Total information
The essence of duodenostasis is a failure in the passage of chyme (a portion of food, partly already processed) through the duodenum . It occurs due to the fact that intestinal peristalsis (wave-like movements of the walls that push the food bolus in the direction from the stomach to the jejunum) is discoordinated.
This pathology is mainly observed at a young age - on average from 20 to 40 years. Women are most often affected.
When diagnosing this condition, mistakes are often made ( it is possible that the frequent absence of organic damage plays a role), because of this, the wrong tactics of surgical treatment are chosen.
Pathogenesis of the disease
Experts consider the development of secondary duodenitis depending on the etiological factor that provoked it. Thus, when infected with Helicobacter pylori infection, the disease not only develops, but also becomes chronic due to the fact that the bacteria produce a large amount of toxins as a result of their vital activity. In the case when the cause of duodenitis is diseases of the internal organs, the pathogenesis is as follows:
- the ulcerative process has a damaging effect on the duodenum and provokes the occurrence of secondary duodenitis due to the aggressive effect of the acid-peptic factor on the duodenal mucosa;
- in chronic pancreatitis and hepatitis, the development of the disease is due to a decrease in the secretion of bicarbonates and increased absorption of pancreatic enzymes;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system and lungs contribute to the development of secondary pathology by causing hypoxia of the duodenal mucosa;
- in case of renal failure, a large amount of nitrogen metabolism products, which are very toxic, are released through the mucous membrane of the duodenum.
Chronic diseases of the liver and pancreas also lead to secondary duodenitis. The cause of the disease is that in these diseases a change in the enzyme balance occurs, which provokes a change in the internal environment of homeostasis.
Causes of duodenostasis
Duodenostasis occurs:
- primary - if no pathology is detected in other organs, which can lead to stagnation in the duodenum;
- secondary – provoked by other diseases and pathological conditions.
In the vast majority, duodenostasis develops due to such types of damage to the gastrointestinal tract as:
- chronic diseases (mainly inflammatory in nature);
- tumors.
The most common diseases that lead to duodenostasis are:
- stomach;
- duodenum;
- hepatobiliary system (liver and biliary tract);
- pancreas.
Basically, duodenostasis develops due to:
gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa);- duodenitis (inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane of the duodenum;
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder wall) - with or without the presence of concretions (stones) in its lumen;
- pancreatitis (inflammation of pancreatic tissue).
A separate group of causes of duodenostasis are those that create mechanical obstacles to the passage of chyme through the duodenum. Such a mechanical obstacle can be:
- internal (blockage of the duodenum);
- external (its compression from the outside by various structures of the abdominal cavity).
The following can block the lumen of the duodenum:
- stones that enter the intestinal bulb (its initial section) from the gallbladder and bile ducts;
- balls of parasites.
Most often the duodenum is compressed from the outside:
vessels of the mesentery (a thin connective tissue film that attaches the abdominal organs to the inner surface of the abdominal wall). Such compression can be observed when these vessels are located in an atypical location;- tumors of the abdominal organs (most often – neoplasms of the biliary tract, liver, pancreas and large intestine);
- connective tissue cords formed during adhesive disease.
Other causes of duodenostasis include:
- improper formation of the duodenum during intrauterine development, which causes its lumen to narrow;
- kinks of the duodenum.
Often, duodenostasis occurs after surgery on the stomach, duodenum itself, and bile ducts. In this case, the scenario of violations may be different - due to the release of stones into the intestinal lumen, compression by adhesions, and so on.
It happens that duodenstasis causes physical inconvenience to the patient, but only at the moment of stagnation - outside of it, no disturbances are found on the part of either the duodenum or neighboring organs. In this case, a purely functional failure is stated, the cause of which is considered to be:
- autonomic disorders (failure of the autonomic nervous system, which ensures the functioning of internal organs);
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- pathology of the endocrine system (in particular, those organs that produce hormones necessary for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract).
