What is diarrhea
In medicine, diarrhea (or diarrhea) is a condition of the body accompanied by nausea, frequent loose, watery stools, pain in the abdomen, and sometimes high fever. Diarrhea causes dehydration and is dangerous for the elderly and children, so it is important to know what treatment to use in order to prevent serious consequences.
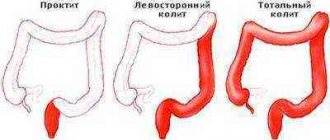
There are acute and chronic diarrhea. The first lasts up to two weeks and is caused by allergic reactions to medications, food poisoning, and infections. A chronic disease is persistent, prolonged diarrhea with periods of remission. Leads to weakening and dehydration of the body, and may be a symptom of a hidden disease. Causes of long-term constant diarrhea can be ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome.
An intestinal infection is accompanied by severe chills and bloody stool. An urgent visit to a doctor is needed if diarrhea lasts more than five days in adults and two in children, dark bloody stool, severe pain, or dehydration. It is especially important to see a doctor if diarrhea develops after returning from Africa or Asia.
Causes of the condition
The main causes of diarrhea with fever can be of various natures, namely:
- intestinal infection (infection with bacteria, viruses or pathogenic fungi);
- poisoning with poor quality food, medications;
- intoxication in various diseases of internal organs;
- pregnancy;
- radiation exposure;
- drug overdose;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
Diarrhea accompanied by a rise in temperature is a condition that requires rapid resolution. With prolonged or rapid loss of fluid, a threat to the health and life of the patient may arise, especially in childhood.
What is temperature
Body temperature is understood as an indicator of the thermal state of the human body, reflecting the relationship between organs and the external environment. Increased and high body temperature is dangerous for humans: up to 38 is subfebrile, up to 39 is febrile, up to 41 is pyretic, above 41 is hyperpyretic. The critical indicator is 42 degrees - at this temperature, brain tissue is destroyed, which leads to death.
The causes of fever are viruses and bacteria. The fever is accompanied by fatigue, weakness, dry skin, mucous membranes, mild or severe chills. A reading above 38.5 degrees is a reason to urgently call a doctor at home, especially if a person has muscle aches, pain in the limbs, arrhythmia, or loss of appetite.
What to do if you have diarrhea
The best thing a person can do is to monitor their health and create all the conditions for good health. Preventing diarrhea is the best treatment. however, what to do if diarrhea and fever appear:
- the occurrence of diarrhea against the background of hyperthermia requires correction of the condition. The first thing you should do is consult a doctor. Especially in case of damage to the child’s body. If dehydration occurs in an adult by the 3rd day of illness, in children it can develop within a few hours;
- If an infection is suspected, the use of loperamide or imodium will not be effective. In case of a food reaction, these drugs will completely solve the problem;
- it is necessary to carry out rehydration in order to restore the salt and water balance of the body: rehydron, mineral water (it is better to release gases), weak fruit drinks, compote. Chamomile decoction;
- normalization of nutrition taking into account the condition. Food should be easily digestible, heat-treated and balanced in terms of essential elements;
- for hyperthermia up to 38 degrees, NSAIDs can be used;
- preparations containing prebiotics and probiotics will also be good helpers in the fight against diarrhea.
Fever and diarrhea in an adult
If a person has a high fever and diarrhea at the same time, doctors suggest a diagnosis of acute diarrhea. It can be caused by viral, parasitic or bacterial infections. The causes of acute diarrhea are a viral disease, traveler's diarrhea. The causative agents of the combination of diarrhea and fever are:
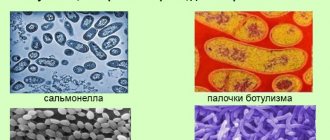
- E. coli – infects meat, fish, milk, vegetables, fruits, water. The infection is transmitted from person to person, symptoms are watery stools with blood, vomiting.
