Preparing for the conversation
A visit to a proctologist always begins with a conversation.
This is an important stage in diagnosing the disease. Based on the nature of the complaints, the doctor can immediately make an accurate diagnosis, determine the scope of additional research and think about treatment options. Therefore, you need to prepare for the visit so that the conversation with the doctor is useful and constructive. Below is a list of questions that you need to be prepared for: Proctological patients are often bothered by pain, bleeding from the anus, itching and burning of the perianal area, a feeling of empty bowels, heaviness and pain in the perineum, and discharge from the rectum of various types. Carefully describe each complaint. For example, if there is pain, then when does it appear (constantly, after defecation), where is it localized. If itching appears, at what time does it intensify (constantly, during the day, at night). If blood is secreted, what is the approximate volume of secretion, what color is the blood itself (scarlet, brown or black).
- How often do you have stool?
The doctor will immediately determine whether you have a tendency to constipation or diarrhea.
- What impurities are found in stool (blood, pus, mucus)?
Please pay attention to these points in advance. . Features of your diet.
- Features of your diet.
Without going into too much detail, describe your diet and indicate which foods you consume most often. The doctor will immediately show you methods for adjusting your diet.
- What treatment did you do on your own?
Write down the names of medications, take prescriptions or empty boxes.
- What comorbidities do you have?
Often, diseases of the gastrointestinal system are closely related to each other.
If you provide the doctor with all the information in the required volume, then your visit will not be in vain. Therefore, you need to prepare even for the conversation, not to mention the readiness for the medical examination itself.
Pre-preparation for a proctological examination of a patient with hemorrhoids
Before visiting a proctologist, special preparation is required, which has two main goals:
- free the intestines from feces and metabolic products;
- will extinguish gas formation.
In addition, pre-preparation (that is, cleansing the intestines) will relieve the patient from the feeling of shame and embarrassment that are associated with the peculiarities of the digestive system: feces, gases, unpleasant odors, impurities. The doctor can safely conduct a complete examination of the large intestine, not only by palpation, but also with the help of special medical equipment. Therefore, it is necessary to make an appointment with a doctor in advance.
For mild illness, if the patient is not bothered by constipation, normal bowel movements and an enema are sufficient. In this case, the rectum will be clean, and there will be no need to go higher. You need little time for such preparation before visiting a proctologist.
How to prepare for your appointment
For an appointment with a proctologist to go smoothly, the intestinal lumen must be free of feces and mucus. Therefore, before visiting a proctologist, it is necessary to properly prepare, namely, cleanse the intestines. An exception to the rule are diseases accompanied by acute pain or bleeding (thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins).
For an appointment with a proctologist, they take an outpatient card, data from previous examinations, and a disposable examination kit.
Preparation for a cleansing enema
Before visiting a proctologist, you can perform a cleansing enema. This method is based on mechanical cleansing of the lower sections using warm boiled water. It can be administered using an Esmarch mug or a rubber bulb. The enema is performed in the evening and in the morning if the visit is scheduled for the first half of the day. When the proctologist's appointment takes place after lunch, it is performed in the morning 4 hours before the examination.
One procedure may require several liters of liquid. Before performing an enema, you need to prepare everything you need:
- boiled water, cooled to body temperature;
- rubber bulb;
- Vaseline or oil;
- towel, oilcloth;
- enema holder.
Esmarch's mug is a sanitary and hygienic device that is used to wash the intestines. It is made of rubber, plastic or silicone, has an open neck and a soft tube with a clamp.
The procedure is performed lying on the left side with the knees brought to the chest. Esmarch's mug is mounted on a tripod at a distance of 1-1.5 m from the couch. The tip is placed on the free end of the tube and lubricated with Vaseline. It is inserted into the anus without strong pressure at a distance of 3-4 cm towards the navel, and then 8 cm parallel to the tailbone.
The clamp is opened and the liquid enters the intestines within 15 minutes. When some liquid remains at the bottom of the mug, close the clamp and remove the tip. After the urge to go to the toilet, its contents are emptied. After 60 minutes, the enema must be repeated.
Preparation with laxatives
These drugs have a number of advantages: ease of use, quick effect, predictable action. They are taken the evening before the test. It is not recommended to eat after using laxatives.
- Fortrans. The drug is produced in powder form in sachets. For 20 kg of body weight, 1 package of the drug is used. For example, a person weighing 80 kg requires 4 packages of the product. The contents of 1 package are dissolved in 1 liter of water and cooled. The solution is drunk 250 ml every 20 minutes. If nausea occurs, you can eat a slice of lemon. The effect occurs within 2-3 hours.
- FLIT phospho-soda. The drug is produced in bottles that need to be dissolved in half a glass of water (120 ml). On the day of taking it, all solid food is excluded. During the day you can eat broth, juice without pulp, non-carbonated drinks, water. The dosage regimen differs depending on when the proctologist will examine you.
