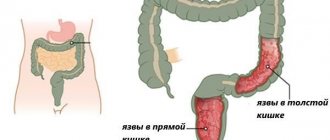
Dolichocolon is a disease that is characterized by elongation of one or more sections of the large intestine without changing the diameter of its cavity and without thickening the muscle layer. The consequence of this abnormal development is a violation of the evacuation function of the intestines, while motor function does not change. The disease occurs in both adults and children.
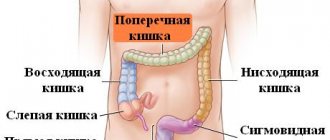
Dolichocolon is characterized by an increase in the length of the large intestine
Causes and risk factors
Dolichocolon can be congenital or develop throughout life. The occurrence of congenital dolichocolon is facilitated by a number of factors that influence the fetus during prenatal development:
- mother's bad habits;
- exposure of a pregnant woman’s body to certain chemicals;
- infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy.
The risk of dolichocolon increases with a family history.
Acquired dolichocolon can develop due to the following reasons:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- frequent use of enemas;
- metabolic disorders;
- vegetarianism;
- past viral infections.
The disease can also occur against the background of biliary dyskinesia, dysbacteriosis, hemorrhoids, and varicose veins of the intestine.
Symptoms
The most specific symptom is that the elongated colon takes on an S-shape or forms several, less often, one loop. The specificity of the disease is that the symptom can only be detected during instrumental diagnostic examinations.
Symptoms of dolichocolon
As for external manifestations, the degree of the disease is dictated by several factors:
- length of elongation of the sigmoid colon or mesentery;
- level of disturbance of tone and peristalsis of the affected organ;
- adaptive reactions of the body.
The main symptom is problems with bowel movements (recurrent or prolonged constipation). The more severe the pathology, the longer the period of absence of spontaneous passage of feces will be.
Associated symptoms of dolichocolon-dolichosigma:
- pain in the abdominal area - the focus is located on the lower left side of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity or in the peri-umbilical area, in some cases the localization of pain remains uncertain;
- excessive gas formation and sweating;
- painful appearance - puffiness of the face and the appearance of dark “bags” under the eyes;
- rashes on the skin of unknown etiology of a purulent nature;
- bloating;
- attacks of nausea ending in vomiting that does not bring relief;
- loss of appetite or complete aversion to food;
- lethargy and weakness of the body;
- pale skin;
- decreased performance;
- dry tongue and white coating;
- increased fragility of nail plates and hair loss;
- bad breath;
- weight loss;
- formation of hemorrhoids of external or internal localization;
- Varicose veins;
- rumbling and seething in the stomach;
- anal fissures;
- the presence of pathological impurities in feces.
All symptoms of the disease are observed in both children and adults.
Forms of the disease
According to the clinical principle of classification, the disease is divided as follows:
- asymptomatic dolichocolon;
- dolichocolon with impaired transit through the large intestine;
- complicated dolichocolon.
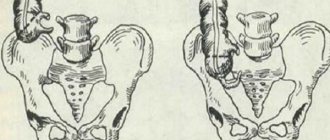
A - Hirschsprung's disease, b - idiopathic megacolon, c - dolichocolon
The asymptomatic form of the disease does not require specific treatment methods. The patient is advised to adhere to preventive measures to prevent possible complications.
Depending on the area of the intestine involved in the pathological process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- dolichosigma;
- right-sided dolichocolon;
- left-sided dolichocolon;
- dolichotransversum;
- total dolichocolon;
- subtotal dolichocolon.
How to treat pathology
Treatment for dolichocolon should be comprehensive and include both drug therapy and nutritional correction, as well as massage. In some cases, surgery is prescribed.
Drug therapy
When the sigmoid colon is lengthened, the doctor may prescribe the following medications, aimed mainly at eliminating unpleasant symptoms:
- anticholinesterase drugs (Prozerin, Dibazol, etc.) - to improve intestinal motility and restore neuromuscular conduction;
- vitamin complexes (including B vitamins) - to strengthen the immune system;
- antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Bral and others) - to reduce pain.
Note! For dolichocolon, laxatives are not prescribed, which is explained by the ineffectiveness of the latter.