- Salmonella - contains raw milk and poorly fried eggs. An excited illness is accompanied by acute abdominal pain, fever, and a frequency of diarrhea 12-15 times a day;
- Shigella - found in food products, loose stools with blood, abdominal cramps are observed;
- Rotavirus (viral infection) - you can become infected from others, a person is bothered by vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea.
Which doctor should I contact?
A gastroenterologist is involved in the treatment of intestinal pathologies; in addition, consultation with an infectious disease specialist or parasitologist may be required. Treatment of serious infectious diseases takes place in a hospital setting; mild forms of diseases can be treated at home, strictly following the recommendations of a specialist.
Important!
Urgent medical attention is required if there is blood in the stool, an increase in temperature to 39 degrees or more, if bowel movements occur more than 10 times a day.
Causes
Loose stools and fever in adults or children are more often associated with food poisoning. Other reasons are:
- eating a lot of food;
- allergic reactions;
- exceeding the dosage of medications;
- severe stress, emotional tension;
- sudden climate change;
- damage to the gastrointestinal tract by an infectious disease;
- stomach ulcer, gastritis;
- poisoning with heavy metals, poisons, chemical toxins;
- radiation damage.
Diarrhea, nausea, fever
Diarrhea with fever and nausea serves as a protective reaction to toxins entering the body. The reasons for the development of these symptoms together are:
- abuse of fatty foods with enzyme deficiency;
- cholera, hepatitis;
- gastritis, ulcer, inflammation of the pancreas, cholecystitis;
- poisoning with mercury vapor, nitrates, poisonous mushrooms.
Loose stools and temperature 37
When diarrhea and a temperature of 37 degrees appear, doctors may suspect gastroenteritis or intestinal flu due to viruses entering the intestines. Their toxins cause inflammation that affects the intestinal mucosa. A person becomes contagious to other people. Viruses can enter the body through food and drinks:
- with unwashed fruits, expired food;
- with unboiled water, when swimming in an infected body of water;
- airborne through sneezing or interacting with large numbers of people.
The incubation period lasts 16 hours, after which the intestinal mucosa is destroyed. Signs of a dangerous disease are:
- frequent liquid diarrhea – 10 times a day;
- nausea, vomiting, cough, sore throat;
- mucus in stool;
- gray-yellow clay-like stool color;
- pain in the stomach area.
- How to crochet a washcloth for beginners
- Instant marinated zucchini
- Tibetan gymnastics for weight loss
Diarrhea and temperature 38 in an adult
With severe diarrhea and a temperature of 38 degrees, doctors diagnose “damage to the gastrointestinal tract due to the development of infection.” The causes may be an overdose of antibiotics, hormonal non-steroidal drugs, and digestive disorders. The latter can be caused by overeating or eating low-quality foods. If you feel worse, visit a gastroenterologist or therapist.
Fever, nausea, diarrhea, weakness
Symptoms of food poisoning include weakness, high fever and watery diarrhea in an adult or child. They appear suddenly after eating foods, without an incubation period. Two hours after ingestion, the pathogen (infection of microbes, viruses or ingestion of chemical toxins) acts on the body. Characteristic symptoms are:
- liquid stool that comes out spasmodically;
- decreased blood pressure;
- cold sweat;
- When poisoned by poisons, vision and brain function are impaired, and muscles lose tone.
Treatment options
If unpleasant symptoms occur, there are ways to treat ailments at home using medications and traditional methods.
Necessary medications
The disease can be cured by taking certain medications:
- saline solutions;
- antipyretic drugs;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- sorbents;
- antispasmodics;
- probiotics.
Restoring salt and water balance during diarrhea is a primary task. In addition to frequent consumption of mineral, alkaline water, it is recommended to take Regidron solution. To lower the temperature, antipyretic drugs are needed. Antibiotics and antibacterial agents help remove infectious microorganisms and toxins from the body. Sorbents help cleanse the body in case of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Antispasmodics help relieve pain syndromes. Probiotics are essential to stop diarrhea.
It is important to use drugs to restore intestinal function throughout the entire therapeutic course. To treat not only symptomatic signs, but also the causes of the pathology, you should consult a specialist. Untimely intervention can lead to progression of the disease.
