General rules
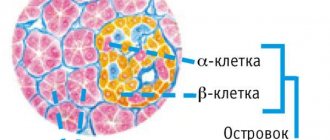
The pancreas (PG) is the most important secretory organ of the child’s body, combining exocrine function (secretion of digestive enzymes involved in the digestion process) and endocrine (production of the most important hormones - insulin , lipocoine and glucagon , which control blood sugar levels).
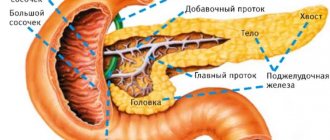
The size of the pancreas in children normally depends on age: from 3 cm in newborns, 5.5 cm per year and about 8 cm by 10 years of age. The gland reaches its full size by the time of puberty. However, in some cases, when examining a child (ultrasound, computed tomography), an enlargement of the pancreas is noted. In this case, total enlargement is distinguished, in which all parts of the gland are uniformly/proportionally increased in size, and local, in which only one of the parts of the gland is enlarged (head, body or tail). The issue of enlarging the pancreas in a child must be approached very carefully, since during the growth process it increases several times in comparison with its original size and, at the same time, its growth at different age periods is not always uniform. In addition to a number of diseases in which the pancreas can be enlarged in size, this phenomenon is often observed in absolutely healthy children with increased indicators of physical development (total increase in size) and in children who are overweight (mainly due to an increase in the head of the organ). That is, such children have significantly increased sizes of the pancreas in relation to their peers who have physiologically normal anthropometric indicators and body weight.
The most common diseases that cause enlargement of the pancreas in a child include pancreatitis , gallbladder disease, toxic poisoning, trauma, tumors of various types, abscess, obstruction of the pancreatic duct, infectious/parasitic diseases, and exposure to drugs. However, in the overwhelming majority of cases, pancreatitis is diagnosed in children with an enlarged pancreas.
Treatment of the child depends on the specific cause that provoked the enlargement of the pancreas. In some cases, surgical intervention is necessary (abscess, tumors). In other cases, conservative treatment of the underlying disease that caused the enlargement of the organ.
A number of pancreatic diseases in children manifest themselves as signs of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, the main manifestation of which is mushy, frequent gray stools with a greasy sheen of a viscous consistency. The consequence of an impaired digestion process is weight loss, hypovitaminosis, in particular, fat-soluble vitamins, and in young children - a lag in psychomotor development. Treatment of an enlarged pancreas is based on:
- Compliance with therapeutic nutrition.
- Suppression of the secretory activity of the gland using histamine receptor blockers/proton pump inhibitors/hormonal drugs.
- Taking digestive enzymes of the pancreas to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
An important aspect of the treatment process is diet therapy, indicated for the underlying disease. However, if a child has prevailing symptoms of acute/chronic pancreatitis, dietary nutrition is carried out within the dietary Table No. 5 - 5G , which allows reducing the load on the pancreas and normalizing its function. The principles of dietary nutrition for adults and children are not particularly different, however, the diet is adjusted in accordance with age-related physiological needs for food nutrients and the energy value of the diet.
Also, it is recommended to include the age-appropriate amount of fat in children’s diets (with the exception of refractory animal fats), since modern replacement therapy drugs (for example, Creon ) compensate for the lack of lipase. This approach allows you to improve the nutritional status of the child, which is extremely important for a growing organism. In addition, this drug does not reduce pancreatic function even with long-term use.
The basis of the diet is vegetarian soups, dietary meat (chicken, rabbit, turkey), protein omelettes (1-2 per week), white crackers, milk porridges, baked fish, minced meat dishes, fermented milk products and boiled vegetables. Allowed in moderation: honey, jam, jams, marshmallows, marmalade. Meals are frequent and small. It is also recommended to add enzyme preparations/fat-soluble vitamins to children’s diet. Dishes that have a juice effect are contraindicated for children: fried foods, mushroom, meat, bone and fish broths.