Drugs for conservative treatment of pathology - gallery
Prozerin improves intestinal motility
Dibazol restores neuromuscular conduction
No-Spa relieves spasms
Diet and lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle modification are the most important components of the treatment of dolichocolon. It is important to normalize your daily routine; regular physical activity and healthy eight-hour sleep are beneficial. Patients should give preference to liquid or pureed foods, boiled or steamed. Your diet should include foods rich in protein and fiber:
- vegetables;
- greenery;
- buckwheat;
- chicken breast;
- low-fat fish (pike perch, pollock, carp, etc.)
Portions should be small.
Patients need to avoid:
- canned foods;
- sweets and baked goods;
- fatty, spicy or overly salty foods;
- fruits and vegetables that cause bloating (apples, grapes, peaches, cabbage, etc.);
- carbonated drinks, strong coffee.
When diagnosing dolichocolon in an infant, it is recommended to switch the baby to formulas with a high content of prebiotics and probiotics.
Prohibited products - gallery
Canned foods harm the digestive system
Sweet cakes, puddings and creams cause digestive upset
Excess fatty foods can cause heartburn, nausea and even vomiting, indigestion
Cabbage causes bloating
Carbonated drinks cause bloating
Coffee drunk immediately after a meal causes great harm to the digestive process that has begun and disrupts the normal rhythm of the intestines.
Yeast baked goods disrupt the natural balance of intestinal microflora
Sample menu for the week - table
| Day of the week | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Monday |
| glass of kefir |
| prunes |
|
| Tuesday |
|
|
| natural yogurt |
|
| Wednesday |
| prunes |
| soaked dried apricots |
|
| Thursday |
|
|
| low-fat cottage cheese |
|
| Friday |
| leaven |
| cottage cheese |
|
| Saturday |
|
|
| natural yogurt |
|
| Sunday |
|
|
| fruits |
|
Physiotherapy
If the disease occurs in a latent form and there are no typical symptoms, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures such as:
- acupuncture - influencing certain points with needles;
- massage - can speed up the movement of feces, should be performed exclusively by a specialist;
- electrical stimulation - impulses sent by a special device stimulate the intestines, provoking contraction of the walls of the organ.
During the decompensation stage, bowel movement is achieved by using a siphon enema.
Siphon enema is used for chronic constipation
Doctor Komarovsky about constipation in children - video
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is indicated for advanced stages of the disease, when conservative therapy is ineffective, as well as for the development of complications such as acute intestinal obstruction and volvulus.
As a rule, they resort to minimally invasive operations, in particular to:
- resection of excess loops of intra-abdominal intestine according to Rehbein - with a high risk of disease relapse;
- resection of the abdominoperineal intestine according to Soave is considered the most preferable method of treatment, but requires a highly qualified doctor.
In case of elongation of the distal sigmoid colon, a radical intervention is performed - proctosigmectomy, during which the affected part of the organ is completely removed.
The choice of surgical intervention tactics remains with the surgeon. Sometimes a specialist is able to make a decision only after seeing the extent of damage to the colon.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy to prevent pneumonia, as well as painkillers.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine is powerless in the fight against dolichocolon. You can get rid of the pathology only with the help of medications or surgery. However, folk remedies help to partially eliminate the symptoms of the disease . For constipation, the following recipes are effective:
- mix 300 g of red rowan and 150 g of sugar. Wait until the berry gives juice. Strain and place the liquid in a glass container for 21 days. Take 3 tbsp on an empty stomach. l.;
- Pour ½ kg of prunes into 3 liters of water, put on medium heat, and after boiling, cook for twenty minutes. Cool and add 50 g of buckthorn to the broth. Boil again and cool. Add 200 ml rosehip syrup. It is recommended to use this product 50 ml daily for two weeks;
- 1 tbsp. l. senna pour 200 ml of water, bring to a boil and cook for another 5–10 minutes, remove from heat and leave to brew for 30 minutes, after wrapping the container with the decoction in a towel. Strain and take throughout the day;
- 2 tbsp. l. Pour boiling water over bran, drain off excess water, and consume the resulting mass 1 tbsp. l. three times a day immediately before meals.
Traditional medicine - photo gallery
Rowan activates the work of the intestinal muscles
Prunes are a mild and effective laxative.
Senna helps with bowel problems
Bran stimulates intestinal function
Symptoms
With asymptomatic dolichocolon, there are no specific manifestations of the disease.
