More about pathology
Antral ulcers occur with a frequency of 10-15% of all gastric ulcers. More often detected in young people. The peculiarity of ulcers is the appearance of “late” pain, as with a duodenal ulcer - an hour and a half after eating. Pain may appear on an empty stomach or at night. In 15-20% of cases, ulcers of this localization are complicated by the appearance of bleeding. Often, an ulcer of the prepyloric stomach degenerates into cancer.
It should be noted that this pathology often occurs in young people, and in most cases it is directly related to provoking factors, such as drinking alcohol in excessive quantities, constant stress, and malnutrition. Pain in the iliac region often bothers the patient in the morning after waking up. Characteristic symptoms include frequent heartburn and belching with a sour taste. In 10% of the total number of clinical cases, the course of the disease is complicated by bleeding.
Structure of the stomach
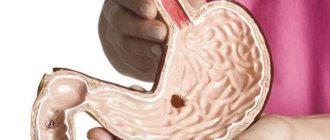
The stomach is located between the esophagus and the duodenum. The organ has three sections:
- Cardiac – next to the esophagus.
- Pyloric – located close to the duodenum.
- Antral (prepyloric) - between the cardiac and pyloric sections.
In the body of the stomach, food is crushed and turned into pulp under the influence of hydrochloric acid. Food in the antrum is gradually mixed until a homogeneous mass is obtained, then it enters the pylorus and the duodenum.
The structure of the human stomach
Causes of pathology
The antrum of the stomach is the lowest region in which food is processed and enters the duodenum. The division of an organ into segments is conditional, since there is no sharp line between them. Only microscopic examination makes it possible to identify differences in the structure of the stomach.
The antral segment is responsible for the breakdown of food and its entry into the initial part of the small intestine. This section contains glands that produce alkaline mucus, which neutralizes the effects of hydrochloric acid. Thanks to this component, the acid-base balance is maintained in the stomach.
Poor passage of food causes stagnation and fermentation processes, as a result of which the production of hydrochloric acid is activated. With prolonged stimulation of the mucous membrane, the entire digestive system is endangered.
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease and untimely treatment will lead to the disease becoming chronic.
Often the starting step towards the onset of the disease is:
- stressful situations;
- abuse of smoked and spicy foods, marinades with an increased amount of vinegar;
- excessive drinking and smoking.
Under the influence of these factors, the level of acidity in the organ declines, which serves as an excellent opportunity for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. In the mucous membranes, the number of cells that are responsible for secretion decreases, and gastric juice begins to separate less well, as a result of which food is not processed enough.
The organ begins to atrophy, which requires replacement therapy and adherence to a strict therapeutic diet. As a result, such disorders entail ulceration (the appearance of ulcers) of the mucous membranes of the antrum, requiring immediate treatment.
Causes of ulcers
A healthy stomach produces some hydrochloric acid necessary for digestion. With slow peristalsis, food is retained in the stomach. This increases the formation of hydrochloric acid, leading to irritation of the mucous membrane. Inflammation occurs, first gastritis, then an ulcer.
Most often, the disease is caused by a pathogenic microbe - Helicobacter pylori, which parasitizes the stomach. The microbe's enzymes produce ammonia, which reacts with hydrochloric acid, interfering with digestion. Bacteria multiply in the gastric mucosa, causing inflammation and later the formation of a defect.
Functions of the antrum
Before finding out what symptoms can be caused by an antrum ulcer, you need to understand what function this department performs. The antrum is the last. If food is broken down in the overlying sections, then a lump is already formed here. This allows you to complete all processes of digesting foods.
As a result of the movement of the walls, food particles are crushed to sizes not exceeding two millimeters. At the same time, the epithelial cells of the antrum secrete mucus, which neutralizes the acid of the juice. In the overlying sections, hydrochloric acid was needed in order to achieve the breakdown of dietary fiber. Further, it can have a negative effect on the delicate intestinal mucosa, in which the environment is slightly alkaline.
The antrum ensures the movement of food chyme through the sphincter due to contraction of the walls. Therefore, violations in this department lead to reverse casting.
The antrum is the last section of the stomach
The antral mucosa performs very important functions for the digestive process. This is achieved through the release of the following enzymes:
Serotonin - provides rhythmic contractions of the walls of the organ, due to which the food bolus smoothly moves into the underlying sections of the digestive organs.
