General treatment tactics
Therapy of gastroenterological pathologies includes taking medications and non-drug auxiliary measures (diet, bed rest for exacerbations).
In order to determine what funds are required, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination, which includes:
- FGDS;
- biopsy of the internal environment of the stomach;
- blood test, including testing for the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
Therapy is carried out in two directions:
- against symptoms of the disease (epigastric pain, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, belching, feeling of heaviness in the stomach, etc.);
- against the cause of the pathology (antibiotics, antisecretory agents, etc.)
Why may the chosen drug therapy regimen be ineffective?
Sometimes there are situations in which a patient who has undergone treatment does not feel any improvement. Based on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies, experts conclude that the chosen drug therapy regimen did not bring the expected results.
The reasons for treatment failure include the following factors::
- The patient was prescribed medications to the components of which he was intolerant.
- Resistance (primary) of the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter is expressed.
- Antibiotics were not included in the regimen, the dosage was prescribed incorrectly, the patient violated the deadline for taking them, and the drug was selected incorrectly.
- There is circulation of Helicobacter within the patient's family, which led to re-infection.
- The gastroenterologist chose an ineffective drug therapy regimen.
Gastritis and gastric ulcers are the most common gastrointestinal ailments that occur due to the pathological effects of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. It follows that drug therapy will have several common features. This is explained not only by the common causes of occurrence, but also by the almost identical symptoms of such ailments. The only difference will be the use of drugs to normalize the acidity level, in cases with low or high levels of hydrochloric acid.
Main groups of medications
The following groups of drugs are used to treat ulcers and gastritis:
- enzymes;
- antacids;
- gastroprotectors;
- antibiotics;
- H2-histamine receptor blockers;
- eubiotics and probiotics that normalize the microflora of the digestive tract;
- adsorbents;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- antispasmodics;
- painkillers;
- antiemetics;
- prokinetics;
- herbal medicines.
Pharmacy drugs
The most popular drugs for the treatment of stomach ulcers, gastritis and other gastropathy are:
- Omeprazole (trade names Ortanol, Omez, Losek maps, Ultop, etc.) - blocks the production of hydrochloric acid, thereby reducing acidity in the stomach. Allowed for pregnant women and children over 4 years of age;
- Emanera , Nexium based on esomeprazole - suppress the production of hydrochloric acid by blocking the enzyme system - the proton pump. Unlike its predecessor omeprazole, it does not have a toxic effect on the liver and has maximum bioavailability. Used in combination with other drugs to treat the stomach from the age of 12;
- Nolpaza and Controloc based on pantoprazole - the mechanism of action is similar to previous drugs. Can be used from 18 years of age;
- Ranitidine and Famotidine block receptors in the gastric mucosa. Reduces acidity and volume of gastric juice. Suppress the activity of pepsin, protect the walls of the digestive organs from the pathological influence of enzymes, bile acids and other substances of biogenic nature. Contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding, children under 14 years of age. The cheapest medicines for the treatment of gastropathy - the price per package is 50 rubles;
- De-nol and Ulkavis are tablets for stomach ulcers and gastritis based on bismuth compounds. They have gastroprotective and antiseptic effects. Protect the surface of the walls of the gastric mucosa from the negative effects of increased acidity, enzymes and bile acids. Heal erosions and ulcers. Reduces the number of Helicobacter pylori bacteria. Increases the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. Can be used from 4 years of age.
