Signs of the disease
As the disease worsens, the patient’s well-being worsens, symptoms become more pronounced, and pain occurs. The pain can be constant or appear in attacks. After eating, the discomfort usually increases. This may cause nausea and vomiting. A sign of an active inflammatory process is the presence of gastric juice and mucus, as well as blood clots, in the vomit.
Erosive gastroduodenitis in chronic form can occur without obvious signs. Usually the patient’s general condition worsens, frequent headaches, weakness, and sleep disturbances are observed. Due to a deficiency of nutrients, pale skin is noted.
Periods of remission and exacerbation alternate. An exacerbation of the disease usually occurs in autumn or spring. With periodic bleeding of erosions, symptoms characteristic of anemia appear: fatigue, dizziness, general weakness, rapid heart rate.
Treatment of erosive gastroduodenitis is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused it, reducing the production of hydrochloric acid, restoring the mucous membrane, and eliminating pain. Folk remedies are used to increase the effectiveness of traditional methods.
It is recommended to take an infusion of celandine for a month. First you need to grind the grass. Pour 1 tbsp into a thermos. l. raw materials, pour 250 ml of boiling water. Leave to infuse, filter after 1.5 hours. Take 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l. medications before meals.
You will need to collect herbs taken in equal parts: peppermint, Voloshsky dill seeds, yarrow and centaury. Brew 2 tbsp. l. herbal mixture 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave to infuse overnight. Drink 50 ml three times a day before meals. The duration of treatment is 4-6 weeks.
In the chronic form of the disease, you can take an infusion of 4 medicinal herbs - chamomile, St. John's wort, plantain and nettle. All herbs need to be taken equally and crushed. 2 tbsp. l. pour the raw materials into a thermos, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for about 8 hours. Drink 50-60 ml of medication 3 times a day for 6 weeks.
In a similar way, you can prepare an infusion of a medicinal mixture consisting of mint, valerian root, hop cones, marsh grass, knotweed, chamomile and yarrow flowers, dill and caraway seeds. The course of treatment is 1.5 months, dosage is 50 ml 3 times a day.
You need to pour 0.5 kg of viburnum berries into 3 liters of water, bring to a boil, remove from heat, leave for 24 hours. Add 2 cups of crushed chaga mushroom to the prepared broth and put it in a cool place. After 2 days, add 100 ml of aloe juice and 300 ml of honey, stir until the honey is completely dissolved. It is recommended to drink this remedy 3 times a day, 100 ml, 30 minutes before meals.
Mix equal amounts of crushed orange peel, calamus root, centaury and wormwood. Add 2 tbsp. l. herbal mixture into a thermos, pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave overnight. Drink 60-80 ml of infusion before meals up to 4 times a day. The duration of the treatment course is 1-1.5 months.
Boil a glass of sea buckthorn berries for 5 minutes, add 1 liter of water, cool slightly and filter. Add 2-3 tbsp to the prepared broth. l. honey You need to drink 400 ml of sea buckthorn decoction per day, taking it 30 minutes before meals.
Gastroduodenitis in erosive form can be successfully treated with traditional medicine
It is important to follow the recommendations for the use of medicinal herbs and adhere to dietary nutrition. Without adequate treatment, this pathology can lead to the development of peptic ulcers.
Erosive gastroduodenitis: diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Erosive gastroduodenitis: treatment with folk remedies.
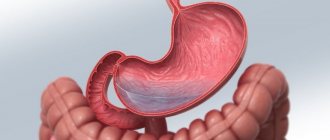
According to medical data, more than 80% of all diseases occur in the digestive system. The most common pathology is erosive gastroduodenitis. What is it? This is an inflammatory disease in which numerous erosive formations and ulcers with mucofibrinous contents form on the gastric mucosa. In addition, the duodenal mucosa is affected. In this case, the nutrition of the mucous membrane is disrupted, increased acidity of the stomach is observed (hypersecretion), and severe swelling occurs.
