Inflammatory diseases of the esophagus are a whole group of nosologies, common to which is an inflammatory-destructive reaction that develops in the mucous membrane of the organ. As the disease progresses, the pathological process may affect the deeper structures of the esophagus. These diseases are collectively called esophagitis. These include:
- acute esophagitis;
- chronic esophagitis;
- GERD.
Depending on the predominant morphological picture, inflammatory diseases of the esophagus are divided:
- catarrhal;
- erosive;
- hemorrhagic;
- necrotic.
Each form requires specific treatment.
What is inflammation of the esophagus
Inflammation of the esophagus is a typical protective reaction of the body aimed at localizing, destroying and removing a pathogenic agent from the body. This process is accompanied by tissue damage (alteration), fluid accumulation (exudation), as well as an increase in the number of cells and tissue proliferation at the site of inflammation (proliferation).
Inflammation of the esophagus occurs in the mucous membrane of the organ, which gives the corresponding symptoms:
- chest pain when swallowing food;
- violation of the act of swallowing;
- heartburn;
- increased salivation.
The method of treatment depends on the causes of inflammation, the severity of damage to the inflamed organ and its duration. Most often, esophagitis is treated conservatively with diet, medications, and physiotherapeutic procedures, but sometimes there is a need for surgical treatment.
Symptoms
Peptic esophagitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Severe pain along the esophagus during eating. The pain radiates to the arm, jaw, shoulder blade.
- Constant heartburn. It becomes pronounced after overeating or intense exercise.
- Darkening of tooth enamel.
- Pain in the throat, cough.
Interesting! Causes and symptoms of superficial reflux esophagitis
Note! The more pronounced disorders of the esophageal mucosa a patient has, the more varied the symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of inflammation of the esophagus in adults
With inflammation of the esophagus, the symptoms may differ slightly depending on the form of the disease.
Symptoms of acute esophagitis
Acute inflammation of the esophageal mucosa is accompanied by a clinical picture, which is determined by the cause of the disease and the severity of the inflammatory reaction:
- With catarrhal and erosive esophagitis, the clinical picture can be moderate and less pronounced. Patients are concerned about moderate dysphagia and odynophagia (pain when swallowing), mainly when swallowing coarse or hot food, belching of air, increased salivation, a feeling of “lump in the throat.”
- With hemorrhagic esophagitis, patients are worried about belching with bloody mucus, vomiting with blood (severe bleeding is possible), melena (black stool due to blood).
- In case of necrotizing esophagitis that occurs due to infections (all forms of sepsis, typhus, diphtheria) as well as chemical burns (acids, alkalis) against the background of a severe general condition, dysphagia, sharp retrosternal pain, vomiting with fragments of necrotic tissue are noted. It is very difficult to treat such conditions.
Symptoms of chronic esophagitis
In chronic esophagitis, most often a syndrome of various pathologies, the main symptom is heartburn and burning in the chest. These signs intensify after eating fatty foods, carbonated drinks, and coffee. Pain in chronic esophagitis is moderate, its typical localization is behind the xiphoid process. A common complaint with chronic esophagitis is belching with a bitter or sour aftertaste.
Symptoms of reflux esophagitis (peptic esophagitis)
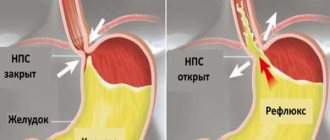
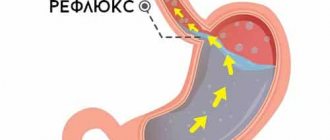
Constant exposure to gastric juice causes irritation and inflammation of the inner lining of the esophagus. A clear and defining sign of reflux esophagitis is heartburn that occurs after eating or during eating. Heartburn is often accompanied by cramping pain, the appearance of which is associated with spasm of the esophagus. Also a common complaint with this pathology is regurgitation of eaten food. Dysphagia with GERD is transient. Constant pain, a burning sensation, regurgitation of food - all this has a negative effect on the patient’s psyche, causing depressive reactions, which makes treatment difficult.
Basic treatment methods
Distal esophagitis can be cured with complex therapy:
- taking medications;
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- traditional medicine.