Gastrin is an enzyme released when a large amount of undigested food accumulates in the stomach. As a result, under the influence of pressure on the walls, gastrin is released. It subsequently affects the glands responsible for the release of hydrochloric acid.
Somatostatin is a substance released when the food mass has already undergone breakdown and it is necessary to stop the production of enzymes.
Any disturbance in the antrum negatively affects the digestive processes and causes certain symptoms.
Damage to the antral mucosa disrupts the digestive process
Types of ulcers of the antrum of the stomach
There are two types of ulcerative lesions of this type:
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
Each of the above types is characterized by certain features, so they should be considered in more detail.
Spicy . An acute ulcer of the antrum of the stomach is characterized by the presence of vivid symptoms. It is simply impossible not to notice the development of this form of the disease. As a rule, the occurrence of an acute ulcer is provoked by the following factors:
- severe stress;
- taking medications.
The development of an acute ulcer in the gastrointestinal tract can lead to serious consequences. For example, some patients develop intraintestinal bleeding due to perforation of the gastric wall.
Chronic . Chronic ulcer in the antrum of the stomach is a disease with a long course. The symptoms in this case are not as pronounced as in the acute form. From time to time, periods of remission occur when the symptoms of the disease fade away.
They are replaced by relapses of the disease, when it begins to resemble the acute form. A feature of the disease is the risk of a malignant process.
Depending on the size, large ulcers are divided into:
- large ulcers (more than 2 centimeters in size);
- giant ulcers (their diameter exceeds 3 centimeters).
During the course of peptic ulcer disease there are:
- exacerbation phase (relapse);
- phase of subsiding or fading exacerbation;
- remission phase.
Possible complications
The main complication of an antral ulcer is internal bleeding. It can occur at any stage of the disease and is often asymptomatic. However, it should be understood that severe bleeding poses a danger not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient. Therefore, without correct treatment, the prognosis is disappointing.
Another complication is perforation of ulcers. We are talking about the appearance of a through hole in the wall of the organ, which can lead to the development of peritonitis. Penetration is also possible when the rupture occurs not into the abdominal cavity, but into one of the neighboring organs.
Thus, an ulcer of the antrum of the stomach requires immediate treatment. Otherwise, it can cause the development of complications that are difficult to treat and pose a certain risk to the patient’s life.
Diagnostic methods
First of all, it is important to emphasize that ulcers of the antrum and pylorus of the stomach are more common in young people. This alone makes the diagnosis much easier. In addition, a characteristic sign of the pathology is pain in the right hypochondrium, directly related to eating. It is also important to note that defects in this area are especially likely to provoke bleeding, which explains the presence of complaints about changes in the color of stool and vomit. Already based on these complaints, a preliminary diagnosis can be made and an additional research plan can be drawn up.
The main diagnostic method for ulcers is FGDS. If an ulcer is suspected, the following types of studies will be mandatory:
- FGDS. The most informative research method that allows you to assess the location of the defect, its depth, shape and stage of scarring.
- Biopsy with histology. It is carried out simultaneously with FGDS in order to collect material for subsequent analysis for the likelihood of cell degeneration and assessment of structural changes.
- Ultrasound. Not only the stomach, but also nearby organs are assessed, which makes it possible to determine the possible cause of the pathology.
- X-ray examination. It is performed using a contrast agent, which makes it possible to evaluate the contours of the organ, possible filling defects and peristalsis disorders.
- Lab tests. All biological fluids are assessed. Particularly indicative is a blood test using PCR and ELISA techniques. Thanks to these tests, it is possible to identify the causative agent of the pathology. An analysis for occult blood and signs of anemia will also be required. To diagnose an ulcer, a blood test using the PCR method is prescribed. An examination of the condition of the ulcer should be carried out both before treatment and after its completion. As a rule, there is scarring of the ulcer and a decrease in its size. In this case, therapy continues until stable remission.
Treatment
Treatment of ulcers with lesser curvature of the stomach and any other peptic ulcers without medication is impossible. Here you need to remember only one piece of advice: do not take medications thoughtlessly, without first consulting a doctor. The fact is that only a specialist can make a diagnosis and prescribe a suitable course of medications corresponding to the degree of development of the problem.
