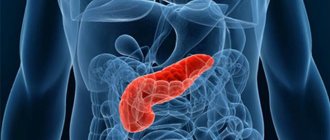
If the examination reveals that the pancreas is enlarged, it is necessary to find out the reasons and begin treatment. It is important to do this in a timely manner, since the size of the organ can change due to various pathologies, including cancer. Considering that the pancreas is a unique organ with a dual function - digestive and endocrine, its topographic location (retroperitoneal), symptoms of a chronic disease do not appear immediately.
Causes of pancreas enlargement
There are two reasons for detecting an enlarged pancreas:
- tissue proliferation to compensate for the reduced functions of individual cells;
- tissue swelling due to inflammation or an autoimmune reaction.
Therefore, the main factors for organ enlargement are:
- alcohol abuse;
- chronic infections;
- blockage of the Wirsung duct;
- intoxication with drugs and chemical agents;
- autoimmune process.
alcohol abuse
An enlarged pancreas can be associated with dangerous conditions:
- an abscess is a cavity containing pus, which affects the functions of the entire organ and increases the risk of sepsis;
- epithelial cysts are usually benign, but cause pain by stretching the organ capsule;
- pseudocysts are formations that contain remains of cells or enzymes and other fluids, which increases the size of the organ and impairs its function;
- cancer causes severe pain that radiates to the back. Its symptoms are associated with stool disorders and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
Most often, an enlarged pancreas is caused by chronic inflammation - pancreatitis. Alcoholism and other intoxications, including excess calcium and fats, are the main mechanisms of the pathology.
Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi is manifested by reflux of duodenal contents into the pancreatic duct, which leads to an inflammatory process. Then changes begin in the form of autolysis - tissue breakdown. The prerequisites for the disorder are: removal of the gallbladder, compression of the vagus nerve at the level of the cervical spine or diaphragmatic opening - a stress factor, as well as gastritis.
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
A dangerous autolytic effect occurs when the destructive effects of the gland's own enzymes are directed against its own tissues. Self-destruction of the organ is observed.
Enlargement of the gland is provoked by spasm of the arteries and ligaments. Compression of the diaphragm changes the position of the stomach and duodenum, as a result the head of the pancreas is pinched, and the outflow of secretions slows down.
At the same time, biliary dyskinesia, cholelithiasis or gastritis are diagnosed as a concomitant or underlying pathology. With severe dysfunction of the liver, worms and helminths can disrupt the functioning of the hepatobiliary tract.
Chronic pancreatitis is considered one of the factors affecting the intestinal papilla by tumors, in addition to genetic predisposition. Enlargement of the tissue of the head of the pancreas due to an abscess or adenoma leads to compression of the common bile duct, which is manifested by jaundice. Islet cell tumors are called insulomas and are found in the tail with local enlargement of the pancreas. Symptoms include hypoglycemia, drowsiness, and sweating.
The child has a stomach ache, bad breath, lethargy and vomiting - these are signs of increased acetone. This is caused by the accumulation of ketone bodies in the blood due to impaired protein or carbohydrate metabolism, liver enzyme deficiency or endocrine dysfunction. Acetonemic syndrome indicates pancreatic dysfunction and enlargement.
The release of pancreatic enzymes into the intestine is affected by the acidity of the stomach. Hydrochloric acid sends a signal to produce secretion. Low acidity increases the risk of stomach cancer caused by chronic gastritis.
The reasons for an enlarged pancreas in a child are usually sought in heredity. Osteopaths view the dysfunction as a consequence of cranial compression during childbirth and decreased vagus nerve signals. It descends along the neck and chest, innervating the organs on its side of the body.
enlarged pancreas
The cause of an enlarged pancreas in an adult is the accumulation of fat, lipomatosis or steatosis. The pathology is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus, acute pancreatitis, and oncology. An MRI examination is required for differential diagnosis.
What does an increase in the size of the gland indicate?
Destructive processes indicate a number of reasons that provoke the disease:
- Hereditary-genetic. One of the manifestations of cystic fibrosis, the disease is characterized by a thicker form of secretory fluids.
- Improper and irregular nutrition.
- Long-term and unnecessary use of medications.
- Abuse of fatty, spicy, smoked foods.
Alcohol abuse.- Inflammatory and congestive processes in the body.
- Disorders and diseases of the circulatory system.
- Increased levels of calcium in the body.
- Stone formation and related dysfunctions.
