More about gastropathy
Gastropathy of the stomach is a violation of the functionality of the digestive process, accompanied by a feeling of discomfort and pain in the abdomen, damage to the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Gastropathy is diagnosed in both sexes and can be found in children. In women, the disease is more common and is usually associated with hormonal problems.
Gastropathy and gastritis have differences and are separate concepts. Gastritis is an inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa, and gastropathy is characterized by the presence of several gastric diseases.
The initial stage of gastropathy often does not manifest itself at all, so it often becomes chronic.
Superficial gastropathy of the stomach
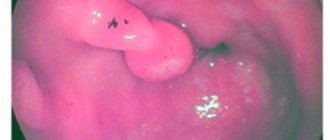
If gastritis is a pathology of the gastric mucosa, accompanied by its inflammation, then gastropathy is the name of various gastric diseases that are characterized by damage to the epithelium and vascular system of the stomach with possible minor inflammation. With this disease, studies will show redness of the surface of the organ. According to ICD-10, the code for this disease is the same as for gastritis - K29.
In many cases, this syndrome indicates superficial gastritis, which developed under the influence of certain factors. In this case, the changes persist for a long time and require therapeutic measures. But other reasons are also possible that cause changes of a transient nature, for example, drinking alcoholic beverages the day before, a large amount of spices in food, highly carbonated water, defects in diet. Therefore, it is important to follow the correct eating regimen and not overuse irritating foods. Diet defects on the eve of fibrogastroscopy can cause hyperemia and slight swelling of the mucous membrane. This condition does not require special treatment.
Classification of the disease
In medicine there are several classifications of gastropathy. Gastropathy is divided according to the type of course (acute and chronic), by stages, and by degrees of development.
According to the degree of development, gastropathy can be:
- 1st degree. Manifests itself in slight deformation of the gastric mucosa, in a slight decrease in the synthesis of hydrochloric acid;
- 2nd degree. It is characterized by the appearance of stronger pathological processes, in which cell damage and necrosis of the gastric epithelium occurs faster than in the first case. These processes can be reversed with timely treatment.
The stage of gastropathy depends on its duration, the nature of its course, the effectiveness of treatment, and the condition of the gastric epithelium. The following stages of gastropathy can be distinguished:
- Initial - characterized by a slight inflammatory process of the mucous membrane without transformation of its structure.
- Chronic - at this stage, ulcers and erosions appear, the glands of the organ are affected. This stage occurs with advanced gastropathy - when the diagnosis was delayed or the treatment was incorrect.
- Atrophic - manifests itself in the degeneration of the gastric walls, replacement of certain areas with connective tissue, and poor health.
- Hypertrophic is the most severe stage, during which thickening and coarsening of the gastric walls occurs, adenomas and cysts form.
According to its form, gastropathy can be divided into:
- spicy. It appears when the stomach is affected by infections, alcoholic beverages, acids, alkalis;
- chronic. It is characterized by a slow course with a gradual transformation of the epithelium of the organ, its atrophy, and a decrease in the functions of the stomach. Often this form of gastropathy is asymptomatic;
- moderate. It is characterized by the degeneration of epithelial cells into connective tissue.
The following types of gastropathy are also distinguished:
Antral
This type of gastropathy occurs in the antrum of the stomach, where food is crushed and subsequently moved into the duodenum. This type of gastropathy helps to reduce the rate of food processing, which causes food stagnation and fermentation. The patient feels heaviness and pain. Delayed treatment can lead to the appearance of ulcers, which can be treated well.
Associated (drug-induced) and induced gastropathy
This type is caused by the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Such drugs can cause damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive organ, the formation of ulcers and erosions, bleeding, and provoke obstruction of the organ. Often these types of gastropathy are asymptomatic, so they are mainly discovered when complications have already developed.
Hyperemic
With hyperemic gastropathy, there is an influx of blood to the stomach, redness of the mucous membrane, swelling, and bruising occur. This form of gastropathy can spread to individual parts of the organ or to small areas of it.
Hyperplastic
There is a strong increase in the number of cells of the gastric glands, stomach tissue grows, folds and growths appear inside the organ. This form of pathology includes hypersecretory gastritis, Menetrier syndrome, Zollinger-Ellison disease.
Diffuse
Gastropathy of this type spreads to the entire gastric body, structural changes occur in the mucous membrane of the organ, the symptoms are similar to those of gastritis. This type of gastropathy can have an acute or chronic course.
Stagnant
This type of gastropathy is characterized by a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, the appearance of erosions and ulcers in the antrum of the stomach and in its upper section. The occurring disturbances in the blood supply system of the stomach originate from the negative effects of alcohol and nicotine, as well as the activity of Helicobacter pylori.
Grainy
Growths in the form of grains form (their size can be from several mm to cm) on the gastric walls. Gastropathy is more often found in men after forty years of age. The early stage of gastropathy is usually asymptomatic; further development leads to disruption of protein metabolism.
