Changing the concentration of certain substances in the body makes it possible to assess the state of health. One of the extremely important enzymes is elastase. Its synthesis occurs in the pancreas. Pancreatic elastase in feces is an important indicator that helps identify disruptions in the functioning of this organ.
What is elastase
A person eats a considerable amount of food every day, which the gastrointestinal tract is designed to digest. In order for this process to be carried out properly, the body produces a huge amount of substances.
These enzymes help break down food. They are synthesized by more than one organ. An important function in this case is performed by the pancreas.
Pancreatic juice consists of a number of enzymes. Among them is elastase. It is necessary so that the protein entering the body is fully broken down.
With a deficiency of this substance, the process of digesting protein foods is disrupted, and various diseases begin to develop.
The enzyme is produced from birth and continues to be produced throughout life. When its concentration decreases, the functioning of the pancreas is disrupted. Elevated rates also indicate serious violations.
Elastase enzyme description
The digestive system cannot do without the pancreas. It is this organ that produces very important enzymes that are necessary for the normal functioning of the body as a whole.
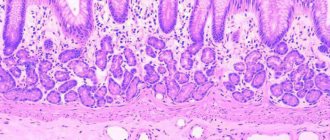
Elastase is a pancreatic enzyme. It is contained in the feces of a healthy person from birth. This enzyme helps break down proteins during digestion. If there are any disorders of the pancreas, this indicator is detected in too low a concentration. This indicates progressive pancreatitis, which is a serious disease that is difficult to treat.
If you see one of these names, you can be sure that we are talking about this very enzyme, which is indispensable in the metabolic processes of the human body.
Indications for testing
A stool test for elastase is prescribed in certain situations.
Namely when:
- pain while eating;
- when there is chronic pancreatitis;
- fibrosis;
- chronic pancreatic insufficiency;
- Crohn's disease;
- malignant, benign formations or suspicions of their presence;
- abdominal injuries that can affect the functioning of the organ;
- a syndrome that develops in people as a result of removal of the gallbladder;
- rapid weight loss;
- there is a suspicion of the onset of the development of cystic fibrosis;
- dyspeptic symptoms in chronic form;
- prolonged, causeless diarrhea.
Study preparation and execution
Biological material for examining a patient for pancreatic elastase is feces. Recommended volume for analysis is 5-10 g.
Since the enzyme is associated with food intake, the results of the analysis directly depend on what the person took. Therefore, preparation is necessary before donating stool. Three days before the study, you need to stop taking medications based on oils (laxatives), pilocarpine (increases the secretion of the digestive glands, increases the tone of the intestinal walls), belladonna (relaxes the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract).
To obtain accurate readings, you should not do cleansing or medicinal enemas before taking the test. X-ray examinations using a contrast agent (barium) are contraindicated.
It is best to perform a stool test for pancreatic elastase in the first half of the day. On the morning of the test, collect the stool in a clean plastic or glass container using a spatula, sign it with your information, and send it to the laboratory. You can collect the evening portion of feces and put it in the refrigerator overnight.
To determine the quantitative content of elastase in feces, an immunological research method is used. It is based on the antibody-antigen reaction. The standard scatological test includes monoclonal bodies that immediately recognize the pancreatic enzyme. This method is a priority because it has high sensitivity and specificity.
This means that the test:
- accurately determines chronic secretory elastase deficiency;
- in 93% of cases it registers chronic pathology of the pancreas;
- detects the disease at the initial stage with mild and moderate forms of the course.
Changing the activity of pancreatic elastase is a very slow process. Its study is carried out no more than 1-2 times a year, since significant changes in indicators will not occur during this period.
What pathologies are detected
Stool examination helps identify many diseases that develop as a result of the following changes:
- inflammatory processes affecting organ tissue;
- disruption of the process of juice outflow;
- parenchymal tissue is gradually destroyed;
- congenital diseases of the organ ducts.
This research method allows you to diagnose a number of conditions and pathologies:
- chronic pancreatitis;
- hepatitis, regardless of its type;
- cholelithiasis, characterized by the formation of stones in the area of the gallbladder and its ducts;
- characteristics of the body, manifested in non-acceptance of lactose;
- cystic fibrosis;
- Crohn's disease;
- cancer.
Coprological elastase
Human pancreatic elastase is one of the pancreatic enzymes found in pancreatic and duodenal juice and belongs to the acid elastase family. The determination of coprological elastase is used to assess the exocrine function of the pancreas. A decrease in its activity is detected in patients with chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and in children with cystic fibrosis, which reflects the insufficiency of the exocrine function of the pancreas in these groups of patients.