Prevention and prognosis of pathology
For prevention, you should follow a gentle diet that excludes spicy, rough and hot foods. In addition, it is necessary to avoid the use of anti-inflammatory drugs that can lead to erosion.
The prognosis of this pathology is favorable, but without proper and timely treatment it can lead to the development of peptic ulcer disease.
List of references: https://www.kp.ru/guide/gastroduodenit.html https://www.nrmed.ru/rus/dlya-vzroslykh/gastroenterologiya/lechenie-gastroduodenita/ https://idoctor.kz/illness/ 2263-erozivnyiy-gastroduodenit https://36on.ru/health/recipes/54536-kak-lechit-erozivnyy-gastroduodenit-narodnymi-sredstvami https://doc.ua/bolezn/gastroduodenit https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru /diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/erosive-gastroduodenitis Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/16/2020
Treatment of erosive gastroduodenitis
Mixed gastritis: causes, symptoms, treatment and recommended diet
Treatment of the disease involves complex therapy, which consists of drug treatment and adherence to a strict diet.
Allowed to include in the daily diet:
- lean fish,
- cereals,
- lean meat,
- potato,
- beets,
- non-sour cottage cheese.
Products are steamed, baked in the oven or boiled.
Drug treatment is prescribed only by a doctor. An endoscopic examination is performed to make a diagnosis.
As a result, the condition of the mucous membrane can be assessed. Swelling, friability, and bleeding of the surface are noted. The treatment is based on the destruction of Helicobacter pylori infection and normalization of acidity in the stomach.
These factors are considered the main sources of the disease. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to neutralize them. It is also recommended to take painkillers to alleviate the condition.
When getting sick, an important step is strengthening the immune system. Vitamin complexes are prescribed, which contain vitamins E and A.
Proper treatment helps scarring of erosions and ulcers, the prognosis in this case is favorable.
In parallel with diet and medication, it is allowed to use traditional medicine methods to speed up the healing process. For gastroduodenitis, celandine, chamomile, St. John's wort, flax seeds, and yarrow are suitable. On their basis, infusions and decoctions are made.
To prevent the formation of erosive gastroduodenitis, the following should be excluded:
- alcohol,
- carbonated drinks,
- caffeine,
- smoking.
A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention of diseases.
It is important not to confuse this disease with others. Learn about the symptoms and treatment of atrophic gastritis
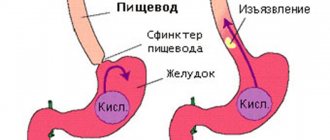
What is erosive duodenitis?
The duodenum (duodenum) is located just behind the stomach. It plays the role of a transition link between the stomach and small intestine.
The duodenum receives the contents of the stomach - food mixed with acidic gastric juice and caustic enzymes, so the duodenum is more susceptible to inflammation than other parts of the intestine.
Inflammation in the duodenum can occur:
- due to food poisoning;
- excessive indulgence in alcohol and spicy food;
- poisoning with medications and chemical poisons;
- mechanical damage.
Duodenitis can also develop against the background of chronic hepatitis and pancreatitis. In this case, inflammation of the duodenum occurs due to increased absorption of pancreatic enzymes.
Chronic gastritis can trigger the onset of duodenitis. In this case, two aggressive factors act on the duodenum at once - acid-peptic and Helicobacter pylori infection.
Important: erosive chronic duodenitis, complicated by Helicobacter pylori infection, is rarely isolated. Gastritis or a stomach ulcer is almost always diagnosed at the same time.
Treatment of atrophic gastroduodenitis
Erosive antral gastritis: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Treatment must be comprehensive. The main points of therapy are listed below.
Compliance with nutrition and diet
Eat often in small portions (fractional meals). If you have reflux, do not lie down or bend over immediately after eating. Food should be warm. Exclude salty, sour, spicy, fried, smoked and canned foods from the menu.
And also alcohol, strong coffee and tea, fast food, carbonated drinks. Meat, fish and vegetables - only boiled, stewed or steamed. Boil soups in water or vegetable broth. Porridge - only with water: milk will lower the already low acidity.