Catarrhal
Catarrhal superficial gastropathy is one of the simplest types of pathology, in which inflammation spreads only to the upper layer of the organ mucosa. There is an increase in the synthesis of hydrochloric acid, or its deficiency. The cause of this type of gastropathy is injury, food poisoning.
Lymphoid (lymphocytic) gastropathy
This form belongs to rare types of gastropathy. It is characterized by the appearance on the epithelium of the organ of lymphocytes that look like follicles. The cause of this form of gastropathy is the influence of Helicobacter pylori, which provokes the proliferation of lymphoid tissue.
Papular
It manifests itself as erosion that does not affect the deep layers of the gastric epithelium. With pathology, papules form in different parts of the digestive organ, which can be either single or multiple formations.
Portal
Appears due to vasodilation - pressure in the veins increases, capillaries expand, filling with blood, mosaic patterns, red fragments or a black-brown pattern may appear on the mucous membrane, characterized by the absence of inflammation.
Reactive (chemical)
The main cause of this type of gastropathy is considered to be bile reflux and prolonged use of NSAIDs. This form occurs more often in patients who have undergone gastric surgery.
Erosive
This type occurs when various factors influence the mucous membrane, characterized by the presence of erosions ranging in size from 1 to 7 centimeters, they resemble pimples in appearance with a depression. The disease may develop without symptoms or with slight pain on the right side in the hypochondrium; gastric bleeding is acceptable.
Erythematous
It is redness of the mucous membrane and is determined using endoscopic examination. It is possible to distinguish between focal, covering one or several zones of the stomach, and widespread, which covers the entire surface of the organ or most of it. Focal gastropathy occurs in the absence of symptoms; if it is more widespread, sensations inherent in gastritis may appear, namely: heaviness and pain in the epigastric area, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, heartburn, belching, and general weakness.
Ulcerative
This form is characterized by the presence of symptoms, as in intoxication. If blood clots are found in the vomit, be sure to consult a doctor.
Mixed
In some cases, patients may develop several forms simultaneously. Most often observed: superficial, erosive, hypertrophic and hemorrhagic gastropathy.
Uremic
This form appears in patients with chronic renal failure.
Exudative
This is a rare disease, it consists in the formation of deep folds on the gastric wall, the height of some can be 3-3.5 cm, in addition, the main and parietal cells decrease, and the number of cells that produce mucus increases. The reasons for the appearance of this form of gastropathy are not well understood. It is assumed that the disease can be caused by prolonged influence on the mucous membrane of alcoholic beverages, heavy metals, heredity and metabolic disorders also occur. Sometimes exudative gastropathy is considered a benign tumor.
Causes
A century ago it was believed that “chronic catarrh of the stomach is also observed in habitual drunkards, gluttons, and in general in people leading an immoderate lifestyle...” (A.P. Chekhov, “Everyday Adversity”). Today the list of reasons is much more extensive:
- poor nutrition - violation of the regime; fried, spicy, fatty, smoked, pickled food. Stale food, food that is too hot or too cold;
- alcohol, especially strong alcohol, dissolves the barrier mucus, allowing aggressive enzymes access to the defenseless surface of the stomach;
- smoking increases the secretory activity of the digestive glands;
- chronic gastritis with improper treatment or lack thereof;
- entry of bile from the duodenum through a loosely closed pylorus;
- long-term use of medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which include Aspirin, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ketorolac, Indomethacin;
- chronic congestion occurring against the background of pancreatitis, pathologies of the liver, kidneys, gastric ulcer;
- injuries, chemical and thermal burns of the gastrointestinal tract;
- poor blood circulation in the stomach;
- gastrointestinal infections (Helicobacter) and helminthiases (roundworms, pinworms);
- An increase in pressure in the portal vein leads to dilation of the arteries, veins, capillaries of the stomach, and their overflow with blood. Possible rupture of blood vessels with bleeding.
Conditions predisposing to the disease are retirement age, female gender, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The causes of the disease can be divided into internal and external. The general list of reasons looks like this:
- improper diet;
- reflux of bile into the stomach;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages, strong coffee;
- burns and other injuries;
- stagnant processes;
- smoking;
- presence of infections;
- lack of enzymes in the body necessary for digestion;
- long-term use of medications;
- the formation of internal pathologies and the resulting incomplete blood supply;
- genetic predisposition;
- age over 50 years;
- hormonal changes occurring in the body.
Superficial gastropathy of the stomach treatment
Treatment will depend on what caused the development of the pathological process. In most cases, the disease is eliminated through conservative measures; in some cases, surgical intervention is practiced. Drug treatment can be based on the following drugs:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antispasmodics;
- sorbents, enterosorbents;
- prokinetics;
- antacids;
- intestinal antiseptics;
- prostaglandins;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- medications to improve gastric motility and enzyme production.
A diet is required. The specific dietary table is determined on an individual basis. Provided that therapeutic measures are started promptly and correctly, complications can be avoided. The forecast is personal in nature.