- Gastrofarm . Lozenges containing live lactobacilli and their metabolic products, organic acids (nucleic, lactic, malic), amino acids and proteins, polypeptides and polysaccharides. The drug stimulates tissue regeneration in the digestive organs, has an analgesic and enveloping effect (due to the presence of protein). Approved for use from 3 years of age, including during breastfeeding and childbearing;
- Phosphalugel envelops the walls of the stomach, neutralizes excess hydrochloric acid without disturbing normal physiological processes. The suspension adsorbs and removes gases, toxins and microorganisms, improves the movement of food mass. Allowed for all categories of patients, including children, pregnant and lactating women;
- Gaviscon is a line of medications in the form of tablets and suspensions with an antacid effect. Active ingredients: brown algae extract and sodium alginate. Eliminate dyspeptic symptoms that accompany diseases of the stomach and intestines. Allowed during pregnancy and lactation, children over 12 years of age;
- Maalox - suspensions and tablets with an adsorbing and enveloping effect. The drug protects and restores the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. Eliminates heartburn, pain, sour belching and other symptoms of dyspepsia. Approved for use during breastfeeding, pregnancy and adolescents over 12 years of age;
- Gastal is an antacid in tablets. Dissolving in the stomach, it is converted into a gel that envelops the walls of the stomach and protects the mucous membranes. It has a gastroprotective effect, heals erosions and ulcers. Can be used by children over 6 years of age and pregnant women;
- Rennie is indicated for the treatment of dyspepsia due to stomach diseases. Indicated for adults and adolescents over 12 years of age, allowed for pregnant and lactating women;
- Almagel is a series of antacids in the form of a suspension to eliminate dyspeptic symptoms in gastroenterological diseases;
- Linex forte is a probiotic for the treatment of erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines. Stimulates the growth of its own beneficial microflora, suppresses the growth of pathogenic bacteria, including Helicobacter pylori. Used in combination therapy. Safe for children, nursing and pregnant women, patients with chronic diseases;
- Activated carbon , Smecta , Enterosgel , Filtrum and other adsorbents are used for acute gastritis. They act locally, in the lumen of the digestive organs, without being absorbed into the blood. Their use is permitted during lactation and pregnancy.
Goals and protocols for treating gastric ulcers
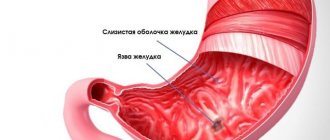
A gastric ulcer is a change in the mucous membrane of the stomach, in which the protective cover is destroyed, erosion begins, and a non-healing trophic disorder occurs
. A stomach ulcer is a change in the mucous membrane of the stomach, in which the protective cover is destroyed, erosion begins, and a non-healing trophic disorder occurs. The disease is difficult to miss: symptoms of an ulcer include severe pain in the upper abdomen, heartburn, indigestion, constipation, a feeling of bloating and fullness in the stomach, and in some cases, stomach bleeding. The cause of the disease is most often the activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Infection with these microorganisms occurs through saliva, contaminated dishes, and sometimes they are transmitted even before birth from mother to fetus. However, a person infected with Helicobacter pylori may not have any signs of stomach ulcers if the immune system successfully repels attacks from the bacteria. However, with chronic infectious diseases, constant stress, and alcoholism, the body’s defenses cease to cope with their tasks and gastric ulcers begin to progress. That is why there is an opinion among people that ulcers are caused by nerves.
A stomach ulcer can be a consequence of taking medications, in particular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, since such drugs irritate the gastric mucosa and lead to its gradual destruction. Severe chronic diseases such as pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, etc., as well as renal and liver failure, also contribute to the occurrence of gastric ulcers. There are approved treatment regimens for stomach ulcers (we'll talk about them below). The goal of therapy is the complete destruction of the bacteria that caused the disease, normalization of acidity and (as a supportive measure) protection of the gastric mucosa from the effects of digestive juice.
Treatment regimens
There are different treatment regimens for gastritis and stomach ulcers, which are selected based on:
- symptoms;
- presence of Helicobacter bacteria;
- patient's age;
- health status.
The most popular options:
- Antacids + proton pump inhibitors;
- Gastroprotectors + proton pump inhibitors;
- Antibiotics + gastroprotectors + proton pump inhibitors;
- Antimicrobial agents + proton pump blockers.
Based on the accompanying symptoms, symptomatic therapy medications may be prescribed:
- antiemetics;
- antacids;
- painkillers;
- antispasmodics;
- prokinetics;
- enzymes.