Fermented milk products are indicated - kefir contains lactic acid bacteria, microelements, vitamins and ethanol. Normalizes intestinal microflora and destroys pathogens.
For atrophic gastroduodenitis, any kefir is indicated, but it is better to use three days old: it contains more acid than one day. And besides, one day can cause fermentation in the intestines. For diarrhea, kefir is contraindicated!
Freshly squeezed juice from white cabbage has a good effect. It is juice, because cabbage contains a large amount of fiber, and this will injure the mucous membrane even more. The juice stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid, accelerates metabolism and the healing process, enhances intestinal motility and relieves inflammation.
In addition, it strengthens the vascular wall and reduces inflammation. You should drink the juice only freshly squeezed - during storage it loses its properties. You don’t need to add anything to it - you can just dilute it with water or another juice: apple or potato.
It is also good to eat sauerkraut. It will increase the production of hydrochloric acid, increase intestinal motility, accelerate mucosal regeneration and improve immunity. In addition, it contains a lot of vitamin C. Before taking, the product should be crushed or squeezed out as much as possible.
Medications
Atrophic gastroduodenitis involves the use of a number of medications. Antibiotic therapy to destroy Helicobacter: Amoxicillin and Tetracycline in combination with gastroprotectors - proton pump inhibitors and bismuth preparations.
The drug based on bismuth tripotassium dicitrate has not only a gastroprotective effect, but also an antibacterial effect.
Sedatives – motherwort, valerian.
Increasing acidity levels and improving digestion of food in the stomach:
- atropine preparations - pure atropine, Bellaspon, Bellataminal,
- enzymes - Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Mezim, Mikrasim (the latter has no age restrictions).
Antispasmodics for pain - No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine. Bellastesin, an atropine preparation, will have a good effect: it will increase secretion and reduce pain.
To normalize intestinal flora (in case of imbalance) and strengthen the immune system - probiotics: Bificol, Bifidumbacterin, Hilak forte for two weeks.
Treatment of erosive gastroduodenitis
Gastroduodenitis: chronic, superficial, erosive, acute
Therapy for the disease is aimed at eliminating or minimizing the influence of provoking factors (treatment of infection, adherence to a special diet). With the help of drug therapy and folk remedies, the mucous membranes are protected from the effects of gastric acids and their regeneration. Measures are being taken to reduce the acidity of the stomach.
The main task, which a special diet for gastroduodenitis helps to solve, is to protect the mucous membranes from further erosive destruction
It is especially important to eat right and follow medical recommendations during an exacerbation of gastroduodenitis. A gentle diet at this stage of the disease completely excludes fatty, fried, spicy foods, rich broths, carbonated drinks, too hot or cold dishes
In some cases, the doctor may recommend completely abstaining from food for 2-3 days.
For patients with erosive gastroduodenopathy, a split, frequent diet is recommended, from 5 to 7 times a day. The patient is advised to drink plenty of non-acidic, non-hot drinks. The daily menu must include:
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- liquid slimy porridges (oatmeal, buckwheat, semolina, cooked in milk);
- jelly;
- vegetable puree soup;
- omelettes;
- lean white fish;
- boiled or steamed lean meat;
- non-acidic, non-rough vegetables and fruits.
Any canned food and alcohol are completely excluded from the diet. Prohibited foods include such healthy foods as bran bread, radishes, rutabaga and other difficult-to-digest vegetables, garlic, fatty or tough meat and other rough foods. It is not recommended to eat legumes (beans, peas), bakery and pasta products, various sauces and seasonings.
Drug therapy
Treatment of erosive gastroduodenitis with the use of medications helps to eliminate or control provoking factors and relieve the main unpleasant symptoms. For these purposes, drugs of the following pharmacological groups are prescribed:
- Antibacterial agents. Needed when establishing an infectious cause of inflammation. The drugs of choice are Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin, Furazolidone.
- Proton pump inhibitors. Prescribed in combination with antibiotics, they reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid and the aggressiveness of gastric juice (Lansoprazole, Nexium, Rabeprazole).