Sources
https://ponosov.net/eritematoznaya-gastropatiya.html
https://simptomer.ru/bolezni/zheludochno-kishechnyj-trakt/3189-gastropatiya
https://tsitologiya .su/zheludok/jeritematoznaja-gastropatija-s-ochagovoj-atrofiej
https://moy-zheludok .ru/voprosy/poverhnostnaya-gastropatiya-chto-eto-takoe
https://nastacio.ru/ poverxnostnaya-gastropatiya-chto-eto-takoe.html
https://tsitolo giya.su/zheludok/jeritematoznaja-gastropatija-s-ochagovoj-atrofiej
Symptoms of the disease
At the very beginning, the disease may not show any symptoms. Some time later, gastropathy may manifest itself with symptoms similar to gastritis - pain, heaviness in the stomach, flatulence, nausea, heartburn.
In addition, the following changes occur:
- appetite is impaired;
- vomiting may occur, bringing relief;
- In some patients, bile synthesis may be impaired;
- disturbance of intestinal tone, constipation occurs.
With pathologies of the antrum, bleeding may occur - the stool becomes reddish in color, and blood impurities appear in the vomit.
Folk remedies
Mixed gastritis: causes, symptoms, treatment and recommended diet
Any folk remedies for the treatment of erosive antral gastritis should be used as an auxiliary therapy and only after approval by the attending physician. Recipes use honey, wheat and oat sprouts, aloe leaf juice, and various bee products. Folk remedies help to quickly restore the changes that have occurred, eliminate painful symptoms, and also help prevent dangerous exacerbations. All drugs that are used for treatment at home can easily be prepared independently based on natural ingredients. One of the most effective methods of treating gastritis, proven in practice for more than one generation, is sea buckthorn oil. When using it, you must follow some conditions, namely:
- Maintain regular intake;
- The first dose should be taken early in the morning, on an empty stomach, 30 minutes before meals;
- Store the oil away from direct sunlight, best in the refrigerator, at a temperature no higher than five degrees;
- For prevention - patients after reaching the age of 14 years, take one teaspoon, two weeks of administration alternated with two weeks of break;
- For the treatment of existing pathology - the same amount, but when treating for three weeks, the break does not exceed one week.
When using traditional methods in the treatment of gastritis, it is necessary to remember that it is unacceptable to refuse prescribed drug therapy, since they serve as an addition to the main course of treatment. It is unacceptable to independently prescribe and apply any folk methods to yourself.
The following are used as therapeutic agents that have shown their effectiveness in the treatment of erosive antral gastritis:
- Juice from white cabbage promotes faster recovery of damage to the gastric mucosa.
- Juice obtained from raw potatoes copes well with any exacerbations of erosive gastritis. Half a glass of freshly prepared juice, drunk on an empty stomach, will be enough.
- Juice from celery and carrots helps eliminate irritation. Take half a glass before lunch and dinner.
- Propolis tincture in the amount of 20 drops per glass of water. Helps cope with painful symptoms, and relief occurs after the first dose.
- Chamomile decoction in milk, dry raw materials in the amount of five tablespoons are brewed in a glass of milk, infused and drunk before meals. This remedy relieves stomach pain and speeds up healing.
- A decoction of plantain leaves is used for both peptic ulcers and erosive gastritis.
- Flax seed. A decoction is prepared from it, for which two full spoons of the seed are brewed in 0.5 liters of boiling water, kept in a water bath for 10 minutes, then left to cool. The squeezed mucus is taken one tablespoon after meals.
Oatmeal, decoctions and infusions from birch leaves, St. John's wort, galangal, cinquefoil, yarrow, oregano, linden and many others are used as effective remedies in the treatment of erosive gastritis.
Choosing any of them must be done with some caution, since some may cause individual intolerance in the form of allergies. Properly selected traditional medicine recipes will help defeat the disease, as well as prevent possible exacerbation during periods of remission
The therapeutic effect will be enhanced by healthy sleep and good mood, which is provided by the natural ingredients included in these recipes.
Features of gastropathy in children
In childhood, this pathology is in second place after ARVI. The disease begins suddenly and has a rapid course. Gastropathy can develop in infancy during the transition to artificial feeding or as an allergic reaction to food. In addition, the occurrence of the disease can be triggered by infection, taking medications, consuming inappropriate milk formulas and expired products.
The pathology is manifested by weakness, anxiety, nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdominal area, loss of appetite, and diarrhea. The acute form often becomes chronic, which is characterized by pain and discomfort in the stomach.
Symptoms
At first, the disease may not manifest itself with symptoms or hide behind signs of another disease, for example, ulcers, pancreatitis. As pathological processes develop, heaviness and abdominal pain are felt after eating. Gastric juice irritates the esophagus, causing heartburn. A decrease in the digestive function of the stomach causes a protective reaction - nausea and vomiting. Food is delayed, fermentation begins with the release of gases through belching, hiccups, and flatulence. Abnormal bowel movements occur in the form of diarrhea or constipation in adults and children. The person cannot eat, loses weight sharply, and becomes weaker.
