Principles of therapy
Treatment of this disease is based on the following principles:
- Maintaining a certain lifestyle and diet.
- Reducing the level of acidity in the stomach.
- Strengthening evacuation activities.
- Stimulation of motility of the digestive tract.
- Restoration of the gastric mucosa and its protection.
Before we talk about how to treat reflux esophagitis, we must make a reservation that therapy lasts 4 weeks. In the case of the erosive form of the disease, the duration is increased to 8 weeks. It is possible to increase the dosage.
If the doctor diagnoses changes that have occurred due to a disease outside the esophagus, treatment is extended to 12 weeks. When remission occurs, the patient is transferred to maintenance therapy.
Treatment regimens may vary. Here are the three most commonly practiced options:
- The patient takes the same drug prescribed by the doctor. Complications, accompanying symptoms and changes in the mucous membrane are not taken into account. This scheme is ineffective.
- The patient follows a diet and takes antacids. When prescribing the drug, the severity of the inflammatory process is taken into account. Several medications may be prescribed.
- First, the patient takes strong proton pump inhibitors, and then weak prokinetics. This method is used if the disease is severe.
The exact regimen that will be chosen is determined by the attending physician, who takes into account the clinical picture and the data obtained as a result of the examination.
Correct diagnosis of the disease
There are different ways to make a diagnosis. The main ones are the following:
- An effective diagnostic method is esophagoscopy. During the examination, the degree of damage to the esophagus, inflammatory manifestations, and the presence of mucus are determined.
- X-rays help detect characteristic dysfunctions in the esophagus.
- Biopsy. The purpose of the study is to clarify specific lesions and malignant neoplasms.
In addition to the methods described above, the doctor will prescribe general tests for blood and urine.
Antacids
Now we can talk about how to treat reflux esophagitis. Antacids are drugs that neutralize hydrochloric acid. They also bind bile acids, accelerate the release of bicarbonates, and also inactivate pepsin. Non-systemic antacids containing magnesium and aluminum are considered the best.
As a rule, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- "Maalox." Available in the form of pleasant-tasting sachets, tablets and suspensions.
- "Almagel". It has a composition similar to the previous drug.
- "Almagel A". Additionally, the drug contains a local anesthetic. Therefore, this remedy also has an analgesic effect. But it cannot be taken for more than 1 month.
- "Almagel NEO". An additional component of this drug is simethicone, which eliminates flatulence and bloating.
- "Gastal." A well-known medicine, available in the form of tablets with various flavors.
- "Phosphalugel". This is a multicomponent antacid, which is produced in the form of a sachet. The drug has a positive effect on peristalsis and also promotes the removal of harmful substances from the intestines.
- "Gastraticide." A well-known remedy for European. In addition to antacids, this drug includes the notorious simethicone and licorice extract, which provides protection to the mucous membrane and has an antispasmodic effect.
- "Talcid". The medication ensures long-term maintenance of acidity at a normal level, as it promotes the gradual release of ions.
- "Rutacid." Chewable tablets, easy to use.
When talking about how to treat reflux esophagitis, it is necessary to make a reservation that experts recommend using drugs in liquid form. This way they are absorbed faster and easier. This is important for this disease.
Alginates
Medicines in this group should also be mentioned, since we are talking about how to treat reflux esophagitis. Alginate preparations, like antacids, are designed to reduce acidity levels. And they have this name because of the alginic acid they contain.
Many doctors consider these drugs to be preferable to antacids. They are almost completely safe, and the effect occurs 4-7 minutes after administration.
The best alginates are:
- "Laminal."
- Gaviscon.
- Sodium, magnesium and calcium alginate.
They are available in the form of suspensions, chewable wafers and capsules. They should be used during long-term meals.
Causes of the disease
For the disease esophagitis, the causes lie in a number of factors that lead to lifestyle changes. In this aspect, there is an unhealthy diet high in fat, frequent consumption of carbonated drinks, etc. The list of reasons also includes the following:
- disturbance of intestinal motility;
- diabetes;
- metabolic syndrome;
- infections (fungi of the genus Candida, herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus);
- hiatal hernia;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- taking certain groups of medications;
- cardiovascular disease.
Proton pump inhibitors
Here's another way to treat reflux esophagitis. PPI drugs have a cumulative effect, so the patient does not notice any changes in the first few days of use. They begin to work in full force when enough active substance accumulates in the secretion of gastric juice.