Treatment of pathology is aimed at eliminating symptomatic signs and the causes of the disease. To completely get rid of distal esophagitis at the first stage, long-term therapy is required.
Drug treatment
The prescription of medications depends on the cause of the pathology. The main means are:
- antibiotics – entry of pathogenic bacteria;
- autoimmune – penetration of viruses;
- prokinetics - impaired motor function of the esophagus;
- antacids – increased level of acidity;
- enveloping drugs – inflammation of the esophageal mucosa;
- painkillers – presence of spasms.
The main functions of taking medications are to protect the mucous membrane from the effects of aggressive factors, normalize acidity levels, and eliminate pain. The duration of taking medications is from 4 to 6 weeks.
Proper nutrition
Diet is the main method of treatment for pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. The basic principles of healthy eating are:
- fractional meals (at least 5 times a day);
- small portions (no more than 200 g);
- prolonged chewing of food;
- inclusion of cereals, broths, soups in the diet;
- refusal of spicy, salty, solid foods;
- maintaining the temperature of food;
- drinking water (at least 2 liters).
It is recommended to consume liquid, crushed food for several weeks. During treatment, you must give up alcohol, tobacco products, and carbonated drinks.
.
The main ingredients of the diet are stewed, baked, boiled lean meats, low-fat dairy products, bananas, peaches, and cereals. After eating, it is advisable not to take a horizontal position for half an hour to avoid gastric juice from entering the esophagus.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine methods are suitable for eliminating the symptoms of the disease - heartburn, pain. Effective methods are herbal infusions, decoctions of calendula, calamus, anise, lemon balm, and licorice. Potato juice, dill water, tea made from mint, chamomile, blackberry and raspberry leaves help get rid of heartburn. Aloe and sea buckthorn oil have enveloping and protective effects.
To avoid recurrence of the pathology and an attack of chronic distal reflux esophagitis, it is necessary to control the diet, give up bad habits, promptly treat viral and infectious diseases, and undergo regular examinations.
We recommend: What is esophageal erosion and how to treat it correctly?
What causes inflammation of the lining of the esophagus
The causes of inflammation of the esophagus (acute form) can be very different. The most common of them:
- infections - viruses (adenovirus, influenza virus), bacteria (beta-streptococcus A, sepsis of any etiology), fungi (Candida genus);
- effect on the mucous membrane of the esophagus of thermal, chemical agents, radioactive substances (hot food or drinks, acids, alkalis, alcohol substitutes, inflammation after irradiation for the treatment of oncological pathology);
- injury to the esophageal mucosa by a foreign body.
Symptoms and treatment of candidal esophagitis with drugs
Causes of development of chronic esophagitis
Chronic esophagitis is also caused by many different factors:
- nutritional esophagitis (habit of too hot and spicy foods);
- occupational esophagitis (when working with caustic substances);
- inflammation of the esophagus due to metabolic disorders (hypovitaminosis, lack of microelements);
- allergic esophagitis (with various types of food allergies);
- idiopathic esophagitis.
Causes of reflux esophagitis
The main cause of reflux esophagitis is the frequent and prolonged reflux of stomach contents and bile into the esophagus as a result of a violation of its closure mechanism, the second important reason is a decrease in the rate of cleansing of the esophagus and neutralization of the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid on the mucosa. This disease is promoted by:
- eating food excessively quickly and swallowing large amounts of air;
- fatty meat foods, spices, pasta;
- the effect of certain medications (nitrates, calcium antagonists, anticholinergics, theophylline).
Important! Before starting to treat the main symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to remove the effects of these factors.
What is esophagitis?
Any manifestation of esophagitis refers to the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the esophagus. There are several forms of the disease:
- chronic;
- spicy.
When pathology develops, inflammation affects not only the upper mucous epithelium, but also the deeper layers. According to statistics, people get sick in 40% of cases. At the same time, the peculiarity of the pathology is that the disease develops without pronounced symptoms.
The chronic form is rare. In this case, the disease occurs in adults. Chronic esophagitis is divided into varieties that depend on the factors causing the inflammatory process. According to statistics, pathology develops in 5% of cases. People who lead an unhealthy lifestyle and do not maintain a balanced diet are at risk.
