction.
Effect of antibiotics on the stomach
Antibacterial therapy has a rather complex effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Microflora is constantly present in the intestines and performs a number of functions. It is represented by hundreds of varieties of microbes: bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, saprophytes, facultative and transient bacteria.
Their function is to process unprocessed food particles, produce some amino acids and vitamin compounds, and produce lysozyme. The latter substance prevents the development of pathogenic bacteria in the intestines, therefore infections that penetrate the digestive tract quickly die in a healthy body. Bacteria also take part in the body's immune defense by interacting with the lymphoid cells lining the intestinal mucosa.
Antibiotic therapy, in turn, destroys not only pathogenic microorganisms, but also the body’s own microflora. Thus, the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract lose their natural protection, immunity decreases and dyspepsia develops. In this case, pathogenic bacteria during weakening of the immune system can infect the mucous membranes.
Efficacy of probiotic preparations
Immune protection is 80% dependent on processes in the intestines. If, after taking antibiotics, the natural balance of microflora is disturbed, pathogens multiply intensively. To maintain health, it is necessary to populate the intestines with “good” bacteria as quickly as possible. When deciding which probiotics are best to give to children after taking antibiotics, a number of factors should be taken into account:
- The number of bacteria in the intestines after birth is low, then gradually colonization by lactobacilli occurs.
- Antibiotics destroy part of the healthy intestinal flora and cause significant damage to the child’s body.
- Dysbacteriosis negatively affects the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections and allergens.
- Restoring the intestinal microflora of a child is much more difficult than that of an adult.
Relatively recently, American scientists studied the effect of taking antimicrobial agents on the intestinal flora and the role of probiotics. 3 days after taking antibiotics, the composition of microorganisms in the children’s intestines changed dramatically. Further treatment led to the fact that almost 1/3 of all types of probiotic bacteria completely disappeared, and dysbiosis developed. It's no surprise that experts have recommended taking probiotics to help children and adults avoid the side effects of antibiotics.
"Important! After taking antibiotics, children require probiotic preparations. They reduce the time it takes to restore the intestinal microflora from 6 months to 4-6 weeks.”
The diversity of intestinal bacterial strains depends on many factors. The microflora is poorer in children born by cesarean section who do not receive breast milk. Intestinal bacteria are “inherited,” so a child will have intestinal problems if the parents have dysbiosis. Poor nutrition, excess of sweets, flour, refined fats, deficiency of vitamins and fiber negatively affect the microflora.
Protection algorithm
To protect the stomach from antibiotics and extract only beneficial qualities from this therapy, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- take in parallel means that protect the natural microflora;
- strictly follow the instructions for using antibiotics;
- maintain a proper diet;
- do not take medications on an empty stomach;
- do not take the tablets with anything other than clean, non-carbonated water;
- combine treatment with any medications with vitamins and minerals.
Whenever possible, it is recommended to use an injectable form of antibiotics to minimize damage to the digestive tract. Additionally, herbal teas, pharmaceutical yoghurts and other products are prescribed to help the natural microflora multiply and colonize the intestines.
Rules for taking medications
Antibiotics should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. It happens that patients take antibiotics on an outpatient basis without prior consultation, since a certain drug has already helped them cope with the disease. But even an experienced doctor without laboratory diagnostics will not be able to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. In addition, with a weakened immune system, one infection can displace another, and taking antibiotics that helped before will not be advisable.
If you choose the tablet form, you must take the medications strictly according to the regimen prescribed by your doctor. Drink only water. If antibiotics are prescribed in injection form, a medical professional must administer the injections, observing aseptic conditions.
Probiotics
For the stomach, it is recommended to take probiotics along with antibiotics. These are bacteria beneficial to the body, producing lactic acids, suppressing the growth of fungi and pathogenic bacteria, synthesizing antibodies to some viruses and performing the same role as beneficial intestinal microflora.
List of popular probiotics:
- Acylact;
- Lactobacterin;
- Linex;
- Hilak;
- Bifiform;
- Acipol;
- Enterol;
- Bifidumbacterin.
Modern probiotics combine up to four strains of beneficial bacteria. Medicines containing only one strain are represented by dietary supplements: Colibacterin, Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin. Often, multicomponent preparations combine strains of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and enterococcus faecium.
The second generation of probiotics contains not only strains, but also the simplest types of fungi. They are not contained in normal microflora, but have an inhibitory effect on existing pathogenic microorganisms:
- Enterol;
- Sporobacterin;
- Bactisuptil.