Popular medications in this group include:
- "Acrilanz". Available in packs of 10, 20 and 30 capsules. You need to drink once a day.
- "Lancid". Treats all acid-dependent gastrointestinal diseases. The dosage is intended for single use. If symptoms are severe, the doctor increases the amount of the drug taken.
- "Epicurus". Each capsule contains as much as 30 mg of active ingredient.
- "Omez." New generation drug. Each capsule contains 40 mg of active ingredient. You need to take it once a day. This is enough to suppress acid production for a day.
- "Bioprazole". It is quickly adsorbed in the stomach, the maximum concentration is recorded within half an hour after administration.
In addition to the listed drugs, the doctor may prescribe Omezol, Losek, Ultera, Controloc, Nolpaza, Pariet, Ontime, Zolispan, Bereta, Zulbex or Rabelok. .
But the most expensive and most effective medications are those based on esomeprazole. These are Nexium and Emanera. And drugs whose active ingredients are pantoprazole and lansoprazole are considered to be the most accessible and safe. They are suitable for almost everyone, and side effects are extremely rare.
How to live with esophagitis
Treatment of inflammation of the esophagus involves not only conservative therapy, but also adherence to strict dietary rules and some restrictions.
First of all, you will have to completely give up smoking and drinking alcohol. After meals, short walks and wearing loose clothing are required. You will have to give up abdominal exercises and eliminate bending of the torso.
The pillow for sleeping must be chosen high so that the head is raised.
If it is known for sure that the patient has a disease such as esophagitis, then a diet is mandatory for all patients. All sour and sweet fruits are eliminated from the diet; citrus fruits must be completely eliminated.
You should not consume carbonated drinks, coffee, marinades, spicy and fatty foods, spices and chocolate. Under no circumstances should you eat food whose temperature exceeds 40 degrees. Food must be chewed thoroughly or brought to a semi-liquid state. You should not snack at night or on the go.
To reduce symptoms and improve the effect of treatment of esophagitis, it is better to take food 4-6 times a day, in small portions.
H2-histamine receptor blockers
These antisecretory agents are aimed at reducing the production of hydrochloric acid. These drugs also have the following effects:
- Accelerate the secretion of prostaglandins.
- Stimulate blood flow in the gastric mucosa.
- Inhibits pepsin synthesis.
- Activate the process of hydrogen carbonate synthesis.
- Stimulates mucus formation.
With the use of these drugs, it is possible to treat reflux esophagitis much faster. Tablets, like the previous listed remedies, are prescribed by a doctor. The most well-known H2-histamine receptors are:
- Cimetidine (Histodil). First generation medicine. Once widely used, but now outdated and therefore not available in many pharmacy chains. Has many side effects.
- "Ranitidine" ("Ranisan", "Zantac", "Ranigast", "Gistak", etc.). Much better tolerated than the previous drug. But practice knows cases of the development of acute hepatitis that occur while taking it.
- Famotidine (Kvamatel). According to research, it is 7-20 times more effective than the previous drug (it’s different for everyone). And it works for 10-12 hours. It is well tolerated by patients even when treating exacerbations. Side effects are minimal. It can even be taken for alcohol addiction.
In general, there are 5 generations of H2-histamine receptors. There are also “Nizatadin” and “Roxatidine”, which were previously used, but are currently not registered in Russia. As a rule, drugs of the 2nd and 3rd generations are used.
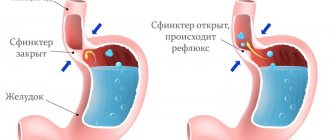
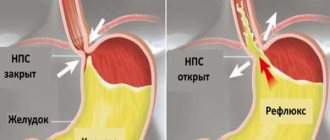
GERD and reflux esophagitis
In Internet resources, on television and even in medical literature, these two concepts are often confused. They must be distinguished, since treatment depends on the diagnosis. To explain the subtleties of terminology, just study the table below:
| GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease) | Reflux esophagitis | |
| What it is? | A disease that develops when food refluxes from the stomach into the lower parts of the esophagus. Accompanied by damage to the organ mucosa. | |
| Are there any changes in the walls of the esophagus? | With a mild course, the mucous membrane may be normal. | Inflammatory changes are always detected. |
| How to make a diagnosis? | At the first examination by a doctor. | Only after endoscopic diagnosis - fibrogastroscopy (FGS). |
| Difference in treatment | Medicines are taken only when necessary. | Regular therapy with pharmacological agents is necessary to prevent stenosis (narrowing of the organ), bleeding, cancer, etc. |
In short, esophagitis is inflammation of the esophagus, which is detected after FGS. GERD can exist without esophagitis, but there is no reflux esophagitis without GERD.