- Antacid drugs. They help regulate the secretion of gastric juice and reduce the acidity of the environment. A doctor may prescribe Famotidine, Omeprazole and their analogues for gastroduodenitis.
- Reparants. They improve the restoration processes of the mucous membrane, accelerate the healing of ulcers (Sorcoseryl, Etaden, Kaleflon).
- Gastroprotectors. Strengthen the protection of mucous membranes, creating a protective film on the internal walls of the gastrointestinal tract (Almagel, De-Nol, Phosphalugel).
- Prokinetics. Prescribed to enhance gastrointestinal motility (for example, Motilium).
The regimen and duration of therapy is selected by the gastroenterologist individually for each clinical case. Possible options for the use of drugs of different pharmacological groups for gastroduodenitis:
A characteristic feature of erosive gastroduodenitis is the presence of erosions in the outer epithelial layer of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Erosive elements tend to bleed, which can result in the development of anemia.
According to ICD 10 (international classification of diseases), this disease belongs to the class of gastritis and duodenitis and is assigned the code: K 29.9, which means “gastroduodenitis, unspecified.”
Causes of pathology in adults
This pathology often occurs against the background of the aggressive influence of negative factors. These factors include:
- hereditary genetic disorders;
- improper diet and consumption of harmful foods;
- presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body;
- prolonged stress;
- various gastrointestinal diseases.
Endogenous causes that may contribute to the development of the disease include:
- increased synthesis of hydrochloric acid (increased acidity);
- various intestinal infections;
- presence of reflux;
- decreased protective properties of stomach mucus;
- concomitant pathologies of the pancreas and liver.
External etiological factors also include:
- taking glucocorticoids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- the presence in the menu of spicy or rough food, too hot or cold drinks;
- alcohol abuse.
Do people with erosive gastroduodenitis join the army?
The disease is not considered dangerous to health. If it is treated in a timely manner, it does not progress
into a severe form. Currently, superficial inflammation of the esophagus is present in every 3 young people. The main reasons for the sad statistics are poor quality nutrition, the presence of chemical additives in foods that are harmful to health, addiction to alcohol, and a sedentary lifestyle. An early stage of the disease or an infrequent exacerbation of chronic gastroduodenitis does not allow a conscript to “move down” from the army.
If the illness worsens, he will be given a reprieve. After recovery, they will be taken away to serve for the glory of the Motherland. If this pathology is suspected, they are referred for examination and appropriate treatment is prescribed. After which they also take it away. There is dark humor about this. To avoid being drafted into the army with erosive gastroduodenitis, it must be brought to the point of ulceration!
The role of proper nutrition
A gentle diet is necessary to restore damaged mucous membranes. Some products are considered dangerous. It is better to refrain from using it. Smoked meats and spicy dishes are undesirable. Digesting such food requires a lot of energy. Coarse particles can injure the inner lining of the intestines and stomach.
The menu includes:
- porridge;
- vegetable soups;
- white fish;
- lean meat;
- sweet fruits;
- omelettes;
- vegetables.
Particular attention should be paid to nutritional rules during exacerbation of the disease. The doctor will recommend completely abstaining from food for 1-2 days. The organs will recover during this period.
The diet after an exacerbation is strict. You need to start expanding your menu with light vegetable-based broths. Food should be homogeneous. This avoids stress on the gastrointestinal tract.
Diet and nutrition
It is considered the main component of treatment for erosive gastroduodenitis. In this case it should
remember that proper food only eases the load on the digestive organs, it does not cure the disease itself. Therefore, it is necessary to use this method along with other, more effective ones. When selecting permitted products, the level of acidity plays an important role. Until it decreases, healing of erosions will not occur.
Authorized products:
- fermented milk with a small percentage of fat content. Homemade yogurt, cottage cheese without adding cream, milk. With high acidity, milk is drunk in large quantities.