Traditional methods
To maintain the water-salt balance, you can consume cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks. Decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, and oak bark have anti-inflammatory properties. You can make an infusion of fennel or dill. Such drinks help stop diarrhea. Chewing mint leaves and dry black tea leaves prevents vomiting.
For adults, an infusion of vodka, water, crushed leaf tea, and sugar is suitable. All ingredients are mixed and cooked until half of the liquid has evaporated. The infusion should be taken on an empty stomach, 100 grams.
Loose stools and temperature are symptomatic signs that signal an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract as a result of poisoning, infection, or non-compliance with the correct diet. Providing first aid, and subsequently taking medications, help improve the patient’s condition.
We recommend: How to quickly get rid of diarrhea at home?
Diarrhea and fever in childhood
In babies, the dangerous temperature for diarrhea is 37 degrees or more. The causes of these symptoms are:
- eating disorder, intoxication of the body - pale face, cold feet and hands, stomach pain;
- reaction to medications;
- acetonemic syndrome - lack of carbohydrates, past infectious diseases of the digestive system, stress, manifested by vomiting, unpleasant odor of acetone from the mouth;
- teething - gums may begin to swell;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules – signs of poisoning are visible;
- helminthic infestations - severe diarrhea;
- gastritis, colitis, dysbacteriosis - signs of toxins entering the body disappear with medication;
- enterovirus – bloody diarrhea (invasive bloody diarrhea);
- rubella, scarlet fever, measles - rashes on the skin;
- flu, sore throat, otitis media, pharyngitis – redness of the throat, enlarged tonsils, nasal congestion, temperature may rise;
- dysentery, salmonellosis - green feces with mucus.
Causes of vomiting, diarrhea and fever, diarrhea without fever
In the body, when there is a threat of general intoxication, a number of protective mechanisms are activated to ensure the removal of harmful substances, be it food allergens, elements of poor-quality food, waste products of infectious agents and pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, gagging, periodic vomiting and diarrhea, and sometimes high fever occur. A set of several symptoms may be a sign of the development of disorders of the digestive system, when unfavorable changes occur in the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to a disorder of the secretory, motor, and digestive functions. Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea are caused by:
1 food intoxication due to poisoning from poor-quality food;
2 consequences of overeating, the body’s inability to cope with a large volume of difficult-to-digest, fatty foods;
3 infections due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the body (Vibrio cholera, Shigella, Salmonella);
4 attack of specific viruses (rotavirus, enterovirus);
5 gastric pathology with disorders of secretory function, changes in the qualitative composition of gastric juice (gastritis of various etiologies, ulcerative damage to the mucous membrane);
6 abnormalities in the functioning of the liver, gall bladder (hepatitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis);
7 disturbances in the production of enzymes by the pancreas (panrkeatitis);
8 intestinal pathologies (colitis, enterocolitis, UC, dysbiosis, irritable bowel syndrome);
9 Intoxication due to poisoning with chemicals, toxic substances (mercury vapor, nitrates, mycotoxins).
What to do
Home treatment can reduce the impact of dangerous symptoms, provided that the following recommendations are followed:
- give the patient plenty of drink - Borzhom or Essentuki mineral water, dried fruit compotes, weak fruit drinks, weak tea with honey;
- follow a dietary diet – boiled cereals, vegetable soups;
- take fermented milk products, non-acidic cheeses, low-fat cottage cheese;
- drink starchy jelly for health;
- eat more boiled vegetables and baked fruits;
- You can bring down the temperature above 38 degrees with Nurofen, Aspirin, Paracetamol;
- take calcium supplements, pro- or prebiotics with pectin, acidophilus.
First aid
If the temperature rises and bowel movements appear, the first aid for the patient will be the following measures:
- at the first signs of intestinal poisoning, induce vomiting to lavage the stomach - drink a solution of potassium permanganate or soda, repeat until the stomach is completely empty, then take an absorbent;
- to prevent signs of dehydration, every 10 minutes give the patient a sip of Regidron (a packet per liter of water), drink plenty of fluids;
- on the first day of treatment for severe weakness, you should refuse to eat, drink more and rest, then follow a light diet and drink broths;
- The temperature during diarrhea should not drop to 37 degrees (it indicates that the body is in the process of independently fighting the infection). In this situation, provide the patient with complete rest.