Prokinetics
These remedies also need to be discussed as part of the topic regarding how to treat reflux esophagitis. Tablets of this group regulate the motility of the digestive tract. The drugs also help move intestinal contents, improve the functioning of the sphincter between the esophagus and stomach, and also prevent the backflow of food.
Therefore, if a person is interested in how to treat GERD (reflux esophagitis), he needs to know the names of effective prokinetics:
- "Metoclopramide", "Raglan", "Cerucal" and "Gastrosil". They stimulate the work of the upper parts of the tract, reduce the excitability of the vomiting center, and do not affect peristalsis.
- "Domperidone", "Motilium", "Motilak" and "Domperon". The drugs are free of side effects from the central nervous system. The effect is on the duodenum and gastric motility. Produce a moderate antiemetic effect.
- "Prucaloprid" ("Rezolor"). It has a pronounced effect on intestinal motility. Produces a good laxative effect.
- "Latran", "Zofran". The main component of these drugs affects the movement of food from the stomach. It also normalizes the tone of the large intestine.
- "Tropindol" ("Navoban", "Tropisetron"). These drugs are even prescribed to cancer patients after chemotherapy. They have a long lasting effect. By taking them, you can normalize the functioning of the lower sphincter, as well as prevent reflux of gastric contents.
- "Itopride" ("Itomed" and "Ganaton"). Tones the lower esophageal sphincter, prevents the reflux of contents, and also stimulates peristalsis and improves emptying. It also has a moderate antiemetic effect.
These drugs are the answer to the question of how and how to treat reflux esophagitis. The doctor will decide which tablets are best.
By the way, there is also a prokinetic agent of plant origin! And this is Iberogast. It contains extracts of 9 plants. Each of them acts on the digestive tract individually. But it is a fact that the drug normalizes motility, speeds up the passage of food, increases mucus production and reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
Treatment
The insidiousness of esophagitis lies in the absence of pronounced symptoms, which is why most patients neglect the recommendations of doctors. As a result, the disease continues to develop and causes dangerous complications. To prevent this outcome, treatment for reflux esophagitis should be started in a timely manner, which consists not only of regularly taking medications, but also of changing lifestyle.
General events
Before you start taking medications and adjusting your diet, you need to make certain lifestyle changes. Following simple guidelines has been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of reflux and damage to the valve muscle. For patients with inflammation of the esophagus, it is fundamentally important to perform the following measures:
- Stop smoking. Nicotine not only increases the acidity of gastric juices, but also has a relaxing effect on the muscles of the digestive tract. The combination of these effects leads to increased symptoms of esophagitis;
- Do not lie down after eating. It is recommended to sit in a comfortable position or walk leisurely for 30 minutes after eating. Lifting weights, running and even brisk walking should also be avoided immediately after lunch;
- Limit physical activity. To reduce the severity of symptoms, women should not lift more than 3 kg, and men should not lift more than 5 kg;
- It is necessary to avoid eating and drinking alcoholic beverages 2-3 hours before bedtime;
- It is necessary to sleep on a high pillow or with the head end raised by 15-20 cm;
- Refuse to wear constricting clothing, including belts, corsets, girdles, etc.;
- If there are concomitant diseases (obesity, gastritis, peptic ulcer, Ellison-Zollinger syndrome and others), it is necessary to carry out their full treatment. Otherwise, treatment of reflux esophagitis will be ineffective.
Diet
Nutrition is an important component of therapy and prevention of complications. For most people, diet treatment is associated with tasteless food and constant restrictions. Indeed, with this disease there is a need to eliminate certain foods from the diet. However, with the help of simple culinary techniques, you can make almost any dish from permitted products. We will show you how to make a diet for reflux esophagitis enjoyable, complete and tasty.
See Diet for reflux esophagitis, weekly menu Heartburn after eating, Heartburn medications, How to get rid of heartburn
What products are not allowed?