- Cereals. Prepare soup with buckwheat, rice, and oatmeal. There is one peculiarity. For diarrhea, you need to eat more buckwheat; for constipation, you need to eat more rice. Oatmeal is a universal product that can be used for any condition. Side dishes are also prepared from them. Legumes, pearl barley, and semolina should be excluded.
- Meat. During an exacerbation, you should limit your consumption of meat products, but you should not give them up completely. Boiled chicken, turkey, stewed rabbit, beef, and veal are allowed. Pork is a difficult product to digest. It's better to wait with him. It is recommended to steam cutlets and soup with meatballs.
- Vegetables. It is healthy to eat raw. You can prepare salads with vegetable oil. At the same time, you should give up tomatoes and hot peppers. If you have increased rumbling in the stomach or severe gas formation, you should not eat cucumber.
- Sweets can be eaten in limited quantities. Cookies without cream, jam, or jam are allowed. Crackers, drying, bagels. Dried fruits, nuts. The latter must be chewed thoroughly so as not to injure the esophagus. With normal acidity, honey is allowed. Fruits excluding citrus fruits, plums, grapes, cherries. Especially with high acidity.
- Drinks: herbal tea, green tea, still mineral water, jelly, apple, pear, raisin soup.
Dishes should be steamed, boiled, baked. You should eat up to 7 times a day, but in small portions. Chew well. In the first 2 days of exacerbation of the disease, fasting is allowed. In this case, you need to drink a lot of fluid.
Prevention
Prevention activities are designed to help at every stage. Primary prevention of erosive gastroduodenitis is to minimize the impact of provoking factors. This helps reduce the occurrence of acute and chronic processes. To do this, you need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- observe sanitary and hygienic standards to reduce the risk of Helicobacter pylori infection;
- eat healthy foods, exclude harmful components from the diet and alcoholic beverages;
- undergo timely treatment of concomitant pathologies;
- avoid stress factors, normalize work and rest schedules;
- identify hereditary risks in advance.
Secondary measures are taken at the treatment stage. This includes compliance with the timing of taking medications, adequate doses of medications, and following dietary recommendations. Thus, the symptoms are relieved and remission occurs. The likelihood of developing complications is reduced, which is especially important for erosive-hemorrhagic pathology.
At the tertiary level, prevention is aimed at preventing relapse. For this, the gastroenterologist develops a rehabilitation plan. Good results are observed after a course of therapy in sanatorium-resort conditions, where they provide a full range of restorative procedures.
Diagnostics
The leading diagnostic method for erosive gastroduodenitis is esophagogastroduodenoscopy. This examination helps determine the presence of inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane in the stomach or duodenum, the size of erosions and their location. The endoscopist detects swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, its friability and increased vulnerability. In addition, bleeding is often observed at the site of formation of defects in the mucous layer. The criterion for diagnosing erosive gastroduodenitis is the identification of small hemorrhages and multiple erosions, which are usually covered with a gray film. As a rule, the size of epithelial defects is in the range of 0.3-0.5 mm. To clarify the nature of morphological changes, endoscopic biopsy is used.
Due to the fact that erosive gastroduodenitis in most cases develops against the background of Helicobacter pylori infection, it is necessary to use special diagnostic methods for identifying this microorganism. Helicobacter pylori can be detected by morphological examination of biopsy samples of the gastric and duodenal mucosa using microscopy. A more accurate method is PCR diagnostics of Helicobacter and a breath test. In addition, they often search for antibodies in the blood and determine Helicobacter in stool using ELISA. All patients with suspected erosive gastroduodenitis must undergo a general blood test. In the presence of frequent and prolonged bleeding from erosive defects, a decrease in the level of red blood cells, hemoglobin and color index can be detected. This indicates anemia due to chronic blood loss.
Treatment methods
Treatment of erosive duodenitis is usually limited to conservative methods; surgery is performed for special indications: necrosis, sepsis, perforation, adhesions, massive bleeding.