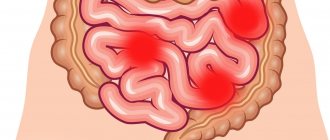
The most common symptoms of dolichocolon:
- regular constipation;
- abdominal pain, aggravated by physical activity and prolonged stay in an upright position;
- headache;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating, flatulence;
- painful sensations during bowel movements;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
Signs of dolichocolon - regular constipation and abdominal pain
Complicated dolichocolon is characterized by periodic development of intestinal volvulus, nodule formation and resulting intestinal obstruction.
Complications
According to statistics, dolichocolon is the cause of acute intestinal obstruction in 8% of cases. The long colon has additional loops and pathological mobility.
Mechanisms of obstruction:
- formation of nodes from intestinal loops;
- intussusception - the introduction of one section of the intestine into another;
- volvulus is a rotation of a loop of intestine around the axis of the mesenteric vessels.
Be sure to read: Details about the intestines: structure, sections and functions of the organ
Blood supply to the affected area is disrupted. When seeking medical help late, intestinal necrosis and peritonitis develop, which often leads to death.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis of dolichocolon includes taking anamnesis and manual examination methods (palpation). To clarify the diagnosis and exclude other intestinal pathologies, the following hardware and laboratory methods are used:
- irrigoscopy with double contrast;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- proctography;
- colonoscopy;
- ultrasound and tomographic examination of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- sphincterometry, electromyometry;
- general blood analysis;
- stool occult blood test; etc.
To diagnose dolichocolon, irrigoscopy with double contrast is indicated.
It is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of dolichocolon with a number of diseases with similar symptoms, namely:
- with intestinal neoplasms;
- with megacolon;
- with Hirschsprung's disease;
- with inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- with ischemic colitis;
- with drug-induced constipation.
Dolichocolon can be congenital or develop throughout life.
Intestinal dolichocolon in adults: definition of pathology and treatment
Dolichocolon is a congenital elongation of one or more anatomical sections of the colon.
In 95% of cases, the sigmoid segment is affected - dolichosigma. The pathology leads to chronic constipation and increases the risk of acute intestinal obstruction.
When examining patients with impaired bowel movement, every second of them is diagnosed with a long colon.
Causes
Dolichocolon is a congenital malformation of the digestive organs and is often combined with other developmental anomalies. The exact causes of the pathology are not known.
Risk factors:
- heredity;
- the age of the parents at the time of conception of the child is more than 35 years;
- adverse effects on the fetus during pregnancy: infections, medications, alcohol, x-rays, household and work factors;
- deterioration of uteroplacental blood flow during pregnancy;
- chronic endocrine diseases: diabetes mellitus, pathology of the adrenal glands and gonads.
According to some scientists, dolichocolon can also be acquired. It is believed to be associated with frequent enemas, abuse of laxatives, and age-related changes in the intestinal wall. But these works do not have an evidence base.
Symptoms
Dolichocolon is often asymptomatic, and its exact prevalence is unknown. In women, the first signs of pathology appear during pregnancy, in men - after 30 years.
- stool less than once every 3 days;
- strong straining during bowel movements;
- hard feces in the form of lumps;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement;
- feeling of obstruction during bowel movements;
- periodic aching or cramping pain in the abdomen;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating;
- symptoms of intoxication: weakness, fatigue, headaches, irritability.
If these complaints have bothered you for at least 12 weeks over the past 6 months, contact a gastroenterologist.
Complications
According to statistics, dolichocolon is the cause of acute intestinal obstruction in 8% of cases. The long colon has additional loops and pathological mobility.
Mechanisms of obstruction:
- formation of nodes from intestinal loops;
- intussusception - the introduction of one section of the intestine into another;
- volvulus is a rotation of a loop of intestine around the axis of the mesenteric vessels.
The blood supply to the affected area is disrupted. When seeking medical help late, intestinal necrosis and peritonitis develop, which often leads to death.
History taking and examination
A gastroenterologist diagnoses dolichocolon. The doctor finds out complaints, medical history, frequency of bowel movements, experience in using laxatives and enemas. A possible intestinal abnormality is indicated by a family pattern of constipation.
Patients have characteristic changes in appearance: asthenic physique, stoop, asymmetry of the ears, arachnodactyly (very long and thin fingers). When palpating the abdomen, rumbling and pain occur in the projection of the colon.
