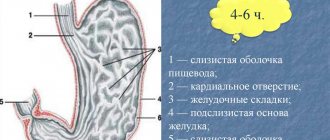
Mucus in the stomach and its meaning
Mucus in the stomach plays an important role in regulating acidity. It contains a large amount of bicarbonates, which, when interacting with hydrochloric acid, neutralize it. Active mucus production occurs in the pyloric region. This is due to the fact that it is necessary to reduce the acidity of food masses before they pass into the cavity of the duodenum. Only then will there be adequate activation of pancreatic enzymes, which is necessary for the breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
The second important aspect is the protection of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum from the aggressive action of various endogenous and exogenous factors. Activation of mucus production occurs during inflammatory processes or disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane, which promotes faster regeneration and recovery.
Why is excess mucus dangerous?
But increased mucus production is not always positive. Normally, increased acidity should be maintained in the stomach cavity, since this ensures the chemical processing of foods, the destruction of pathogenic bacteria and the activation of stomach enzymes (pepsinogen, lipase).
If there is a lot of mucus in the stomach, then the acidity in the entire cavity of the digestive tract decreases. This promotes more active intestinal motility, which leads to the development of functional digestive disorders and decreased appetite. There is also a disruption in bile production.
Causes of excess mucus in the stomach
The causes of increased mucus formation in the stomach can be divided into several main groups:
- Active inflammatory processes ( gastritis , Crohn's disease , malignant neoplasms , ulcers ). The release of a large number of biologically active molecules leads to activation of the gastric glands.
- Food poisoning and intestinal infections. Many pathogenic viral or bacterial pathogens disrupt the permeability of cell membranes and disrupt ion exchange.
- Traumatic or radiation damage to the stomach. External damage to the stomach wall leads to increased mucus production.
- Chronic somatic diseases of other organs and systems (diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, polyneuropathy, autoimmune pathologies) disrupt the trophism and innervation of the organ wall. The glands are activated as a compensatory reaction.
- Congenital enzymatic disorders and malformations of the esophagus or stomach. There is a disruption in the regulation of the mucous glands, which often leads to their hyperactivation.
Gallbladder pain: symptoms
- With cholelithiasis, pain is localized in the right hypochondrium and can radiate to the right shoulder blade, shoulder, collarbone or left half of the body. The pain has an acute paroxysmal nature and is provoked by errors in nutrition.
- Chronic cholecystitis is manifested by aching pain, the intensity of which increases with a violation of the diet. Painful sensations are localized in the hypochondrium on the right, and sometimes in the epigastrium and can be projected to the right scapula, collarbone or shoulder.
- Dyskinesia of the gallbladder. In patients with the hyperkinetic type of dyskinesia, paroxysmal pain is observed. With hypokinetic dyskinesia, patients complain of a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the right hypochondrium or aching pain that radiates to the right half of the body, scapula, shoulder or collarbone.
- Acute cholangitis is manifested by quite severe pain, which can even cause painful shock. Localization and irradiation of pain similar to the diseases described above.
- Gallbladder carcinoma is asymptomatic for a long time. In the later stages of the disease, patients experience severe pain that is not relieved even by painkillers.
Signs of the disease
The clinical picture of increased mucus production is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- a feeling of heaviness or obstruction in the epigastric region, which intensifies after eating;
- periodic stomach pain;
- nausea, repeated vomiting;
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss;
- increased gas formation in the intestines;
- tendency to diarrhea;
- belching (sometimes with an unpleasant odor);
- general weakness, decreased performance.
The severity of clinical symptoms depends on the cause of increased mucus production. However, the clinic mainly develops gradually.
How to recognize?
In a healthy person, the mucus in the stomach is transparent and present in small quantities. Its importance is quite important, since it serves as a protective barrier against the effects of irritating factors. In older newborns and adults, when the function of the mucus-secreting glands is impaired, pathological manifestations appear. An increase in mucous fluid in the stomach can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- feeling of heaviness after eating;
- attacks of nausea;
- cloudy vomit;
- mucous impurities in stool;
- bloating;
- stomach colic;
- diarrhea.
The main manifestations of the pathology can also be supplemented by painful attacks in the organ area.
Soon, vomiting mucus and other pathological manifestations are complemented by painful attacks in the stomach. Without identifying the problem in a timely manner, the function of the gastrointestinal tract is significantly impaired. The food begins to fester, inflammation develops, leading to the death of certain types of glandular cells or their degeneration into another type. Such disorders cause gastritis, ulcers or cancer.