Synonyms Russian
CE-1, elastase-1 in feces; pancreatic elastase-1.
Research method
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Units
μg/g (micrograms per gram).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Cal.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Avoid taking laxatives, administering rectal suppositories, oils, limit (in consultation with your doctor) taking medications that affect intestinal motility (belladonna, pilocarpine, etc.) and drugs that affect the color of stool (iron, bismuth, barium sulfate), within 72 hours before stool collection.
General information about the study
In medical practice, determining the amount of elastase-1 in feces, taking into account clinical manifestations, is used to diagnose exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
The study is recommended to be carried out when examining patients with suspected diabetes mellitus (secondary diabetes mellitus due to exocrine pancreatic dysfunction is much more common than previously thought, the results of numerous studies prove that low levels of pancreatic elastase significantly affect the ability to control blood glucose levels); cholelithiasis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, osteoporosis (a third of patients suffering from osteoporosis have a decrease in the level of pancreatic elastase and vitamin D), involutive (age-related) changes in the pancreas, in patients with cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases .
Measuring the amount of pancreatic elastase is a simple, non-invasive way to assess pancreatic function, allowing you to diagnose exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (sensitivity of the method from 90 to 100%, specificity from 93 to 98%). The sensitivity of the method is lower in cases of mild pancreatic insufficiency, but in cases of moderate and severe pancreatic dysfunction it reaches 100%.
Pancreatic elastase is a specific protein produced by the pancreas. It is secreted into the duodenum, where it participates in the digestion process. The lack of this protein causes a number of physiological disorders. Determination of the amount of pancreatic elastase-1 in stool is used to assess the ability of the pancreas to produce digestive enzymes (exocrine function).
Elastase belongs to the family of proteases, is an endoprotease (breaks down previously modified protein molecules), participates in the digestion process, breaking down other proteins. The enzyme originally called pancreatic elastase turned out to be another type of elastase, not specific to the pancreas. This term is still used by clinicians, but in fact this enzyme is part of the chymotrypsin-like elastase family. In the medical literature, this enzyme is often called coprological elastase.
Symptoms of pancreatic insufficiency may include bloating, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, undigested dietary fiber in the stool, low acidity, symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux, and intolerance to certain types of food.
Detection of insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function and its correction in the early stages allows one to avoid pronounced metabolic changes in the body associated with inadequate nutrition. Malabsorption (malabsorption) of fats and proteins is usually accompanied by a deficiency of vitamins (especially fat-soluble ones - A, D, E, K) and essential microelements. With concomitant exocrine pancreatic dysfunction, patients with diabetes find it more difficult to control blood glucose levels within target limits.
What is the research used for?
- Examination of patients with suspected pancreatic dysfunction;
- differential diagnosis with other causes of chronic diarrhea;
- preventive examination of healthy people.
When is the study scheduled?
- If diabetes mellitus, cholelithiasis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, stenosis of the major duodenal papilla, malignant neoplasms of the pancreas, osteoporosis, involutive (age-related) changes in the pancreas, cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, malabsorption in autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases are suspected.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: > 200.00 µg/g.
If the level of coprological elastase in feces is within the reference values, then there is no insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function.
A decrease in values in the range from 100 to 200 mcg/g of feces indicates moderate insufficiency, and less than 100 mcg/g of feces is characteristic of severe pancreatic insufficiency.
What can influence the result?
- A pronounced comorbid background (the presence of concomitant pathologies) may reduce the specificity of the method and require targeted differential diagnosis.
Important Notes
- With concomitant exocrine pancreatic dysfunction, patients with diabetes find it more difficult to control blood glucose levels within target limits.
Also recommended
- [06-006] Serum total amylase
- [02-009] Pancreatic amylase
- [08-042] Coprogram
- [08-006] Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
- [06-050] C-reactive protein, quantitative (high sensitivity method)
- [13-020] Rheumatoid factor
- [13-015] Antibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA), screening
Who orders the study?
Gastroenterologist, pediatrician, therapist, general practitioner.
Literature
- J. Walkowiak, S. Nousia-Arvanitakis, J. Henker, S. Stern, M. Sinaasappel, J. A. Dodge Indirect pancreatic function tests in children // J. Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 40 (2) (2005), pp. 107–114.
- J. Balo, J. Banga The elastolytic activity of pancreatic extracts // Biochem J, 46 (1950), pp. 384–387.