Morning inspection:
| Breakfast | 240 ml of liquid food + 120 ml of drug solution. Next, drink 240 ml of liquid again. |
| Dinner | 720 ml liquid food |
| Dinner | 240 ml of liquid food + 120 ml of drug solution. Next, drink 240 ml of liquid again. |
Afternoon visit:
| Dinner | Eating light food |
| Dinner | 240 ml of liquid food + 120 ml of drug solution. Next, drink 240 ml of liquid again. Before going to bed, you need to take another 720 ml of liquid food in small portions |
| Breakfast | 240 ml of liquid food + 120 ml of drug solution. Next, drink 240 ml of liquid again. |
If the examination is carried out in the morning, the last fluid intake should be no later than 8 am.
- Endofalk is a drug related to osmotic laxatives. It contains crystalline substances in varying proportions. To prepare for the examination, you need 2-3 sachets of the product. They are dissolved in water and taken orally, 300 ml every 10 minutes at 5-6 pm on the eve of a visit to the doctor. Eating before using Endofalk is allowed 2-3 hours.
How is a proctological examination performed?
At a doctor's appointment
You can make an appointment with a proctologist at the reception desk or take a referral from a therapist. At an appointment with a proctologist, women, men and children (if necessary) are examined. A proctologist is recommended by a therapist to examine children in rare cases, since children do not often suffer from rectal diseases. This is mainly due to poor nutrition (hemorrhoidal inflammation, constipation, diarrhea, dysbacteriosis) or anatomical features of the body.
How does a woman’s proctologist appointment go? The science of proctology involves the treatment of hemorrhoids and other intestinal diseases.
When examining a female patient, the specialist prescribes the following diagnostic measures, which include:
- collecting anamnesis for concomitant pathologies;
- visual examination of the anorectal and rectal area;
- finger palpation of the organ.
For a more informative picture of the intestinal condition, additional studies may be required. How is an instrumental examination by a proctologist performed in women?
The specialist prescribes:
Carrying out the procedure
- anoscopy - testing the anorectal passage using an anoscope to examine the lower intestine;
- sigmoidoscopy - examination of the patient using a sigmoidoscope to detect even minor neoplasms of various nature;
- ultrasound diagnostics - examination of the peritoneal organs through the abdominal wall;
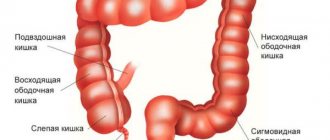
- colonoscopy – visualization of the entire intestine and its parts using a colonoscope (the most informative method for identifying all intestinal pathologies).
How an appointment with a proctologist goes, you can consult with the specialist himself at the first appointment or with a therapist who has written a referral to a highly specialized specialist. During an examination by a proctologist, women can find out the condition of the anorectal area, the functioning of the sphincter, recognize the presence of hemorrhoidal cones, benign and malignant neoplasms, assess the stage of pathology, the size of tumors, and receive a prescription plan for effective therapy.
The simplest procedure is a digital rectal examination, which is usually performed at the first visit to the doctor. For the convenience of the research procedure, women are recommended to purchase special panties with a hole in the anorectal area. This way the patient will not have a psychological disorder and embarrassment in front of the doctor. During examination there is no pain or discomfort. To visit a specialist, a woman must undergo a preparatory colon cleanse.
Stages of inspection
Before visiting a proctologist, girls often have questions about how women are examined, whether there are any peculiarities and nuances during the examination.
Usually, both sexes receive the same treatment according to the standard procedure.
The examination is carried out in several stages, some of them are additional and are prescribed for the purpose of additional examination.
- First of all, the proctologist begins the consultation by interviewing the patient and his complaints. The initial appointment includes the mandatory collection of anamnesis and detailed information about the patient’s condition. On a second visit, the doctor assesses the effectiveness of treatment and the dynamics of the course of the disease from the patient’s words.
It is advisable to prepare in advance to answer the most common questions about stool frequency, consistency, the presence of impurities in it, the quality of nutrition, and report on concomitant diseases.
In case of complaints of pain or discomfort, one should try to explain their nature and location as accurately as possible.
The more accurately the clinical picture is formulated, the easier it is for the doctor at the appointment to establish a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe additional studies and therapy.
- The second stage is a visual examination of the patient. The girl must undress from the waist down and sit in a chair resembling a gynecological one. Sometimes an examination by a proctologist is carried out on a couch in the knee-elbow position. The doctor examines the perianal area, examines hemorrhoids if there are external nodes, and can also identify cracks, various formations (papillomas, condylomas), paraproctitis (fistula tracts).
- The third stage is a digital examination of the rectum and anus. The procedure is painless, but some discomfort may be present. The doctor checks hemorrhoids (the presence of internal nodes), its stage, assesses sphincter tone, volitional effort, and can identify ulcers, cracks, and tumors.
- The fourth stage is an instrumental examination, which is prescribed additionally and requires preparation. These research methods are widely used in medicine because they have high reliability of results.