Children, starting from infancy, suffer from the disease no less than adults. The acute form of the disease predominates in them. It begins suddenly and develops rapidly. The child cannot indicate where it hurts. The baby has a fever, refuses to eat, cries, sleeps poorly, vomits and diarrhea. The cause is gastrointestinal infections, allergies, low-quality products and infant formula. Without treatment, the disease will become chronic.
Diagnosis of the disease
A history alone is not enough to make a diagnosis. For an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes laboratory, instrumental and differential diagnostics:
- urine and stool analysis;
- a pepsin and acidity test is performed;
- a test is performed for the presence of Helicobacter pylori;
- fluoroscopy;
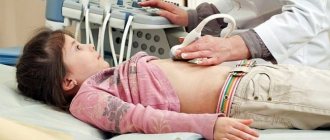
- ultrasound endoscopy;
- General and biochemical blood test.
The main objective of the examinations is to differentiate gastropathy and other similar diseases (gastritis, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis or chronic cholecystitis).
Characteristics of the disease, including causes, symptoms and methods of detection
Etiology and pathogenesis
The pathogenesis is due to the depth and extent of changes in the structure of the gastric membranes and impaired functionality of the digestive glands. Diseases are based on the degeneration of one type of tissue into another. In adults, the development of the disease occurs gradually, and in children it develops quickly and is caused by helminthic infestations, the transition from breastfeeding to artificial feeding, and replacement of the nutritional formula. The development of gastropathy can be triggered by the following internal and external factors:
- burns;
- injuries;
- taking NSAIDs;
- reflux of bile from the duodenum;
- errors and irregularities in nutrition;
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- stress.
Classification of gastropathy
Uncontrolled use of painkillers destroys stomach tissue.
It is based on morphological changes in stomach tissue, which go through 4 stages:
- The first degree is hyperemic gastropathy. Occurs under short-term influence of an aggressive factor, characterized by minor inflammation, without violating the integrity of the mucous membrane.
- The second stage is chronic. In this case, ulcers, erosions, and impaired secretion of the gastric glands are formed.
- Third subatrophic stage. An atrophic type of change appears, in some places it will be replaced by connective tissue.
- Hypertrophic gastropathy is characteristic of the fourth stage. The walls of the stomach become thickened, inelastic, and cysts and adenomas are visible on the mucous membrane.
Types of gastropathy and characteristic symptoms
| Type | Morphological changes | Symptoms |
| Hyperemic | The mucous membrane is locally or completely hyperemic, edematous, with bruising | Pain, heaviness, belching, heartburn |
| Erosive | Damage to the lining of the stomach with the formation of erosions | Flatulence, stomach bleeding, pain |
| Stagnant | Impaired blood supply, hypoxic changes, ulcers and erosions in the lower part of the organ | Decreased motor skills, pain syndrome |
| Subatrophic and atrophic | Complete degeneration and atrophy of the gastric glands | Characteristic of hypoacid conditions and oncology |
| Antral | Disorders of the antrum of the stomach, congestion | Heaviness in the stomach, bloating, belching |
| Superficial | Minor changes in the upper layers of the mucous membrane | Increase or decrease in gastric acidity |
| Hyperplastic | A sharp increase in the number of secretory glands, the mucosa is comb-shaped | Associated with pH changes |
| Hypertrophic | Deformation of the mucous and muscle layer with neoplasms | Pain, bleeding, heaviness |
| Portal | The surface layer of the mucous membrane is changed, the presence of papules | Heartburn, decreased motility, pain |
| Mixed | Characteristic changes for those species that are inherent | Various symptoms |
Complications
Ulcers form as a result of damage to muscle tissue.
Delayed diagnosis and incorrect therapy can provoke the development of complications. This is a violation of the integrity of the stomach lining and the functionality of their glands, insufficient secretion of hydrochloric acid and enzymes, and congestion. The most dangerous of them are:
- oncological formations, which are most often provoked by hyperplastic gastropathy;
- ulcers, erosions, perforations;
- gastric bleeding (caused by congestive gastropathy).
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a gastroenterologist. Diagnosis begins with collecting a complete medical history. Then laboratory tests are carried out (general and biochemical analysis of blood, urine, feces), instrumental tests - fibrogastroduodenoscopy and ultrasound diagnostics, histological analysis, fluoroscopy, tests for the detection of Helicobacter, tests for acidity and enzyme ratios. They also conduct a differential examination with cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and malignant neoplasms.
Treatment
Drug treatment is carried out using the following drugs:
- Antisecretory drugs: Kvamatel, Ranitidine, Famotidine.
- Proton pump inhibitors - Omeprazole, Esomeprazole, Lansoprazole.
- Gastrocytoprotectors that protect the mucous membrane from aggressive influences: Almagel, Maalox, Gastromax, Phosphalugel.
- Sorbents (for acute pathology): Enterosgel, Atoxil, activated carbon.
- Enzyme preparations that promote food digestion: “Creon”, “Mezim”, “Festal”.
- To improve gastric motility: Motilium, Cerucal.
- To relieve pain and relieve spasms, the following are prescribed: “No-shpu”, “Riabal”.