Duodenostasis of the duodenum: symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment
Sometimes a disturbance in the digestive process can be a manifestation of a disease that is not so easy to identify, for example, duodenostasis. But the problem needs to be treated as early as possible. Therefore, you should be attentive to your health and undergo examinations on time.
Concept of illness
If the duodenum has a reduced rate of passage of food coma, then this disorder is called duodenostasis. This phenomenon can be initiated by various factors.
The pathology is classified as a polyetiological disease. In addition to disruption of the movement of chyme through the initial section of the intestine, disharmony in the coordination of the work of its individual parts is also possible.
Factors that cause duodenostasis are divided according to the nature of their origin into three groups:
- due to functional disorders, this may be a consequence of: diseases of the nervous system,
- disruption of the endocrine organs,
- autonomic disorders due to diseases of the digestive tract;
- tumors in the small intestine or nearby organs,
Symptoms of duodenostasis
Manifestations of disorders are similar to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and are not clear signs of duodenostasis. But with careful observation of the patient, signals indicating problems in the functioning of the duodenum still become noticeable.
The first group of symptoms is caused by disorders of the digestive function:
- rumbling in the intestinal area,
- pain in the abdomen (in the right hypochondrium and in the epigastric region),
- noticeable intestinal flatulence,
- belching,
- nausea and possibly vomiting,
- bloating.
Symptoms that indicate that the body is being poisoned by toxins:
- a person loses weight
- poor health, lack of strength;
- irritability,
- loss of appetite,
- apathy,
- in severe cases, damage to the heart and kidneys occurs.
Complications
The disease is fraught with the following consequences:
- Weak intestinal motility, through negative processes, leads to thinning of the walls of the duodenum, the passage of irreversible phenomena in them and, ultimately, the creation of a situation where the organ becomes impassable.
- Intoxication of the body largely affects the kidneys and heart and can be fatal.
Development of the condition
During this pathology there are three stages:
- compensation - despite periodic stagnation, the duodenum copes with its functional responsibilities;
- subcompensation (incomplete compensation) – the duodenum copes with its responsibilities partially;
- decompensation - the 12-ring intestine is completely “turned off” from the digestive process.
At the stage of compensation, disturbances in motility (motor activity) of the duodenum occur from time to time, they are inconsistent and inexpressive. Individual fragments of the intestine may be affected: some parts of the intestinal wall are spasmed, others are relaxed. Because of this, the peristaltic movements of the duodenum are chaotic, and the contents can backflow into the initial segment of the intestine - its bulb.
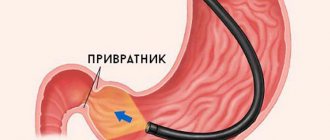
At the stage of subcompensation, peristalsis disturbances become more frequent, and there is a tendency towards a constant nature of chaotic peristaltic movements. The process involves the pylorus (the final fragment of the stomach that passes into the duodenal bulb) and the antrum of the stomach (the part that is adjacent to the pylorus). The pylorus may gape (that is, remain constantly half-open or open, which should not normally be observed).
note
If stagnation in the duodenum worsens, reflux of its contents into the stomach is observed (so-called duodenogastric reflux).
At the stage of decompensation, peristalsis of the duodenum is constantly impaired. The lower parts of the intestine are dilated. Due to the constant throwing of chyme into the stomach, its mucous membrane becomes inflamed (reflux gastritis occurs), and the stomach itself stretches.
If duodenostasis progresses further, the inflammatory process due to stagnation in the duodenum can spread to the biliary tract, gallbladder and pancreas. A vicious circle is formed: pathologies of the digestive tract provoke duodenostasis, which only worsens the course of these diseases.
Classification
Duodenostasis is divided into 2 forms:
- Primary – during diagnosis, no other diseases were found that could be the cause of development.
- Secondary – problems have been identified in the body that have led to pathology. For example, chronic disorders of the digestive tract, pancreas, liver, diseases of the duodenum.
There are 3 stages of development of duodenostasis:
- Compensation – contractile functions of the intestine are constantly changing. There is uncoordinated spasm and relaxation of some areas, as a result of which peristalsis is disrupted, and the contents return into the duodenal bulb.