- Cysts, tumors, adenomas.
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach.
- Infections and complications associated with them.
- Malignant tumors.
- Ulcers, primarily in the stomach.
- Disease leading to decreased immunity.
- Injuries.
Answer to the question: How to treat diffuse changes in the pancreas? – read here.
The disease may be hidden and not manifest itself for a long time. Only sometimes certain signals arise in the form of nausea or passing pain (latent form).
Painful sensations with this pathology
Another symptom of pancreatic dysfunction is pain in the area of the pancreas - in the left hypochondrium. The pain usually radiates to the lumbar region. Painful sensations can have a clear relationship with dietary errors. Usually the pain intensifies after eating fatty, fried, spicy, smoked and pickled foods. In addition, many patients report increased pain due to psychoemotional stress. Another symptom of this disorder is weight loss, which occurs with prolonged disruption of the absorption of nutrients and their digestion.
Symptoms and treatment of pancreatic dysfunction are interrelated.
Characteristics of the gland
- The pancreas is located behind the stomach, in the region of the 1st and 2nd sections of the spine.
- Approximately 6-9 centimeters above the navel.
- The shape is oblong, up to 23 centimeters long.
- Weight up to 115 gr.
- The size of the pancreas can vary individually for each person. Adjustments also occur with age-related changes.
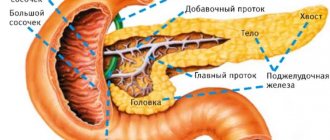
- They are conventionally divided into three sections: head, body and tail.
- A structural feature is the division of tissues into small capsules (acini). Each capsule is equipped with a small excretory duct and produces enzymes.
- It has an extensive circulatory system.
Methods and rules for treating illness, illness
Any therapy begins with finding out the causes of the disease. Sometimes it is enough to eliminate the provoking factor and pancreatitis will subside. Separately, congenital anomalies should be touched upon - this requires medical supervision of the child for many years.
One of the main reasons for the progression of inflammatory processes in the pancreas in adolescents is malnutrition - schoolchildren's pancreatitis. The main thing in the treatment of such a pathology will be a strict diet.
Nutrition for pancreatitis in children
Diet is an essential component of therapy. You need to know what to feed and what products to buy. It will help eliminate problems in all organs of the abdominal cavity and the pancreas as well.
Basic nutrition rules:
- fractional meals - 5-7 times a day in small portions;
- refusal of unhealthy foods: fast food, fizzy drinks, fatty, fried, salty, spicy, preservatives;
- a balanced diet, which includes various cereals, pasta, dairy products, lean meat and fish, vegetables and fruits;
- predominance of boiled and steamed food;
- eating not hot, but only warm food;
- fresh food for cooking.
Drug treatment
The diet will help reduce the load on the digestive organs. In addition, the doctor prescribes enzyme preparations that improve the digestion process:
- "Creon."
- "Festal".
- "Mezim forte."
These medications are taken with meals. Children may also be prescribed medications containing bifidobacteria, for example, Bifacil.
To alleviate the patient's condition, the following is prescribed:
- Pirenzepine, Famotidine.
- Pancreatin.
- No-spa, Mebeverine, children's Paracetamol.
In more severe cases, antibiotics are prescribed; antihistamines; drugs that help improve blood microcirculation; protease inhibitors.
Important!
Treatment comes down to following simple measures, the main thing is that the child understands the importance of these actions - this will benefit him not only now, but will also allow him to live fully in the future
What to do with very young children
If the disease is diagnosed in a very young patient, the nutritional rules will be as follows:
- predominance of protein foods;
- cooking any porridge with water;
- vegetables and fruits should be heat treated.
Sometimes surgical intervention is necessary, for example, in cases where there are congenital anomalies in the pancreas. The decision to undergo surgery is made after a comprehensive examination and only if there are no results from conservative therapy.
Treatment of pancreatitis in children is often performed in a hospital setting. Only here doctors will be able not only to treat the baby, but also to monitor his nutrition, observing the dynamics of therapy.
Traditional methods of treatment
From time immemorial, potato juice has been considered one of the effective methods of treating pancreatitis. You need to grate 2-3 potatoes along with the peel and squeeze out the juice. Directions for use: 50 ml 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. Then a week break and repeat the course. An excellent addition to kefir is low-fat kefir, which is consumed 5-10 minutes after taking the main product.
Important!