Drug treatment
In case of a complicated course of the disease, diagnostics are required to prescribe the correct drugs for treatment. Diagnosis measures include the use of coprograms, stool tests for dysbacteriosis and helminths, general and biochemical blood tests, and abdominal ultrasound. Depending on the cause of diarrhea, treatment methods include:
- reception of sorbents.
- gastric lavage in case of severe vomiting;
- rehydration therapy for fluid loss - Regidron, Gastrolita, Citroglucosolan, chamomile tea, pharmaceutical saline solution;
- antipyretics for headaches - Paracetamol, Nurofen;
- taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics or cephalosporins - in severe condition, presence of blood in diarrhea
- lacto- and bifidobacteria to restore intestinal microflora during rotavirus infection;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs on the first day of illness - Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Sulfasalosin;
- When diarrhea occurs, it is useful to take Festal or Mezim to stimulate intestinal function and remove toxins.
Traditional treatment
If diarrhea and high fever appear in an adult or child, you can use traditional medicine recipes to help get rid of dehydration:
- Taking rice or pomegranate broth, mint infusion, fresh blueberries.
- Consuming dry starch dissolved in water, diluted carrot puree, chamomile or mint tea.
- Taking rehydration solutions - take a tablespoon of sugar, a teaspoon of salt and half a teaspoon of soda per liter of boiled water. Or dissolve eight teaspoons of sugar, a teaspoon of salt, and the fresh juice of two oranges or grapefruits in a liter. It is necessary to give the patient food every five minutes in small portions.
What to do if you have a fever with diarrhea?
It takes 3–4 weeks for the body to recover after poisoning, depending on the severity of intoxication. To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to adhere to proper nutrition, maintain a drinking regime, and regularly take medications in combination with folk remedies.
Drug treatment
For diarrhea and elevated temperature, it is necessary to take medications whose action is aimed at eliminating intoxication, dehydration, lowering temperature, and restoring the balance of enzymes.
How to treat intestinal disorder:
- adsorbents – activated carbon, Smecta, remove toxins, eliminate diarrhea;
- antibiotics – Furazolidone, must be taken for intestinal infections of bacterial origin;
- antiviral drugs - Viferon, Tsitovir;
- rehydration drugs – Regidron, Gastrolit, help prevent dehydration;
- painkillers and antispasmodics - Diclofenac, Indomethacin, No-shpa;
- antipyretic medications – Paracetamol;
- enzymes - Mezim, Festal, prescribed for pancreatitis;
- antiparasitic drugs – Dekaris, Nemozol.
→ Read more about anti-diarrhea remedies
Cytovir is an antiviral drug
Important!
Nifuroxazide is considered the best treatment for intestinal infections - the drug effectively destroys bacteria, but is not an antibacterial drug. It acts selectively and has a detrimental effect exclusively on pathogenic microorganisms, which reduces the likelihood of developing dysbacteriosis.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine will help cope with diarrhea, destroy parasites and other pathogenic microorganisms, restore strength, and eliminate micronutrient deficiencies.
Oak bark decoction has binding properties
What to do if you have diarrhea and fever at home:
- Blueberry decoction helps with all forms of diarrhea. Pour 400 ml of water 1 tbsp. l. chopped leaves, cook the mixture over low heat for a quarter of an hour, leave in a closed container for 30 minutes. Take the medicine three times a day, 100 ml.
- Wormwood copes well with various harmful bacteria and parasites. Pour 220 ml of water 1 tbsp. l. dry chopped herbs, cook for 15 minutes over low heat. Cool, drink strained, 15 ml every 8 hours.
- Brew strong black tea, add 5 g of potato starch, drink the entire portion of the medicine at once. For severe diarrhea, you can chew 0.5 tsp. tea leaves, swallow, drink with plenty of water.