To reduce the number of reflux and acidity of gastric juice, it is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- Caffeine-containing drinks: energy drinks, coffee, Coca-Cola, some cocktails, etc.;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Alcohol;
- Any flour dishes, as they increase the secretion of acid in the stomach;
- Limit intake of chocolate and sweets;
- Fermented milk products;
- Olive and flaxseed oil, animal fats;
- “Sour” fruits and vegetables: citrus fruits, radishes, pomegranates, radishes, etc.;
What's the best way to prepare food?
First of all, you should avoid fried foods in vegetable or animal oils. Such products lead to a massive release of gastric juice and the appearance of aggressive reflux. Preference should be given to boiled food, steamed or stewed in its own juice. For this purpose, you can use not only classic cooking methods, but also modern gadgets.
Here are some tips on how to prepare tasty and low-fat meat dishes:
- Wrap. In almost any chain store you can purchase special sets with paper bags/sheets. Their use allows you to cook almost any meat dish without a drop of oil. Instead of the spices that come with the kit, you can use a sufficient amount of salt, fresh or dried herbs (dill, parsley, basil) and natural chopped vegetables (sweet peppers, cucumbers, eggplants, zucchini, a small amount of onions and garlic);
- Baking in the oven. This is the optimal way to prepare any dish for the patient. The absence of additional oil, in addition to what is present in the meat, allows you to prepare any low-fat dish. The water with which the ingredients are poured makes them soft and easy to digest. The ability to cook a side dish and a main dish in one baking sheet/frying pan saves a lot of time. However, it should be remembered that the minimum duration of such baking is 60-70 minutes. Recommended temperature 180-200oC.
- Microwave cooking. Modern models make it possible to cook almost any type of meat or fish using exclusively wave radiation. Contrary to popular belief, it does not in any way affect the quality and safety of food, which is confirmed by scientific research by Western doctors. At the same time, the food turns out to be low-fat and quite tasty. The main thing is to follow the cooking regime, which is described in the instructions. This will protect food from harmful microorganisms and save time on selecting the optimal cooking scheme;
- Using a steamer/multi-cooker. To prepare a tasty and healthy dish with the help of these gadgets, you need to add juicy vegetables such as carrots, onions, tomatoes or pumpkin pieces to the meat or side dish. Thanks to steaming, they produce abundant juice that permeates dishes and gives it a pleasant taste. Also, do not forget to add salt to food to taste and add herbs (dill, coriander, parsley, etc.);
- Cooking over an open fire. This method is not suitable for daily use, but when you go out into nature, it will be indispensable. Since all excess fat is evaporated from the food over the fire and no additional oil is added, the meat turns out to be lean and quite tasty. It is suitable for a patient with esophagitis under one condition - if no spicy marinade was used to treat it.
When dressing dishes, you should limit the amount of mayonnaise and oils. You should also avoid ketchup, mustard and hot sauces. They not only damage the mucous membrane, but also increase acid secretion in the organ. Food consumed should be at room temperature - too hot or cold food also has a negative effect on the digestive organs.
Pharmacotherapy
Medicines to reduce acidity of reflux
Various groups of drugs can be used to treat reflux esophagitis, but one of them is prescribed to almost all patients - proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These medications effectively reduce the acidity of gastric juice. By influencing the cells that produce hydrochloric acid, they reduce its concentration. Thanks to this effect, the reflux of gastric contents causes less damage to the mucous membrane.
At the moment, there are 5 main types of PPIs: omeprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole. To choose the optimal drug for yourself, you need to contact a competent therapist or gastroenterologist. He will assess the condition of the body and the course of the disease, and then prescribe therapy.