Regular honey can protect you from many diseases. If the child does not have an individual intolerance to this product or diabetes, a good habit would be to eat 1 tsp. honey in the morning, diluted in milk or water.
It is necessary to take St. John's wort, motherwort, and immortelle inflorescences in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. Boil the collection for 10–15 minutes in 1 liter of water, let the broth brew for 2 hours, strain. The course of administration is 50 days, half a glass before meals.
A complex but very effective collection. You should take equal proportions of dry burdock root, buckthorn bark, plantain, blueberry leaves, dill and flaxseeds. Add dandelion root, knotweed and sage. The preparation method is identical to the previous remedy - for 1 liter of water, 2 tbsp. collection, boil for 10–15 minutes. The course of administration is 14–20 days, half a glass after meals.
Important!Any treatment methods for very young patients must be agreed with a doctor, otherwise self-medication can lead to irreversible consequences.
Diet
For diseases of the pancreas, gentle nutrition is prescribed, which corresponds to the fifth dietary table. Basic rules that must be followed in the patient’s diet:
- Portions should be small. It is recommended to eat 4-5 times a day. This reduces the load on the digestive organs and also ensures regular outflow of bile.
- Meals should be rich in vitamins and fully satisfy protein and carbohydrate needs. It is recommended to consume fats of plant origin, and their total amount in the diet should be reduced.
- The method of cooking and the temperature of the food are important. Preference is given to boiling and baking. If possible, the finished dish should be pureed. It is optimal to take warm food, and exclude cold and hot dishes, so as not to irritate the pancreas.
- Vegetables and fruits should be eaten daily; you can prepare stews from them.
- Warm soup or low-fat broth is well received by the pancreas. It is allowed to cook them from kritsa, lean pork or fish.
Detailed list of products for inflammation of the pancreas
When choosing products for cooking, you can rely on the following table:
| Forbidden | Allowed |
| Sweet products, creams | Natural sweets, dried bread, jam, honey, crackers, marshmallows |
| Fried, smoked, spicy | Chicken, lean fish |
| Legumes, all mushrooms | Low-fat lactic acid products |
| Sorrel, onion, garlic, radish | Porridge cooked in water |
| Carbonated drinks, alcohol | Dried fruit compote, jelly, sweet tea |
Diet for pancreatitis
Below is a menu with which you can provide yourself with a complete and varied diet:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Semolina porridge with apple and green tea; rice porridge with orange; oatmeal and jelly; rice porridge with crackers; barley porridge with honey | Pumpkin puree; baked apple; cottage cheese with honey and tea; steam cutlet and rosehip infusion; grated apple with cottage cheese and biscuits | Vegetable broth with boiled meat, crackers; carrot soup with other vegetables and meatballs, compote; vegetable puree soup, meatballs; low-fat steamed fish, mashed potatoes; rabbit cutlets, stew | Low-fat cottage cheese with fruit; low-fat yogurt with crackers, honey and apple; steam omelette; cottage cheese casserole; baked apple | Beef cutlet, compote; potato casserole with minced meat, jelly; baked fish with vegetables; mashed potatoes, steamed fish; vegetable casserole, boiled chicken |
On a note! At the end of the acute period, the patient can eat quite varied, the main thing is a gentle cooking regime.
Video - Diet No. 5 according to Pevzner
Symptoms of pain in the pancreas and how to get rid of them
When pain occurs in the pancreas, you need to know what to do to relieve the syndrome and try to find out the cause. Since pain symptoms can be caused by other diseases, you need to carefully study the symptoms of the disease, and in the best case, consult a doctor.
The symptoms of acute and chronic inflammation of the pancreas are significantly different, and the clinical picture of the course also has its own characteristics. The symptoms of chronic pancreatitis are not clearly expressed, but as for the acute type of inflammatory process of the gland, the attack is pronounced and carries possible severe complications of a person’s health.
In the acute phase, only calling an ambulance and hospitalization with a strict diet will prevent the development of pathologies of other organs and the appearance of necrosis of pancreatic tissue. Often, during remission of the disease, after treatment with hunger, the pancreas is restored and treated using folk methods and means.
propolis to eliminate nausea
To eliminate nausea, pain and other symptoms of pancreatitis, it is recommended to use propolis. The pure product (propolis) is chewed when signs of exacerbation occur. The product relieves the inflammatory process and heals open internal wounds well, restoring the functioning of the gland.
raisins for compote will help with indigestion
And also with pancreatitis, the main symptom and manifestation is diarrhea and intestinal upset. These symptoms are well removed by fresh raisin compote. Take 4-5 sips until diarrhea completely stops.
