Is reflux normal?
Gastroesophageal reflux is characterized by the backflow of gastric contents into the esophagus, and in some cases into the oral cavity. In infants, this content is represented by semi-curdled milk or an adapted formula, depending on what the child eats. Because some acids can leak from the stomach into the esophagus, reflux is sometimes called acid reflux.
According to statistics, 50% of children under 3 months of age burp 1 to 4 times a day. The peak of regurgitation in frequency occurs in the 4th month of life. And having reached six months, such excesses become less and less, completely disappearing by 1-1.5 years.
If regurgitation is infrequent, the child eats enough and gains weight normally, and feels well, it is customary to talk about “uncomplicated” reflux, which does not require special treatment. How does it arise?
It's all about the structure of the gastrointestinal tract. In a newborn, the esophagus is shorter than in an adult, and the initial volume of the stomach does not exceed 30 ml. The stomach itself is still located horizontally, and the muscle located on the border with the esophagus (sphincter) is poorly developed. All these factors together contribute to the fact that a portion of milk that gets in during a meal often and almost unhinderedly comes back out during active movements after eating or in a horizontal position.
While eating, food moves through the esophagus due to the process of peristalsis - special muscles, contracting and unclenching, create a kind of wave, pushing food to the stomach. Having reached the lower part of the esophagus, food encounters another obstacle - the esophageal sphincter. It resembles a muscular ring, a gate through which the contents pass further into the stomach. As soon as a portion of food has passed “customs”, the sphincter closes tightly to prevent backflow. Weakness of the muscle ring can occur at any age, but it occurs much more often in young children.
Due to a weak sphincter, almost all babies spit up a small amount of milk 20-30 minutes after eating
Is a baby's crying related to reflux? There is no evidence that spitting up causes pain. Discomfort - yes. However, problems falling asleep and increased irritability are not considered clinical symptoms of reflux. Therefore, look for the reason for crying in other areas: perhaps the baby needs a diaper changed, fed, or simply cuddled.
What unusual symptoms in children indicate - Dr. Komarovsky
Gastroesophageal reflux GER is the medical term for regurgitation of stomach contents back into the esophagus and sometimes into the mouth. Since certain acids are normally found in the lumen of the stomach, GER is sometimes called acid reflux, especially abroad. Reflux is normal and occurs in healthy babies, children and adults. Uncomplicated reflux usually does not bother the baby, has a low risk of developing chronic complications, and usually does not require treatment. In contrast, children with gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD are whiny, gain weight more slowly, and often have recurrent pneumonia or hemoptysis. Children with these symptoms usually require further evaluation and treatment. Although most children with gastroesophageal reflux disease have symptoms that go away on their own as they grow, some children continue to have these symptoms as they get older.
Sometimes children have some unusual symptoms that you don't understand. Children may sometimes complain of abdominal pain.
Symptoms of reflux disease
We recommend reading: Symptoms of pyloric stenosis in newborns
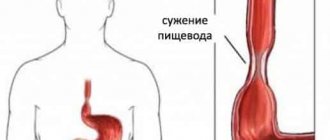
When does reflux stop being harmless and people start talking about gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)? When stomach acid enters the esophagus too often, causing irritation or damage. Symptoms of GERD:
- frequent and profuse regurgitation, often gushing;
- the child cries and refuses to eat;
- the baby arches his neck and back, thus trying to take a less painful position (Sandifer syndrome);
- poor weight gain;
- cough that is not a consequence of an infectious disease.
Recommendations from experts
There is no need to panic if your baby burps. In frequent cases, regurgitation is a normal physiological feature of the baby’s body. Only when the baby’s general health has deteriorated significantly (regurgitation is profuse and systematic) is it important to immediately go to the hospital or call an ambulance. Under such conditions, irreversible health problems may occur.
Self-medication is prohibited, since the child’s body is especially vulnerable to the effects of any medications. Delay can only provoke the development of complications and worsen the child’s well-being. It is forbidden to use any traditional methods of treatment, since various herbs and infusions can only aggravate the problem. During the process of excessive regurgitation, the baby’s body becomes dehydrated, which leads to the development of serious pathologies. To prevent this, it is important not to delay going to the pediatrician. The doctor will carry out a thorough diagnosis of the baby and prescribe a comprehensive treatment that will help get rid of the problem.
Causes
The prerequisites for the development of GERD are not only a weakening of the antireflux mechanism, the reflux of acids (hydrochloric and bile) and pepsin into the esophagus, but also various anomalies that occur in childhood:
- Pyloric stenosis is a pathological narrowing of the pylorus of the stomach, which makes the movement of food difficult; accompanied by vomiting.
- Pylorospasm is a temporary contraction of the pylorus, which also delays the evacuation of food.