- Subcompensation - changes in the movement of the food bolus through the small intestine become permanent. The lower region of the stomach and the valve system are involved in the pathological process. The pylorus is not able to protect the stomach from duodenogastric reflux, which adversely affects the organ.
- Decompensation is a permanent disorder, and the negative impact on nearby organs leads to a chronic disorder of their functions. A cycle of disorders has occurred: a disorder of the duodenum picks up the improper functioning of neighboring organs, and vice versa.
Therefore, it is important to notice pathology at the initial stage of development.
Symptoms of duodenostasis
Manifestations of duodenostasis are divided into two groups:
- dyspeptic (disorders from the digestive tract);
- intoxicating.
Dyspeptic signs are:
stomach ache;- belching;
- nausea;
- regurgitation;
- vomit;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- bloating in the upper abdomen (flatulence);
- a feeling of incomprehensible discomfort in the upper abdomen, which the patient cannot clearly characterize.
Characteristics of pain during duodenostasis:
- pain occurs a short time after eating (from half an hour to 40 minutes);
- localized in the epigastric region (under the sternum), may also disturb under the costal arch on the right;
- paroxysmal, in the form of spasms, which stop for a certain time, and then the patient feels better;
- in the early stages of the disease they may subside after vomiting (patients often induce vomiting themselves in order to alleviate the condition), but not at the stage of decompensation.
Characteristics of nausea:
- constant, with progression debilitates patients;
- at the initial stages of the disease it may weaken after vomiting, but as it progresses - not;
- accompanied by a feeling of aversion to food.
note
Regurgitation is a lighter version of vomiting, in which the contents of the stomach and duodenum are expelled through the mouth in small portions, without convulsive contraction of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
With duodenostasis, regurgitation may gradually give way to vomiting.
Characteristics of vomiting:
- most often occurs a short time after eating;
- traces of bile are observed in the vomit;
- at the initial stages of pathology it brings relief, at the stage of decompensation it does not.
Intoxication is caused by the fact that, stagnating in the duodenum, partially processed food begins to ferment, and fermentation products are absorbed into the blood. The following signs of intoxication occur:
increased fatigue, disproportionate to the work performed;- altered reaction to events around – in some patients it is apathy, in others it is increased irritability;
- deterioration of appetite, and in the stage of decompensation – its complete absence;
- with the progression of duodenostasis - exhaustion and progressive loss of body weight.
note
If treatment is not started, then very severe intoxication develops, due to which, first of all, the kidneys and heart suffer, and then multiple organ failure develops (the inability of all organs to perform their functions), which can result in the death of the patient.
Duodenostasis
Duodenostasis
is a violation of the patency of the duodenum of a mechanical or functional nature.
Manifested by symptoms of dyspepsia (belching, nausea, vomiting of bile, spastic abdominal pain), symptoms of intoxication (fatigue, irritability or apathy, significant weight loss).
Endoscopy, X-ray examination of the duodenum with contrast, duodenal intubation, mesenteric angiography, etc. are indicated. Treatment in the initial stages is conservative (prokinetics, antispasmodics, duodenal lavage, vitamins), if it is ineffective - surgical.
Duodenostasis is a polyetiological disease characterized by impaired passage of food chyme through the initial parts of the small intestine with discoordination of duodenal peristalsis, its gradual expansion, and involvement of nearby organs in the pathological process. Most often, it first appears at a young age (20-40 years), predominantly affecting women.
In most cases, the cause of the development of duodenostasis is chronic diseases of the stomach and duodenum, hepatobiliary system, pancreas, and tumors of the digestive tract.
But in some cases, the organic cause of the pathology cannot be identified, which indicates its functional basis.
This disease is characterized by frequent diagnostic errors followed by the adoption of incorrect surgical tactics, therefore, sufficient attention should be paid to the examination of patients with suspected duodenostasis.
Duodenostasis
The pathology can be caused by various diseases of the digestive tract: gastritis, gastric ulcer and peptic ulcer 12p. intestines, duodenitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis and others.