A decoction of burdock root will help restore pancreatic function.
Decoctions of medicinal herbs are widely used. Brewed burdock roots bring good benefits. To prepare, take 2 tablespoons of roots and pour 300 ml of boiling water. Take 50 ml 3-4 times a day in between meals. Within a month, the symptoms go away and the functioning of the pancreas is restored.
oatmeal jelly for pancreatic self-healing
Eat oatmeal jelly. This remedy, in addition to quenching thirst for hunger, brings benefits with its properties. Envelops the walls of the stomach, pancreas, and intestines, which provides a kind of respite and the possibility of self-healing.
How does the pancreas hurt during acute pancreatitis?
Pain in the pancreas is a sign of developing pancreatitis. The disease itself has two forms of development, acute and chronic. In acute inflammation, it passes abruptly and provokes the very digestion of the pancreatic organ. In this situation, timely access to a hospital will bring the possibility of quick treatment. In a different scenario, there are consequences and death. What symptoms of pain in the pancreas indicate developing acute pancreatitis of the pancreas:
- gagging, severe vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- severe cutting pain moves from the stomach to the back.
hospital treatment for acute pancreatitis
Treatment in a hospital, where the patient will be under round-the-clock supervision, and constant diagnostics will ensure timely stopping of the development of the disease. This pathology leads to a latent form of diabetes mellitus, so it is necessary to carry out a full diagnosis and treatment in hospital.
How does chronic pancreatitis hurt?
Pain in the pancreas with chronic pancreatitis, also with its own characteristics. How to relieve pain in the pancreas, what are the symptoms of this pathology?
Chronic disease is a gradually progressive process. The variability of the pain state, from a severe attack to a smooth progression and mitigation of symptoms, does not create a very pleasant clinical picture. In this type of disease, the pancreas develops both in the tail of the pancreas and in the head of the gland.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis:
- inflammation of the head of the gland - pain in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region;
- if the source of inflammation is in the tail, the left hypochondrium hurts;
- if the entire pancreatic organ is affected, then the pain is encircling, radiating to the back and the left scapular part of the body;
- There is also a shooting pain in the groin, in the tailbone, and radiates to the thigh.
To fully diagnose the disease, tests are necessary. Since, the inconstancy of pain and jumps in pain symptoms roll from a strong cutting syndrome to a constantly aching one, which corresponds to an acute attack of pancreatitis.
Signs and causes of illness in a child
Enlargement of the tail of the pancreas (or head) can also be diagnosed in a child. Symptoms of damage:
- Painful sensations in the upper abdomen.
- Fever (during the acute period).
Increased pain in the abdominal area is observed in the chronic form of the disease.
The disease also affects infants. Causes of the condition:
- low body resistance to microbes;
- weak immunity;
- insufficient and unbalanced nutrition;
- lack of physical activity;
- non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards of maintenance.
All this negatively affects not only the health, but also the overall development of the baby.
Sometimes ultrasound shows diffuse (or uniform) changes in the organ. This pathology of the gland has the following causes:
- food poisoning;
- getting injured;
- excessive physical activity;
- excessive pill intake;
- hereditary diseases;
- eating fatty and fried foods;
- non-compliance with diet.
Important information: What you can and cannot eat when your pancreas hurts
Such changes are a cause for concern for parents, because inflammation of the pancreas can lead to liver disease, which, together with the organ in question, is important for human life.
When the echogenicity of the entire gland increases
A diffuse change in the permeability of pancreatic tissue to ultrasound can be a symptom of pathology, but can also be observed normally. This cannot be said about foci with increased echogenicity - this is almost always a pathology.
The gland has normal dimensions, but its echogenicity is increased (this can be seen in the two-dimensional graph that displays the density of the liver)The echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is increased in the following pathologies:
- Glandular lipomatosis, when glandular tissue is replaced by fat cells containing almost no intracellular fluid; however, the size of the pancreas is not increased. This condition is most often asymptomatic. Read more about this disease in the article: How to recognize and treat pancreatic lipomatosis in time?
- Swelling of the gland that develops with acute pancreatitis. Accompanied by abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting.
- Organ tumor. If the ultrasound describes the pancreas with increased echogenicity, then there are necessarily symptoms of the disease: weight loss, pallor, weakness, lack of appetite, frequent bowel movements.
