What is surface bulbite
A feature of superficial bulbitis is inflammation of the duodenal bulb, which occurs in a mild form and can be cured without much difficulty. However, it is much more difficult to control the running process.
The disease is characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane of this section, which causes stagnation of bile and enzymes, which are necessary for the complete digestion and absorption of food.
Ducts from the pancreas and gallbladder exit into the bulb. Due to such anatomical features, the inflammatory process can spread to the pancreas or duodenum. Often this phenomenon precedes a peptic ulcer.
When the duodenal bulb is inflamed, the specialist diagnoses “Superficial gastritis bulbitis.”
The following forms of superficial bulbitis are distinguished: acute and chronic. In the first case, the inflammatory process develops in response to nutritional disorders, intoxication of the body, or damage to the intestinal mucosa by a foreign object.
The chronic form can be primary or secondary. In the primary version, the pathology develops due to stress and poor nutrition, in the secondary - against the background of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostics
Patients who present with clinical manifestations require immediate consultation with a gastroenterologist. This is necessary to identify the causes of the disease, prescribe laboratory and instrumental examinations, as well as develop effective treatment tactics.
The first step in diagnosing superficial bulbitis is a specialist’s examination of the patient’s medical history. This is necessary to search for hereditary factors in the occurrence of such a disorder, as well as to identify the pathology against which such a disease began to progress. In addition, it is necessary to conduct a detailed conversation and examination of the patient. These manipulations will help the doctor determine the presence and intensity of symptoms, as well as their location. To do this, palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity is performed.
The next stage of diagnostic measures is laboratory studies of blood tests. A decrease in protein concentration is observed. The latest and main diagnostic methods are instrumental examinations of the patient, which include:
- breath test - to determine the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- FGDS - examination of the surface and mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. During this procedure, an endoscopic biopsy is performed;
- radiography of the above organs - can be performed with or without the use of a contrast agent;
- impedansometry of the gastrointestinal tract - the resistance between the electrodes of the probe is assessed, which allows you to examine the condition of the esophagus and stomach;
- determination of acidity;
- antroduodenal manometry - study of peristalsis of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Carrying out FGDS
Such diagnostic methods allow a specialist not only to prescribe the most effective treatment, but also to differentiate such a disease from chronic gastritis and pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gastric or duodenal ulcers, as well as oncology and hiatal hernia.
Causes of the disease
Superficial bulbitis of the stomach develops as a result of factors such as:
- complicated family history;
- penetration of foreign bodies into the intestines and their traumatic effect on the bulb;
- violation of the diet, predominance of fried, spicy and fatty foods in the diet;
- helminthic infestations (enterobiasis, ascariasis);
- eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, which causes infection;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- eating too hot food and drinks;
- decreased protective functions of the body;
- chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract characterized by inflammation (Crohn's disease);
- gastritis.
The causes of the disease can be different. To get rid of inflammation, it is necessary to find out what triggered it, based on diagnostic measures.
Prevention of bulbitis
In order to avoid the appearance of the disease or protect yourself from its return, you must follow the rules of prevention:
- promptly treat all diseases related to the health of the digestive system, promptly go to the hospital for examination;
- give up the abuse of bad habits, if this is impossible, then try to reduce them to a minimum;
- adjust your diet, eliminate all harmful foods;
- Maintain your immune system, exercise, ensure healthy sleep and try not to be stressed.
A person’s health depends on himself, on how carefully he monitors his body and how quickly he provides himself with medical care. The main thing is to remember that in the first stages you can cope with any disease without causing damage to your health.
We recommend: What does the tongue look like with gastritis - assessment of the condition
Symptoms of pathology
Characteristic symptoms of superficial gastritis bulbitis are:
- constant rumbling in the stomach;
- attacks of nausea ending in vomiting, after which a bitter taste appears in the mouth;
- constant feeling of hunger, even after eating enough;
- pain in the stomach;
- bad breath;
- abdominal pain localized in the navel area and appearing 1-1.5 hours after eating;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- increased irritability;
- constipation
In the superficial form of this pathology, pain is not the leading symptom. Typically, severe pain occurs already in advanced stages, as well as in the case of chronic inflammation .