If Helicobacter bacteria are present in the body, anti-Helicobacter therapy is carried out, which includes taking the following drugs: Amoxicillin, Ornidazole, Metronidazole, Vikalin, De-Nol.
In addition, vitamin preparations are prescribed, since there is a lack of them in the body due to disruption of the digestive process.
The purpose of vitamin complexes depends on the type of gastropathy and stomach acidity. For the hypoacid type, vitamin E is prescribed; this vitamin is found in vegetable oil, fats, and milk. For low acidity, vitamins C (found in citrus fruits, rose hips, cabbage) and PP (in fish, meat) are prescribed. Vitamin B6 deficiency may occur, which leads to metabolic disorders and nervous disorders. This vitamin is found in grain bread, beans, and peas. Lack of B12 can cause anemia; absorption of the vitamin occurs better together with folic acid, which is found in products of animal origin.
Surgical treatment is resorted to if it is not possible to relieve pain or stop gastric bleeding. The most commonly used method is the laparoscopic method, which is carried out using special instruments and does not deeply injure the organ tissue.
In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy is used. The following methods help to get rid of the disease:
- vegetative corrective (aerotherapy, electrosleep);
- stabilization of secretion (drinking mineral waters, magnetic therapy);
- regenerative (infrared laser therapy, infrasound);
- anti-inflammatory (UHF, cryotherapy);
- antispasmodic (paraffin therapy, galvanization);
- immunomodulatory (magnetic therapy of the umbilical region and thymus gland);
- sedative (mineral and pine baths).
Diet for gastropathy
Following a diet for pathology is one of the mandatory points along with therapeutic methods.
All diets recommended for pathology are based on the following principles:
- fragmentation of nutrition, its regularity, small size of consumed portions;
- quality of products, exclusion from the diet of fatty, spicy foods, freshly baked baked goods;
- eating dishes prepared using gentle methods - boiling or steaming;
- exclusion of cold and hot foods from the diet;
- refusal of sour vegetables and fruits when increased stomach acidity is diagnosed;
- avoidance of foods that increase gastric motility with reduced secretion.
Treatment with traditional methods
In addition to drug treatment and diet, traditional methods of treatment can be used, but only in combination with the main treatment.
Many traditional medicine recipes contain beekeeping products:
Dissolve a spoonful of honey in 1 tbsp. warm water and drink 20-30 minutes before meals.
Mix aloe juice with honey in equal proportions and consume a tablespoon before meals.
It is good to take propolis tincture in the amount of 30-40 drops on an empty stomach. This remedy has an antiseptic and healing effect.
In addition to honey products, sea buckthorn has a positive effect on the body in this disease. Sea buckthorn oil has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and regenerating effects.
Herbal treatment is often used for this diagnosis. These are products prepared on the basis of chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula, sage, immortelle, thyme, string, plantain, flax seeds, oak bark and others. They can be brewed as tea and taken before meals, or you can buy ready-made preparations at the pharmacy and take according to the instructions.
Homeopathic treatment
This therapy is carried out in conjunction with the main treatment and only under the supervision of a homeopath, who prescribes treatment strictly according to individual indicators, taking into account the form of the disease, the nature of the disease, and the individual characteristics of the patient.
The following types of medications are usually prescribed:
- “Amarin” is an oral drop containing substances of plant origin. The drug is used for gastrointestinal disorders caused by impaired secretion and motility of the stomach. Contraindications: stomach and duodenal ulcers, high blood pressure, possible allergies.
- "Gastrikumel" - tablets, which contain substances of plant and mineral origin, activate the body's defenses and normalize dysfunction of the stomach.
- "Hepar compositum" is an injection solution, it is prescribed for disorders of the digestive organs.
- “Kalium floratum” are tablets that are used in all weight categories, the differences are only in the doses taken and the frequency of administration. The dosage and number of times per day depends on age and type of pathology. If you are hypersensitive to the components of the drug, an allergic reaction is possible.
Superficial erythematous gastropathy is
When a problem is discovered, during the examination the doctor determines the degree of damage to the mucosa and the type of erythematous gastopathy.
When a problem is discovered, during the examination the doctor determines the degree of damage to the mucosa and the type of erythematous gastopathy. There are two types of gastropathy - focal and diffuse (or widespread). What is the difference between them? Focal is characterized by local redness of the mucous membrane, that is, the inflammation does not spread to the entire stomach cavity, but is concentrated in one small area. The diffuse type of gastropathy is characterized by the fact that the inflammatory process covers the entire surface of the mucous membrane or most of it. With focal gastropathy, gastritis and other stomach diseases most often do not yet develop, in contrast to the diffuse type of erythematous gastropathy.
Determining the main reason why this pathology began to develop plays an important role in subsequent treatment.
Focal superficial gastropathy
If the damage to the mucous membrane is more serious and a diagnosis of “diffuse erythematous gastropathy” or “focal” is made, then the doctor will prescribe treatment appropriate to the type of disease. It must be strictly observed, and if one or more of the rules are neglected, complications such as gastritis or gastric ulcer may soon appear.