- Pancreatic necrosis, accompanied by the death of organ cells, will also appear on ultrasound as a lighter area. This disease has such signs as severe abdominal pain (up to the development of painful shock), disturbance of the general condition, uncontrollable vomiting, and diarrhea.
- As a result of diabetes mellitus, which is manifested by thirst in the absence of hot conditions, elevated temperature, active work, as well as frequent and abundant (including night) urination.
- Development of connective tissue in the gland (fibrosis) - usually as a result of inflammation or metabolic disorders. In this case, a person may remember cases of unstable stool and abdominal pain. Ultrasound shows not only an increase in echogenicity, but also a decrease in the size of the gland and the tuberosity of its contours.
The hyperechoic pancreas can also be a temporary phenomenon, manifested by:
- as a result of reactive inflammation in many infectious diseases: influenza, pneumonia, meningococcal infection. This requires treatment of the underlying disease;
- when changing the type of food consumed;
- after a lifestyle change;
- at certain times of the year (usually spring and autumn);
- after a recent heavy meal.
In such temporary conditions, the echogenicity of the pancreas is moderately increased, in contrast to pathologies, when significant hyperechogenicity is noted.
Local increase in echogenicity
Fatty inclusions in the pancreatic tissue will appear hyperechoic
What are hyperechoic inclusions in the pancreas? It can be:
- pseudocysts - liquid formations that develop as a result of acute pancreatitis; with this disease, the contour of the pancreas becomes uneven, jagged, hyperechoic;
- calcification of tissue areas - calcifications; they are also formed as a result of inflammation (usually chronic);
- areas of adipose tissue; they replace normal gland cells in case of obesity and excessive consumption of fatty foods;
- fibrous areas - where areas of normal cells have been replaced by scar tissue; usually this occurs as a result of pancreatic necrosis;
- stones in the gland ducts;
- fibrocystic degeneration of the gland is either an independent disease or an outcome of chronic pancreatitis;
- metastatic tumors.
Diagnostics
A correct diagnosis can only be made using instrumental diagnostic methods. However, before prescribing them, the gastroenterologist must personally perform several manipulations, including:
- a detailed survey of the patient or his parents - to obtain information regarding the first time and severity of symptoms;
- familiarization with the patient’s medical history and life history to identify the possible cause of pancreatic enlargement;
- a thorough physical examination - involves palpation of the entire surface of the abdomen, examination of the condition of the skin and sclera, and measurement of temperature.
The main instrumental examination is ultrasound - using this method it is possible to diagnose a total change in the volume of the pancreas, to reveal that the tail of the pancreas or the head of this organ is enlarged. In addition, such a diagnostic measure will make it possible to detect pseudocysts, stones and neoplasms that can become a source of pathology. An alternative to ultrasound is CT and MRI.
Laboratory tests of blood, urine and stool may be required to determine the root cause of organ enlargement.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
Methods and rules for treating illness, illness
Any therapy begins with finding out the causes of the disease. Sometimes it is enough to eliminate the provoking factor and pancreatitis will subside. Separately, congenital anomalies should be touched upon - this requires medical supervision of the child for many years.
One of the main reasons for the progression of inflammatory processes in the pancreas in adolescents is malnutrition - schoolchildren's pancreatitis. The main thing in the treatment of such a pathology will be a strict diet.
Nutrition for pancreatitis in children
Diet is an essential component of therapy. You need to know what to feed and what products to buy. It will help eliminate problems in all organs of the abdominal cavity and the pancreas as well.
Basic nutrition rules:
- fractional meals - 5-7 times a day in small portions;
- refusal of unhealthy foods: fast food, fizzy drinks, fatty, fried, salty, spicy, preservatives;
- a balanced diet, which includes various cereals, pasta, dairy products, lean meat and fish, vegetables and fruits;
- predominance of boiled and steamed food;
- eating not hot, but only warm food;
- fresh food for cooking.
Drug treatment
The diet will help reduce the load on the digestive organs. In addition, the doctor prescribes enzyme preparations that improve the digestion process:
- "Creon."
- "Festal".
- "Mezim forte."
These medications are taken with meals. Children may also be prescribed medications containing bifidobacteria, for example, Bifacil.
To alleviate the patient's condition, the following is prescribed:
- Pirenzepine, Famotidine.
- Pancreatin.
- No-spa, Mebeverine, children's Paracetamol.