Anoscopy - the doctor examines the patient using a rectal speculum with an LED - anoscope - to assess the condition of the distal intestine at a distance of up to 14 cm.
Sigmoidoscopy - an endoscopic device allows the proctologist to penetrate a length of about 40 cm in order to examine the mucous epithelium of the rectum and sigmoid colon. The method is effective in determining in these areas of oncology what the doctor looks at first.
Colonoscopy is the most reliable endoscopic method for diagnosing the large intestine, capable of examining all its parts and, if necessary, part of the small intestine. Additionally, there is the opportunity to perform some surgical procedures (taking a biopsy, removing a polyp, cauterization). The procedure is characterized by significant discomfort and pain during the procedure, so in some cases it can be performed under general anesthesia.
To clarify the diagnosis, a proctologist may prescribe x-ray examinations, as well as a set of laboratory tests.
Contraindications for examination
Without digital examination it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis. In some cases, it is impossible to do without instrumental examination methods. But there are a number of contraindications to their implementation. Palpation of the rectum is not performed if:
- unbearable pain in the anus, which should be stopped, then the patient should be examined (sometimes an anesthetic is not necessary);
- narrowing of the anus, stricture, rectal stenosis are dangerous due to injuries and uncontrolled bleeding;
- acute conditions of any etiology (examination after relief of the severity of the process);
- paraproctitis;
- thrombosis of hemorrhoids;
- pinching of hemorrhoid cones.
A more serious examination (sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, irrigoscopy) is postponed if:
- severe cardiorespiratory pathology;
- profuse bleeding from the rectum (it is stopped, the cause is found out through a series of tests);
- course of treatment with anesthetics (inability to control pain from manipulation).
In all other cases, examination of the large intestine is necessary.
When to see a doctor
Proctologists are specialists in diseases localized in the large intestine and pararectal space. They are contacted if you suspect:
- polyps;
Polyps in the intestines
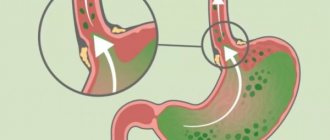
- hemorrhoids;
- colitis;
Colitis of the intestines
- tumors;
- fistulas;
What does a fistula look like?
- rectal prolapse;
- injury;
Causes of intestinal injury
- proctitis;
- cracks.
Anal fissure
Sometimes a therapist refers you to a proctologist after an initial examination, in other cases patients turn on their own. No doctor of any other specialization will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct therapy when it comes to the problems described above.
The therapist can refer the patient to a proctologist
There are five main signs that you should visit a proctologist:
- pain that occurs in the rectal area during bowel movements;
Pain during bowel movements
- regular occurrence of constipation or diarrhea, especially in chronic form;
Constant constipation indicates the need to visit a doctor
- presence of hemorrhoids;
Haemorrhoids
- itchy sensations;
Itching in the anus
- purulent, bloody impurities in the stool or mucus.
Blood in the stool indicates obvious intestinal pathologies
Often patients wait for these symptoms to go away on their own, which poses a health hazard – especially in the case of oncology.
For preventive purposes, you should visit a doctor if:
- pregnancy;
During pregnancy, the fetus puts pressure on the intestines, which can cause a number of proctological problems.
- postpartum period;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle;
- obesity;
Obese people are at risk. They often require consultation with a proctologist
- old age;
- menopause;
- chronic diseases according to the profile of a proctologist.
This will prevent the development of many diseases and unpleasant conditions.
Who is a proctologist
What does a proctologist treat in women? Proctology deals with the study of the condition of the large, rectal, sigmoid and small intestines.
A proctologist is a doctor who treats the following pathologies:
Doctor for sensitive problems
- hemorrhoidal inflammation;
- colitis;
- polyposis;
- tumor processes;
- prolapse;
- fistula formations of the rectal organ;
- paroproctitis, proctitis;
- intestinal injury.
Where does the proctologist meet? You can make an appointment with a doctor yourself or get examined by a therapist. The clinic does not always have a proctologist on staff, so a highly specialized specialist can be found in the regional hospital.
A coloproctologist and a regular proctologist differ slightly in the scope of their study of the organ. The proctologist examines the lower parts of the rectum and sigmoid organ, the coloproctologist treats the large and small intestines along the entire length.
Highly specialized specialists are required to be visited in the following cases:
- frequent constipation or diarrhea indicate an imbalance in the functioning of the organ; due to chronic constipation, the walls of the rectal organ are injured, hemorrhoidal cones and fissures in the anorectal area are formed;
- painful bowel movements;
- inflammation of hemorrhoidal cones;
- bloody-purulent, mucous traces in the stool warn of a serious illness in the form of polyposis, fistulas, and oncological processes.
It is impossible to postpone going to the proctologist if there are signs of rectal pathologies; diseases are better treated at the initial stage of development. Before a proctological examination, it is necessary to carry out preparatory measures, which the doctor will advise on.