According to modern research (2014-2016), some pump inhibitors have features of action that are important to consider before taking them. We list the most important of them below:
| Patient Feature | Optimal drugs | Why these drugs? |
| The need to take medications that reduce the activity of the AP enzyme (enalapril, captopril, lisinopril, ramipril, etc.) | Pantoprazole, rabeprazole. | Doctors have determined that for people with heart disease or high blood pressure, the risk of heart attacks and strokes increases after taking omeprazole or esomeprazole. Subsequently, it was found that these drugs neutralize the protective effect of drugs that reduce the concentration of the AP enzyme. |
| During pregnancy (after the 13th week) | Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole. | The American Medical Association (FDA), which evaluates the safety of drugs, has not found any toxic effects of these drugs on the fetus or mother. However, their use is not recommended until the 13th week of pregnancy, since at this time all the main organs of the child are forming. Omeprazole, rabeprazole and esomeprazole are prohibited for use during pregnancy. |
| If you have bronchial asthma | Esomeprazole, Omeprazole | There is no doubt that reflux esophagitis and asthma are interrelated. There is research proving the positive effect of these medications on the course of respiratory disorders. |
| In case of liver dysfunction (hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcoholic or fatty hepatosis and others) | It is possible to use any PPI, but it is better to use rabeprazole. | The minimum dosage of rabeprazole is 10 mg, which is half as much as other medications in this group. According to some scientists, its use can reduce the load on liver cells. |
| Requires rapid and sustained reduction in acidity | Lansoprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole. | Scientific studies have proven that the maximum effect of omeprazole and esomeprazole develops only on the 3-4th day of administration. The listed medications take effect within one day. |
Only if PPIs are intolerant or ineffective, a group of histamine H2 blockers is used to reduce acidity. They have been proven to be less effective and require larger doses, so they are prescribed only as a last resort. These include famotidine, ranitidine, nizatidine, roxatidine.
Medicines to improve gastrointestinal motility
In addition to reducing the aggressiveness of reflux, it is necessary to reduce their number. Not only lifestyle changes, but also some medications can help with this. They belong to the group of prokinetics - drugs that improve the motility of the digestive tract and facilitate the movement of the food bolus. These include:
- Domperidone (Motilium, Motilak, Motonium) is the optimal remedy for inflammation of the esophageal mucosa. Allows you to improve the functioning of sphincters, peristalsis of the stomach and intestines;
- Cisapride (Coordinax, Peristil) - the drug has a targeted effect on the lower sphincter of the esophagus and stomach, increasing their tone and reducing the frequency of reflux;
- Metoclopramide (Raglan, Perinorm, Cerucal) – is used when other drugs are ineffective and there are frequent discharges. Not recommended as a starter drug due to frequent side effects such as constant fatigue, weakness, muscle twitching, etc.
Only the attending physician can prescribe a drug for treatment. Each of them has its own contraindications and side effects that must be taken into account before starting therapy.
Antacids
For immediate relief of heartburn or esophageal pain, this group of medications is perfect. Antacids do not cure the disease, but they can temporarily relieve its symptoms. They have virtually no contraindications, so they can be taken without a doctor's prescription.
Almagel is the most famous antacid, which was one of the first to appear on the market. At the moment, it is significantly inferior in effectiveness to such drugs as:
- Gaviscon;
- Rennie;
- Maalox;
- Megalac.
According to recent studies, the listed pharmacological agents begin to act faster, retain their effect longer and more strongly reduce the acidity of gastric juice.
A few words need to be said about an aqueous solution of soda, which is widely used to relieve heartburn. Such treatment with a folk remedy only has a negative effect on the organs. When alkali first passes through the esophagus, irritation of the mucous membrane occurs. In response to immediate alkalization of the stomach, a strong release of acid occurs and reflux becomes more aggressive. Doctors strongly recommend not using soda, but using regular antacids.
When is surgery needed?
Esophagitis is almost always treated without surgery. Surgery is a last resort measure that is used in the event of severe complications. Consultation with a surgeon to determine the need and extent of surgery is recommended in the following situations:
- If there is constant bleeding from the esophageal vessels;
- Against the background of persistent narrowing of the esophageal tube (stricture), which prevents the passage of food;
- With irreversible damage to the esophageal sphincter;
- A precancerous condition of the mucous membrane is degeneration and random proliferation of cells. This condition is called “Barrett's esophagus”;
- Esophageal cancer stages 1-2.
In each of these cases, the decision on the type of operation is made individually. Removal of a pathological formation, removal of part of the esophageal tube, or restoration of the integrity of the organ using the remaining part of the esophagus or intestines can be carried out. These operations have two common features - they are all carried out for life-saving reasons and each is quite difficult for the patient to tolerate.
Cytoprotectors
Much has been said above about how to treat reflux esophagitis. What other tablets are suitable for eliminating this disease? Of course, cytoprotectors. These are products that improve the protective properties of the inner wall of the stomach and esophagus. They also accelerate the healing of ulcers and erosions, reduce acidity and improve blood circulation.
Here are some drugs belonging to this group that treat reflux esophagitis:
- "Dalargin." The substance is of peptide nature. Heals ulcers of the duodenum and stomach, suppresses proteolysis, and has a pronounced hypotensive effect.