In more severe cases, antibiotics are prescribed; antihistamines; drugs that help improve blood microcirculation; protease inhibitors.
Important!
Treatment comes down to following simple measures, the main thing is that the child understands the importance of these actions - this will benefit him not only now, but will also allow him to live fully in the future
What to do with very young children
If the disease is diagnosed in a very young patient, the nutritional rules will be as follows:
- predominance of protein foods;
- cooking any porridge with water;
- vegetables and fruits should be heat treated.
Sometimes surgical intervention is necessary, for example, in cases where there are congenital anomalies in the pancreas. The decision to undergo surgery is made after a comprehensive examination and only if there are no results from conservative therapy.
Treatment of pancreatitis in children is often performed in a hospital setting. Only here doctors will be able not only to treat the baby, but also to monitor his nutrition, observing the dynamics of therapy.
Traditional methods of treatment
From time immemorial, potato juice has been considered one of the effective methods of treating pancreatitis. You need to grate 2-3 potatoes along with the peel and squeeze out the juice. Directions for use: 50 ml 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. Then a week break and repeat the course. An excellent addition to kefir is low-fat kefir, which is consumed 5-10 minutes after taking the main product.
Important!
Regular honey can protect you from many diseases. If the child does not have an individual intolerance to this product or diabetes, a good habit would be to eat 1 tsp. honey in the morning, diluted in milk or water.
It is necessary to take St. John's wort, motherwort, and immortelle inflorescences in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. Boil the collection for 10–15 minutes in 1 liter of water, let the broth brew for 2 hours, strain. The course of administration is 50 days, half a glass before meals.
A complex but very effective collection. You should take equal proportions of dry burdock root, buckthorn bark, plantain, blueberry leaves, dill and flaxseeds. Add dandelion root, knotweed and sage. The preparation method is identical to the previous remedy - for 1 liter of water, 2 tbsp. collection, boil for 10–15 minutes. The course of administration is 14–20 days, half a glass after meals.
Important!
Any treatment methods for very young patients must be agreed with a doctor, otherwise self-medication can lead to irreversible consequences.
Consequences of diseases
If pathologies are detected in the pancreas, treatment is recommended to begin immediately. Delayed therapy leads to deterioration of the patient's condition, even death. Due to organ dysfunction, disturbances of all types of metabolism in the body (carbohydrate, fat and protein) occur, as well as endocrine disruptions. An enlarged pancreas can subsequently cause:
- Pancreatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Pancreatic necrosis.
- Purulent processes, release of toxins into the blood.
- Benign formations.
- Pathologies of the hepatobiliary apparatus.
- Acetonemic syndrome (especially in children).
Pathogenesis of pancreatitis
Patients should remember that after completing the course of treatment, food restrictions must still be observed. For many people, dietary table No. 5 is the basis of nutrition for the rest of their lives. The pancreas is an organ that is difficult to treat, and surgery and resection are quite dangerous and do not always lead to recovery.
Anyone can avoid problems with the pancreas in the absence of congenital pathologies. To do this, you need to adjust your lifestyle and pay great attention to proper nutrition. Following a diet, eliminating alcohol and spicy foods will help prevent serious pathologies and maintain health for many years.
Why is it necessary to screen children?
Children's problems associated with the enlargement of this organ are in many ways similar to those that affect adults. Children of any age must be carefully examined in order to promptly identify such pathology. This is explained by the fact that the gland can grow several times, but not always proportionally.
Quite often it happens that the growth of an organ does not always correspond to accepted standards, but in relation to other organs it will be proportional. In this case, it is in childhood that congenital malformations of the pancreas and its enlargement are first diagnosed.
Reasons for local increase
The structure of the pancreas is divided into three conventional parts: head (beginning), body (middle) and tail (end). Depending on the location of the pathological process, doctors may suspect different diseases.
Pancreas image
An increase in a separate part of the secretory organ may indicate the presence of the following conditions:
- Pseudocyst.
- Abscess.
- Benign tumor.
- Malignant formation.
- Presence of stones.
- Duodenitis with inflammation of the intestinal papilla.
On a note! Local enlargement of the middle part of the organ is much less common than the head or tail.
The structure of the pancreas
Treatment
The treatment of the pancreatic organ, as well as the diagnosis of its pathologies, is approached in a comprehensive manner. The treatment process is based on the use of the following techniques:
- Taking medications;
- Diet therapy;
- Surgery;
- Phytotherapy.