Laxatives in preparation for a visit to the doctor
You need to properly prepare for a visit to a proctologist
If a democratic enema is for some reason impossible or the patient does not like the procedure, then you can turn to laxatives. Doctors recommend using either Microlax microenemas or Fortrans sachets.
How to use Microlax?
The drug is a capsule with a viscous white solution. The product contains sodium citrate, sodium lauryl sulfoacetate and sorbitol. The volume of one tube is 5 ml. Microlax is a combination drug. Its action is based on softening stool and increasing the volume of fluid in the intestines. The body cleansing process will begin in 15 minutes.
Preparing for an appointment with a proctologist
First of all, on the day before the visit, it is not recommended to eat foods that cause the release of gases in the intestines:
- sweet carbonated water;
- dairy products;
- Rye bread;
- cereals (except for rice dishes);
- mushrooms;
- peas, beans;
- cabbage;
- some fruits, such as apples or pears.
However, preparing for an appointment with a proctologist includes not only following a diet, but also administering an enema. Read below about how to do this correctly.
Indications and contraindications in food
If there are problems with the intestines, a person must exclude from the diet foods that cause fermentation, bloating, and irritation of the digestive organs. If this has already been done, there are no food restrictions before the diagnosis. The last meal should be light, 1.5 hours before the procedure.
If a visit to the proctologist is scheduled for the morning, you can get by with a cup of tea with a sandwich, or a glass of kefir. If the examination is carried out at lunch, you can eat salad or porridge in the morning.
If your diet has not been adjusted before visiting the proctologist, you will have to do so.
You can't eat:
- spicy foods, fatty, salty, fried;
- give up coffee, alcoholic beverages, whole milk, beer;
- products that cause fermentation - cabbage, grapes;
- cucumbers, canned food, and legumes provoke bloating;
- peppers, citrus fruits, nuts irritate the intestines;
- sweets with cream, jam, buns.
Proper nutrition:
- porridge made from rice, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- mashed potatoes;
- dietary meat – chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- baked, boiled, stewed dishes;
- cookies, bagels;
- mineral water, herbal tea, dried fruit compote;
- strawberries, raspberries, apricots;
- honey;
- fermented milk products.
Before manipulation, the intestines must be in normal condition - not swollen, not overloaded with work.
Who needs and doesn’t need to prepare for the reception
Everyone needs to prepare for an appointment with a proctologist. But there is an exception to the rule - this is the initial consultation. Such a visit to a proctologist lasts about an hour, involves collecting an anamnesis (including family, genetic), and reconstructs the exact picture of the disease in a question-and-answer mode. If the anamnesis provides a clear picture of the suspected pathology, the patient receives a referral for a follow-up visit for an internal examination of the intestine. If things are unclear, the patient is referred to related specialists for a differential diagnosis.
There is another option when you can show up for the first appointment without preparation - this is severe pain. In such a situation, the doctor will provide all possible first aid, but will not be able to carry out a full diagnosis. Only after the pain attack has subsided and preparation has been carried out, the patient will return for the second appointment.
What does a proctologist examine and how is the examination performed?
To obtain an accurate diagnosis, the proctologist performs a thorough visual examination. Many people are interested in the question of how the inspection is carried out. Typically, diagnosis is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Conversation with a proctologist. It should give the doctor the most accurate idea of the disease. It may be based on the following questions:
- Complaints. Usually a person talks about pain, burning and discomfort in the anus, bleeding, a feeling of incomplete bowel movement, the presence of heaviness, and pain in the lower abdomen. The patient must at least roughly describe the nature of the pain and its location. The same applies to burning and itching. If there is blood discharge, it should be explained what color and consistency it is;
- Frequency of bowel movements. This information will allow you to determine the adult’s tendency to constipation or diarrhea;
- The presence of foreign impurities in the feces;
- Features of the diet. It is important to list the main products consumed. For a doctor this is enough;
- Have you undergone self-treatment for the disease? The patient should make a list of the drugs used in advance, if this is the case;
- Accompanying illnesses. With proctological disorders, problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract almost always occur.
- Visual inspection. The doctor carefully examines the anal area and the area next to it. If the cause of complaints is hemorrhoids, fistulas, fissures, then already at this stage the proctologist diagnoses the problem.
- Finger diagnostics. Fear of this procedure makes patients refuse to visit the doctor for a long time. It doesn't really hurt. First, the doctor treats the edges of the anus and gloves with an antiseptic solution. Then palpation occurs. The manipulation allows you to check the normal functioning of muscles, identify neoplasms and assess the condition of hemorrhoids.
- Anoscopy. It is implemented when there is not enough information to make a diagnosis after palpation or when the doctor has doubts about the accuracy of the alleged diagnosis of the disease. This is an endoscopic procedure that helps to examine the condition of the internal walls of the organ. The proctologist takes a smear, and if severe intestinal damage is suspected, a biopsy is organized.