When a problem is detected, during the examination the doctor determines the degree of damage to the mucous membrane and the type of erythematous gastopathy. There are two types of gastropathy - focal and diffuse (or widespread). What is the difference between them? Focal is characterized by local redness of the mucous membrane, that is, the inflammation does not spread to the entire stomach cavity, but is concentrated in one small area. The diffuse type of gastropathy is characterized by the fact that the inflammatory process covers the entire surface of the mucous membrane or most of it. With focal gastropathy, gastritis and other stomach diseases most often do not yet develop, in contrast to the diffuse type of erythematous gastropathy.
Treatment is based on 4 basic rules:
- Food should not overload the stomach cavity - the intervals between meals should be at least 2-3 hours, and you need to eat in small portions.
- The daily menu should contain products that help restore the structure of the gastric mucosa and do not injure it. Slimy porridges, chicken broth, jelly, and jelly are perfect for this.
- Coffee and black tea should be replaced with plain clean water and herbal tea should be drunk.
- Prerequisite: a break or cessation of smoking and drinking alcohol.
These rules will be effective in combating the inflammatory process, because by adhering to them, all the necessary conditions are created. Some doctors recommend patients drink freshly squeezed cabbage juice and acidify food. Most older people take many medications, but many of them cause irritation and congestion of the stomach cavity. Before taking them, you need to find out the opinion of a gastroenterologist.
Therapy must necessarily include medications whose mechanism of action is aimed at eliminating inflammation and has a beneficial effect on the healing process. For erythematous gastropathy, astringents, antacid drugs and proton pump inhibitors have worked well.
Surgery, as a method of treatment, is considered the most extreme measure and is carried out only when therapeutic measures no longer bring the desired effect. The most popular surgical method is gastric resection. This type of operation causes a minimum of trauma, since it does not require making an incision in the stomach tissue. To perform a resection, a tube must be inserted through the mouth through the esophagus into the stomach. Then, using the necessary equipment, the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane are carefully removed.
Prevention of gastropathy
To prevent gastropathy it is recommended:
- take care of proper nutrition;
- get rid of bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking;
- take medications strictly for medical reasons;
- avoid stressful situations.
List of references: https://ilive.com.ua/health/gastropatiya-zheludka-chto-eto-takoe-i-kak-lechit_124297i15938.html https://professor.perm.ru/klinika/novosti-i-aktsii/ 201-gastropatiya-prichiny-vidy-simptomy.html Karateev A.E. NSAID GASTROPATHY: DYNAMICS OVER 12 YEARS. Scientific and practical rheumatology. 2011;49(3):20-24. https://www.lvrach.ru/2004/07/4531495/ https://mosapteki.ru/material/npvpgastropatiya-i-effektivnost-ee-lecheniya-8782 https://www.rlsnet.ru/articles_507.htm Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/17/2020
Prevention
Simple preventive measures will help prevent the disease:
- proper nutrition, normal drinking regime;
- absence of harmful addictions - alcohol, smoking;
- taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- annual medical examination;
- moderate physical activity;
- adequate rest;
- optimistic attitude.
If taking NSAIDs is vital, protect the stomach with Omez, Lanzap, Pariet.
Gastropathy is familiar to many people from their own bitter experience. The ways to cure the disease depend on the nuances of the course of the disease and the individual data of the patient. Medicines and procedures have contraindications. Self-medication threatens to move the disease into an advanced stage, when only surgery will help. Listen to your body and do not ignore the alarm signals it gives. Always remember that a positive, friendly attitude and peace of mind are considered the leading factors in maintaining health and maintaining a high quality of life.
We recommend: Is it possible to eat sauerkraut if you have gastritis?
Diagnosis of the disease
This disease occurs unnoticed and there are no specific symptoms. It is difficult to recognize the disease, so laboratory examinations and tests are prescribed, on the basis of which a diagnosis is made. List of necessary examinations that the patient must undergo:
- General blood analysis.
- Detailed blood test.
- Biochemical tests.
- Bacteriological studies of stomach contents.
- Fibrogastroscopy.
- Biopsy.
- X-ray.
- Sonography of the abdominal organs.
- MRI or CT.
Symptoms of the disease
Almost always, concomitant diseases with hyperemia are gastritis, stomach ulcers, and duodenitis. Less commonly, diseases that are not related to the gastrointestinal system are associated with hyperemia (overflow of blood in the vessels of the circulatory system of any organ or area of the body).
Thus, the following symptoms are characteristic of different forms of gastritis:
- Symptoms of hyperemia (overflow of blood in the vessels of the circulatory system of any organ or area of the body) (overflow of blood in the vessels of the circulatory system of any organ or area of the body) of the gastric mucosa. The gastric mucosa is focally hyperemic, there is a coating with whitish foamy mucus on the surfaces of the organ in “mucus lakes”, the folds are compacted and are not completely smoothed out with the help of air.