Diet
For the effective action of medications in treating the disease, as well as normalizing the functioning of the digestive system, it is recommended to follow a comprehensive diet. With these pathologies, it is forbidden to eat harmful and irritating foods. It includes spicy, salty, fatty, smoked, canned, butter and confectionery products. You should also refrain from rich meat and mushroom broths, foods with a high percentage of fiber, salt and sugar. Eliminate alcohol, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea from the diet completely.
A proper diet should include:
- porridge with water;
- baked apples;
- low-fat yoghurts;
- lean meat;
- vegetable soups;
- Among sweets, marmalade, pastille and jelly are allowed.
When gastritis worsens, it is recommended to take mucous, enveloping foods, such as oatmeal, and drink herbal infusions.
Important! For stomach ulcers and gastritis, it is necessary to observe the frequency of meals, portion sizes, heat treatment temperature and the temperature of the dish when consumed.
Self-medication
Only a doctor can prescribe individually appropriate treatment for each case of gastritis and ulcers. Therapeutic measures should be carried out under the close supervision of a specialist.
Important! Self-treatment is not allowed. Incorrect treatment will not only be ineffective, but even dangerous to human health and life.
It is dangerous to take antibacterial drugs, sulfonamides and other medications without a doctor’s prescription. All medications are selected individually. Self-medication is prohibited for pregnant women, children and the elderly.
It is possible to achieve effective treatment of gastritis and ulcers by following a set of actions. Compliance with all treatment regimens, proper diet and nutrition, giving up bad habits, and exercising will help not only get rid of stomach diseases, but also improve the condition of the whole body.
In what cases is antibiotic therapy required?
Prescription of antibiotics for gastritis and stomach ulcers is required when infected with Helicobacter pylori, whose presence is determined by the results of the examination.
Combination of penicillins and macrolides
Antibiotic therapy, which includes a combination of penicillins and macrolides, is conventionally called first line.
Penicillin-containing antibiotics:
- Amoxicillin (Flemoxin Solutab, Amosin);
- Complex products of Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (Amoxiclav, Flemoclav solutab, Augmentin, Ecoclave).
Macrolides:
- Clarithromycin (trade names Klacid, Fromilid);
- Josamycin (Vilprafen).
Combinations of these drugs are used together with drugs that inhibit the synthesis of hydrochloric acid:
- Amoxicillin – 1000 mg;
- Clarithromycin - 500 mg;
- Blocker of hydrochloric acid secretion.
Frequency of application – 2 times a day. The minimum duration of treatment is 7 days.
Combination of tetracyclines and metronidazole
This combination refers to second-line therapy, when Metronidazole is used in combination with Tetracycline, proton pump inhibitors and bismuth compounds:
- Tetracycline 500 mg - 4 times a day;
- Antisecretory agent and bismuth preparations - 2 times a day;
- Metronidazole 500 mg - 3 times a day.
The minimum course of taking antibacterial agents is 7 days.
Medicines for the treatment of acid-dependent conditions of the stomach (PPI)
Proton pump inhibitors are medications that suppress the secretion of hydrochloric acid. They have a delayed effect, so they do not eliminate high acidity instantly. To quickly eliminate heartburn, sour belching and other symptoms characteristic of high acidity, antacids are used. PPIs maintain a normal pH environment in the stomach, which eliminates pain, accelerates the healing of ulcers and erosions, and increases the effectiveness of antibacterial therapy.
List of drugs:
- Omeprazole (Omez, Losek, Ultop, etc.);
- Lansoprazole (Epicure, Lanzap, Lanzaptol);
- Pantoprazole (Controloc, Nolpaza);
- Rabeprazole (Razo, Zulbex, Rabeloc, Pariet, Rabiet);
- Esomeprazole (Nexium, Neo-Zext, Emanera).
What is the difference between gastritis and stomach ulcers?
Symptoms of inflammation and peptic ulcer are known to all gastroenterologists. These are one of the most common diseases among the adult population.