The third generation of these drugs are combination products containing an increased number of individual cultures:
- Acylact;
- Linex Forte;
- Linex Immuno.
The fourth generation of drugs contains activated carbon or silicon dioxide as a sorbent:
- Florin;
- Probiform;
- Probilak.
Which of the stomach tablets when taking antibiotics will be required in an individual case must be decided by the doctor prescribing the therapy. Probiotics are prescribed two to three doses per day, half an hour before meals. The duration of treatment is up to 4 weeks. Children under 12 years of age are prescribed reduced dosages.
Contraindications
There is a very short list of situations where taking probiotics is prohibited or undesirable. First of all, this is individual intolerance to the components of the drug. For some probiotics, contraindications include lactose intolerance.
Probiotic preparations contribute to the formation and development of healthy intestinal flora in children from birth. Therefore, the use of probiotics for children when taking antibiotics is mandatory. These two groups of drugs have opposite effects. It should be remembered that probiotics should be taken from the first days of antibiotic therapy and at least two weeks after completion of treatment.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are nutrients fermented by lactobacteria and bifidobacteria. They ensure the vital activity of these bacilli and stimulate their reproduction. Prebiotics include:
- Duphalac;
- Ambien;
- Pamba;
- Hilak-Forte.
If the drug is used incorrectly, they can cause a number of adverse reactions, stomach upset and electrolyte imbalance. The choice of prebiotic should also be made only by a doctor. The drug should be taken in the concentrations specified by the doctor three to four times a day.
Types of drugs for intestinal microflora
What should I take along with antibiotics to protect myself from their negative effects on the intestinal microflora? Doctors prescribe probiotics and prebiotics for this purpose.
Probiotics are medications containing strains of live bacteria. Once inside the intestines, beneficial microorganisms populate the mucous membranes and, under favorable conditions, begin to actively multiply. And other drugs help them with this - prebiotics. Prebiotic supplements contain components that create a breeding ground for beneficial bacteria and accelerate colony growth.
Currently, probiotics containing various strains of bacteria are produced. These can be either single-component preparations, in which only one specific type of microorganism is present, or multicomponent preparations, containing simultaneously two or more strains of bacteria.
Most common gut probiotics include:
- aerococci;
- bifidobacteria;
- yeast-like fungi;
- lacto- and colibacteria;
- enterococci.
In addition, the tablet or capsule may also contain prebiotic additives that help beneficial bacteria “take root” in a new place.
Important! Combined probiotic agents are preferable for restoring intestinal microflora after antibiotics. However, only a doctor can accurately determine which specific probiotic to prescribe in each specific case.
Recovery after antibiotics
If antibiotics have already led to the development of dysbiosis and weakened immunity, the use of the following methods and drugs is recommended:
- Creon , Mezim - enzymes to improve digestion;
- Essentiale , Karsil - to improve absorption function;
- Loperamide , Trimebutin - to restore microflora;
- Smecta , Enterosgel - for removing toxins and pathogenic microflora from the body;
- Vitamin complexes for general strengthening of the body.
In case of severe diarrhea and exhaustion, you should urgently seek help from a gastroenterologist to prevent the development of severe gastrointestinal diseases.
The effect of antibiotics on the human body
First, it’s worth finding out why treating a person with antibiotics can lead to intestinal dysfunction. According to experts, the adult body contains about 2-2.5 kg of beneficial microorganisms, which amounts to hundreds of trillions of bacteria. They are our constant companions, help digest food, create a favorable acid-base environment, improve the absorption of vitamins and nutrients, protect against harmful microbes and infectious diseases.
When taking antibiotics, the bacteria necessary for the normal functioning of the body suffer no less than those that harm human health. Powerful antibacterial drugs have a detrimental effect on both “bad” and “good” microorganisms. As a result, the intestinal microflora suffers (microbiocenosis) and antibiotic-associated diarrhea develops.
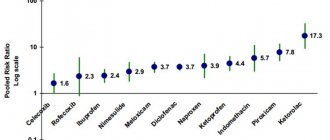
The adverse effects of antibiotics on the intestines do not affect everyone. This depends on what antibiotics the doctor prescribed, as well as on the patient’s health status, his immunity and the duration of antibiotic therapy. According to doctors, at least a third of people taking quinolones, macrolides, cephalosporins, lincomycins and aminopenicillins experience problems with the gastrointestinal tract. And this happens regardless of whether the patient has a sore throat, pneumonia or inflammation of the intestines - antibiotics harm beneficial microflora and provoke the appearance of dysbiosis.