- A. Sziegoleit, D. Linder Studies on the sterol-binding capacity of human pancreatic elastase // Gastroenterology, 100 (1991), p. 768.
- J. Stein, M. Jung, A. Sziegoleit, Zeuzem, W. F. Caspary, B. Lembcke Immunoreactive elastase-1: clinical evaluation of a new noninvasive test of pancreatic function // Clin Chem, 42 (1996), pp. 222–226.
- A. Hamwi, M. Vietl, G. Maenner, H. Vogelsang, T. Szekeres Pancreatic elastase 1 in stool: variations within one stool passage and individual changes from day to day // Wein Klin Wochenschr, 112 (1) (2000) , pp. 32–35.
- Y. Miendje, D. Maisin, M. J. Sipewa, P. Deprez, J. P. Buts, P. De Nayer et al. Polyclonal versus monoclonal ELISA for the determination of fecal elastase 1: diagnostic value in cystic fibrosis and chronic pancreatic insufficiency // Clin Lab, 50 (7–8) (2004), pp. 419–424.
Preparing for the study
Preparation for analysis involves eliminating the following manipulations several days before the procedure:
- stopping taking medications that stimulate intestinal motility;
- stopping the use of rectal suppositories;
- avoiding the use of laxatives;
- stopping the use of medications that have a fixative effect;
- refusal to douche and use enemas;
- minimal consumption of foods that put stress on the organ.
Material that was collected during the period of critical days and after irrigography is not suitable for research.
Preparation
The study of elastase concentration does not require special preparation. The patient does not need to follow a strict diet or stop treatment with enzyme preparations, since substances of animal origin do not affect the result of scatological analysis. The list of drugs that must be excluded before taking biomaterial is quite small.
When to stop taking medications before getting tested?
3-4 days before the elastase test, you must stop taking medications such as:
- laxatives, including petroleum jelly and castor oil;
- medications that affect intestinal contractions (Belladonna, Pilocarpine, etc.);
- rectal suppositories and ointments;
- other medications that affect the secretory ability of the pancreas.
It is advisable to limit the consumption of fatty, fried, smoked, spicy and overly salty foods. It is prohibited to take biomaterial after an enema and irrigoscopy. Preparations of bismuth, barium and magnesium sharply reduce the diagnostic value of the analysis.
Rules for collecting material
To get tested, it is enough to collect only a gram of feces, but it is recommended to send at least ten grams of material for testing.
Before performing basic manipulations, you need to urinate and be sure to wash your perineum.
You need to collect feces immediately after completing the bowel movement. In this case, a special container is used, which is filled to a third. Immediately after this, it is closed with a lid.
It is recommended to send the material to the laboratory without delay. It can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than six hours.
Stool analysis for elastase preparation and collection of material
To find out about the elastase content, you need to take a stool test.
This will give an idea of whether the pancreas is functioning properly and whether it is producing the necessary enzymes in the quantities that are optimal for normal digestion. The test can be taken at any clinic. Before taking the test, you must visit a doctor. The patient should not stop taking medications if he is undergoing any therapy. You must collect the feces yourself in a plastic container. It can be purchased at any pharmacy or hospital
Containers for urine and feces differ, you need to pay attention to this, since in the second case there is a special spatula inside for collecting material, which facilitates the procedure
The container must be filled to 1/3 of its volume. In this case, you need to wash yourself and ensure that genital secretions and urine do not get into the biomaterial. Feces can be collected in the morning or evening and then stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2 to 6 degrees. Under favorable conditions, enzymes remain unchanged for quite a long time, so you can rest assured that the results are correct. The laboratory performs an enzyme immunoassay, which gives a complete picture of the content and quantity of enzymes in the stool.
This test is so important because elastase levels in stool are not affected by gender, age, medications, or other conditions that typically confound the results of other tests. The biomaterial can be preserved for a long time, while the enzymes do not lose their properties. It is elastase that is not able to change in the colon, unlike other pancreatic enzymes, so this study is actively used by doctors.
Features of decoding results
Interpretation of the results should be carried out exclusively by a doctor. Only he can determine with maximum accuracy what the elastase level shows.
Deviations up or down do not in all cases signal the development of pathologies. Therefore, self-diagnosis is strictly prohibited.
After receiving data from the laboratory, you need to come to an appointment with a specialist.