- As cells die, the surface becomes thinner and turns pale. In this case, the foci of the disease do not become hyperemic, and the vascular web is clearly visible.
- In the superficial form of gastritis, the mucous surface of the stomach (a hollow muscular organ, part of the digestive tract, lies between the esophagus and the duodenum) is hyperemic throughout or only in the body and antrum of the stomach. Sometimes hyperemia is focal in nature or can be diffuse.
- If there is fibrous gastritis, hyperemia is most pronounced, while it is focal and characterized by the presence of pus. This inflammation can be caused by measles or scarlet fever infection. The patient may vomit blood frequently.
- The phlegmonous form of the disease can be triggered by trauma to the stomach with sharp objects, such as fish bones. In such cases, this indicates possible hyperemic foci.
- Bulbit is characterized by swelling and redness, thickening of folds in the antrum. Among the reasons are Helicobacter pylori infection of the antrum of the stomach (a hollow muscular organ, part of the digestive tract, lying between the esophagus and the duodenum) and unhealthy diet.
- Renal dysfunction (various degrees of swelling).
- Depression and permanent stress also provoke hyperemia.
The main symptoms of gastropathy include:
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
- pain in the stomach;
- nausea, vomiting;
- heaviness, weakness;
- loss of appetite.
If such symptoms appear, patients should undergo an examination and consult a doctor - an endoscopist, who will prescribe antigastritis therapy based on the diagnostic results. If necessary, with severe manifestations of pathology in the stomach, endoscopic resection will be prescribed. The prognosis after the operation is quite favorable.
The essence of treating stomach ulcers with alcohol
Alcohol in its pure form burns mucous membranes. The principle of action is based on the fact that ulcerative erosions are cauterized. For these purposes, take 20 g of pure alcohol in the morning on an empty stomach. However, doctors warn that this technique is dangerous to health, as side effects may occur in the form of irritation and severe internal burns. Ethanol can be used as one of the constituent components.
For example, on an empty stomach take 1 tbsp. a spoonful of alcohol and eat a piece of butter. This method is gentle on the stomach. The treatment course is 10 days. Then they pause for 10 days, after which the treatment is repeated. After a month, the erosions in the stomach should heal. Instead of oil, you can use eggs, animal fats, or drink the medicine with potato or cabbage juice.
Clinical picture
Complaints from patients who were diagnosed with erythematous gastropathy during FEGDS directly depend on the prevalence of erythema in the stomach.
The focal form of erythematous gastropathy can, in most cases, be asymptomatic and detected by chance. With diffuse damage to the gastric mucosa, patients may present with the following symptoms:
- aching pain in the epigastrium that appears or intensifies after eating or drinking;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea sometimes with vomiting, which brings relief;
- belching of air or rotten matter;
- weight loss;
- fast fatiguability;
- fragility and hair loss;
- lamination and fragility of nail plates;
- flatulence;
- intestinal colic;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- white or white-yellow coating on the tongue.
Some of the symptoms of gastropathy are associated with a slowdown in digestive processes, congestion in the stomach, fermentation processes, and some with anemia, which can occur due to impaired absorption of nutrients, iron and vitamins.
What is the treatment?
To eliminate such pathology in case of lesions in the gastrointestinal tract caused by NSAIDs, Nexium is prescribed. It is possible to use Nexium for prophylactic purposes in elderly people, when gastric ulcers or gastritis are observed in almost everyone.
It is the h3 group drugs, histamine blockers, ranitidine that can eliminate unpleasant symptoms and chronic gastritis and lead to normalization of the gastric mucosa.
For gastropathy, it is possible to prescribe astringents, antacids, and proton pump inhibitors.
The standard treatment regimen used for gastritis will not work here. Of course, the doctor can prescribe drugs that reduce acid production, as well as painkillers. But along with them you will have to take some gastric enzymes and gastrocytoprotectors. Has Helicobacter bacteria been detected? Only antibiotics can suppress its activity.
When gastropathy is diagnosed, treatment cannot be delayed. In some forms of the disease, bleeding may occur. It is not always possible to stop it using conservative methods. And doctors resort to laparoscopy. In addition to medications, diet and vitamin intake are recommended.
Sometimes it is impossible to do without surgical intervention to excise the affected areas in the stomach with instruments.
If you do not contact a gastroenterologist in a timely manner when unpleasant symptoms appear, complications such as stomach ulcers and dangerous diabetic gastropathy, when the mucous membrane is inflamed due to diabetes, are possible.
In the future, this situation can lead to paralysis of the stomach, a slowdown in its timely emptying due to damage to the nervous system or atrophy of the gastrointestinal tract muscles, paralysis of all organs of the digestive tract. The heart, which will also be subject to pathological changes and the development of anomalies, does not go unnoticed. Cardiac muscle dysfunction may occur, followed by heart failure. The liver will also fail due to the accumulation of hepatocytes against the background of excessive fat accumulation, coma will develop due to diabetes, insulin deficiency, and metabolism will be disrupted. The condition will become life-threatening.