How to protect the digestive organs from the harmful effects of antimicrobial drugs? Intestinal upset, which is always accompanied by abdominal pain and diarrhea, can be prevented if, while taking antibiotics, you take a medicine that supports the intestinal microflora.
Diet correction
To restore the gastrointestinal tract, not only tablets are recommended when taking antibiotics, but also correction of your own diet. Pathogenic microflora often feed on carbohydrate foods, so bread, pasta, sweets, confectionery, bananas and other carbohydrate foods should be excluded from the diet.
To maintain microflora, it is recommended to consume yogurt, kefir, fermented baked milk and other fermented milk products. Ideally, it should be prepared at home - you can buy starter cultures in pharmacies. If this is not possible, you should choose the product that has the shortest shelf life when unopened. Natural yogurt cannot stay fresh for a month.
Lifestyle after treatment
Parents should understand that during an illness, the limited resources of the child’s body are spent at triple speed, and antibiotics only aggravate this process, so after recovery the child needs time to get stronger. A number of important rules will help restore the crumbling health of the baby and strengthen its immunity:
- You should not send your child to school or kindergarten immediately after recovery. If conditions allow, it is better to keep the child for several days, or even weeks, at home, paying special attention to post-infectious rehabilitation. Otherwise, there is a high probability that the weakened body will react to the first infection, and the disease will recur, only in a more severe form.
- Take walks in the fresh air more often, while trying not to overheat or overcool your child. The desire to protect him from all existing viruses and bacteria with several layers of unseasonably warm clothing can lead to the opposite effect - a sweaty baby will simply be blown away. But clothing that is too light is also not suitable - hypothermia can be dangerous for a weakened body. Therefore, when choosing a wardrobe for a walk, it is better to be guided by weather conditions and common sense.
- Reconsider the decor in the children's room. After antibiotic therapy, the child needs the most healthy living environment possible, so it is better to get rid of all “dust collectors” in the nursery. Minimize the number of soft toys, and wash those that remain thoroughly using baby powder. Vacuum the room daily, wipe the dust, do wet cleaning and ventilate. It is also advisable to install a humidifier in the nursery during the heating season.
- Don't rush back to hardening. Of course, regular restorative procedures are extremely beneficial for the child’s health, but this does not mean that you should get too carried away with them immediately after recovery. Even if before illness the child easily tolerated a contrast or cool shower, you should not immediately return to the original temperatures - it is better to wait until the body has fully recovered, and then start hardening from the very beginning, gradually lowering the water temperature by 1-2 degrees.
Don’t be too afraid of the need to take antibiotics - no doctor will prescribe them without a reason. In addition, the correct approach to treatment will allow the child’s body to quickly recover after serious therapy, strengthen the child’s immunity and prevent possible negative consequences of dysbiosis.
I like 1
Antibiotics Antibiotics for a child Treatment for a child Recovery after antibiotics Treatment Health Child health Dysbacteriosis
Related Posts
leave a comment
Only 4 comments.
Sakura
with us 5 months, 27 days
2020-09-07 16:46:00We drank Active Flora Baby 1 drop per day for a month before meals to restore microflora after antibiotics. Excellent drops based on olive oil. The child's intestinal microflora has normalized.
Marina
with us 1 year, 4 months, 10 days
2020-04-16 09:58:02Multiflora Evalarova is suitable for us) helps restore the intestinal microflora and can be used for children from 3 years old) There is a feeling of lightness and results) digestion is restored)
Daryvan
with us 10 months, 28 days
2020-04-02 15:31:08Good afternoon, while taking an antibiotic, my family tried many probiotics, but the effect was not particularly noticeable. The doctor advised me to try the drug Bifiten. It really helped. I advise everyone to remember that Bifiten is effective during and after antibiotic therapy to restore intestinal microflora and immunity. It can also be used by children over 3 years old, 1 capsule once a day.
Prevention and useful tips
Intestinal microflora is an important part of the body's entire immune system. To maintain it, you should maintain a balance in your diet - do not overindulge in fatty, spicy, or too hot foods. The use of natural fermented milk products will stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Additionally, vitamin complexes can be prescribed to prevent dysbiosis, improving the body's immune response. Liquid food should be present in the diet every day; food rich in fiber will be beneficial for intestinal function.