In addition, the disease can develop against the background of a mechanical obstruction to the passage of food: when the duodenum is compressed by mesenteric vessels (due to their abnormal location), or by abdominal tumors; when stones from the gallbladder or parasites enter the duodenal bulb; with abnormalities in the development of the duodenum, its kinks, adhesions.
A fairly common cause of the disease is surgery on the stomach, duodenum, and bile ducts. When duodenostasis is suspected, it is not always possible to identify its organic cause. In this case, they talk about the functional nature of the pathology due to autonomic disorders, against the background of diseases of the nervous system, digestive tract, and endocrine organs.
In the classification, modern gastroenterologists distinguish between the primary form (if no other diseases are identified that could lead to pathology) and secondary; duodenostasis of a functional nature (against the background of a disorder of autonomic innervation) and mechanical (in the presence of an obstacle to the movement of the food bolus). In addition, the following stages are distinguished during the course of the disease:
- Compensation
. Changes in duodenal motility are not permanent and are temporary. There may be a spasm of some parts of the duodenum with simultaneous relaxation of others, which disrupts normal intestinal motility, and the contents can backflow into the duodenal bulb. - Subcompensation
. The changes become permanent, the pylorus and the antrum of the stomach are involved in the process, due to stagnation in the duodenum, duodenogastric reflux is formed, the pylorus gapes. - Decompensation
. A persistent dilatation of the lower parts of the duodenum, reflux gastritis, followed by distension of the stomach cavity is formed. In the future, these changes can lead to the development of an inflammatory process in the biliary tract and pancreas.
Thus, a vicious circle is formed - diseases of the digestive system lead to the development of duodenostasis, and its progression leads to a worsening of these diseases and the emergence of other concomitant pathologies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z3Tne5y7N3c
From the onset of pathology to the development of the stage of decompensation, it can take from several weeks to several years.
There is a known case where the patient’s symptoms persisted for 35 years, only after which complete small intestinal obstruction occurred and surgical treatment was performed.
However, it should be remembered that the longer the symptoms of the disease persist without proper treatment, the higher the likelihood of irreversible changes in the intestines and an unfavorable outcome for the patient.
All symptoms of duodenostasis are divided into two groups: dyspeptic and intoxicating. Dyspeptic symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, belching and regurgitation, rumbling and increased intestinal flatulence.
Abdominal pain is paroxysmal, spastic in nature. Most often, pain occurs some time after eating, its intensity may decrease after vomiting.
Localization of pain is in the epigastric region and right hypochondrium.
Nausea can be debilitating and cause the patient to have an aversion to food. Vomiting often occurs after eating; the vomit contains varying amounts of bile.
In the initial stages of the disease, relief comes after vomiting; in the decompensation stage, pain and nausea persist even after vomiting.
Patients complain of bloating in the epigastrium, rumbling intestines, and vague discomfort in the upper abdominal cavity.
Symptoms of intoxication are associated with stagnation of contents in the duodenum, fermentation of the food bolus, and absorption of toxic products into the bloodstream.
Patients complain of increased fatigue, apathy or irritability, lack of appetite, exhaustion and weight loss.
If treatment for duodenostasis is not started on time, severe intoxication can lead to damage to the kidneys and heart, the development of multiple organ failure and death.
If this pathology is suspected, consultation not only with a gastroenterologist, but also with a surgeon is necessary. Duodenostasis can be quite difficult to distinguish from other gastrointestinal pathologies; consultation with an endoscopist will help in differential diagnosis.
When performing esophagogastroduodenoscopy, gaping of the pylorus, reflux of duodenal contents and bile into the stomach cavity, expansion and relaxation of the duodenum are noted. With a long course, dystrophic changes are formed in the intestinal wall, which leads to aggravation of symptoms.
An endoscopic biopsy is performed to identify these changes.
Radiography of the passage of barium through the small intestine is of great importance in making a diagnosis.
Normally, when examining the duodenum, there may be a slowdown in the movement of contents in places of natural bends of the intestine, areas of antiperistalsis with a slight retrograde reflux of food masses and duodenal juices.