Inflammation of the stomach can be acute and chronic, hyperacid and with reduced acidity, catarrhal and hemorrhagic. The atrophic form of the disease is often diagnosed.
Depending on the etiology, infectious and non-infectious (drug, alcohol, toxic) types of inflammation are distinguished.
The most commonly diagnosed form is catarrhal form. The causes of gastritis are the penetration of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, alcohol abuse, eating spicy food and intoxication.
The following symptoms are characteristic of catarrhal inflammation:
- general malaise;
- heaviness in the epigastric region;
- pain;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- hypersalivation;
- nausea;
- decreased appetite.
Dizziness and weakness may occur. The first symptoms appear within half a day after exposure to the irritating factor.
Gastritis differs from a stomach ulcer in that it only inflames the mucous membrane. Ulcerative defects do not form.
The difference between gastritis and a stomach ulcer is the time at which pain occurs. With inflammation, it is observed immediately after eating, and with an ulcer - after 30-60 minutes or on an empty stomach.
The first signs of gastritis include vomiting. During it, the following are possible: tachycardia, diarrhea-type bowel movements and decreased blood pressure.
The tongue of patients is often covered with a white coating. Abdominal bloating is observed. Palpation reveals sharp pain.
Other symptoms include dry mouth and foul odor.
If left untreated, the disease can become chronic and lead to ulcers.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic inflammation
Signs of peptic ulcer and inflammation are nonspecific. The hemorrhagic form is often diagnosed.
A synonym is erosive inflammation. Only the mucous membrane is involved in the process. The size of the erosion is less than 3 mm.
If gastritis is not treated, bleeding may develop. Alcoholics are at risk.
With this pathology the following symptoms are observed:
- lack of appetite;
- dull pain in the upper abdomen;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- vomiting with blood;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- weakness;
- dizziness.
With massive bleeding, the stool becomes dark. Heart rate increases.
Possible depression of consciousness. In this case, you need to rule out a stomach ulcer.
Chronic gastritis may differ from acute gastritis in trophic disorders such as dry skin and brittle nails.
When bleeding occurs, a headache occurs and weakness worries you.
Symptoms of hypoacid form of inflammation
With gastritis and stomach ulcers, symptoms largely depend on acidity. The attending physician should know the signs of chronic hypoacid inflammation.
This disease is characterized by a decrease in acidity due to gland atrophy. We are talking about atrophic and autoimmune types of this pathology. The disease occurs in a relapsing form.
Pathology can develop into ulcers and cancer. This is due to mucosal atrophy and tissue dysplasia. Not everyone knows how to distinguish gastritis and ulcers.
With inflammation of the stomach with low acidity, the following symptoms are possible:
- rotten or airy belching;
- nausea;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- decreased appetite;
- aching pain after eating;
- stool instability.
Atrophy leads to impaired absorption of nutrients and vitamins. Possible weight loss.
If you have gastritis or a stomach ulcer, their symptoms are not known to everyone. In the case of achylia (lack of hydrochloric acid), glossitis and gingivitis develop.
The tongue of patients becomes bright red. The intestines are often affected. Dysbacteriosis develops.
Persistent neurological impairment is possible. Anemia develops with internal bleeding.
The pressure drops. Pain is not a constant symptom of hemorrhagic gastritis.
Symptoms of peptic ulcer
Signs of a stomach ulcer resemble inflammation, but there are differences. The main symptom is pain.
It has the following characteristics:
- dull, piercing or cutting in nature;
- felt in the upper abdomen;
- appears on an empty stomach or 30-60 minutes after eating;
- subsides after 2 hours;
- radiates to the right hypochondrium;
- eliminated by antacids and proton pump inhibitors;
- more disturbing in autumn and spring;
- combined with dyspeptic disorders.
Gastric and duodenal ulcers differ from gastritis in that the pain syndrome depends on the location of the defect.
When the body of the organ is affected, discomfort is noted to the left of the midline.
If there is an ulcerative defect of the pyloric region, then the pain is felt on the right.