Meals before appointment
When a person is scheduled to visit a proctologist/coloproctologist, he should avoid fried and fatty foods and moderate his consumption of heavy meals. It is recommended to eat cereals, vegetable soups, chicken or turkey for several days. You need to include more fruits and vegetables in your diet, as they promote intestinal motility.
Before going to the doctor, foods that cause gas formation are prohibited: potatoes, legumes, cabbage, any carbonated and alcoholic drinks, whole grain bread, caffeine, fermented milk products.
Knowing how to prepare for an initial appointment with a doctor, a person guarantees himself a high-quality and complete examination. This way, the doctor will detect the problem in time, which will allow you to get rid of it faster and with minimal consequences.
Proctologist services at SM-Clinic
Consultation with a proctologist.
Diagnosis of proctological diseases.
- Anoscopy
is a diagnosis of the condition of the rectal lumen using an anoscope, which allows the doctor to examine the anal canal and part of the rectum. Using anoscopy, hemorrhoids, polyps, and inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane are diagnosed. Anoscopy usually complements a rectal examination and precedes sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy. - Sigmoidoscopy (rectoscopy)
is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure for examining the lumen of the rectum and lower lobe of the sigmoid colon. Using sigmoidoscopy, you can diagnose colitis, hemorrhoids, growths of the intestinal mucosa, fissures and fistulas of the rectum. - Irrigoscopy
is an X-ray method for examining the intestines, usually performed with contrast. X-ray examination allows us to identify fistulas, polyps, colitis, malignant neoplasms and other anomalies and malformations. - Colonoscopy.
This method allows you to examine the entire large intestine, from the rectum to the cecum.
Today, colonoscopy is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods in proctology. It allows for the timely detection of formations such as ulcers and polyps. At SM-Clinic, colonoscopy is performed “in your sleep”
(under sedation - short-term medicinal sleep), without pain or discomfort.
During a colonoscopy, a biopsy
- taking samples of tissue from the intestinal mucosa for subsequent laboratory analysis. In this way, the form of the disease (inflammatory, tumor, infectious) is clarified. - Coprogram
is an advanced laboratory analysis of stool, allowing one to draw a conclusion about the presence of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, peptic ulcers, colitis, dysbacteriosis, etc.
Treatment of proctological diseases.
- Treatment of hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids have been and remain the most common reason for visiting a proctologist. The SM-Clinic uses the latest non-surgical and minimally invasive methods of treating this disease (infrared and radio wave coagulation, sclerotherapy, ligation with latex rings, ligation of hemorrhoidal arteries under the control of Doppler ultrasound (operation HAL-RAR). - Treatment of anal fissures
Pain, itching, bleeding with anal fissures is another common reason why people consult a proctologist. The SM-Clinic uses comprehensive treatment for this unpleasant disease, including lifestyle correction, the use of medications, and, if necessary, surgical treatment. The high level of skill of the clinic’s doctors guarantees that the surgical intervention will be effective and safe. - Removal of polyps
The mucous membrane of the rectum is often subject to an “invasion” of polyps, as well as other unwanted benign neoplasms. If they are not removed in time, they may well degenerate into cancer, so polyps must be disposed of as quickly as possible. SM-Clinic performs removal of rectal polyps (polypectomy), removal of condylomas, excision of anal fimbriae (cosmetic proctology), various plastic and reconstructive surgeries on the perineum, anal canal, and rectum. - Also, SM-Clinic patients successfully undergo treatment for paraproctitis, fistulas, abscesses of the intestinal mucosa, rectal prolapse, ulcerative lesions, colitis and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If necessary, treatment is carried out in the clinic's hospital.
By clicking the button, you agree to
Finger examination
This type of diagnosis is decisive for proctological diseases
Carrying out a digital examination of the rectum, the proctologist determines:
- presence/absence of contractile function of the anal sphincter;
- the degree of pain the patient experienced during the examination;
- the presence of scars and polyps on the mucous membrane of the anal canal.
Since the hemorrhoidal tissue in the anal canal is very soft and elastic, during a digital examination, hemorrhoids and defects in the form of polyps or scars are reduced and simply not detected. Displacement of the mucous membrane during palpation indicates the presence of these defects.
Determining the degree of node loss
The stage of node prolapse is clearly determined when the patient strains. To assess the actual size of the nodes, the patient is asked to sit on a chair and strain very hard. At this point, you can find out whether he will be able to insert them into the anus on his own.
It is this indicator that often serves as the basis for choosing a minimally invasive intervention technique in the treatment of hemorrhoids.
Even during anoscopy it is not always possible to determine the size of the nodes. When held in the anus, they appear much smaller.