With duodenostasis, antiperistalsis will be pronounced, and the movement of masses through the intestines will be difficult. The main criterion for duodenostasis is a delay in the advancement of contrast from the duodenum by more than 40 seconds.
Relaxation duodenography (in conditions of hypotension), antroduodenal manometry will also confirm a decrease in the tone of the intestinal wall, expansion of the duodenal cavity, and the absence of passage of contents into the small intestine. Duodenal intubation with examination of the contents of the duodenum will help determine the degree of stagnation in the intestines and assess the possibility of developing intoxication syndrome.
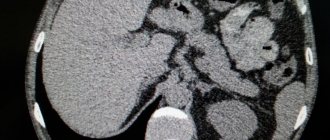
Studies such as ultrasound of the abdominal organs and angiography of mesenteric vessels (mesentericography) will allow us to determine the mechanical cause of duodenostasis. These techniques help to detect tumors, abnormal vessels, stones and adhesions, and also provide significant assistance in further planning of the treatment process and deciding on surgical treatment.
If a significant obstruction of the duodenal patency is detected, the patient must be hospitalized in the gastroenterology department for a more thorough examination and conservative treatment.
It is recommended to start with non-surgical methods of therapy at any stage (including decompensation) - even if they are not radical enough, the condition of the intestines will improve, intoxication phenomena will be stopped, thanks to which the operation will be tolerated by the patient much easier, and its results will be better.
Conservative therapy includes following a diet, prescribing vitamins and antispasmodics. The diet consists of small frequent meals, rich in nutrients and vitamins, but poor in fiber. Self-massage of the abdomen and physical therapy exercises significantly ease the patient's condition.
Moderate physical activity will strengthen the muscular corset of the torso and normalize intestinal activity.
Researchers have noted that weight normalization has a fairly beneficial effect on the patient’s condition - restoration of the fat layer around the internal organs will allow the intestines to return to their normal position, prevent it from being kinked, or being squeezed by abnormal vessels.
An important element in the treatment of duodenostasis is intestinal lavage. To do this, a special probe is inserted into the duodenum and 300-350 ml of mineral water is poured through it several times a day.
The improved technique allows you to insert a double-lumen probe, through one of the channels of which liquid enters the intestine, and through the other, it is removed.
This procedure allows you to normalize the evacuation of contents from the duodenum, improve its peristalsis, and prevent intoxication of the body by fermentation products in the intestines.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgery is indicated, most often duodenectomy with duodenojejunostomy.
It is also possible to carry out various operations to exclude the duodenum from the process of moving the food bolus (in particular, gastric resection according to Billroth II).
Before deciding on surgical treatment, all possibilities of conservative therapy should be tried, since surgery in a third of cases does not bring the desired effect.
The prognosis is more favorable with timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment for the pathology, but it largely depends on the cause that caused it.
With prolonged absence of treatment, the prognosis worsens significantly; severe intoxication can lead to death.
Prevention consists of following a regimen of physical activity and nutrition, and timely treatment of diseases that can lead to duodenostasis.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/duodenostasis
Diagnostics
The patient’s complaints due to developing duodenostasis are not specific - it is quite difficult to make a diagnosis based on them.
The data from a physical examination (examination, palpation, tapping and listening to the abdomen with a phonendoscope) are also not highly informative, since both individually and collectively can be characteristic of many diseases and conditions of the gastrointestinal tract. Upon examination, it is possible to ascertain the patient’s weight loss, but only in the late stages of duodenostasis. When palpating the upper abdomen, pain is revealed, which may be characteristic of many lesions of the digestive tract in this location. When listening to the abdomen in the late stages of duodenostasis, a weakening of bowel sounds is noted.
Important
A patient with suspected duodenostasis should be examined jointly by a gastroenterologist and a surgeon.
To clarify the picture, additional examination methods are used.