In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapy is used. After the acute period is over, magnetic therapy, aerotherapy, pine and mineral baths, the use of infrasound and galvanization are prescribed.
Recommendations for nutrition in pathology
Very often, hyperemia does not need to be treated, because it means that your body is trying to restore itself, self-regenerating. Hyperemia (overflow of blood in the vessels of the circulatory system of any organ or area of the body) accelerates metabolism in tissues, but such a diagnosis is only normal if it is arterial hyperemia, but more often redness and swelling are harbingers of gastritis.
To treat and prevent the disease, the diet of the scientist M.I. Pevzner is used. The Pevzner diet is a system of therapeutic tables that are differentiated according to various types of diseases. Pevzner's diet No. 1 is intended for people suffering from gastritis and ulcers. It is also prescribed during the recovery period after surgery and for duodenal ulcers.
Difficult to digest foods are completely excluded from the diet, as well as foods that actively irritate the mucous membrane (tunica mucosa, often just mucosa - the inner lining of hollow organs communicating with the external environment). Those who adhere to this diet eat a menu consisting of berries and fruits, condensed milk and cream, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, fish and poultry. All products included in this dietary table must be used either stewed or steamed. In any case, it is forbidden to eat fatty meat, salted fish, fresh baked goods, hot dishes and dairy products that increase acidity.
Treatment with folk remedies
Herbal decoctions gently but effectively stimulate gastric motility, coat the mucous membrane, and replenish the loss of vitamins and minerals. To prepare the collection, take a teaspoon of dry herb of each type and mix it. A tablespoon of the resulting mixture is brewed with 500 ml of boiling water in a thermos and left for an hour. Take 100–150 ml of warm broth half an hour before meals. They are treated with herbal teas for up to two weeks, followed by a break of 20 days and a change in the healing mixture.
Collection No. 1 is intended for erythematous, hyperemic gastropathy: chamomile, yarrow, sage, dandelion.
Collection No. 2 will help with the congestive form of the disease: linden flowers, flaxseed, licorice root, peppermint.
Collection No. 3 is recommended for inflammatory changes in the stomach: chamomile, fennel fruits, wheatgrass root, flaxseed, yarrow. Sea buckthorn oil shows good results. It envelops, reduces the acidity of gastric juice, and heals erosions. A teaspoon of oil is taken orally 20 minutes before meals, 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Classification
Gastroenterological disease is classified according to several criteria:
- the nature of the flow;
- stage of development;
- clinical and morphological signs.
According to the nature of the course, the pathological process is considered in the following forms:
- initial (hyperemic gastropathy) - the mucous membrane is not changed, slight redness is possible, which indicates the early onset of the inflammatory process;
- atrophic - replacement of some parts of the esophagus with connective tissue;
- hypertrophic gastropathy - cysts form, scarring of the stomach walls occurs, the stage is characterized as extremely severe.
Regarding the degree of development of the pathological process, the classification is as follows:
- 1st degree - slight decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid, the clinical picture is absent or manifests itself in a latent form;
- 2nd degree - pronounced symptoms, significant deterioration in well-being.
Even with the second degree of development of gastropathy, if treatment is started correctly, complications can be avoided.
Symptoms of gastropathy
After clinical studies are carried out and tests are submitted to the laboratory, the doctor diagnoses the form of the disease. The epithelial layer of cells located on the inner surface of the stomach serves as a protective barrier - mucus forms on it, which prevents hydrochloric acid from corroding the tissue.
By determining how damaged the walls of the stomach are, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis of what kind of disease the patient has.
| Hyperemic gastropathy | The mucous membrane is red, with swelling, the vessels are dilated, and increased blood flow is observed in the walls of the stomach. |
| Hemorrhagic | Damage to tissues of the vascular system, gastric bleeding is observed. |
| Erythematous | Redness is observed in individual areas or throughout the entire mucous membrane. |
| Congestive gastropathy | The motility of the stomach is impaired, small ulcers appear on the walls, and the blood supply is disrupted. |
| Papular gastropathy | Papules appear on the tissues of the stomach in the form of small swellings, they are located on the surface; When healing occurs, scars do not remain. |
| Erosive gastropathy | Ulcers appear on the mucous membrane. |
Symptoms of atrophic gastritis
If the patient experiences the symptoms described below, it can be assumed that pathological processes have begun in the body. To cope with the disease at an early stage, it is necessary to seek medical help and undergo a full examination to confirm the problem.
Symptoms include:
- Painful sensations in the gastric and abdominal area;
- Feeling of heaviness and lump;
- Food, even light food, is practically not digested. because of which the patient complains of heaviness of the stomach, bloating, increased gas formation;
- Constant constipation or stomach upsets;
- Severe pain caused by unhealthy foods and alcohol abuse;
- At an advanced stage of gastritis, skin problems are observed, hair falls out, and nails become brittle.
Most often, atrophic gastritis develops without visible symptoms, so it is advisable to seek medical help if there is a lack of appetite and discomfort in the abdominal area.
If the disease is detected at an early stage, it will be easier to treat.