Hemorrhoids acute
Home» Diseases» Acute hemorrhoids
Make an appointment with a proctologist in St. Petersburg
How to prepare for a consultation with a proctologist
As I already wrote in an article about chronic hemorrhoids (which I highly recommend reading to understand the general essence of hemorrhoidal disease), our Center is often approached for a “second opinion” by very puzzled, and often very frightened patients after visiting other clinics, who are under terrible fairy tales about cancer, sadistic surgeons whom it is better not to go to, etc., very intrusively offering urgent treatment for acute hemorrhoids for fabulous money. Often these numbers are so curiously large that you think: if such gratitude were offered to me, I would gladly carry the patient in my arms to the operating room and back and organize personal night shifts at his bedside :)... It’s not always about money, it’s clear that there’s a crisis I haven’t finished all of them yet, and there are people who are willing to pay a lot for quality treatment. But the problem is that in this case, for your own money, they offer you manipulations that are absolutely unnecessary in this situation, moreover, in a certain percentage of cases they are fraught with complications and are definitely accompanied by additional discomfort. I think that if you look at the problem from this point of view, it is worth your time to discuss it, regardless of the size of your family budget.
What are the causes of acute hemorrhoids (exacerbations of hemorrhoids)?
I again recommend reading about the reasons for the development of hemorrhoids as a chronic disease in the articles “Chronic hemorrhoids” and “Prevention of hemorrhoids.” It is not always possible in a conversation with a patient to identify a specific factor that led to an exacerbation of the disease in this particular case, but most often such factors are:
- Unusual heavy physical activity
- prolonged forced sitting, for example, a long drive
- dietary errors, especially holiday feasts
- episode of difficulty defecating
- overheating (in our latitudes we are most often talking about a bathhouse)
- For women, an additional factor is pregnancy and childbirth
From my clinical experience, I can say that we usually have long lines of sad people with thrombosis after all the long holidays, in particular May and New Year. During the summer season, what most often brings us is everyone’s favorite, but not the most healthy, mixture of health-improving bath activities, completed or accompanied by a vodka-kebab blow to the newly healed body. Another fairly common cause of exacerbations is the healthy lifestyle sung by the great Russian poet Shnur: the patient finally decides to take care of himself, goes to the gym, but weakened by alcohol, nicotine and other bad excesses, the body does not tolerate unusual stress. Bus tours in Europe have been a constant source of sufferers from among the forced lovers of such extreme sports, although in recent years the fashion for this type of recreation has subsided (I suspect that the crisis will soon add more enthusiasts again). Finally, pregnancy and childbirth are a topic for a separate discussion.
What is acute hemorrhoids or exacerbation of hemorrhoids?
So, to understand the essence of the problem, again briefly about the anatomy. The substrate of hemorrhoidal disease is the venous plexuses located under the mucous membrane of the rectum and anal canal. These plexuses form islands of the so-called cavernous tissue that are very specific in structure, which are present in all people and are normal anatomical formations. With a certain combination of external factors, in the vessels of the hemorrhoidal plexuses, which are already in constantly unfavorable conditions due to our lifestyle, the balance of blood inflow and outflow is disturbed, which leads to acute hemorrhoids (or exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids, both terms are correct), which is realized by two main types of vascular dysfunction:
- formation of blood clots (thrombosis) due to blood stagnation
- prolonged heavy bleeding during defecation due to impaired permeability and arrosion of the vascular walls
Symptoms of acute hemorrhoids or how do exacerbations of hemorrhoids manifest themselves?
It was exacerbations of hemorrhoids that made this disease worldwide famous. Mentions of it are found in the most ancient written sources, and jokes and sayings about “hemorrhoidal life” are heard in all languages of our planet. What symptoms are characteristic of both variants of the course of acute hemorrhoids and why do they spoil the mood of patients so much (at the same time they are very pleasing to the medical business, since they are a powerful motivator for seeking medical help)?
The first variant of the course of acute hemorrhoids is thrombosis. Just in case, let me remind you that the term “thrombus” means clotted blood. In the case of hemorrhoidal thrombosis, the patient feels it as dense subcutaneous “balls”, which vary in size (from a millet grain to a plum), and can be single or multiple. In addition to the size and number of blood clots, the clinical picture is also determined by the reaction of the surrounding tissues to the process, in the form of their inflammation and swelling, often with the formation of areas of necrosis. The most unfavorable course of acute hemorrhoids is the so-called total thrombosis, when the formation of multiple blood clots leads to circular (in a circle) inversion and pinching of the cavernous tissue and mucous membrane of the anal canal and rectum. Small blood clots practically do not hurt; the patient, as a rule, is frightened by the very fact of their appearance. Large, multiple and especially total thromboses are accompanied by very severe and painful pain. In most cases, with proper drug therapy, blood clots resolve completely, after which other symptoms of exacerbation of hemorrhoids (inflammation, swelling) also disappear. Much less often, skin necrosis occurs above the blood clot and it comes out, this is also a favorable outcome of the disease, the only peculiarity is that at the time of evacuation of the blood clot, bleeding occurs, sometimes quite profusely. In very rare cases, a purulent process called acute paraproctitis occurs in the area of thrombosis, which requires surgical treatment.