- Oak bark contains many tannins, which have a binding effect. Pour 2 tsp. raw materials 250 ml of boiling water, cover the pan, leave for 45 minutes, strain. Drink 15 ml every 2–3 hours.
- One of the best and most effective remedies for treating infectious diarrhea is a decoction of pomegranate peels:
- pour 700 ml of boiling water, 10 g of powdered dry raw materials;
- simmer in a water bath for a quarter of an hour;
- leave for 40 minutes;
- take 10 ml of drink 4-5 times a day.
→ More folk recipes
Prevention
To prevent weakness, fever, diarrhea and vomiting, you need to follow simple but effective rules of prevention:
- When preparing food, observe the shelf life of products;
- Avoid self-treatment with antibiotics;
- store ingredients only in the refrigerator in compliance with the commodity proximity, do not keep raw meat next to fresh vegetables;
- choose only high-quality food products, without expired expiration dates;
- do not eat raw fish in rolls, cook steaks without blood, do not drink unpasteurized milk, untested water;
- wash your hands more often;
- eliminate insects in the kitchen;
- wash dishes thoroughly.
In what cases should you call an ambulance?
Feeling unwell, mildly unwell, or having a fever is not a reason to call an ambulance. You shouldn’t take up the team’s time if someone with more serious illnesses needs help. When calling a doctor you must:
- describe the condition as accurately as possible in order to know which team to send to the call;
- how to get to the house;
- intercom code.
Tell the dispatcher the exact address (city, house, apartment, entrance number). Describe the complaints in detail. A telephone number where the team can contact if necessary. If the call is to a dacha where there is no exact address, explain the route to the place and landmarks.
Fever, aches, headache, nausea, VOMITING, DIARRHEA
Affecting the stomach and intestines, rotaviruses, enteroviruses (noroviruses), astroviruses, and adenoviruses cause repeated vomiting and uncontrollable diarrhea.
Intestinal (stomach) flu is transmitted from person to person through kissing and coughing, as well as through dishes, hygiene items and the toilet. You can become infected through water - bleach does not kill the virus. By attacking everyone around, the virus spreads quickly. Often entire families, classes, departments, divisions get sick...
Video. Uncontrollable vomiting by the whole family
The health of those infected can vary greatly, from mild illness to life-threatening conditions. The most vulnerable are young children and the elderly. Do not give up! It will be unpleasant, but not for long. In adults, intestinal flu lasts 12-48 hours, and in young children up to 5-7 days.
IMPORTANT. 3-5 days after recovery, the person is still contagious.
Nutrition for diarrhea
Diarrhea requires proper nutrition, because if you do not use a diet, the disorder will worsen. Doctors advise using dietary food table No. 4, its basic principles are as follows:
- It is prohibited to consume baked goods, rich soups containing cereals, pasta, as well as unhealthy foods such as fatty, smoked, etc.
- It is allowed to eat more crackers instead of bread, and eat light soups, preferably with the addition of rice or oatmeal. You need to eat only lean types of meat and fish.
If eggs are used, they should be soft-boiled or cooked as an omelet. Vegetable decoctions, jelly, and grated apples are allowed.
It is worth noting that the diet should not exceed more than 1800 calories per day. It is very important that the amount of proteins (80 g), carbohydrates (250 g), and fats (70 g) be taken into account.
It is better to avoid salt or add it to a minimum, no more than 10 grams per day. Water consumption necessarily increases, to about 3 liters.
Disease Prevention
We have learned that the main sources of symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea and fever are infectious and viral diseases. Prevention of infection is carried out using vaccination, which has undergone clinical trials. There are two types. Both are used orally and contain live virus. But, they are only available abroad for now. But the most effective and accessible prevention is compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules (drinking boiled, bottled water, washing hands). To avoid getting infected you need to:
- avoid contact with sick people, wear a mask when communicating;
- wash your hands after contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth;
- do not rub your eyes or mouth with dirty hands;
- cover yourself with a handkerchief when you sneeze;
- do not go to places where there are large crowds of people;
- ventilate the premises, do wet cleaning regularly.