Diagnostic methods
The doctor begins the diagnosis by asking the patient or his relatives about when and how the symptoms appeared. He pays special attention to the patient’s possible contacts with infectious patients, diet, bad habits, exposure to chemical or radiation factors. After examining the patient, he is sent to laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- coprogram (with determination of occult blood);
- biochemical blood test (sugar, bilirubin, protein and its fractions, liver enzymes, urea, creatinine);
- immunological studies (antibodies to parietal cells of the mucous membrane);
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy with acidity measurement (gastroscopy), Helicobacter pylori test;
- bacteriological examination of stomach mucus;
- biopsy of altered areas of the mucous membrane with further cytological examination.
Sometimes consultation with other specialists (surgeon, oncologist, immunologist) is also required. After this, the diagnosis is finally made and the patient’s treatment tactics are determined.
Diagnostic tests
If an excessive amount of mucus accumulates in the stomach and pathological symptoms appear, then you need to contact a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. The specialist will palpate the abdominal cavity and collect a detailed history of the disorder. The following examinations are required to make a diagnosis:
- detailed blood test;
- laboratory examination of stool and urine;
- diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract using ultrasound;
- X-rays of the peritoneum;
- MRI and CT.
Basic treatment methods
How to get rid of mucus in the stomach? All therapeutic measures that are prescribed to the patient can be divided into several main groups:
- Drug therapy.
- Correction of the patient’s diet, habits, as well as harmful factors that led to the development of the disease.
- Ethnoscience.
- Long-term prevention of new exacerbations of the disease.
Drug treatment for excess stomach mucus
Pharmacological treatment of excess mucus in the stomach is aimed at the factor that caused it. Therefore, in case of Helicobacter pylori infection, the patient is prescribed multicomponent eradication therapy (two antibiotics and antisecretory drug tablets).
In case of poisoning, it is recommended to use sorbents - medications that absorb toxins and particles of pathogenic microorganisms. If reactive inflammation is detected, then antacids are actively prescribed, which cover the gastric mucosa and promote its accelerated regeneration. In case of enzyme deficiency, their natural analogues are used.
ethnoscience
How to remove mucus from the stomach using folk remedies? For example, you can use cabbage juice. It stimulates the production of parietal cells and increases acidity in the stomach cavity. Coffee and green tea have the same ability, but they should not be brewed too strongly. Potato juice on an empty stomach also helps normalize the function of the glands.
or St. John's wort tea helps with inflammatory processes . You can drink it 3-4 times a day on an empty stomach.
In a hypoacid state, it makes sense to use citrus juice. There is also a method in which you need to grind horseradish and add it to lemon juice. This solution should be drunk a teaspoon after meals. A good result is obtained from tea made from pounded ginger, which must be prepared by adding a teaspoon of root to 500 ml of table water.
Prevention
Preventive measures include following the principles of a healthy diet. Annual visits to the doctor for preventive purposes are recommended. If you have symptoms of gastrointestinal pathology (bloating, flatulence, nausea, pain), you must contact a specialized specialist for examination and correction of the condition.
Comments:
- Causes of mucus accumulation Composition of mucous gastric secretion
- The influence of nutritional quality on the formation of excess mucous secretion
- Methods for cleaning the gastrointestinal tract from excess mucous secretions
- Traditional recipes for clearing mucus
The accumulation of mucus in the body can cause intoxication and give impetus to the development of many diseases. Let's consider how to get rid of mucus in the stomach, what causes its appearance, and what kind of nutrition is healthy in this case.
Useful video
Why a lot of mucus can form in the stomach can be found in this video.
Nutrition correction
The diet for increased mucus production is based on several principles:
- Mechanical protection of the mucous membrane. Before cooking, it is necessary to remove all solid particles from food (scales from fish, cartilage from meat). Vegetables and fruits can be mashed.
- Chemical protection. All foods and dishes that can contribute to damage to the mucous membrane are removed from the diet. Therefore, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, citrus fruits, canned and pickled foods, fatty meats, fresh baked goods, and dark chocolate are prohibited.
- It is necessary to eat in smaller portions, but much more often (5-6 times a day).
- Thermal protection. All dishes must be served warm, but not hot.
- Focus on the cause of increased mucus production. In case of poisoning in the first days, food is quite severely limited; in case of hypoacid gastritis, fermented milk products are included.
- Completeness of the diet. It should contain a sufficient amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, microelements and vitamins.
Diet
For gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by an increase in the proportion of mucus, it is recommended to adhere to the general principles of nutrition developed for gastroenterological patients. You should avoid fatty, spicy, overly salty, smoked foods and marinades. Lean meat, dried bread, lean fish, scrambled eggs, raw or stewed vegetables are recommended.
Mucus producing foods
Mucus is formed when eating excessively fatty foods
Fat and protein emulsions, whole milk, fatty meat, and lard contribute to an increase in the amount of mucus. However, during normal functioning of the digestive structures, the resulting lipid suspension is quickly broken down and absorbed, after which the mucoid volume returns to normal. With prolonged use, the amount of mucus produced by mucocytes increases in any food that has an irritating effect.