Treatment
Drug treatment is used exclusively in the exacerbation phase of the disease, provided that the cause of the inflammation is identified. They begin to treat not the disease itself, but its root cause (for example, Helicobacter pylori - with the help of antibiotics). In addition to the use of medications, special treatment tables are used - special types of diets developed for each group of diseases. This allows you to reduce the load on the stomach and intestines, as well as normalize their functioning in the future. During the treatment process, they try to normalize the acidity of the stomach, since increased acidity can aggravate the course of bulbitis.
Diet: sample menu for the day
- 8 am (breakfast) - omelette with carrots, always steamed; a glass of weak tea with milk with a little sugar;
- 10 o’clock (2nd breakfast) – applesauce;
- 11.30 (snack) - rosehip decoction;
- 12.30 (lunch) - soup with chicken fillet; boiled rice with veal cutlet (steamed); fruit compote;
- 15.00 (afternoon snack) - a glass of jelly and crackers;
- 17.30 (dinner) - carrot salad; fish soufflé; buckwheat porridge;
- 19.00 (2nd dinner) - cracker pudding with pear puree; tea;
- 21.00 (before bedtime) - milk.
And don’t forget - you shouldn’t suddenly stop using the diet even if you feel well and have no pain symptoms. Otherwise, you risk resuming the course of the disease, perhaps even in a more severe form.
A mild form of inflammation in the duodenal bulb is superficial bulbitis . However, the signs of the disease do not have features that could help differentiate the diagnosis. The disease can only be determined through endoscopic and radiographic examination.
Treatment of superficial bulbitis
Treatment of superficial bulbitis requires not only taking medications, but also following diet rules.
Drug treatment
Medicines are used only during periods of exacerbation of the disease.
The doctor selects the medicine based on what factor provoked the development of the pathology:
- If Helicobacter pylori (a bacteria that provokes the development of ulcers, gastroenteritis, duodenitis, and stomach cancer) is present in the gastrointestinal tract, antibiotics are prescribed. Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin are usually prescribed.
- Antacids are prescribed to neutralize hydrochloric acid. These are Maalox, Reni, Gastal.
- In order to stimulate the process of mucus formation, which helps heal erosion of the membranes, medications such as Liquiriton, Biogastron are prescribed.
- For severe pain, taking No-Shpa and Drotaverine is indicated.
Diet for bulbitis and gastritis
Proper treatment of superficial gastritis bulbitis involves following a diet. Food should be light and in no case irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Be sure to exclude foods that stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid. These are chocolate, spices and herbs, bakery yeast products, smoked meats, pickles. It is prohibited to drink coffee, carbonated waters and drinks, kvass.
The patient's meals should be divided: you can eat up to 5-6 times a day, but in small portions.
Allowed to eat:
- lean fish and meat, boiled or baked;
- vegetables cooked steamed or in water (except cabbage, mushrooms, sorrel);
- cereal side dishes with milk or water (excluding corn and pearl barley);
- soft-boiled eggs.
Traditional medicine recipes
Herbal treatment is another way to correct the patient’s condition. It must be taken into account that traditional medicine is purely auxiliary in nature and can only complement the main course of therapy.
For superficial bulbitis, the following folk recipes are useful:
- Plant composition. To prepare, mix chamomile, St. John's wort, yarrow, celandine in equal proportions, take 2 tablespoons of this raw material. Pour the mixture into 0.5 liters of boiling water and let it brew for 3-4 hours. You need to drink 100 ml of this composition before each meal.
- Plantain-based medicine. You will need 3 tablespoons of fresh plantain juice and a tablespoon of honey. The components need to be mixed. Before meals, eat a teaspoon of the prepared product.
- Infusion based on propolis. To prepare, 60 g of raw material is poured with a glass of alcohol and left in a dark place for a week. Take 1-2 times a day, adding 5 ml of infusion to a glass of warm water.
Superficial bulbitis is a pathological process in which one of the parts of the stomach becomes inflamed. This process can be easily treated, but in advanced cases the situation gets worse.
Treatment of bulbitis involves taking medications during the period of exacerbation, as well as following a special diet.
Nutrition rules and diet for bulbitis
We should also talk about diet during the treatment of bulbitis. This is a very important factor on the path to recovery.
Proper nutrition is necessary for every person. This is good. But, as a rule, it is not possible to monitor your diet, and most people do not even know what proper nutrition is. It is especially important for people suffering from inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Diet is not precisely the identity of the products that are approved for use, since all diseases are individual, like each organism.