Medicines
The drug therapy regimen consists of prescribing the following drugs:
- antibacterial therapy for confirmed Helicobacter pylori (Clarithromycin, Tetracycline);
- proton pump inhibitors to reduce the acidity of gastric secretions (“Omeprazole”);
- antacids to protect the gastrointestinal tract (enveloping “Maalox”, “Almagel A” with anesthetic);
- antispasmodics to reduce pain (“Drotaverine”, “Papaverine”).
Additionally, enzyme preparations (Creon), vitamin complexes, immunocorrectors, anti-diarrhea drugs (Smecta), absorbents to accelerate the elimination of toxins (Enterosgel, Polysorb) are prescribed.
Surgical intervention
Indications for surgery are structural changes in the membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, perforation of ulcerative-erosive lesions, perforation, massive bleeding. The operation can be performed endoscopic, laparoscopic or abdominal method. After surgery, long-term rehabilitation is indicated, which consists of taking medications and diet therapy.
Physiotherapy
Auxiliary methods of conservative treatment and recovery after surgery are electrophoresis with lidase, ultrasound, ultraviolet heating. The goal of physiotherapy is to activate lymph and blood flow in the peritoneum, reduce symptomatic manifestations, stabilize the production of gastric secretions, and relieve the inflammatory process.
Folk remedies
Among the traditional methods of therapy, which can only be used as auxiliary ones, the following are considered popular:
- A decoction based on oak bark and chamomile. 1 tbsp. l. mixtures of plants are poured into 500 ml of boiling water, infused, filtered and drunk in small portions throughout the day.
- A decoction of stinging nettle and licorice roots. A small handful of the mixture is poured into 500 ml of boiling water, brought to low heat, a few tablespoons of honey are added and drunk throughout the day.
- Oatmeal broth. 2 tbsp. l. rolled oats are steamed in 300 ml of boiling water and left for about three hours. The resulting decoction is filtered, and the liquid is drunk on an empty stomach and at night.
It is useful to eat honey, drink aloe decoction, and natural juices from vegetables. The latter should be diluted with water before use; pumpkin and beetroot juices are especially useful.
Diet
Diet therapy involves the appointment of table No. 1, and after a decrease in active symptoms, they switch to table No. 5. The principles of a healthy diet for erosive duodenitis include the following aspects:
- eating small meals frequently;
- maintaining a proper diet (do not starve, eat at the same time);
- drinking plenty of water;
- ban on smoked foods, canned food, sweets, fatty and fried foods;
- exclusion of fresh bread, confectionery baked goods.
It is recommended to include in the diet simple soups, slimy dishes (jelly, boiled porridge), stewed and steamed vegetables, and lean meat. Natural juices and sour fruits can be consumed only after the active symptoms have stopped.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease is determined by the stage of the process, the degree of impairment of motor and secretory function. Most often, patients are faced with a chronic variant of the pathology, which develops gradually under the influence of negative factors. The acute process occurs due to infectious and non-infectious causes, which provoke the rapid development of inflammation.
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis in acute cases appear suddenly and are pronounced. The first place is taken by pain syndrome, which is accompanied by vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, the appearance of undigested lumps of food and mucus in the stool.
This condition should be differentiated from acute intestinal infection. Therefore, the patient needs to immediately go to the doctor. In this case, adequate therapy will help get rid of the problem forever.
The chronic process is characterized by the periodic appearance of unfavorable symptoms. Typically, symptoms of exacerbation occur in spring and autumn and are associated with a violation of a person’s immune status. In such cases, patients complain of:
- Pain and discomfort in the projection of the stomach and the initial parts of the small intestine can occur 4-5 hours after falling asleep during sleep, or when hungry, with a decrease in intensity after breakfast, as well as late - 1-3 hours after eating.
- Dyspeptic symptoms - vomiting, nausea, belching, heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, bloating, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, flatulence, bad breath.
- Disorders of stool and bowel movements - constipation is more common, and with a decrease in acidity - diarrhea. Sometimes there is a symptom of slippage, when the urge occurs immediately after eating.
- Asthenovegetative manifestations in the form of weakness, lethargy, impaired performance, fatigue, decreased blood pressure, and rare pulse.