Treatment
Each disease with such symptoms (diarrhea and temperature 38) in a child requires special treatment. Here we will tell you how to cope with loose stools caused by any of these diseases. Depending on the severity of the condition, both drug therapy and traditional medicine can be used, the recipes of which are sometimes no less effective.
Medicines
Drug treatment involves a complex of actions:
- Sorbents that will remove toxins and harmful substances from the body (Enterosgel, activated carbon, Smecta, Neosmectin, Polysorb)
- Preparations that will restore the water-salt balance (Regidron and other saline solutions)
- Means for reducing temperature. Children can only take paracetamol-based medications
ethnoscience
- The most popular folk remedy for diarrhea for children is rice water. Boil the rice in plenty of water. As soon as the liquid becomes jelly-like, drain it, strain and give it to your baby to drink.
- Another simple remedy is a spoonful of starch dissolved in a glass of water.
- Make an infusion of pomegranate peels. Grind them with a knife, in a coffee grinder, or blender, and then pour a glass of boiling water and let it brew for half an hour. Then strain and give it to your child to drink.
- Make a weak solution of potassium permanganate. It should be pale pink. This product is an excellent disinfectant.
When to call a doctor
Vomiting, diarrhea, and fever indicate severe intoxication of the adult body. If you do everything correctly, home treatment quickly brings relief, but it is not always possible to independently determine the cause of the disease.
You should consult a doctor if diarrhea and vomiting last more than three days in an adult, regardless of whether the temperature rises or not (for some diseases it can stay at 37 degrees for several days - this is the so-called low-grade fever).
A doctor should be called immediately if the vomit and then diarrhea are streaked with blood. When the patient experiences nausea, abdominal pain, severe weakness, or headache, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
A combination of these signs may indicate an infection, dysentery, Crohn's disease or a stomach ulcer. The temperature may rise or remain at around 37 degrees. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and then begin to treat the patient correctly!
Thus, vomiting and diarrhea (with or without fever) in an adult can be caused by a number of reasons, many of which are life-threatening. The treatment of such diseases may differ significantly from the treatment of infections. Correctly provided first aid, as well as timely consultation with a doctor, will help you quickly get rid of unpleasant symptoms while maintaining your health.
First aid
It should be remembered that if a child has diarrhea and a fever, he needs competent help from adults. Parents should:
- Call a doctor.
- Separate the patient's personal items (dishes, towels, bedding) to avoid the spread of infection (even if the causes of the illness are still unknown).
- Give any enterosorbent (Smecta, Microsorb, Polysorb, Activated carbon, Atoxil). Such drugs should always be present in every family's medicine cabinet.
- Give an antipyretic when the temperature exceeds 38°C. If the child has a slight fever, then you can wait for the doctor without resorting to antipyretic drugs. You can alleviate the patient's condition by removing his clothes and ventilating the room.
Important! Together with loose stools and vomit, the body loses fluid, which leads to dehydration. This is an extremely dangerous condition in both newborns and older children. If the patient experiences increased drowsiness, dry lips, prolonged absence of urination, or rapid heartbeat, then emergency medical intervention is necessary.
Excessive fluid loss can be prevented by providing the patient with plenty of fluids. If the disorder occurs in a breastfed baby, it is recommended to put it to the breast frequently. If the baby is artificial, then it is necessary to feed him a mixture that includes adsorbents. Rehydration drinks/solutions that can be prepared at home will help older children avoid dehydration:
- For a liter of boiled chilled water, take 20 g of sugar, 8 g of salt and 5 g of baking soda. Everything is thoroughly mixed and offered to the child.
- Per liter of boiled chilled water add 40 g of sugar, 8 g of salt and the juice of two oranges. This drink is suitable for children who are not allergic to citrus fruits.
You should not force your baby to drink, as this can cause a gag reflex. It is enough to give him a teaspoon every five to ten minutes.