A nutritionist, together with a gastroenterologist, will help you choose the right diet, which will need to be followed for a fairly long period of time - about six months. And even if the symptoms of the disease have passed, you still need to continue to adhere to the diet.
When bulbitis worsens, it is important to immediately give up foods that irritate the mucous membrane - coffee, strong tea, alcoholic drinks, spicy, smoked, salty and fatty foods. After all, they became the provoking link in the occurrence of the attack.
In the first days after an attack, you should eat only liquid food. Since food for such a patient should be easily digestible and even a kind of “unloading”. Subsequently, a mandatory condition for treatment should be separate and fractional meals. Food intake should be increased to 6 times a day. Food must be kept warm. Table salt is limited to 5 grams per day, sugar - to 50 grams.
In the first weeks, the foods allowed for consumption include soft-boiled eggs, scrambled eggs, steamed slimy porridges, baked apples, chicken broth and fillet, compotes and jelly, up to four glasses of milk, milk and cereal soups, meat and fish in the form of a soufflé. Bakery products are prohibited.
After two weeks of treatment, you can slightly expand your food intake to include day-old white bread, crackers, biscuits, low-fat sour cream, butter, low-fat cottage cheese, steamed pork cutlets, boiled veal, and pasta. The only drinks you can include for now are tea, and even a weak one. And freshly squeezed juices from non-acidic fruits and vegetables. Nutritionists can also recommend drinking one tablespoon of olive oil half an hour before meals. And so twice a day - morning and evening. This suppresses the secretion of gastric contents well and helps in treating the disease.
What is the prevention of focal bulbitis?
Preventive measures include:
- Passing a medical examination;
- Treatment of other inflammatory processes in the body;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Proper nutrition, avoiding overeating and excessively fatty foods;
- Maintaining hygiene rules.
After treatment with antibiotics and medications, following a diet and certain lifestyle rules allows us to hope for a complete recovery.
We recommend: Is it possible to eat apples if you have gastritis? - application options
Bulbit and superficial gastritis: common symptoms and differences
Due to the fast pace of modern life, there is no time left for proper nutrition, which is fraught with the occurrence of bulbitis and superficial gastritis. Diseases are widespread and dangerous.
Characteristics of diseases
Superficial gastritis is an initial stage disease that can subsequently develop into an ulcer. During illness, the glandular epithelium of the stomach becomes inflamed and changes. Basically, the disease occurs against the background of other disorders, often called concomitant.
Bulbit affects and inflames the most important organ of digestion (duodenum, directly the bulb). It is considered a type of duodenitis.
General symptoms
Rotten breath and stomach pain combine both diseases. In the initial stages, the symptoms are mild and not too pronounced. If you experience frequent nausea or even vomiting, you should definitely consult a doctor; either bulbitis or gastritis may develop.
The main differences between diseases
The causes of both pathologies are both similar and different. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori plays a major role in both diseases, plus the common cause of inflammation is poor diet and constant stress. The similarities in the causes of the disease end with these signs.
Completely different diseases can accompany the occurrence of foci of both pathologies. Bulbit occurs due to diseases: Crohn's disease, giardiasis, infection with worms, foreign body entering the stomach. Superficial gastritis is not far from: diabetes, hormonal imbalance and hypertension.
The main difference is localization. Bulbit is located in the duodenal bulb, gastritis is located directly in the stomach. At the first symptoms, it will hurt in different parts of the abdomen, depending on the disease.
Bulbit is distinguished by a related predisposition, which plays a huge role in the occurrence of the disease. Superficial gastritis exhibits obvious and unique symptoms. Already at the second stage, gastritis can be clearly determined by the following criteria:
- Bloating, burning and discomfort in the epigastric region;
- Stomach pain after eating;
- Poor appetite;
- Rotten breath;
- On palpation there is pain in the stomach;
- Fatty and floury foods cause heartburn.
Treatment
Superficial gastritis, bulbitis often requires the use of diet in treatment. When the disease transforms into an acute form, therapy is carried out in a hospital.
Treatment of bulbitis begins after examination by a gastroenterologist; only a doctor is able to quickly identify the disease and prescribe medications. Treatment depends on the course and type of the disease; accordingly, medications and methods for the patient’s recovery will change.
The doctor prescribes antibiotics in prescribed dosages. An attempt at self-treatment can lead to dysbiosis, which is difficult to treat. In cases of infection with worms, treatment is drawn up, and the prerogative is to remove the parasites from the body.