- Loss of body weight during a long course of the disease.
Incomplete recovery is characterized by moderately expressed dyspeptic symptoms in the absence of pain. During remission, there are no clinical manifestations. However, endoscopy reveals changes in the mucous membrane in the area of the stomach and duodenum.
Endoscopic signs
To differentiate the type of disease, an instrumental examination of the patient is performed. With the help of FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy), it is possible to identify endoscopic signs of gastroduodenitis, determine changes in the mucous membrane, and the degree of spread of the inflammatory process. The following variants of the endoscopic picture are distinguished depending on the morphological type of pathology.
Table 3. Endoscopic signs of gastroduodenitis
| Type of gastroduodenitis | Signs |
| Superficial (catarrhal) | There is moderate inflammation of the epithelium in the form of alternating areas of hyperemia and edema with unchanged areas. As the process progresses, the swelling of the mucous membrane increases, and when the endoscope touches it, hemorrhage occurs |
| Erosive | There are tissue defects surrounded by an inflammatory cushion, which can cause bleeding. With deep lesions, fibrin deposits appear in the center of erosion. |
| Hypertrophic | Growth and thickening of the mucous membrane without atrophy is determined. |
| Atrophic | In places, thinned epithelium is visualized with tissue atrophy in the form of whitish areas, the folds are smoothed. |
| Mixed | It is a combination of several types of inflammation. |
Attention!
Special forms of damage to the mucosa are characteristic of radiation injury, reflux, and chemical burns. In this case, for a reliable interpretation of the results, it is necessary to obtain a detailed medical history.
Characteristic symptoms
Erosive gastroduodenitis has similar symptoms to other inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The main symptom is pain. They can be either permanent or temporary. Discomfort usually worsens after eating. The pain is localized in the upper abdomen.
Other signs of the disease are:
Unlike the situation with ulcers and gastritis, with this pathology the patient can maintain a normal appetite. Weight also remains within normal limits. With complications, as well as during periods of exacerbation, health worsens.
Weakness and malaise appear. An admixture of blood may be detected in the stool, indicating large lesions of the duodenum.
If the condition worsens, you should consult a doctor. The gastroenterologist will examine the patient and prescribe additional examinations. If a disease is detected, drug treatment will be prescribed.
Prognosis and complications
Timely and adequate treatment provides a favorable prognosis. The addition of complications makes it doubtful: an advanced pathological process leads to peptic ulcer disease and the need for surgical intervention.
Frequent complications:
- adhesions and intestinal obstruction;
- impaired absorption: malabsorption and maldigestion syndrome, celiac disease;
- duodenal ulcer;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- cancer.
Following all medical recommendations and adequate therapy allows you to completely cure erosive duodenitis, and in case of a chronic course, achieve a stable six-month remission.
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves depending on the stage of its development, the degree of damage to the mucous membranes, and the location of erosive elements and ulcers. Signs of gastroduodenitis are the following:
- Nausea, belching, gastroduodenal reflux (heartburn).
- Stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea).
- Flatulence.
- Pain in the stomach and abdomen.
- Decreased appetite.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Blood clots in vomit or feces (with the formation of bleeding erosions).
- Symptoms of posthemorrhagic anemia (with internal erosive hemorrhages) are weakness and fatigue, dizziness and headaches, sleep disturbances.
Article on the topic: Atarax - instructions for use
A characteristic symptom of the disease in the acute stage is morning sickness, accompanied by severe pain in the stomach. After eating, the patient experiences a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness, sharp attacks of pain in the epigastric zone, and heartburn. Gastroduodenitis usually develops rapidly, and the patient’s condition quickly deteriorates. In the chronic course, the symptoms are in most cases not clearly expressed, and pain may be absent.
Treatment methods
Treatment of erosive gastroduodenitis should be carried out comprehensively and include the following measures:
- drug treatment aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and relieving stomach pain and cramps;
- therapeutic nutrition;
- the use of traditional methods: decoctions, infusions, mixtures of medicinal herbs.