Types of Elastase
Elastase is of two types: in feces, or pancreatic (No. 1) and in the blood, or serum (No. 2). Descriptions of both are presented in the table.
| View | Description |
| №1 | Produced exclusively in pancreatic cells, it passes into the intestines, where, combining with trypsin, it breaks down protein. |
| №2 | Produced by the pancreas during inflammation. Penetrates into the blood. Detected by a blood test. It can persist in the blood for a long time (up to seven days) and is quickly produced after illness (concentration increases within 6 hours). |
Fecal elastase, like all pancreatic enzymes, begins to be released after exposure to food (smell, taste, sight) or distension of the intestine.
Serum elastase is suppressed by blood components called inhibitors. During normal functioning of the pancreas, this type of active elastase is not observed in the plasma.
High levels of elastase are usually accompanied by weight loss, flatulence and diarrhea, weakening of bones, anemia, low performance, and pain. A low level is manifested by constipation, color transformations of feces, changes in the structure of feces (foam, pieces of food, blood and mucus), girdle pain, nausea and vomiting, the smell of rotten eggs from feces and from the mouth.
The level of serum elastase is determined by blood test results
Increased rate
Concomitant symptoms of intense organ activity, in which elastase is increased, are the following:
- cutting pain syndrome localized in the abdominal area;
- paleness of the skin;
- sudden weight loss;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- feeling of weakness.
Similar clinical manifestations are characteristic of the following pathologies:
- cholelithiasis;
- oncology;
- pancreatitis.
The following reasons can provoke an increase in enzyme levels:
- congenital disruption of cell activity and their gradual replacement with connective tissue;
- inflammatory processes;
- blocked ducts;
- destruction of secretory cells of the organ.
Serum elastase
To clarify the diagnosis, if there is a suspected pathology of the pancreas or digestive organs with severe pain in a child or adult, a blood serum test for elastase is performed. There are:
- Pancreatic elastase 1 is an enzyme with a molecular weight of 30,000, which is synthesized by the pancreas into the blood, where it circulates freely. If there is a lot of elastase, it is inhibited by proteins, but continues to move freely through the bloodstream in an already bound state.
- Pancreatic elastase 2 - with a low molecular weight of 25,000. Such an enzyme can indicate the degree of damage to the kidneys (nephritis), joints (arthritis) or talk about emphysema.
- In both cases, to confirm the diagnosis, an additional test is prescribed for pancreatic lipase, which is responsible for the breakdown of fats and their derivatives. All together presupposes the correct interpretation of test results.
Reduced rate
Exocrine organ deficiency can be due to various reasons.
As a rule, a decrease in the concentration of a substance is accompanied by additional symptoms:
- constipation;
- feces become yellow in color;
- bowel movements with the presence of foam and undigested food residues are observed;
- feces acquire a putrid, sour aroma;
- pain localized in the epigastric region;
- gagging and nausea;
- after the end of the defecation process, blood and mucus are discharged from the anus.
The following pathologies can provoke such changes:
- oncology;
- inflammatory processes localized in the intestinal cavity;
- blocked ducts;
- cystic fibrosis;
- diabetes;
- hepatitis.
Pancreatic elastase in feces is normal in adults with chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatic elastase is present in the body of every person literally from birth. A deficiency of this enzyme in the body can lead to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and the development of pancreatitis.
A stool test for elastase is recommended for everyone, regardless of age or gender, as well as the current state of health; a timely study can prevent problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Elastase (coprological elastase, Pancreatopeptidase E) is one of the few enzymes in the human body that does not change when passing through the intestines.
Therefore, by analyzing stool for pancreatic elastase, it is possible to assess the current state of the pancreas, the main function of which is the synthesis of most enzymes that enter the intestines along with pancreatic juice.
The task of elastase is to break down protein, elastic and other proteins that a person receives with food.
Elastin has, in fact, only one analogue - collagen. However, collagen is found exclusively in foods of animal origin, while elastin is found in animal and plant products. Regular consumption of foods containing this enzyme has a good effect on the skin, hair, and gastrointestinal tract.
Elastase will be present in feces in children and adults in any case. The question is whether a person’s body produces enough enzyme or whether it is less than normal. If the value is increased or decreased, you should consult your doctor and take appropriate action.
You can get tested for pancreatic elastase at any diagnostic center, since this test is included in the list of standard tests.
How to get tested?
Human feces do not require special preparation before delivery. It consists of collecting samples and submitting them for research. A referral for an elastase enzyme test can be issued by a surgeon or gastroenterologist after consultation and appropriate examination.
The following symptoms may be a sign that you should get tested:
- painful, unpleasant and bright sensations in the abdominal area,
- girdling and concentrated pain,
- stool takes on a yellowish tint,
- the whites of the eyes and skin turn yellow,
- there are suspicions after an ultrasound (inflammation of the pancreas).