- Diaphragmatic hernia is a displacement of the lower esophagus into the chest cavity through the opening of the diaphragm.
Spitting up is not always harmless. The general condition of the child and the frequency of reflux manifestations will tell you when it is time to be examined to find the true cause of such conditions.
Diagnostics
There is no need to diagnose uncomplicated reflux in any special way. For the pediatrician, as well as for parents, it is already obvious, is regarded as a variant of the norm and does not cause concern.
If there are serious suspicions of gastroesophageal reflux disease, the child is referred for consultation to a pediatric gastroenterologist. At your doctor's appointment, a detailed medical history is taken and a general physical examination is performed. Further, at the doctor’s discretion, the following examinations may be performed:
- X-ray examination. A contrast agent (barium) is injected into the gastrointestinal tract, and then its movement through the digestive tract is monitored on a monitor screen.
- Endoscopy. Thanks to this study, it is possible to assess the condition and color of the mucous membrane, whether there is swelling in the folds of the esophagus or cardiac sphincter, and whether the surface is eroded. If indicated, a biopsy is taken.
- Sphincteromanometry. An examination to assess the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter.
- pH test. Daily monitoring of acidity is carried out, thanks to which it is clear how many episodes of reflux occur per day and for what duration. To do this, a probe with a special sensor at the end is inserted into the esophagus for 24 hours, which measures the acidity level.
- Examination of the stomach cavities. It is checked whether there is anything in the gastrointestinal tract that interferes with the movement of food and its timely evacuation.
Good mixtures
Under such conditions, it is important to choose a dairy-free formula that contains protein hydrolysate. It is recommended to feed a child up to 1 year with “Nutrilak” and “Nutrilon Pepti”. It is advisable to use a thickener (strictly as prescribed by the pediatrician). Quite often, doctors prescribe anti-reflux mixtures to babies, which help prevent the occurrence of pathology. Such special foods help food stay in the stomach longer. There are several types of thickeners:
- digestible (corn, rice, potato);
- indigestible (gums).
Thanks to carob gum, you can get rid of excessive regurgitation and constipation, since the substance has a laxative effect.
“Humana antireflux” or “Nutrilon antireflux” should be fed to the baby in order to prevent regurgitation.
Treatment
Treatment of simple cases, the main symptom of which is small regular regurgitation, is often limited to adjusting the baby’s lifestyle:
- experimenting with eliminating cow's milk from the diet;
- protect the baby from inhaling tobacco smoke, which irritates the respiratory tract and causes coughing;
- add special thickeners to food;
- review the diet of a nursing mother.
Principles of “safe” feeding
The first thing people pay attention to when regurgitating is their feeding style. Is it possible that a caring mother tries to feed her child “well and satisfyingly” even against his will? This, unfortunately, happens.
Therefore, the first rule: feed small amounts, but more often. In practice, this means that the baby needs to be taken from the breast 4-5 minutes earlier than usual or as soon as the baby begins to get distracted. If the basis of nutrition is adapted mixtures, then the volume of an individual serving is reduced by 10-20 ml, as recommended by the pediatrician.
If the child is already receiving complementary foods, but reflux still makes itself felt, the diet will focus on protein and carbohydrate foods in small portions. Juices and tomatoes are excluded from the diet
The second rule: no sudden movements and a vertical position for half an hour after feeding. The well-known posture is simply necessary in the first 4 months of life if you want to reduce the frequency of regurgitation as much as possible. It is not necessary to walk around the room for 30 minutes; you can sit down in a comfortable chair while the baby calmly falls asleep on your shoulder in a semi-upright position.
These two steps alone can reduce reflux symptoms in 85% of cases. But it happens that other changes are needed.
Diet food
According to studies, 15-36% of children who were diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease had intolerance to cow's milk protein.
Nutrition correction consists of eliminating dairy products from the diet of a breastfeeding mother. The experiment is carried out over 3 weeks. If during this time the baby’s condition has improved, they talk about milk protein intolerance and the diet is maintained until the child reaches 1 year.
If the baby is bottle-fed, a dairy-free formula based on protein hydrolyzate is selected: “NutrilonPepti”, “Frisopep”, “Nutrilak Peptidi MCT”.
Thickeners
Today, the use of so-called antireflux mixtures plays an important role in diet therapy. These are special products for young children with increased viscosity, so that food stays in the stomach longer. There are two types of thickeners used in baby food:
- Digestible (corn, rice, potato starch).
- Indigestible (gums).