Laboratory methods
In uncomplicated pathology, there are no specific changes in the tests. Laboratory tests are prescribed to assess the patient’s general condition and differential diagnosis of dolichocolon with other diseases.
Instrumental methods
Dolichocolon can only be determined using instrumental studies.
- Irrigoscopy with double contrast - at the first stage, barium is injected into the intestine using an enema, and a series of X-rays are taken. Then, after bowel movement, air is introduced, and the images are repeated. Using irrigoscopy, the length and shape of all parts of the colon, their mobility, and position in the abdominal cavity are assessed.
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the large intestine, allowing you to evaluate the size of each section, the condition of the mucous membrane, the severity of folds, tone, looping.
- Determination of the speed of movement of the contrast agent through the intestines - the patient takes barium sulfate, then for 5 days at certain intervals he takes X-rays of the abdomen. The speed of contrast passage through the small and large intestines is determined. The persistence of barium in the intestines for more than 3 days indicates dolichocolon.
- Computed tomography (CT) of the intestine is a modern method of radiological diagnostics. During the examination, the X-ray tube moves and takes pictures of the abdomen from different angles. The information is transferred to a computer, where a special program creates a three-dimensional image. Using CT, the condition of the intestines is assessed and pathology of nearby organs is identified.
- Intraoperative colon measurement - determining the size of the colon during surgery, for example, for intestinal obstruction.
We recommend reading:
What is anoscopy and how is it performed?
Treatment
Asymptomatic dolichocolon is not considered a disease and does not require treatment. For chronic constipation, therapeutic measures restore bowel movement and improve well-being.
Treatment should be comprehensive and step-by-step. To stimulate your intestines, try to move more: do morning exercises, walk, sign up for a pool or gym.
Diet
Adjust your diet and eating habits.
Principles of nutrition
- Eat regularly. Long breaks in eating increase the risk of complications. It is no coincidence that volvulus is called “the disease of a hungry man.”
- Eat food in a calm environment, without rushing.
- Maintain drinking regime. For normal bowel function, 1.5-2 liters of fluid per day is required, including first courses, vegetables, and fruits.
- Include foods rich in dietary fiber in your diet.
- Avoid foods that are too rough. Increased peristalsis can cause intestinal obstruction.
- Eliminate foods that increase the formation of gases in the intestines. Flatulence causes abdominal pain.
- Any methods of culinary processing of products are allowed.
Grocery list
| Recommended | Not recommended |
|
|
Adjust the list depending on individual preferences and food intolerances.
Medicines
- Laxatives - treatment begins with preparations based on dietary fiber (Psyllium, wheat bran, Mucofalk). If ineffective, osmotic agents are prescribed: Macrogol (polyethylene glycol) and Duphalac (lactulose). Irritating drugs (Bisacodyl, Senade) are used to a limited extent, as they are addictive.
- Antispasmodics - reduce the tone of intestinal smooth muscles, relieve painful spasms (Papaverine hydrochloride, Duspatalin, No-shpa).
- Defoamers are drugs to combat flatulence, prescribed for bloating (Espumizan, Sab Simplex).
- Eubiotics (probiotics) are drugs for correcting the microflora of the colon, prescribed for concomitant dysbacteriosis (Linex, Helac Forte, Bifiliz).
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods stimulate intestinal motor activity.
- acupuncture;
- cutaneous and rectal electromyostimulation;
- laser therapy;
- acupuncture.
Surgery
If conservative treatment is ineffective or there is a significant deterioration in health, surgery is recommended.
Basic techniques:
- subtotal resection of the colon - removal of all parts of the colon except the lower part of the sigmoid segment;
- segmental resection of the colon - excision of a pathologically changed section;
- colectomy – removal of the entire colon.
In case of intestinal obstruction, endoscopic detorsion is performed - straightening the volvulus. If the procedure is ineffective, a laparotomy is performed, the intussusception or volvulus is removed, the knot from the loops is untangled, and the viability of the intestine is assessed. In case of necrosis, the affected area is removed.
Forecast
The effectiveness of conservative treatment depends on the severity of changes in the colon. The incidence of constipation increases with age. The younger the patient, the better the results of therapy. The probability of recurrence of constipation after surgical treatment is 10%.