Exacerbations are more often observed in people who are accustomed to eating spicy foods.
A duodenal ulcer is different in that pain appears only after 1.5-2 hours.
Sometimes it occurs at night. Other symptoms of a stomach ulcer include a burning sensation in the chest, flatulence, and abnormal bowel movements.
Nausea and vomiting are possible. If you eat incorrectly during an ulcer, there is a high probability of bleeding and perforation of the organ wall.
In the atypical form of this pathology, pain in the lower back and heart area may occur.
Increased acidity of the gastric environment: treatment
For the treatment of hyperacid conditions, 3 groups of drugs that reduce the secretory function of the stomach walls are recommended:
- Antacids;
- H2-histamine receptor blockers;
- Proton pump inhibitors.
The drugs can be used either independently or in combination. Most often, proton pump inhibitors and histamine H2 receptor blockers are combined with antacids. The use of antacids is advisable at the beginning of treatment, when the discomfort is pronounced.
Reduced synthesis of hydrochloric acid: drugs
There are forms of gastritis with reduced secretion of hydrochloric acid. Such cases require taking medications:
- Acidin-pepsin;
- Enzymes (Mezim, Creon, Mikrasim, Panzinorm, Festal, Enzistal);
- Hilak forte;
- Plantaglucid.
Auxiliary treatment
In addition to drug therapy, diet therapy is prescribed, limiting fatty, fried, spicy and smoked foods. The consistency of the products should be soft, preventing irritation to the walls of the stomach and intestines. Eating excessively hot or cold food is not recommended. It is possible to take medicinal table mineral waters (Essentuki, Narzan), which can be purchased at the pharmacy.
Effective use of herbal remedies:
- Iberogasta;
- Gastrointestinal fees;
- Sea buckthorn oil;
- Romazulan (chamomile extract);
- Aloe extract.
With the permission of the doctor, basic therapy can be combined with traditional medicine recipes.
Antiemetic and painkillers
Antiemetics include:
- antiemetics themselves, affecting nervous regulation;
- local anesthetics;
- antacids;
- enveloping and astringent agents.
For vomiting caused by gastritis, use:
- Domperidone (available under the names Motilak, Motilium, Motonium, Passazhiks);
- Metoclopramide (Cerucal, Reglan);
- Mint tablets;
- Mint tincture.
For pain, it is recommended to take anesthetics, which include:
- Almagel A;
- Bellasthesina;
- Bellalgina.
Some antacids also relieve pain, mainly suspensions:
- Phosphalugel;
- Maalox;
- Gaviscon.
To relieve painful spasms, use:
- Buscopan;
- Dicetel;
- Duspatalin;
- But-shpu.
What can trigger the development of pathology?
If a patient was diagnosed with acute gastritis, then, as a rule, its development was facilitated by strong irritants that caused foci of inflammation on the walls of the stomach. In the case when the disease occurs in a chronic form, then during diagnosis, specialists can identify progressive atrophy and structural changes in the mucosa.
Factors that provoke the development of this pathology include the following::
- penetration of pathogenic microflora into the body;
- bad habits;
- eating poor quality food;
- eating disorder;
- stress;
- taking medications;
- chemical and food poisoning, etc.
Treatment with antacids
Treatment with antacids is possible in combination with other drugs. By themselves, they are not very effective, because their effect is short-term and does not treat the cause of the pathologies. Compounds of magnesium, calcium, and aluminum are used as active substances. Most medications can be used during pregnancy.
According to patient reviews, the best medications are:
- Gastal;
- Rennie;
- Maalox;
- Phosphalugel;
- Almagel;
- Gaviscon;
- Rutacid;
- Gastracid.
They are available in tablets and suspensions.
Prevention measures
Prevention of gastritis and ulcers is based on three pillars:
- proper nutrition;
- healthy lifestyle;
- regime and rest.