- "Misoprostol." It has a powerful cytoprotective effect, increases the formation of mucus in the stomach and increases the protection of its lining. Affects parietal cells directly.
- "Altan". A complex preparation containing polyphenolic substances.
- "Gastritol" A multicomponent herbal remedy that helps with gastrointestinal disorders.
- "Gastroflox". This is a herbal tea that has a stimulating effect on the reparative processes occurring in the mucous membrane. It also improves digestion and reduces dyspeptic symptoms.
- "Caleflon." A good anti-inflammatory agent that stimulates healing processes even with ulcers and chronic gastritis.
- "Yazbin." A combined preparation of plant origin that has an anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effect, and also neutralizes stomach acid and improves digestion.
You should also pay attention to such a medicine as Cytotec. A good antiulcer drug that also has a cytoprotective effect. But it cannot be used to treat reflux esophagitis during pregnancy. The doctor will tell you what to treat, but definitely not Cytotek. This remedy, on the contrary, is used by many to terminate pregnancy for up to 42 days.
Classification
What is esophagitis? It is an inflammation that is localized on the surface of the mucous membrane of the esophagus. The pathology has a variety of symptoms and can cause severe complications: peptic ulcers or Barrett's disease.
Pathology can manifest itself in acute, subacute and chronic forms. The acute form has three degrees:
- superficial inflammation, without the formation of ulcers and erosions;
- inflammation with the development of ulcers and tissue necrosis;
- the damage affects the submucosal layers, which may result in perforation of the esophageal walls and bleeding. After treated esophagitis, scars may appear on the esophagus.
Chronic esophagitis is classified according to Savary and Miller into 4 degrees:
- Excessive blood overflow of blood vessels, without the formation of erosions in the distal sections.
- Defects on the mucosa in the form of erosions.
- Erosive defects that merge with each other over time.
- Lesions in the form of ulcers, and as a result - the development of stenosis.
Classification according to the degree of mucosal defects:
- Catarrhal esophagitis and the edematous form are usually diagnosed simultaneously.
- Erosive. Most often it is a consequence of exposure to high temperatures on the mucous membrane or chemicals, or the presence of infectious diseases.
- Pseudomembranous. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of a fibrinous film that does not adhere tightly to the esophageal mucosa and appears against the background of infectious diseases.
- Hemorrhagic. Characterized by hemorrhage into the wall of the esophagus.
- Exfoliative, or membranous. This pathology is characterized by a protrusion in the lumen of the esophagus, which is from 0.5 to 4 cm in diameter.
- Necrotic. The appearance of this type is possible against the background of a severe course of the disease.
- Phlegmonous. This type of esophagitis is typical for cases where there has been damage to the stomach by a foreign body.
Other drugs
Continuing to talk about how and how to treat reflux esophagitis of erosive or other origin, it should be noted that symptomatic therapy is often prescribed. The fact is that this disease can be caused by another illness. And it often occurs against the background of some pathology. These are individual cases:
- If the cause is a psychological, neurological or nervous problem, then antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed.
- If you have a stomach ulcer, you need to take additional antibacterial drugs.
- It is necessary to use immunostimulating agents if the mucous membrane is exposed to external influences, which negatively affects the overall health.
In such cases, what drugs to treat reflux esophagitis is decided by a highly specialized specialist.
Homeopathic remedies may also be prescribed. They are needed to enhance the effect of the main therapy. Homeopathic medicines normalize the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract and accelerate tissue regeneration. The most popular medications are:
- Magnesium phosphate, which relieves pain.
- “Veratrumalbum” and “Iris Verzicolor”, which eliminate discomfort localized behind the sternum and heartburn.
- Potassium bichromicum, which minimizes the release of hydrochloric acid.
- "Argentumnitricum" and belladonna, helping to cope with erosions in the esophagus and severe inflammation.
As mentioned earlier, it takes quite a long time to treat reflux esophagitis. How to speed up tissue regeneration and improve local and general immunity? Multivitamins, micro- and macroelements will help with this. Because a regular diet is not able to provide sufficient intake of them into the body.
Mechanism of origin and development of pathology
The main causes of acute esophagitis are infections and the influence of chemicals. The appearance of an acute form is possible after irritation by foreign objects, for example, trauma due to diagnostic measures, all kinds of bone damage, tissue damage due to exposure to high temperatures. Manifestations of pathology may be associated with an allergic reaction.