The chronic form of pancreatitis in children develops most often against the background of diseases of the duodenum/biliary tract, that is, it is secondary. The chronic form is most often the outcome of the acute form of the disease, cystic fibrosis , cholelithiasis, anomalies of the sphincter of Oddi, or a consequence of damage to the gland by drugs. During the period of exacerbation, the child must follow a strict diet for at least a month, after which you can stop chopping food, but culinary methods of preparing dishes should remain gentle (boiling, steaming, baking).
The diet includes chicken meat, lean fish, cottage cheese, fermented milk products, and pasta. Be sure to include boiled/baked vegetables in your diet (carrots, potatoes, broccoli, zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower, beets). The food is undersalted.
Soups/vegetable purees are seasoned with sour cream/vegetable oil. You can add a little butter to the porridge; mild cheeses are allowed. After a month, the diet is gradually expanded, but all the basic principles of Diet No. 5 must be followed even in the absence of symptoms until the diagnosis is removed.
At the same time, gross dietary violations are undesirable in a longer period.
Is it possible to have sausages if you have pancreatitis?
Sausages are of little use for the menu of patients with pancreatitis. Despite the ease of preparation, homogeneous structure and the presence of animal protein (according to the manufacturers), they can lead to the recurrence of the inflammatory process.
- Salt helps to delay the removal of fluid, which means it provokes swelling, which is unacceptable. Salt also has an irritating effect on the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
- They contain bone meal, tendons, fats, leather, cartilage and soy - agree, these are the ingredients. Frankly speaking, low-quality raw materials. All of them are not recommended even in the absence of health problems.
- About 80% of the contents are all kinds of additives, color and taste enhancers, preservatives, flavors, thickeners and other “chemicals” that increase inflammation, stop the process of regeneration of damaged tissues and can even provoke the growth of cancer cells.
- Sausages are also famous for their high fat content, which is difficult to digest when the organ is inflamed.
- Various types of spices are prohibited for inflammation of the pancreas, without which it is impossible to imagine sausages. Garlic, pepper and other spices irritate the intestinal walls, which require maximum rest during pancreatitis.
During an acute attack, as well as during an exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease, sausages are strictly prohibited. Their use can result in severe negative consequences and complications.
Upon the onset of the remission phase, it is extremely rare for nutritionists to allow you to diversify the menu with such a delicacy. Under no circumstances should sausages be consumed regularly, and their volume should not exceed 1 piece.
When choosing, you need to pay attention to the following factors:
- The composition should not contain spices or additives, for example, fragments of vegetables, cheese, garlic, etc.
- Choose a product with a minimum percentage of fat content.
- Give preference to sausages marked with compliance with GOST.
- The meat content should be 30% or higher.
- Sodium nitrate reveals itself in the bright colors of the product. Its smallest dosage is present in sausages of a gray-pinkish hue, so make your choice in their favor.
- Eat the sausage warm and freshly boiled.
- The ideal side dish for a meal with sausage would be boiled vegetables or pasta.
- Under no circumstances should you include hot dogs, sausages, smoked sausages and other similar dishes in your diet.
- Once, maximum twice a week - this is the frequency of use that will be safe if all the conditions described above are met.
- However, it would still be better to avoid eating sausages altogether. Use them solely as a backup option.
Young children and adolescents may experience reactive inflammation of the pancreas when they eat fried or fatty foods. This condition is called acute pancreatitis. Its therapy is long-term; a prerequisite is the prescription of a diet.
Authorized Products
A diet for an enlarged pancreas in a child includes the following foods in the diet:
- Vegetable broths/soups based on vegetable broths, into which thoroughly pureed vegetables are added and well-cooked/mashed grains are added. Soups can be seasoned with butter, sour cream, butter; frying is prohibited.
- Lean meat (beef, rabbit, veal, chicken, turkey) in the form of chopped products (meatballs, cutlets, soufflés, quenelles, meatballs), steamed. Boiled poultry/rabbit can be eaten in pieces.
- Porridge (semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat), rice, cooked in water with the addition of milk and well ground to a semi-viscous consistency.