Why is inflammation of the esophagus dangerous?
Inflammatory diseases can lead not only to surgery or disability, but can even threaten the patient’s life if you do not consult a doctor in time - this is why inflammation of the esophagus is dangerous.
Of course, catarrhal and erosive forms of esophagitis, after eliminating the causes that caused them, go away on their own and rarely cause complications. With more severe esophagitis, the following consequences are possible:
- Narrowing of the esophageal opening (stenosis) is most often the result of chemical burns or severe infections (tuberculosis, diphtheria, typhus); a massive deposition of connective tissue forms at the site of narrowing, which significantly complicates the peristalsis of the esophagus. Above the site of narrowing, as a result of the constant accumulation of food, the wall of the esophagus stretches and bulges, diverticula of the esophagus appear, which often become infected. Post-burn stenoses have a large extent.
- Perforation of the esophagus is a serious complication requiring urgent surgical care. The causes of perforation can be burn esophagitis, esophagitis due to severe infections, and peptic ulcers. The first symptom of perforation may be vomiting, first of scarlet blood, and then of “coffee grounds”. The clinical picture of shock increases very quickly (blood pressure drops sharply, against the background of tachycardia, followed by arrhythmia).
- Barrett's esophagus – This condition is most often the result of GRD. As a result of constant exposure to the acidic contents of the stomach on the mucous membrane of the esophagus, the cells of the mucous membrane are damaged and changed. Such metaplastic cells often give rise to adenocarcinoma.
- Purulent complications of esophagitis. When the esophagus is damaged by foreign bodies (fish bones, accidentally swallowed sharp objects), abscesses and phlegmon of the esophagus occur.
Complications of the disease
If treatment is incorrect or recommendations are not followed, unpleasant consequences arise. Complications of esophagitis in chronic form are diseases of the digestive organ. Due to inflammation, a peptic ulcer of the esophagus develops. Severe deformation of the mucosa occurs in the form of scars.
Due to frequent exacerbation of the disease, a narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus occurs. This leads to impaired gastric motility. The patient begins to lose weight. A dangerous complication is perforation of the esophageal wall. In this case, the patient undergoes surgery. This also includes the development of Barrett's esophagus. This occurs due to reflux esophagitis. Without proper treatment, degeneration of the esophageal wall occurs.
The development of chronic esophagitis is considered to be a consequence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The pathology in the early stages is asymptomatic. Therefore, the patient begins to think about health when heartburn occurs or acute pain in the chest suddenly appears. Especially after eating, this symptom intensifies and does not go away for a long time. To avoid complications, medical treatment is required. To prevent a chronic disease, it is worth eliminating the signs of acute esophagitis or another disease that causes the development of pathology.
We recommend: What is esophageal candidiasis and what treatment is prescribed?
Diagnosis of inflammatory diseases of the esophagus
Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process, the patient is examined on an emergency or scheduled basis.
The main types of examination for esophagitis are as follows:
- If an infectious nature of the lesion is suspected, a blood test is done for viral and bacterial infection (antibody titers to viruses, diphtheria, typhus pathogens are determined, and a blood test is done for HIV infection).
- X-ray with contrast of the esophagus is a low-traumatic and highly informative examination. Allows you to identify the lesion, detect a foreign body in the esophagus, and assess the degree of narrowing of the esophagus. For chemical burns of the esophagus, examination can be scheduled already on the second day after the injury.
- Esophagomanometry - the study allows you to evaluate the peristaltic activity of the esophagus, determine the pH inside the organ, and determine the rate of emptying of the esophagus (esophageal clearance).
- Esophagoscopy is an examination of the esophagus from the inside using an esophagoscope. The method allows not only to examine the esophageal mucosa in detail, but, if necessary, to take a biopsy of the organ for histological analysis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out in order to differentiate esophagitis from diseases with similar symptoms, as well as to identify the cause of the development of the disease. The easiest way to make a diagnosis is for an acute disease: patients complain of specific pain. A burning sensation behind the sternum (heartburn) is a typical symptom of inflammation of the esophagus, which forces the patient to consult a gastroenterologist. The doctor conducts a survey, finding out the possible causes of the disease, examination, and then prescribes additional examinations.