Since the trigger mechanism for pathological processes is inflammatory damage to the organ, therapy is primarily aimed at stopping the inflammatory process.
For this purpose the following medications are prescribed:
- Antibiotics from the group of penicillins or cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and intestinal antiseptics such as Amoxiclav, Nifuroxazide, etc. The duration of therapy lasts about 2 weeks and only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve pain in the gland and stomach, such as Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Ketorol, etc.
- Painkillers such as antispasmodics, which effectively relieve spasms and relax muscles. Such drugs include No-shpu, Spazmalgon, Drotaverine, etc.
- Replacement therapy with enzyme preparations such as Mezim, Creon or Pancreatin.
If the clinical situation is severely advanced or the cause of the pancreatic pathology is a tumor, then surgical therapy is indicated.
Causes of the disease
The causes of the disease are: destruction of tissue structures, hereditary characteristics, the presence of a concomitant disease that was not identified and not treated immediately. These reasons can be in combination or separately.
Local enlargement is more dangerous, as opposed to a general change in the organ.
It often happens that with chronic or acute pancreatitis, not the entire gland enlarges, but parts of it - the tail, head or body. An enlarged tail of the pancreas can be due to the following conditions:
- the presence of a stone that blocks the additional duct of the gland;
- cystic adenoma;
- pseudocyst in this area;
- suppuration in the head of the pancreas;
- malignant tumor;
- duodenitis of the duodenum;
- tumor of the minor duodenal papilla;
- scar of the small intestinal papilla.
Manifestations of inflammation of the tail and head of the pancreas
Signs can be of a different nature and vary depending on the type, individual and degree of the disease.
Painful symptoms can be cutting and pulling in nature. The pain persists for a long time and is in no way related to food intake; it intensifies as the disease progresses. Often such pain is observed in the area of the heart or chest. In practice, there have been cases of death due to painful shock resulting from severe pain.
Dyspeptic signs include nausea, lack of appetite, vomiting, and unstable stool. These symptoms are especially characteristic for the initial stage of enlargement of the tail and head of the pancreas. The most striking confirmation of an increase in the size of the head is a change in skin color. It becomes pale or yellowish. The nasolabial area and fingers become bluish. This is an indicator of intoxication of the body with special enzymes. Possible increase in body temperature.
Laboratory methods detect changes in urine and blood tests.
Martingale and Anti-Martingale
Proper money management and an effective trading strategy is the Grail that all traders are looking for. By changing the size of the transaction, the trader receives advantages and regulates risks. However, the cost of error is high. These include monetary losses and psychological experiences.
The main ways to work with lots are adding decreases and rollovers.
There are other techniques. Today our topic continues with Martingale and Anti-Martingale. They are not straightforward, but they are popular as money management systems.
– The Martingale concept was invented for playing in casinos. Do you think a casino and an exchange are the same thing?
My answer is absolutely not. Roulette is a game with a known negative outcome. The casino will still win. Any other gambling also refers to games with a negative outcome.
Stock trading is something else. If your method is profitable, then in the medium term you will make money. The exchange and the casino have something in common – the psychology of the users.
An attempt to quickly recoup or get rich leads to the fact that a person loses money at a tremendous speed. An outwardly intelligent person can turn into a complete player both on the stock exchange and in the casino. In the market, the rules of the game are yours. In a casino you must play according to the rules of the casino.
– Can Martingale be used in stock trading?
– This approach has a right to exist. In order to use the method, you need to study the transactions that you carried out using your system. If a profitable transaction is followed by a losing one, and this is almost always the case, then this method can be justified.
– What can you say about Anti-Martingale? Can it be used in stock trading?
– There are trading systems in the world that are characterized by sequences of winning or losing closed positions. For such systems, it is reasonable to increase the position size after a win, and reduce it after a loss. This is called Anti-Martingale. Both Martingale and Anti-Martingale are successfully used in trading to reduce risks to an acceptable level.
We must not forget that Martingale and Anti-Martingale have disadvantages. Firstly. Martingale greatly increases risks.
Secondly, Anti-Martingale, of course, does not pose the danger of a counter method, however, it is also not flawless. Because as the account decreases due to losses, the ability to compensate for losses decreases. If the losses amounted to 20% of the account, then 25% of the profit is already needed to compensate. And a 50% loss requires 100% profit to ensure the recovery of the account.