The pathogenesis of chronic esophagitis of the esophagus is characterized by the following factors:
- consumption of too hot and spicy food, strong drinks, and as a result – the development of nutritional esophagitis;
- professional activities in enterprises where inhalation of chemical fumes is possible;
- if there are problems with excretion of waste products, food can accumulate, and congestive esophagitis appears;
- the disease may appear against the background of food allergies;
- due to hypovitaminosis or against the background of tissue hypoxia, lack of microelements in the body, prolonged intoxication;
- pathology of unknown etiology; with esophagitis, the symptoms of the disease are similar to ulcerative colitis.
A separate group includes reflux esophagitis, or peptic pathology, characterized by the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. This condition may occur due to the presence of a hiatal hernia or too short a length of the esophagus.
Interesting! Medicine Dexlansoprazole - indications for use and analogues
The main cause of esophagitis is neglect of diet and frequent consumption of fatty foods. Excess body weight is a provoking factor for the appearance of pathology.
Surgical intervention
So, above we talked in detail about how to treat reflux esophagitis. Reviews from people who have experienced this disease make it clear that drug therapy is quite effective.
However, if medications do not help or complications arise, surgery is required. Here are the cases in which surgical intervention is needed:
- The patient suffers from chronic, constantly recurring reflux esophagitis.
- The person has been diagnosed with an advanced stage of the disease.
- The patient has a diaphragmatic hernia.
Surgery is not recommended for patients over 35, as well as for those who have chronic or infectious severe diseases. In any case, before prescribing the intervention, a repeated detailed diagnosis is carried out. The person must also be examined by a surgeon and a nutritionist.
According to doctors, surgery is the most effective way to eliminate reflux esophagitis. How long does it take to treat pathology with medications? A month, at least, and in some cases about a year. The operation helps to fix the problem quickly. And here are some more advantages of intervention:
- Through surgery, the cause of the pathology can be eliminated.
- More than 85% of patients are satisfied with their dynamics.
- After surgery, many people do not need to take medications.
- There is no need to constantly see a doctor.
However, it is the doctor who decides how to treat reflux esophagitis, catarrhal or other type. Some people don't need surgery.
It should also be noted that repeated pathologies extremely rarely develop. In about 3% of cases. But even those patients with whom everything went well must undergo periodic examinations for two years.
Each patient must also be aware of the possible consequences. They are rare, but possible. Among them:
- Infection of the esophageal sphincter and its soft tissues.
- Blood loss. This happens if the doctor has not performed a clotting test.
- Problems with the swallowing reflex.
- Inability to burp.
- Abnormal patient response to anesthesia.
- Damage to internal organs due to inexperience of the doctor.
Repeated intervention may be necessary if reflux esophagitis returns. This is usually caused by diabetes of any type, cardiovascular disease, excess weight, unhealthy lifestyle and nicotine abuse.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the form of the pathology. But there are signs of esophagitis that are characteristic of almost any form of pathology:
- burning sensation in the esophagus;
- pain in the chest area;
- problems with swallowing even thoroughly chewed food;
- regurgitation;
- difficulty breathing;
- insufficient absorption of food.
The main symptoms of esophagitis (the first two) can spread to the back and neck.
Characteristic symptoms for chronic and acute forms:
- swelling in the larynx, face and neck, hoarseness;
- problems with swallowing, especially solid foods that must be washed down with liquid;
- hacking cough with aggravation at night;
- laryngospasms, and as a result – frequent inflammatory processes in the bronchi;
- with reflux, a state of shock is possible if the inflammation “spreads” to nearby tissues.
The acute form of the disease periodically gives way to a period of imaginary well-being, that is, the symptoms practically disappear. This condition can last more than 3 months, but then the symptoms worsen, and scarring may appear on the walls of the esophagus or the development of stenosis.
The severity of symptoms depends entirely on the causes of esophagitis and the intensity of the inflammatory process.
Catarrhal esophagitis can be generally asymptomatic, except that the patient will find it difficult to tolerate both cold and hot food.
Very rarely, symptoms of inflammation of the esophagus can manifest themselves in the form of bloody vomiting, which ends in the patient’s state of shock.
The chronic condition has all the common symptoms that worsen after eating fatty, spicy and salty foods or after overeating. Breathing problems appear during sleep, or when a person is in a horizontal position.
Inflammation of the esophagus may have symptoms of phlegmon and abscess, which is typical for the underlying disease, scarlet fever and diphtheria.