As part of the diagnosis of esophagitis, the following methods are used:
- Endoscopic examination of the esophagus (esophagoscopy). The study makes it possible to determine the degree of damage to the mucosa and the location of defects.
- Biopsy. Biological material is collected during endoscopy. Histological examination allows us to determine the nature of changes in the mucosa, identify neoplastic processes, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
- To diagnose disorders of the motor function of the esophagus, esophagomanometry is prescribed.
- X-ray examination of the esophagus. The study is used to identify stenosis, diverticula, and hiatal hernia.
- Daily pH-metry to identify reflux disease as a cause of esophagitis.
Based on the examination results, the attending physician chooses treatment tactics.
Inflammation of the esophagus: how to treat it
Treatment of acute inflammation of the esophagus:
- for the treatment of infectious diseases that cause esophagitis, antibiotics are used in full dose (parenterally);
- food intake is stopped for several days, and in the case of chemical burns, necrotic or severe hemorrhagic esophagitis, the patient is transferred to parenteral nutrition, with a subsequent transition to chemically and mechanically gentle food;
- to relieve the symptoms of inflammation, solutions of the medications novocaine, collargol, tannin are used internally;
- To reduce the phenomena of esophageal dyskinesia, prokinetics in tablets are used (Domperidol, Itoprid);
- for multiple erosions, solcoseryl is used;
- for hemorrhagic esophagitis complicated by bleeding, aminocaproic acid, Dicynon, Vikasol are used;
- Correction of strictures is carried out by bougienage.
How to treat chronic inflammatory processes in the esophagus:
- Diet therapy. The frequency of meals, methods of cooking, the list of permitted and requested products are discussed in detail with the attending physician.
- Drugs that reduce the pH of the stomach contents by neutralizing hydrochloric acid (antacids - Maalox, Almagel, Gaviscon, Phosphalugel), or by suppressing its formation in the stomach: PPI (Omeprazole, Rabeprozole) or IGR (Famotidine, Roxatidine, Nizatidine).
- Drugs that enhance the motility of the stomach and intestines, accelerate the movement of food from the stomach into the intestines, enhance peristalsis of the esophagus, normalize the tone of the sphincters - prokinetics (Domperidol, Itopride).
- Physiotherapeutic treatment (laser therapy, magnetic therapy, balneotherapy, cryotherapy).
- Folk remedies.
Inflammation of the esophagus and treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine in the treatment of inflammation of the esophagus uses drugs that reduce the severity of the local inflammatory reaction, thereby reducing pain and heartburn.
The simplest recipes to prepare at home, for treatment with folk remedies that relieve symptoms of inflammation, are discussed in the diagram below (Table 1):
Table 1. Recipes for preparing remedies for inflammation of the esophagus
| Sea buckthorn oil | Method of preparation: Purchased at the pharmacy Method of administration: 1 tablespoon 3 times a day on an empty stomach |
| pharmaceutical camomile | Method of preparation: Brewed like tea Method of administration: Drink a cup 5 times a day before meals |
| Aloe vera + water | Method of preparation: Dilute freshly squeezed aloe juice in water (0.060 - 0.030) Method of administration: Drink when heartburn occurs |
| Pomegranate fruit peels | Method of preparation: Take 1 liter of boiling water + 2 tablespoons of dry pomegranate peels. Pour the crusts into a thermos and pour boiling water, close tightly, and leave for a day. Method of administration: Drink 0.025 liters of infusion every 5 - 6 hours on an empty stomach for 5 days, repeat the course after a month |
| Bee Honey | Method of preparation: 50 gr. Divide fresh bee honey into two doses. Method of administration: Take 25 grams. 2 times a day |
Prevention
You need to learn to eat regularly and on time. Completely eliminate foods that cause heartburn (coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits). Avoid hyperphagia. Quit cigarettes and alcohol.
It is necessary to get regular and complete rest and avoid stressful situations.
You should not wear clothes with very tight belts, and avoid straining your abdominal muscles. It is necessary to sleep with the head of the bed raised.
Observe safety precautions when working with hazardous substances.