The results of such instrumental examination methods as:
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EFGDS) – study of the stomach and duodenum using a probe with built-in optics;
- passage of barium to the small intestine - the patient is given a barium suspension to drink, after which its passage through the duodenum is studied;
duodenal intubation - insertion into the duodenum of a probe with a metal olive at the end, through which the contents of the duodenum are taken;- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- relaxation duodenography - the patient is administered anticholinergics, which lead to a decrease in the tone of the duodenum, after which the patient is given a barium suspension to drink and X-rays are performed;
- antroduodenal manometry - simultaneous measurement of pressure in the stomach, duodenum and jejunum. The study is carried out using special catheters and sensors;
- angiography of mesenteric vessels - injection of a contrast agent into the bloodstream and then x-ray examination of the mesenteric vessels, changes in which can also play a role in the occurrence of duodenostasis.
note
With EGD, duodenostasis is indicated by endoscopic signs such as gaping (constant opening) of the pylorus of the stomach, throwing of chyme and bile into the stomach cavity, relaxation of the duodenum.
If the disease is characterized by a long course, then dystrophic changes can be seen in the mucous membrane of the duodenum (thinning due to impaired tissue nutrition). To confirm degenerative changes in the mucosa, during EGD a biopsy is performed - pinching off a small piece of tissue in different places for the purpose of their subsequent examination under a microscope.
Important
The high performance of radiography with barium is explained by the fact that it is a contrast agent - in X-ray images it differs from body tissues. Therefore, using a contrast image, you can clearly assess how the duodenum is emptied from barium. In the normal state, emptying occurs with a certain slowdown, since barium is retained in the folds and bends of the duodenum - however, it moves towards the jejunum.
With duodenostasis, there is not only a slowdown in the movement of barium, but also its throwing back into the stomach, which occurs due to antiperistalsis (movements of the wall of the duodenum in the direction of the stomach). The most important sign in a barium x-ray is a delay in its progress of more than 40 seconds.
In case of duodenostasis, during duodenal intubation, the stagnant contents of the duodenum with an admixture of bile are removed. Using this method, it is also possible to assess the prospects for the development of intoxication with fermentation products in the duodenum.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs allows us to determine their pathology, which could provoke duodenostasis - for example, compression of the duodenum by a tumor of the liver or pancreas, adhesions or abnormal vessels.
In conditions of duodenostasis, relaxation duodenography and antroduodenal manometry state:
- decreased tone of the duodenal wall;
- expansion of its cavity;
- stagnation of chyme and lack of its movement into the jejunum.
Thanks to angiography of the mesenteric vessels, it is possible to determine their atypical location, which is why they are able to put pressure on the duodenum, thereby causing duodenostasis.
Laboratory research methods are not informative enough. They are used to obtain a holistic diagnostic picture for suspected duodenostasis: .
general blood test - with the development of an inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa due to the fact that the contents of the duodenum are thrown into it (reflux gastritis), as well as with intoxication damage to the body, an increase in the number of blood leukocytes and ESR is possible;- microscopic examination of the contents of the duodenum obtained by probing it - the products of chyme fermentation are determined in it;
- study of duodenal biopsy;
- general urine analysis - in case of serious intoxication at the stage of decompensation, signs of kidney damage are noted, such as the presence of casts (casts of different cells) and red blood cells, changes in the specific gravity of urine.
Diagnostic methods used
Specific patient complaints indicating symptoms do not allow a quick and accurate diagnosis. Most gastrointestinal diseases have similar symptoms. When determining the disease, consultations with a gastroenterologist, surgeon, and endoscopist are required.
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy can reveal a gaping valve device, the return of duodenal contents to the stomach, dilatation of the intestine and its inability to contractile function.
- Endoscopic biopsy reveals dystrophic changes in the intestine, leading to aggravation of the situation.
- Barium passage X-ray identifies the area of the intestine through which the movement of contents is difficult. A delay of more than 40 seconds is considered a deviation from the norm.
- Relaxation duodenography: with the help of anticholinergics, the duodenum is brought into a hypotonic state and its capabilities are checked using drunk barium.
- Antroduodenal manometry confirms decreased activity and expansion of the duodenum.
- Duodenal intubation ascertains the degree of congestion in the intestine.