Doctors' recommendations for the prevention of gastroenterological pathologies:
- Refusal of alcohol, smoking, junk food, fast food, snacks on the run and dry food;
- Frequent walks in the fresh air;
- Taking vitamins, fruits and vegetables;
- Chewing food thoroughly;
- Before eating, wash your hands and pour boiling water over vegetables and fruits;
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases that can lead to Helicobacter pylori infection (sore throat, caries, etc.).
Menu for peptic ulcer disease
With this diagnosis, too cold and too hot dishes are excluded. Carbonated drinks and alcohol are strictly prohibited. That is, the principle is this: you need to eat less of what can irritate the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
Usually, for duodenal and gastric ulcers, the gastroenterologist prescribes diet No. 1.
Diet No. 1
Used for gentle treatment of the disease. Such nutrition reduces the severity of inflammation, which causes healing of ulcers and normalization of the motor function of the stomach.
List of useful products:
- dried or yesterday's bread;
- dry or biscuits;
- milk soups, curdled milk, non-acidic kefir, cream, low-fat cottage cheese;
- rice, semolina and oatmeal;
- lean poultry or beef, lean fish - steam it all;
- beets, potatoes, cauliflower, carrots;
- boiled or baked and grated berries and fruits;
- unsweetened fruit juices, herbal teas and coffee.
Marinades, canned food, mushrooms, cucumbers and puff pastry are strictly prohibited.
The table does not imply serious restrictions on food, but you will have to give up highly fatty and fried foods. You need to eat in small portions, food should be carefully cut into small pieces and freshly prepared. The recipes for such dishes are very simple and do not require much work to prepare them.
Meals for 7 days
You can choose this sample menu for the week with recipes.
| Monday | Breakfast | Oatmeal with milk, unsweetened tea. |
| Lunch | Baked apple. | |
| Dinner | Lean and steamed meat, boiled beets, bread. | |
| Afternoon snack | Low-fat cottage cheese and non-sour fruit jelly. | |
| Dinner | Boiled rabbit meat, boiled vermicelli, herbal tea. | |
| Tuesday | Breakfast | Soft-boiled egg, herbal tea and semolina porridge. |
| Lunch | A glass of fermented baked milk. | |
| Dinner | Steamed beef meatballs, lean soup with vegetables. | |
| Afternoon snack | Low-fat cottage cheese. | |
| Dinner | Stewed rabbit with vegetables, a glass of kefir. | |
| Wednesday | Breakfast | Omelet, sweet yogurt, tea. |
| Lunch | Yesterday's pastries, a cup of tea. | |
| Dinner | Baked potatoes with vegetables, stewed chicken. | |
| Afternoon snack | Curd. | |
| Dinner | Buckwheat porridge with stewed chicken fillet. | |
| Thursday | Breakfast | A glass of warm milk, rice milk porridge. |
| Lunch | Cottage cheese casserole with dried apricots. | |
| Dinner | Boiled beef with potatoes and vegetables. | |
| Afternoon snack | Yesterday's baking with butter. | |
| Dinner | Mashed potatoes with steamed cutlet. | |
| Friday | Breakfast | Oatmeal with dried apricots, a glass of compote. |
| Lunch | Applesauce with yesterday's baked goods. | |
| Dinner | Potato soup with beef, a piece of bread, compote. | |
| Afternoon snack | Yogurt. | |
| Dinner | Baked chicken breast with apples. | |
| Saturday | Breakfast | Omelet with grated carrots, tea with herbs. |
| Lunch | Baked apple. | |
| Dinner | Rice cutlets with stewed rabbit. | |
| Afternoon snack | Unpeppered cheese with a bun. | |
| Dinner | Stewed pollock with buckwheat porridge. | |
| Sunday | Breakfast | Curd mousse with dried apricots. |
| Lunch | Diet cookies and a glass of milk. | |
| Dinner | Soup with dumplings, compote. | |
| Afternoon snack | Baked pears. | |
| Dinner | Zucchini stew with boiled chicken. |
It is better to prepare a menu for the week in advance if you have a stomach ulcer, this will save a large supply of your time for pleasant activities.