It is important for the patient to understand the main points associated with acute hemorrhoidal thrombosis, namely:
- What appears on your outside is a blood clot located under the skin, and not an external hemorrhoid; most often, with proper treatment, it resolves, so there is no need for its urgent surgical removal
- The fact that this happened at all does not mean that you have “general” chronic hemorrhoids. When exposed to unfavorable “stress” factors, thrombosis can (and does) visit any person, and this does not always require urgent treatment of chronic hemorrhoids. It often happens that after the first exacerbation, the symptoms of hemorrhoids do not bother a person for years
The second variant of the course of acute hemorrhoids is bleeding. The severity of this problem also varies - from regular, light bleeding, in the form of traces of blood on toilet paper or blood spatters on the walls of the toilet, to very heavy bleeding, when the patient, when straining, feels a stream of blood flowing or sees blood clots in the stool (the latter is not common). , is not very typical for hemorrhoids and should especially alert you and your doctor).
Bleeding is the second most common reason after thrombosis for visiting a proctologist, and with the same frequency is used to aggressively motivate patients for urgent minimally invasive or surgical treatment. Key points that are important to understand for this type of exacerbation of hemorrhoids:
- Any bleeding from the anus, even in the form of traces of blood on toilet paper, is a clear reason for an in-person consultation with a proctologist for the purpose of differential diagnosis
- Heavy bleeding is a clear reason for an urgent consultation with a proctologist or surgeon, and if your health worsens, for an emergency visit to the hospital
- Bleeding is a very common symptom of the disease (the term “hemorrhoids” is translated from Greek as “stream of blood”), starting from the earliest stages. Therefore, if for the first time in your life you experienced a short-term episode of light bleeding, this does not mean at all that everything is “very advanced.” After a course of conservative drug therapy, there may also be no problems with hemorrhoids for many years
What to do or how to treat acute hemorrhoids?
There are three approaches to the treatment of hemorrhoidal thrombosis :
- drug therapy
- surgical treatment (removal of a thrombosed node or full hemorrhoidectomy)
- thrombectomy (thromt evacuation)
In the price lists of some clinics posted on the World Wide Web, I periodically see the position “reduction of a thrombosed node,” which is surprising, since such manipulations have long been abandoned due to their complete futility. Unified approaches to the tactics of treating hemorrhoidal thrombosis have not yet been developed: in domestic clinical recommendations, all three options are prescribed as equally acceptable. As often happens in such cases in our age of victorious capitalism, when choosing a treatment method, paramedical factors become the main ones. It is clear that any surgical manipulation makes the doctor a little richer and the management of the clinic you went to a little happier, and the prescription of various pills, suppositories and ointments only lifts the spirits of investors of pharmaceutical companies who are infinitely classist and geographically distant from us. Therefore, most often, patients who managed to escape in time and turn to us for a “second opinion” say that they were recommended either thrombectomy or removal of the thrombosed node. In the absence of common approaches to this issue, I can only share my own thoughts on this issue.
Although patients themselves sometimes insist on surgical treatment, in the hope of quick relief from pain and other unpleasant sensations characteristic of exacerbation of hemorrhoids, it is extremely undesirable to carry out classical surgical treatment (hemorrhoidectomy) in the acute period, especially with total thrombosis, since this greatly complicates the technique surgery and significantly increases the likelihood of serious postoperative complications.
Removing a single thrombosed node is also a very controversial idea. The patient turned to the doctor in the hope of quickly getting rid of his complaints, and what will he get after this manipulation? Instead of a blood clot, which with proper treatment will resolve on its own in one or two, maximum three weeks, he will have a wound that hurts no less, but heals in 1-2 months. At the same time, the problem with chronic hemorrhoids is not solved: removing a single node does not relieve you of the need to do something with the remaining ones. The question is - do you need it?
Thrombectomy is a very minor and almost painless manipulation, therefore, in my opinion, it has a right to exist, but I don’t see any reason to do it to all patients with thrombosis indiscriminately. If the blood clot is small and does not cause significant discomfort, it will definitely resolve with drug therapy. Yes, thrombectomy can speed up the healing process, but it is not very critical, and the wound itself will ache after the manipulation. In case of multiple and total thrombosis with severe edema, thrombotomy is not indicated at all, since it is technically impossible to carry out adequately.