- The study of the contents of the duodenum determines the degree of intoxication of the body.
- Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of mechanical causes of pathology.
- Mesentericography allows you to detect tumors, vascular abnormalities, adhesions, and stones. This is necessary to determine treatment tactics.
To compile a general picture of the disease, laboratory methods are used:
- According to a blood test, the pathology is confirmed by an increase in ESR and leukocytosis;
- A urine test reveals the level of poisoning in the body and kidney damage by changes in red blood cell counts and the specific gravity of urine.
Differential diagnosis allows you to separate the following diseases from duodenostasis:
- gastritis in acute form and acute chronic stage;
- acute and aggravated chronic duodenitis;
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
Differential diagnosis
Due to the typical symptoms, differential diagnosis of duodenostasis is carried out with many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which are characterized by abdominal pain, belching, nausea, vomiting . Most often, confusion arises with diseases such as:
- acute and exacerbation of chronic gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa);
- acute and exacerbation of chronic duodenitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum);
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity.
Prevention and prognosis for duodenitis
With timely consultation with a doctor and treatment aimed at preventing atrophy, the prognosis is favorable, the disease is not life-threatening.
Primary prevention of duodenitis has not been developed. To prevent exacerbations, a healthy lifestyle, regular nutrition, adequate sleep and moderate physical activity are recommended.
[1] D.I. Trukhan, L.V. Tarasova. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment of chronic duodenitis. Experimental and clinical gastroenterology. 2012.
[2] ibid.
Treatment of duodenostasis
If there are signs characteristic of duodenostasis, it is recommended to hospitalize the patient in the gastroenterology department. Pathology is treated using the following methods:
- conservative;
- operational.
Even if conservative therapy does not give the expected result, you still need to start with it - it will help prepare the patient for surgery.
Conservative methods of treating duodenostasis are:
- the patient's diet;
- physiotherapy;
- abdominal massage;
- lavage (washing) of the intestines;
- drug therapy, which consists of the use of prokinetics (drugs that improve intestinal motility), antispasmodics and vitamins.
The basic requirements for diet for duodenostasis are as follows:
- frequent split meals;
- small portions of food;
- food should be rich in nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) and vitamins, but limited in fiber.
The effect of weight normalization is being studied - if a fat layer is formed around the internal organs, which helps ensure that the intestines are in a normal position. Result:
- normalization of intestinal function;
- prevention of kinks;
- prevention of pressure from improperly located vessels (a kind of shock absorption is maintained).
Therapeutic exercise helps strengthen the muscular corset of the torso - if it is weakened, this negatively affects the tone of the intestines.
note
Abdominal massage helps improve blood circulation in the intestines, and therefore improves its function. The patient can be taught self-massage techniques.
The benefit of lavage is to improve the peristalsis of the duodenum, which means normalizing the evacuation (movement) of chyme from the duodenum. Thanks to this, the part of digestion for which the duodenum is responsible is improved, and poisoning of the body by fermentation products is also prevented.
By improving gastrointestinal motility, prokinetics promote the movement of chyme through the duodenum and prevent the development of stagnation in it , which means the formation of fermentation products and intoxication by them.
Antispasmodics are indicated for attacks of pain due to chaotic contraction of the muscle fibers of the duodenum.
Vitamins normalize biochemical processes in the wall of the duodenum, thereby improving its functioning.
Important
If conservative therapy is ineffective (most often this is observed at the stage of decompensation and often at the stage of subcompensation), then surgical correction of duodenostasis is necessary.
Most often, a duodenectomy is performed (excision of the compromised duodenum), in which the end of the stomach is sutured to the end of the jejunum following the duodenum. But before performing excision of the duodenum, doctors use all options for conservative treatment, remembering that duodenectomy in 30% of cases does not give the expected result.
Treatment
Regardless of the stage of development of the disease, conservative methods of therapy are used. Complex treatment of duodenostasis is carried out with mandatory adherence to diet and medication. During the stage of decompensation, surgical intervention will be required to help improve the condition of the intestines and eliminate substances that lead to intoxication.