The stool must be submitted for special examination to a diagnostic laboratory in a sterile container, which you can purchase at any pharmacy. Almost nothing affects the distortion of the results, so there is no need to stop taking medications or change your diet in any way.
It is recommended to fill the standard container in which a stool test is taken approximately 30-40%. If the collection from a child or adult was carried out in the evening, then the container should be placed in the refrigerator overnight and stored at a temperature in the range of 2-6 degrees. This will keep the elastase unchanged and achieve optimal research results.
The only exception is the use of laxatives or rectal suppositories to provide samples. They negatively affect the accuracy of the result.
Serum elastase
If there are suspicions of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas in a child or adult, the analysis can be done on the basis of stool or blood serum. A serum elastase test is prescribed in case of abdominal pain in a patient.
However, it comes in two types:
- Pancreatic elastase 1. This is an enzyme whose molecular weight is 30,000. The substance is produced by the pancreas and circulates freely throughout the body through the blood. Or it may circulate with an inhibitor that inhibits enzyme activity.
- Pancreatic elastase 2. Its molecular weight is 25,000. An analysis is recommended if nephritis, arthritis or emphysema is suspected.
Along with examining blood and stool for elastase, doctors may prescribe an analysis of another enzyme - pancreatic lipase. This is a pancreatic enzyme whose task is to break down fatty acids, fats and glycerol.
Normal elastase levels
The normal level of elastase in feces is 200 mcg or more per 1 gram of material. The upper limit is 500 units. High rates do not provide important information for clinical diagnosis. However, borderline numbers, for example 200 or 201, 500 may be a reason for re-checking or prescribing additional tests.
Depending on the digital equivalent, minor deficiency and severe elastase deficiency are distinguished.
In newborn children, the level of elastase is less than normal.
The first is characterized by values from 100 to 200 mcg per unit of material. For the second type – below 100 mcg. Abnormally high levels may indicate oncology or abuse of laxatives and general relaxing substances.
The level of pancreatic elastase, depending on the modification of the stool immunoassay, may differ slightly in different laboratories. Associated with the country of origin of the test and the selected method itself (ELISA, monoclonal, polyclonal). The classic and most common type is the second one named. It is more effective and specific. The limits are always indicated on the packaging of the test accessories.
In newly born children, the values are always somewhat lower, but by two weeks the values become similar to those of an adult.
In the video you will find more information about what a stool analysis shows:
What is this?
Pancreatic elastase is an indicative pancreatic enzyme, by the content of which experts determine the functional state of the gland, structural changes in its parenchyma and the physiological state of the tissues.
This enzyme takes an active part in the breakdown of protein components of food into the state of amino acids. Pancreatic elastase, in addition to participating in digestion, also performs intrasecretory functions, adjusting carbohydrate metabolic processes and producing the insulin hormone.
The mass fraction of elastase in pancreatic juice is about 9%. The enzyme penetrates the small intestine, where it begins to actively break down proteins.
If the patient has a pathology of the duodenum, then the level of pancreatic elastase drops significantly below the normal level. Therefore, determining its level is considered a standard marker for identifying various types of pancreatic insufficiency.
This enzyme does not change its quantitative or qualitative composition in the process of moving through the structures of the gastrointestinal tract, therefore the results obtained from the study of feces will clearly reveal the picture of the existing pathology.
Indications
For gastrointestinal pathologies, laboratory examination of stool is considered one of the most indicative and informative tests, therefore, a study of the level of pancreatic elastase is indicated if the development of pathological processes such as is suspected:
- Chronic inflammation of the pancreas;
- Chronic glandular deficiency;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Gallstone pathology;
- Delays in the physical development of children;
- Tumor intraorganic formations and processes;
- Thermal ileitis, Crohn's pathology;
- Traumatic injuries to the pancreas, etc.
The study is also used as part of differential diagnosis to determine malabsorption or cystic fibrosis. In addition, testing stool for the content of pancreatic elastase is indicated for the development of the syndrome after pancreatectomy (surgical removal of the pancreas).
Analysis price
The cost of testing stool for pancreatic elastase content in Moscow clinics is 1705-2400 rubles.
Gastrointestinal pathologies are found everywhere in patients of all age groups, since we are all exposed to the negative influence of poor environmental conditions, unhealthy diet, stress, etc.
These factors have a destructive effect on the body, causing many disorders and diseases. And with the help of informative diagnostic procedures such as stool examination for the level of pancreatic elastase, a specialist will be able to make a reliable diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.