What medications are most often used for ulceration of the antrum? Today, the following drugs are used to treat stomach ulcers:
- Antracids (Almagel, Maalox, Sucralfate, Keal, Bellalgin, Vikair, Bekarbon, Vikalin, Phosphalugel). Neutralizes hydrochloric acid and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Medicines that inhibit the secretion of gastric glands (Gastric secretion blockers: Nizotidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine).
- H2-histamine receptor blockers (Ranitidine, Rhinit, fFmotidine, Kvamatel). Increases the secretion of gastric juice.
- Proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Omez, Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Esomeprazole). Helps reduce hydrochloric acid and eliminate heartburn and pain.
- Antibiotics (Tetracycline, Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin).
- Prokinetics (Coordinax, Motilium, Cerucal). Help stimulate the motor function of the stomach and reduce nausea and vomiting.
- Antispasmodics (Mebeverine, Duspatalin, Drotaverine, No-shpa). Eliminate spasm of muscle cells of the stomach wall, reduce pain.
- Probiotics (Enterozermina, Bifiform, Linex). Prescribed for antibiotic therapy.
- Sedatives (Tenoten, valerian). Antidepressants (Amitriptyline).
- Tranquilizers (Seduxen, Elenium, Tazepam).
Only a specialist can prescribe the appropriate dosage of medications, and only he can monitor the dynamics of the development of the disease. Usually, using the right diet and a whole range of medications, you can get rid of the alarming signs of the disease in just 2–2.5 weeks. If no positive dynamics are observed, a new examination is carried out and the diagnosis is clarified.
Doctors also recommend sticking to the prescribed diet for as long as possible, at least for a month, to prevent a relapse of the disease. The question often arises regarding the consequences of an antral ulcer of the stomach.
What happens if you ignore alarming symptoms for a long time? To begin with, a person will have to face a chronic form of the disease, which is extremely dangerous. In case of a chronic form of ulcer, examination will have to be carried out on a regular basis, and diet will forever become a part of a person’s life. Any relaxation in the diet can lead to a sharp deterioration in well-being.
There are often cases when a peptic ulcer develops into an oncological disease, and it can only be eliminated through surgery, which additionally becomes a huge stress for the body. That is why it is not recommended to start the problem and it is better to start treatment as soon as the first symptoms appear.
Nutrition
It is not only difficult, but also practically impossible to cure an ulcer of the antrum of the stomach without dietary nutrition. The diet helps to cope with the symptoms of the disease, improve metabolic processes in the body and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. At first, the patient is prescribed to adhere to diet No. 1a, 16. If the disease has uncomplicated nutrition, it is limited to table No. 1. When creating a menu, the patient must remember about foods that are prohibited:
- unripe fruits and berries, especially if they have thick skins;
- smoked, salted or fried foods;
- baked goods made from wholemeal flour;
- carbonated drinks;
- broths;
- canned food;
- radish and other products that act as irritants to the mucous membranes of the digestive tract;
- food that contains coarse connective tissue (cartilage, fish and poultry skins, etc.).
The patient should eat only warm foods, small portions. It is best to break your food into 5-6 meals. Food should be steamed, boiled or baked. For the first 2 weeks, food should be crushed to the consistency of puree, then you can introduce food little by little in pieces. Drinking alcohol and smoking are strictly prohibited during the treatment period.
Folk remedies
As an addition to drug therapy, doctors can prescribe the following folk remedies to patients:
- Potato juice. Provides protection to mucous membranes from damage. To prepare the juice, you need to peel fresh potatoes, which are then grated on a fine grater. Using gauze, squeeze out the juice. You can also use a juicer. The product is taken immediately after spinning (no later than 10 minutes) half an hour before meals.
- Aloe leaves. It is necessary to cut off the leaves of a plant that is more than three years old. After this, they should be kept in the cold for 10 days. Then grind the leaves with a blender until smooth. It should be taken half an hour before meals, one tablespoon at a time. The standard course of treatment is a month.
- A decoction of flax seeds. An excellent remedy for the treatment and prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. To prepare the product, you need to pour a teaspoon of seeds into a glass. Pour 100 ml of boiling water over them and leave for 15 minutes. Then the product is filtered and taken half an hour before meals three times a day.