Previous Forex for beginnersSimple formulas for determining a correction in Forex and approaches to working with it Next Forex IndicatorsPrinciples on which Gann indicators are built - Gann HiLo Activator
Symptoms
An enlarged pancreas is more often recognized during examination for other problems not related to digestion. The problem is recognized by several symptoms:
- Oily stool indicates that fats are not digested. Persistent diarrhea is one of the signs of disease.
- Unreasonable acceleration of heartbeat.
- Low-grade fever that lasts for a long time, without infection.
- Constant nausea indicates a problem with nutrient absorption.
One of the main manifestations is jaundice, which occurs from time to time. Inability to gain weight, as well as sudden weight loss, requires an ultrasound and examination by an endocrinologist.
Symptoms of pathology
Pronounced diffuse changes on sonography are visualized as uniform light, almost white, inclusions on a light gray background of the parenchyma. This indicates their high density and echogenicity. They are accompanied by symptoms of gland failure, which force the patient to see a doctor.
Depending on the duration of the process and the extent of damage to the parenchyma, dyspepsia, weight loss, anemia, and a violation of the general condition develop. With extensive changes in the parenchyma, the islets of Langerhans are involved in the pathological process with the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus. In such cases, a picture of diabetes develops: dry mouth, thirst, involvement of the nervous and cardiovascular systems in the process, and kidney damage. In the absence of diet and adequate treatment, the process progresses and becomes irreversible.
Symptoms of diffuse damage to the pancreas depend, first of all, on the underlying disease that caused the transformation of its tissues. Most often this is the result of developed pancreatitis. Pancreatic juice containing enzymes, during acute inflammation, stagnates in the ducts, not having access to the small intestine due to swelling of the pancreas. Enzymes under pressure enter the pancreas tissue, are activated not in the lumen of the small intestine, but in the parenchyma and increase inflammation: the process of autolysis occurs - self-digestion of organ tissue. This manifests itself in a pronounced clinical picture:
- pain of varying intensity and location,
- nausea,
- vomiting without feeling of relief,
- diarrhea,
- bloating.
Such symptoms of varying severity always accompany damage to pancreatic tissue. With chronic inflammation or other lesions, the manifestations are mild, but the main symptoms of dyspepsia are present. In severe cases, this is confirmed by pathological laboratory tests. In cases with moderate changes in the parenchyma, the main indicators may be within normal limits.
If the changes are caused by a neoplasm or infectious process, in addition to dyspepsia, signs of intoxication appear. Then there may be an increase in body temperature, headaches, dizziness, and poor sleep.
In all cases of changes during ultrasound, additional diagnostics are required
This is important for treatment tactics, which must be started as early as possible
Methods for diagnosing the disease
It is impossible to determine the enlargement of the pancreas during an objective examination: due to the retroperitoneal location, the iron cannot be palpated. The screening method is ultrasound examination (US). It is used to determine:
- sizes,
- clarity of boundaries,
- echogenicity (density) of tissues - increased or decreased,
- presence of formations,
- expansion of the common duct.
If necessary, the following is carried out:
- x-ray examination,
- CT (computed tomography) with the introduction of a contrast agent,
- endoscopic resonance cholangiopancreatography,
- magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
Additionally, EGD (esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy) is prescribed to study the condition of the stomach and duodenal bulb and pH-metry to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
Laboratory research methods include blood tests:
- general clinical,
- for sugar
- stress tests with carbohydrate breakfast, insulin,
- amylase,
- insulin during a spontaneous attack of insulinoma,
- glucagon,
- gastrin on an empty stomach.
All studies are recommended to be done only as prescribed by a specialist. Their volume necessary to verify the diagnosis is determined by the doctor. He also analyzes what the test results may mean and, if necessary, prescribes medications that can be used to treat the identified pathology.
First aid when identifying signs of disease
You must begin fasting for at least 24 hours. Be sure to drink a lot of mineral water with a high content of alkalis. To relieve pain, apply ice on the left side just above the navel. Only a doctor prescribes tablets. But to relieve spasm and severe pain, you can drink Papaverine or No-shpa and immediately call a doctor at home. If the pain is acute, seek emergency help. Other medications should not be taken unless prescribed by a specialist.
It is important to know that pain appears for a reason; it warns of possible tissue necrosis. Signs of cancer can also begin with severe pain. This may result in complete removal of the organ.
The function of the pancreas is extremely important. If pain occurs in the corresponding place, you should immediately consult a doctor, since a malfunction of this organ can lead to irreversible changes in the body.