The treatment method is used exclusively for people infected with worms.
It is necessary to treat superficial gastritis, starting with an examination by a doctor; the doctor’s first action will be to send the patient to a procedure called fibrogastroduodenoendoscopy. After receiving complete information from the diagnosis, treatment is drawn up. At best, you will have to give up bad habits and follow the diet prescribed by your doctor.
Chronic gastritis looks like a punishment for not following doctor's advice. For a long time, continuing the same lifestyle, a person will lead to the proliferation of Helicobacter pylori inside the body.
Further inaction regarding helicobacteriosis will end fatally. The pathogenic bacterium will begin to destroy the first layers of the epithelium, then go further, destroying the deeper layers.
The doctor prescribes antibiotics, as in the case of bulbitis, the main goal will be to reduce stomach acidity.
Helicobacter pylori bacterium
Causes of pathology
The development of surface bulbite occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- chronic or acute course of gastritis, regardless of the treatment provided;
- infection with various types of parasites: Giardia, helminths, fungi;
- decreased immunity;
- infections caused by Helicobacter pylori;
- hormonal imbalances associated with the functioning of the adrenal glands.
These factors belong to the group of internal causes of superficial bulbitis. Very often the disease is provoked by an exacerbation of other pathologies that occur in people:
- due to a stable diet violation: consumption of salty, spicy or smoked foods, irregular meals, strict diets;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics, NSAIDs, and other drugs that can act on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- regular consumption of large doses of alcohol, smoking;
- frequent stress, anxiety, tension and emotional turmoil.
Superficial bulbitis is found in adults and children. In childhood, this pathology develops mainly due to the ingestion of foreign objects.
Symptoms of bulbitis
The signs of the disease are very similar to the characteristic manifestations of gastritis. Bitterness in the throat, heartburn, nausea, bowel dysfunction, stomach pain, discomfort in the stomach felt after eating - all these are also symptoms of bulbitis. But such obvious signs are typical if acute or erosive bulbitis has developed.
The superficial form of the disease is not so obvious; it is completely invisible to the patient, so you can skip the moment when you should begin to treat the disease. As a result of an undistinguished superficial bulbitis, a precursor to more severe forms of intestinal diseases, complications arise; erosion can develop, which, if the problem is further ignored, turns into ulcers on the intestinal walls.
Superficial antral gastritis treatment with drugs
For superficial antral gastritis, the drug treatment regimen in most cases is as follows:
- antibiotics to destroy bacterial microflora and reduce inflammation;
- antisecretory drugs to reduce the acidity of gastric juice;
- gastroprotectors , such as rebagite , to trigger natural defense mechanisms through the production of one’s own mucus;
- enzymes and antispasmodics to facilitate the digestion of food;
- painkillers to relieve discomfort.
Causes
The causes of bulbitis are in many ways similar to the causes of gastritis:
- pharmaceuticals;
- chemical burns;
- love of alcoholic drinks;
- habit of eating too hot food;
- infection with helminths or lamblia (especially typical for children);
- variant of manifestation of Crohn's disease, etc.;
- poor nutrition (eating on the go, addiction to junk food, habit of eating once a day, but a lot, etc.);
- bacteria Helicobacter pylori (especially in the case of catarrhal form or mixed bulbitis);
- mechanical trauma to an organ (swallowing an indestructible object, which can damage the walls of the organ, often leading to focal damage).
Prevention
As in the case of duodenogastric reflux (DGR), the occurrence of bulbitis can be prevented if you live by the new rules:
- Following the principles of healthy food consumption.
- Quit smoking and all alcoholic drinks, even beer.
- Avoiding stressful situations.
- Attentive attitude to health and treatment of emerging diseases.
The prognosis for recovery is most favorable provided that you seek medical help in a timely manner and comply with all prescriptions and recommendations of the attending physician.
General information
Superficial bulbitis is a fairly common disease, more often found as part of another pathology (peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, chronic gastritis, etc.). This disease is rarely observed in isolation, and is almost three times more common in men than in the female population. The reason for the development of bulbitis is the special location of the duodenal bulb: this part of the digestive tract is located at the junction of the stomach and intestines, here the acidified food bolus is subjected to alkalization and preparation for further digestion. In addition, it is into the duodenal bulb that the common bile duct opens. The combination of these facts leads to the fact that other diseases of the digestive tract, poor diet, smoking, and stress cause changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum, the most vulnerable part of which is the bulb.