From the foregoing follows the most reasonable tactics for the treatment of hemorrhoidal thrombosis, adopted, for example, in our Coloproctology Center. The main method of treating exacerbations of the disease is drug treatment . A diet, suppositories, ointments and drugs from the venotonic group are prescribed. Additionally, cool showers and baths and limiting physical activity are recommended. In cases of total thrombosis with severe edema and multiple necrosis, antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy may additionally be prescribed. If the examination reveals a single blood clot without a pronounced inflammatory reaction, then it is possible to perform a small (and, I emphasize, simple and inexpensive) surgical procedure called thrombectomy (a small incision in the skin under local anesthesia through which the blood clot is squeezed out). This manipulation is not necessary and is suggested only if the patient complains that the existing blood clot is causing very great discomfort. In case of multiple blood clots, severe inflammation and total thrombosis, thrombectomy is ineffective. Treatment does not require daily medical supervision. Most often, a second consultation is scheduled after 7-14 days (the expected period for complete resorption of the blood clot). The purpose of the repeated consultation is to monitor the results of treatment and additional examination to clarify the stage of chronic hemorrhoids. If the patient has suffered thrombosis for the first time in his life and does not have regular complaints outside of exacerbations, then with a high degree of probability communication with the proctologist after a conversation about a healthy lifestyle ends there. If there are regular symptoms of hemorrhoids and during the examination sufficiently large internal hemorrhoids are identified, the patient is unobtrusively invited to undergo minimally invasive or surgical treatment of hemorrhoids in the foreseeable future.
uniform approaches to the treatment of profusely or long-term bleeding hemorrhoids . It is clear that if a patient is brought to us on a gurney with large blood loss and ongoing bleeding, there is nothing special to philosophize about, we are only talking about the operating room, but this happens relatively rarely. If you see traces of blood for the first time in your life and you have no other complaints, you definitely need to start with drug therapy; if it is ineffective, the issue of minimally invasive treatment is decided. If you turned to a proctologist after a very long period of bleeding with severe anemia, this is a really difficult question and there are several approaches to it. Main topics for discussion among specialists:
- Is it possible to use outpatient minimally invasive techniques or is inpatient surgical treatment safer?
- Should patients with anemia be operated on immediately or after a course of drug therapy and stabilization of red blood counts?
Most specialists I know (including me) adhere to conservative patient management tactics in this matter. Radical surgery against the background of significant anemia is fraught with a significant increase in the risk of postoperative complications, wounds take much longer to heal, etc. Therefore, it is optimal to prescribe drug therapy: suppositories, venotonics, iron supplements, hemostatic drugs. In most cases, with this treatment, intense bleeding stops. If examination reveals a profusely bleeding single vessel, latex ligation or infrared coagulation can be used as a method of temporarily stopping bleeding. And only after the hemoglobin level reaches 100 g/l and above, the issue of radical treatment, including minimally invasive techniques, is decided.
How dangerous is it or complications of acute hemorrhoids
The very term “thrombus” often frightens patients, since from films, books and television shows it is known that it can somehow come off and clog a larger vessel of the heart, lungs, brain, etc., which is a life-threatening condition. In this regard, I can reassure readers: due to the structural features of the hemorrhoidal plexuses, such complications are almost completely excluded (in 20 years of work, I have never encountered such cases).
The most likely complications of hemorrhoidal thrombosis are the occurrence of a purulent process, the so-called acute paraproctitis, or the germination of a blood clot by connective tissue (“enclosure”). Both problems are quite rare and are not life-threatening, but require surgical treatment.
Bleeding is a more serious problem, but if you contact specialists in time, it also does not pose a threat to life.
Conclusions and advice
If, after reading this article, you have a question - if everything is so simple and drug therapy helps in most cases, why contact a proctologist at all, then you did not read the article carefully... The main reason for an in-person consultation is differential diagnosis. In case of bleeding, it is carried out with a very wide range of serious pathologies, which are listed in the article on chronic hemorrhoids. In case of thrombosis, you need to make sure that it is not acute paraproctitis, which happens quite often.
As for practical advice, if, when you go to the clinic, you are very intrusively, with intimidation, something outside the above-mentioned treatment regimens is offered: urgently cut something off for unrealistic money, immediately begin minimally invasive treatment of chronic hemorrhoids, buy unsigned containers for the same unrealistic money with a “magic” drug, etc., you definitely need to not be lazy and look for another medical institution.
If you live in St. Petersburg, we invite you to come to us for a “second opinion”: since such a need often arises among patients, we have prepared a special offer, which can be found in the “Promotions” section.
The site provides a lot of additional information about hemorrhoids, which can be found on other pages:
- Anatomy of the anal canal and rectum
- Chronic hemorrhoids
- Treatment of hemorrhoids (this is a whole section with descriptions of all existing treatment methods)
- Prevention of hemorrhoids
There are also pages with a detailed description of the main diagnostic methods (consultation with a proctologist, anoscopy, rectoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy) and how much mental and physical torment you will experience if you decide to seek help from a specialist.
And finally, if I was convincing enough, I invite readers to take an autograph during a face-to-face meeting (coordinates and telephone numbers are in the “Contacts” section), or continue communication in absentia, for this there are the “Ask a Question” and “Reviews” sections.
Sincerely, Anatoly Ivanovich Nedozimovany, associate professor of the course of coloproctology at Pavlov State Medical University of St. Petersburg.