Drug therapy
Treatment with drugs is prescribed by a gastroenterologist taking into account the clinical manifestations of the disease, the results of laboratory and instrumental research methods. An integrated approach to treatment ensures effectiveness in restoring damaged mucous membranes of the digestive system. Drug therapy for gastroduodenitis is carried out using broad-spectrum drugs, such as:
- Amoxicillin, Metronidazole - antibiotics prescribed for bacterial infection by Helicobacter pylori;
- De-Nol is a drug containing bismuth salts that relieves inflammation in the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- Almagel, Maalox - agents that reduce the acidity of gastric juice and have an enveloping property;
- Etaden, Solcoseryl - drugs that promote regenerative and stimulating processes during the healing of erosions and ulcers;
- Domperidone, Dimetpramide – prokinetics that stimulate gastric and intestinal motility;
- Spazgan, Spazmalgon - painkillers that relieve spasm of smooth muscles;
- Persen, Novopassit - sedative medications with a mild hypnotic effect;
- restorative therapy.
Medical nutrition
Drug treatment of gastroduodenitis must be combined with proper therapeutic nutrition. The diet is prescribed by the attending physician immediately after diagnosis of the disease. It must be strictly observed by the patient, since the slightest error in following the rules will cause the next stage of exacerbation of the disease.
In this case, diet number 1 is prescribed, which has its own characteristics and is prescribed to patients with ulcerative or inflammatory processes in the digestive system. In the presence of erosive gastroduodenitis, the use of the diet should be constant. Considering the characteristics of the damaged gastrointestinal mucosa, food is consumed pureed and warm in order to eliminate mechanical effects on the altered mucous membrane. Preference is given to various soups made with vegetable or weak chicken broth with pureed vegetables.
Meals should be fractional: 5 - 6 times a day in small portions, no more than 200 grams at a time. Long breaks between meals are not allowed.
Food is prepared by steaming or stewing. Spicy, salty, smoked, canned foods, as well as vegetables and fruits containing coarse fiber, are excluded from the diet.
Folk remedies
On the recommendation of a gastroenterologist, medication therapy can be combined with the use of traditional medicine. This complex treatment gives a good effect in healing ulcers on the mucous membranes of the digestive system. The most popular are the following recipes:
- sea buckthorn oil - purchased at the pharmacy or prepared independently from crushed dried berries and olive oil in a 1:1 ratio. This mixture is kept in a cool, dark place for three weeks. Take 15 grams three times a day before meals;
- aloe juice - prepared from the leaves of a three-year-old plant. The leaves are cut and kept, wrapped in cling film, in the refrigerator for two weeks. Juice is prepared from crushed leaves, which is mixed with honey in a 1:1 ratio. Take 15 grams before meals 20–30 minutes;
- sprouted wheat - grains are filled with a small amount of water and, after sprouts appear, crushed using a blender or meat grinder. A few drops of olive oil are added to the wheat mass. The mixture is taken 30 grams on an empty stomach.
Diagnosis of the condition
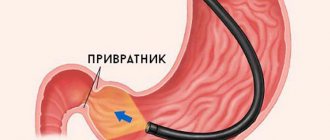
The diagnosis is not made based on visual examination and questioning. To obtain reliable information about the state of the digestive tract, the patient will undergo fibrogastroduodenoscopy. During the study, a gastroscope, a device with a camera that transmits an image to a monitor, is inserted into the stomach and duodenum through the esophagus.
The doctor will be able to determine not only the presence of ulcerated surfaces. The diagnostic method allows you to assess the size and exact location of damage . If tissue degeneration is suspected during manipulation, the doctor will take a sample of the mucous membrane for further histological analysis.
Ultrasound is considered a less accurate diagnostic technique. This type of research is often used due to its simplicity. The patient does not experience discomfort or pain.
The ultrasound machine will also show the presence of changes in the inner walls of the stomach and intestines.
Additional research methods include radiography and determination of the pH level of the stomach.