- Vegetables (boiled/grated) until pureed - zucchini, carrots, potatoes, pumpkin, cauliflower, beets, green peas, peeled tomatoes and grated cucumbers. Later, grated pumpkin/raw carrots are allowed.
- Low-fat fish (pike, pollock, pike perch, hake, blue whiting, cod, carp, perch). Used in the form of cutlets, steamed/boiled in pieces.
- Low-fat dairy/fermented milk products (cottage cheese, mild grated cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk).
- Milk/sour cream - as an additive to dishes.
- Dried wheat bread, savory biscuits (biscuits).
- Steamed protein omelettes (1 egg per day).
- Sauces based on vegetable broth (do not fry flour) with the addition of sour cream/milk.
- Baked sweet apples, pureed dried fruits. Boiled, mousses, jelly, sweet fruit pastilles. Limited - pureed raw fruits/berries.
- Fats, first carefully introduce butter, and later refined sunflower oil.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| curdled milk 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,1 | 40 |
| acidophilus 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
| cottage cheese 1.8% (low-fat) | 18,0 | 1,8 | 3,3 | 101 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| blue whiting | 16,1 | 0,9 | — | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
| pike | 18,4 | 0,8 | — | 82 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for a child with an enlarged pancreas excludes:
- Soups with meat/mushroom/fish broth, cabbage soup, borscht, okroshka, beetroot soup.
- Offal (liver, kidneys, brains, tongue).
- Fatty fish, smoked meats, meat, goose/duck meat, all fried foods, fish caviar, stewed meat and fish, sausages, fast food products, canned food, salted fish.
- Vegetables containing coarse fiber (radish, turnip, rutabaga, white cabbage, radish, eggplant), legumes, mushrooms.
- Fresh wheat and rye bread, yeasted pastries, pastries with cream, puff pastry, cakes, pancakes, fried pies, pancakes, cheesecakes.
- Some types of porridges (barley, pearl barley, corn, millet).
- Cooking/animal fats, seasonings/spice, spices (ketchup, horseradish mayonnaise, herbs, pepper, mustard).
- Fried/hard-boiled chicken eggs, salty spicy cheese, full-fat milk, cream, high-fat, high-acid cottage cheese.
- Boiled and baked vegetables/fruits, raw vegetables must be introduced into the diet with caution.
- Chocolate, black strong coffee, ice cream, grape juice, cocoa, carbonated/alcoholic drinks.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| seeds | 22,6 | 49,4 | 4,1 | 567 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Reviews and results
Therapeutic nutrition for an enlarged pancreas in a child, along with taking enzymatic preparations, according to parents, serves as the basis for pancreatic burning and normalization of its function.
- “... During an ultrasound, my child was found to have an enlarged pancreas in the tail area, and foci of fibrosis were found. There are also problems with the gallbladder - cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia. There are constipations. They prescribed treatment, including dietary Table No. 5. I cook for her separately from other family members, according to the instructions for preparing dietary dishes. Everything prohibited was excluded. I don’t know if this will help”;
- “... The daughter complained of minor abdominal pain for almost a week, while her stool was normal, her appetite did not suffer, and there were no other complaints. They sent me for an ultrasound scan - reactive pancreatitis, dyscholia due to deformation of the gallbladder, the pancreas was enlarged 39*17 mm. They prescribed a diet excluding fried, fatty/spicy foods, pickled, salted and smoked foods, seasonings, sauces and spices. I feed the child in small portions, but often. Now the situation has stabilized a little, let’s go for a re-examination.”
Is baby food good for pancreatitis?
Many types of foods and dishes are completely excluded from the diet of patients with pancreatitis. In this regard, patients and their relatives raise the question of whether it is possible to diversify the diet of a person suffering from this type of pathology. In addition, there are situations when it is not possible to prepare the dishes necessary for a sick person.
Many adults found a fairly simple way out of this difficult situation. They turned their attention to baby food, which is freely available in any store. In terms of their composition, fruit purees, canned meat, and milk porridges are adapted to the needs of the child’s body. Are they able to fully satisfy the needs for vitamins and nutrients in an adult?