Drug treatment
In gastroenterology, the following drugs are used for duodenostasis:
- Antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Drotaverine) - to relieve pain in chronic obstruction.
- Prokinetics (Domidon, Itomed) - intended for intestinal motility.
- Ranitidine, Maalox - help reduce acidity and the release of hydrochloric acid.
- Vitamins.
For any diseases of the abdominal cavity, treatment of duodenostasis with medication should be carried out as prescribed by a specialist, since incorrect actions can lead to negative consequences.
Physiotherapy
At the initial 2 stages of the disease, physiotherapeutic measures are carried out:
- Therapeutic gymnastics - exercises help strengthen muscles and have a beneficial effect on the condition of the intestines.
- Washing – eliminates intoxication of the body, normalizes contractile function. Using a probe, 300-500 ml of mineral water is poured into the duodenum, then removed.
- Self-massage of the abdomen - increases the contraction of the walls of the organ, increases the movement of chyme.
If conservative therapy fails, surgical intervention is performed. Resection of the digestive organ is performed according to Billroth 2. But, unfortunately, the operation in many cases does not have the desired result, so it is performed in extreme cases.
Diet
A mandatory method of treating duodenostasis is diet. It is important to exclude fermented products from the diet: juices, grapes, baked goods.
| Prohibited | Allowed |
| Fatty, salty, fried foods. | Dried yesterday's bread. |
| Preservation, marinades. | Dried fruit compotes. |
| Dairy fatty products. | Not strong brewed tea, cocoa. |
| Alcohol, soda, tea, coffee. | Low-fat milk. |
| Cream confectionery products. | Vegetable soups. |
| Fatty fish, meat. | Porridge on the water. |
| White wheat bread. | Dietary meat, fish. |
It is necessary to follow a diet. Eat food in small portions 5-6 times a day. Dishes should not be cold or hot, liquid or puree food should be taken.
In more severe cases or with obstruction of duodenostasis, dietary adherence will be lifelong.
In addition, the disease can be treated using traditional methods. Anti-inflammatory, restorative, choleretic plants are used: plantain, chamomile, currant, rose hips, dandelion.
Forecast
The prognosis for duodenostasis is ambiguous. It will be beneficial for health and life if diseases that can provoke duodenostasis are identified and treated in a short time.
The rate of development of duodenostasis varies greatly: from the onset of this pathology and its first symptoms to the stage of decompensation, it can take from several weeks to several years. Surgeons know of cases where symptoms of duodenostasis were periodically observed in patients 25-35 years old, and only after this time did complete obstruction of the duodenum occur, which had to be treated surgically.
Important
The longer duodenostasis is observed in patients and treatment is not carried out, the greater the likelihood of irreversible changes in the intestinal wall, which lead to an unfavorable outcome (including death due to severe intoxication with fermentation products). This can occur when patients ignore treatment, because the manifestations of the pathology until a certain point were not critical, and, according to the patients, they could be tolerated.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
16, total, today
( 175 votes, average: 4.64 out of 5)
Rectal bleeding: causes, symptoms, treatment
Inguinal lymphadenitis
Related Posts
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, you need to:
- Healthy food;
- timely treatment of any gastrointestinal ailments;
- strengthen immunity;
- eliminate bad habits;
- physical activity should be moderate.
You should take care of your health. Neglecting the symptoms of duodenostasis leads to unfavorable disorders in the duodenum, long treatment and complications.
We recommend: What is the danger of adenocarcinoma of the sigmoid colon and how is it treated?
Prognosis and prevention
The result of treatment depends on the following components:
- the reasons that provoked the disease,
- at what stage treatment was started.
If the disease is very advanced and severe intoxication of the body occurs, then the prognosis is negative.
To avoid illness, you must follow simple rules:
- diseases that can initiate duodenostasis should be treated without allowing chronic conditions;
- regulate physical activity;
- maintain a diet;
- eat healthy food, and if there is a tendency to duodenostasis, then the diet should be composed of dietary high-calorie foods (with a low fiber content).