Types of surface form
Depending on what form was detected, treatment tactics are prescribed. Basically, superficial bulbitis is acute and chronic. With a timely diagnosis, the consequences of pathology can be completely eliminated. If it takes a chronic course, focal damage to the intestines and stomach may develop.
- Surface form. Mild degree of the disease - if it was detected during diagnosis, one can hope for a quick and simple restoration of the mucous membrane. With this form of bulbitis, the epithelium is slightly damaged, inflammation is accompanied by swelling and pain, and the release of digestive juices is disrupted. It can occur acutely or chronically. In the first case, the infectious nature of bulbitis is almost always diagnosed.
- Catarrhal form. The catarrhal form is a severe stage of superficial bulbitis, which is accompanied not only by swelling and inflammation, but also by problems with the capillaries. They increase, resulting in poorer movement of food through the intestines. As a result of the catarrhal course of bulbitis, superficial reflux gastritis is formed (reflux of stomach contents back into the esophagus). Catarrhal bulbitis often worsens in spring and autumn. It may go without symptoms for several years, but show signs after stress, spicy food or alcohol.
Causes
Bulbit is a type of duodenitis, an inflammatory process in the area of the duodenum, concentrated in the area of its initial, or upper, part close to the stomach. It develops acutely or chronically, in the second case it lasts for a long time, months and years with periods of relapse (worsening of the condition) and remission (minimization or absence of symptoms).
What is surface bulbite? We are talking about a type of inflammation without defects in the mucous membrane (erosions, ulcers, neoplasms predisposing to bleeding and scar formation), but with redness (hyperemia) and swelling of the affected tissues. The pathology can also be characterized as a focal process, although there are also total (with widespread lesions) variants; Among the reasons for development are:
- consumption of spicy foods, alcohol;
- dry food and/or with long “hungry” pauses;
- smoking;
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- trauma to the mucous membrane (for example, when eating coarse, solid food fragments);
- use of anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids;
- diseases of the hepatobiliary system, pancreas;
- gastritis, endocrine dysfunction;
- intoxication, intestinal infections;
- allergic reactions to foods, medications.
The risk of developing the disease increases in people with a hereditary predisposition, as well as in frequent stressful situations, when emotional stress becomes excessive.
The main cause of bulbitis is infection with Helicobacter pylori
Superficial type bulbitis usually occurs along with inflammation of the stomach, that is, patients suffer from gastroduodenitis. The pathology is most often chronic.
Mechanisms of bulbit
The duodenum is the first to digest food and is responsible for the normal functioning of bile and pancreatic juice. These liquids contain enzymes, without which normal absorption of all nutrients in the small intestine is impossible.
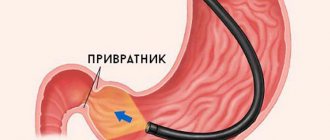
The intestinal bulb - bulbus - is a round thickening located immediately behind the sphincter of the stomach, which is located next to the intestine and connects it to the digestive organ. Inflammation of the bulb develops mainly due to untimely entry of stomach contents into the intestines.
Important! Superficial bulbitis never develops as an independent disease (less than 1 chance per 1 million patients).
Particularly dangerous is the condition accompanied by high acidity, when the bacterium Helicobacter pylori penetrates the intestines. With low acidity, other pathogenic microorganisms often enter with food, which, during normal digestion, almost always die under the influence of hydrochloric acid.
What is surface bulbite? This is a disease that appears under the influence of external or internal factors. Most often, the pathology mechanism is triggered by gastritis. Sometimes bulbitis is called inflammation of the stomach, but this is not entirely true, because it develops in the intestines.
Treatment options
The treatment of bulbitis is approached in a comprehensive manner; medications are an integral part of the treatment regimen. They also follow a strict diet and sometimes use traditional methods. Main groups of drugs:
- Elimination of infection. Antibiotics and gastroprotectors prescribed by the doctor are used. Antiparasitic drugs are required if the disease is caused by microorganisms.
- Decreased stomach acidity. Regardless of the type of disease, enveloping drugs and substances that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid are prescribed.
- Normalization of digestion and enzyme production. Substances based on pancreatin and similar components are prescribed.
- Eliminate pain. Use antispasmodics or painkillers.
Sometimes substances that calm the nervous system are prescribed if the emotional, psychological cause of the disease is precisely known.