Source: https://ProKishechnik.info/zabolevaniya/dolixokolon-kishechnika.html
Treatment
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the form and stage of dolichocolon.
The asymptomatic form of the disease does not require specific treatment methods. The patient is advised to adhere to preventive measures to prevent possible complications.
If a diagnosis of dolichocolon is established with the presence of obvious disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, drug and (or) surgical treatment may be prescribed. Complex step-by-step therapy is preferable. In some cases, it is performed in a hospital setting.
Drug treatment consists of taking laxatives and vitamin complexes. If there are severe pain sensations, they are relieved with analgesic and antispasmodic drugs.
For severe abdominal pain, antispasmodics and analgesics are indicated
The main treatment can be supplemented with herbal medicine, physiotherapeutic methods (laser therapy, acupuncture), and physical therapy. To speed up the process of bowel movement, siphon enemas can be prescribed. It is also necessary to follow a diet: you should avoid eating sweets, legumes, rice, potatoes, canned food and fried foods.
If the patient's condition is severe or there is no effect of drug therapy, surgical intervention by laparoscopy or laparotomy is indicated. After surgery, patients are subject to clinical observation with frequency of examinations in the first year after surgical treatment - once every 6 months, subsequently - once a year.
Signs
At first, a person is not bothered by such a pathology as intestinal elongation.
As the disease progresses, characteristic symptoms begin to appear.
- The abdomen is swollen, with this sign there is also constant rumbling.
- Reflexes are reduced.
- Constipation is a concern (often lasting up to two weeks). Often, stool remains in the intestines for more than five days.
- The defecation reflex is impaired.
- Fecal masses pass with difficulty, against this background inflammation begins in the intestines.
- The feces thicken and a pungent odor develops.
- Blood particles are often present in the stool.
- Pain may appear near the navel, in the anus.
- The digestive tract is disrupted.
- I'm worried about intestinal obstruction.
- Flatulence occurs.
If the intestine is greatly elongated, then dolichomegacolon is formed. This form of the disease is characterized not only by expansion and lengthening of the intestine, but also by the appearance of wall hypertrophy. The signs are similar to the usual form.
Dolichomegacolon occurs more often in newborns and men. In children the disease is congenital, in men it is acquired. There are a number of reasons for the appearance of the disease in men:
- the formation of too large a transverse fold;
- poor intestinal muscles;
- the formation of kinks and scars on the intestines after various injuries;
- abuse of bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- poor nutrition.
The signs of the disease are similar to dolichocolon, but they are brighter.
- Worried about diarrhea or chronic constipation.
- There is a feeling that the stomach is overly distended.
- After a bowel movement, there is a feeling that the colon is still full.
The doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis only after a thorough examination. You cannot self-medicate. Sometimes excessive use of enemas or use of laxatives can lead to serious consequences.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, as well as to reduce the risk of possible relapses and complications in patients with dolichocolon, it is recommended to follow a number of preventive measures, which include:
- active lifestyle, regular and sufficient physical activity;
- normalization of diet;
- drinking enough water;
- giving up the habit of suppressing the urge to defecate;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules.
To avoid the development of a congenital form of the disease in the fetus, pregnant women are advised to give up bad habits and avoid the influence of unfavorable environmental factors on the body.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Nutrition for dolichocolon
To normalize the condition, first of all, pay attention to the diet for dolichocolon. Patients are advised to adhere to the following principles:
1. The diet should be balanced and contain a sufficient amount of fiber: bran, whole wheat grains, fresh vegetables, herbs and fruits.
2. Eating 4-5 times a day, in small portions.
3. Refusal of fatty meats and poultry, preference for fish dishes.
4. Regular consumption of fermented milk products.
5. Preferring vegetable fats to animal fats: olive and flaxseed oil are useful.
6. Exclusion from the diet of the following foods: beans, cabbage, rice, potatoes, sweets, sausages, canned food.
7. An increase in the drinking regime is indicated: water, unsweetened compotes with prunes, apples, berries, fruit drinks, herbal decoctions. Refusal of strong tea and coffee, alcohol, kvass, carbonated drinks.
8. It is recommended to prepare all dishes using gentle heat treatment: in the oven, steamed, or boiled.
Regular, feasible physical activity and taking multivitamin complexes are necessary. It is important to create conditions for a calm visit to the toilet, without ignoring the urge to defecate.