Locust bean gum and other non-digestible thickeners have not only an anti-reflux effect, but also a laxative effect. As an indigestible polysaccharide, the gum reaches the colon unchanged and becomes a substrate for the growth of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Compared to starches, gums have a more pronounced anti-reflux effect. Representatives of medicinal mixtures: “Humana Antireflux”, “Nutrilak AR antireflux”, “Nutrilon Antireflux”, “Frisov”. The same mixtures are recommended for children prone to constipation and intestinal colic.
If there is a need to use mixtures with thickeners, it is better to choose those that contain gum
Mixtures that use starch as a thickener are considered milder in action. The effect of their use is noticeable after a month of use. Representatives: “Samper Lemolak”, “Nan antireflux”.
What if the newborn is breastfed? You shouldn't give it up. The milk is expressed and a thickener purchased at the pharmacy is added to it, according to the recommendations from the manufacturer and the doctor.
Please note that the nipple on the bottle will have to be changed: the hole must be wide enough to allow the thick mixture to pass through. A pacifier “for porridge” is suitable.
Attention! All thickeners used to correct the nutrition of children under 3 months, especially those prone to allergies, should be prescribed only by a doctor. They are practically not used as the sole therapeutic component and are not recommended for children who have already developed esophagitis (inflammation or damage to the lining of the esophagus).
Drug treatment
In the event that all of the above measures are ineffective, a treatment strategy with drugs from different pharmacological groups is developed. For informational purposes, here are examples of such drugs:
- Proton pump inhibitors. Drugs such as omeprazole and pantoprazole block the last stage of hydrochloric acid formation, thereby reducing its production. As a rule, omeprazole is the gold standard in the treatment of GERD in children starting from 2 years of age.
- Antacids. The purpose of antacids is also to neutralize hydrochloric acid. In pediatric practice, Phosphalugel and Maalox are used, which, in addition to their main function, have a restorative effect on damaged mucous membranes.
- Histamine H-2 blockers (ranitidine, famotidine). Treatment of children under one year of age rarely includes taking these drugs.
- Prokinetics (domperidone). They enhance the motility of the stomach, thereby facilitating its rapid emptying and strengthening the sphincter.
Drugs that reduce stomach acidity are selected by the doctor
Persistent regurgitation leads to dehydration and water-electrolyte imbalance. Very often, such losses can only be restored in a hospital by administering infusion solutions.
All medications have a number of side effects, as well as age restrictions. Therefore, their appointment must be fully justified. The doctor takes into account all the nuances and decides which groups of medications are best suited.
Principle of therapy
For small and regular regurgitation, the doctor recommends:
- adjust the child’s nutrition;
- it is important to exclude cow's milk from the diet;
- protect your baby from passive smoking of cigarettes, since tobacco smoke irritates the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and provokes a severe cough;
- add a special thickener to food;
- review the diet of a nursing mother.
These simple recommendations will help improve your baby's condition. If there are symptoms of bladder reflux in a baby, it is important to consult a doctor immediately. Self-medication can provoke the development of complications.
Reason to call an ambulance
Reflux complicated by esophagitis must be treated. If your newborn has one or more of the following symptoms, seek help immediately:
- the child is rapidly losing weight;
- daily regurgitation in a baby less than 3 months old leads to starvation of the baby;
- categorical refusal to drink and eat during the day;
- blood in vomit or stool, severe diarrhea;
- the baby’s condition is excessively depressed, inhibited;
- pneumonia develops.
So, reflux itself, or, as people say, regurgitation, in infancy should not frighten parents, since it is understandable from the point of view of physiology and anatomy. Difficulties arise with frequent vomiting, when there is so much acid in the esophagus that it can cause damage to the mucous membrane - and this is associated with heartburn and pain for the baby. Then they talk about reflux disease.
On the other hand, pathological regurgitation is a reason to undergo a thorough examination in order to exclude the presence of concomitant serious diseases. Parental intuition and the local pediatrician will tell you that it is time for an examination.
The basis of proper feeding
After visiting a doctor, the specialist not only carries out a thorough diagnosis of the baby, but also analyzes the feeding style. In some cases, mothers try to feed their child well, which causes the baby to overeat. Under such conditions, profuse regurgitation occurs.
If reflux esophagitis is detected in an infant, experts recommend feeding the baby frequently and in small amounts. If the baby is distracted during breastfeeding, you need to take the breast. When artificial feeding, the portion must be reduced by 15 ml. Doctors recommend that mothers make sudden movements with the baby in their arms. After feeding the baby, you need to pick him up and hold him in an upright position for 20 minutes. This will help prevent excessive vomiting. It is not at all necessary to run or walk around the house during this time; it is enough to simply take the baby in your arms and sit with him in a chair. This way, the baby will be able to sleep peacefully in your arms, taking a semi-vertical position. In many cases, these simple recommendations help prevent reflux.